As technology keeps advancing at a rapid pace, the demand for wireless earphones has surged dramatically. People are increasingly opting for the convenience and freedom offered by these small yet powerful devices. However, despite their growing popularity, wireless earphones have often faced criticism for their subpar audio quality. This issue has raised important questions about the intricacies involved in delivering impeccable sound reproduction without compromising on the convenience of a wireless connection.
One of the fundamental challenges that engineers encounter when designing wireless earphones is the need to balance size and audio performance. Unlike their wired counterparts, wireless earphones must incorporate additional components such as Bluetooth receivers and batteries, leaving less room for advanced audio processing technologies. This trade-off between miniaturization and audio quality has posed a significant obstacle in achieving the same level of fidelity that wired headphones can provide.
Another factor that contributes to the audio limitations of wireless earphones is the inherent compression applied during the transmission of audio signals. In order to ensure smooth communication between the earphones and the connected device, audio data needs to be compressed and decompressed in real-time. While this compression technique allows for seamless wireless streaming, it inevitably compromises some of the original sound details, resulting in a loss of audio clarity and depth.
Factors Influencing Sound Performance of Wireless Earphones

When examining the audio experience provided by cordless earbuds, numerous factors come into play, ultimately influencing the overall sound quality. Understanding the various elements that affect the performance of wireless audio devices is crucial in making informed decisions when choosing the right pair of earphones.
| Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Codec | The choice of audio codec utilized by wireless headphones significantly impacts the sound quality. Different codecs have varying levels of compression and lossless capabilities, resulting in variations in audio fidelity and the resolution of sound details. |
| Bluetooth Version | The version of Bluetooth technology supported by earphones plays a crucial role in sound performance. Newer Bluetooth versions often provide improved data transmission rates and reduced latency, enhancing audio quality and minimizing audio sync issues. |
| Wireless Interference | Environmental factors and the presence of other wireless devices can introduce interference, negatively impacting audio quality. Interference can result in distortion, dropouts, or reduced range, causing sound degradation and an overall poor listening experience. |
| Driver Quality | The quality and design of the earphone drivers significantly affect sound reproduction. Driver size, materials, and magnet types influence the frequency response, accuracy, and clarity of audio output. |
| Battery Performance | The duration and stability of battery performance can impact the sound quality of wireless earphones. Insufficient battery capacity or low voltage levels may result in reduced power delivery to the drivers, leading to compromised audio quality. |
| Fit and Isolation | The fit of earbuds in the ear canal and their ability to create an effective seal greatly influence the bass response, soundstage, and overall audio quality. Proper isolation from ambient noise ensures a more immersive listening experience. |
Considering these various factors and their interplay is essential in comprehending the sound quality offered by wireless earphones. To ensure an optimal listening experience, individuals should consider the specifications and features related to these factors when choosing wireless headphones.
Bluetooth Compression Technology: The Culprit Behind Distorted Sound
When it comes to the audio experience delivered by wireless headphones, there exists a key factor that often goes unnoticed – the impact of Bluetooth compression technology. While these advanced devices give us the convenience of wireless listening, they can sometimes fall short in terms of sound quality. Understanding the role of Bluetooth compression technology in causing distorted sound is crucial for anyone seeking an enhanced audio experience.
Bluetooth compression technology, also known as audio coding, plays a significant role in transmitting audio wirelessly between devices. However, this technology utilizes compression algorithms to reduce the size of audio files, which in turn results in a compromise in sound quality. This compression process involves eliminating certain audio data, particularly those that are less noticeable to the human ear, to make the file size smaller.
- One of the primary drawbacks of Bluetooth compression technology is the loss of fine details in the audio. The compression algorithms prioritize data reduction, leading to the omission of subtle nuances in the sound, such as the delicate harmonics of musical instruments or the richness of vocals.
- Another challenge is the reduction of dynamic range. Bluetooth compression technology tends to compress both the loudest and softest parts of the audio signal, resulting in a loss of depth and variation in sound intensity.
- Moreover, the compression process introduces artifacts and distortions into the audio stream. These can manifest as unwanted hissing or buzzing sounds, particularly noticeable in high-frequency components or during quiet moments in the audio.
Despite these drawbacks, it's essential to acknowledge that Bluetooth compression technology has come a long way and continues to improve with each new iteration. Manufacturers are working on developing enhanced compression algorithms that aim to minimize the impact on sound quality. Additionally, advancements in wireless transmission protocols and hardware components allow for higher bit rates, resulting in improved audio fidelity.
In conclusion, Bluetooth compression technology plays a significant role in the compromised sound quality experienced with wireless headphones. While it enables the convenience of wireless listening, the compression process introduces loss of details, reduction in dynamic range, and unwanted artifacts. However, ongoing advancements in technology are gradually addressing these limitations, promising a brighter audio future for wireless headphones.
Limited Frequency Response: How Wireless Connectivity Affects the Range of Sound
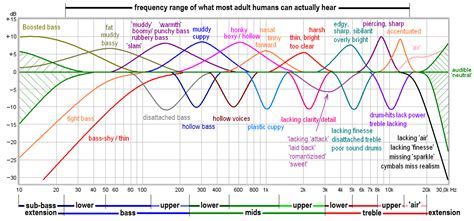
When it comes to the performance of wireless headphones, one crucial aspect that significantly impacts the overall experience is the limited frequency response due to the inherent constraints of wireless connectivity. The range of sound frequencies that can be reproduced by wireless headphones is restricted, leading to a compromise in the quality and richness of the audio produced.
The connectivity between wireless headphones and devices relies on the transmission and reception of audio signals through wireless technology. This technology allows for convenience and flexibility, enabling users to move freely without tangled cables. However, this convenience comes at a cost when it comes to sound quality. The transmission of audio signals wirelessly inherently introduces limitations that affect the frequency response capabilities of headphones.
The limited frequency response occurs due to the compression and decompression process required during wireless transmission. As audio signals are transferred wirelessly, they undergo compression to reduce the file size for efficient transmission. This compression leads to the elimination of certain frequencies, resulting in a loss of subtle nuances and details in the sound. Additionally, decompression at the receiver end leads to a further degradation in audio quality, as some frequencies may be inaccurately reproduced or lost completely.
Another factor influencing the limited frequency response is the bandwidth allocated to wireless audio transmission. To ensure the stability and reliability of wireless connections, a limited bandwidth is typically assigned, which restricts the range of frequencies that can be transmitted. As a result, the dynamic range and depth of sound reproduction are compromised.
It is important to note that the extent of limited frequency response may vary among different wireless headphone models and manufacturers. Some headphones may employ advanced technologies and codecs that mitigate these limitations to a certain extent, allowing for a more extended frequency range. Nevertheless, it remains an inherent challenge for wireless headphones to reproduce audio with the same fidelity as their wired counterparts.
Interference Issues: External Factors that Impact Sound Clarity
When it comes to enjoying audio content through wireless headphones, various external factors can potentially affect the clarity of the sound, taking away from the optimal listening experience. Understanding these interference issues is crucial in identifying the potential drawbacks of wireless audio transmission.
1. Radio Frequency Interference (RFI)
- Radio frequency interference can disrupt the transmission of sound signals, resulting in poor sound quality. RFI can occur when wireless headphones operate in close proximity to other electronic devices, such as Wi-Fi routers, cordless phones, or other Bluetooth-enabled devices.
- RFI can cause audio distortion, dropouts, or even complete signal loss, leading to a compromised listening experience.
2. Bluetooth Interference
- Bluetooth is the most common wireless technology used in headphones, but it is susceptible to interference from other Bluetooth devices in the surrounding area.
- When multiple Bluetooth devices are operating simultaneously, they can interfere with each other, resulting in signal degradation and diminished sound quality. This interference is more likely to occur in crowded environments, where numerous Bluetooth-enabled devices are present.
3. Obstacles and Distance
- Obstacles, such as walls or physical objects, can obstruct the signal transmission between wireless headphones and the audio source, causing audio quality issues.
- Moreover, the distance between the headphones and the audio source can impact the strength and stability of the signal. The farther the headphones are from the audio source, the greater the chance of experiencing signal degradation and audio dropouts.
4. Electromagnetic Interference (EMI)
- Electromagnetic interference can occur when wireless headphones are used near devices that generate strong electromagnetic fields, like microwaves, power lines, or certain medical equipment.
- EMI can disrupt the wireless audio signal, leading to crackling sounds, buzzing noises, or overall reduction in sound quality.
5. Environmental Factors
- Environmental factors such as radio signals from nearby broadcasting stations, crowded areas with high wireless communication activity, or even extreme weather conditions can introduce interference that affects the clarity of sound in wireless headphones.
- These external elements can create fluctuations in the wireless signal, resulting in audio inconsistencies and distortion.
Understanding and considering these interference issues can help users make informed choices while using wireless headphones and optimize their audio experience despite the external factors that may impact sound clarity.
Understanding Latency Problems: The Delay in Wireless Audio Transmission

When it comes to the world of wireless audio, one issue that often arises is the problem of latency. Latency refers to the delay in signal transmission between the audio source and the wireless headphones. This delay can have a significant impact on the overall user experience, as it can affect the synchronization between audio and video, hinder real-time communication, and result in noticeable audio lag.
The challenge of latency:
Latency is a complex challenge that arises due to the inherent limitations of wireless audio transmission. Unlike wired headphones, which transmit audio signals directly through a physical connection, wireless headphones rely on wireless technologies like Bluetooth or Wi-Fi to transmit audio over the airwaves.
Despite advancements in wireless technology, there are inherent limitations that contribute to latency issues. These limitations include signal processing, data compression, and transmission protocols.
Synchronization issues:
One of the most noticeable impacts of latency in wireless audio transmission is the synchronization problem. When watching videos or playing games, audio that lags behind the corresponding visual cues can be incredibly frustrating. The delay in audio transmission can disrupt the immersive experience and hinder the overall enjoyment of the content.
In addition to entertainment purposes, latency issues can also be problematic for tasks requiring real-time communication, such as voice and video calls. The delay in audio transmission can result in disjointed conversations, making it difficult for users to engage in natural and fluid communication.
Factors affecting latency:
Several factors contribute to the latency experienced in wireless audio transmission. Signal processing, which involves converting analog audio signals into digital data, can introduce latency due to the time required for this conversion process. Additionally, data compression algorithms used to minimize audio file size can also cause latency as they require time to encode and decode the audio.
Furthermore, the wireless transmission protocols employed, such as Bluetooth or Wi-Fi, introduce additional latency in the transfer of audio data. The various actions taken to ensure stable and reliable wireless connections can result in a delay in transmitting the audio signals to the connected headphones.
Addressing latency concerns:
While wireless audio technology has made great strides in recent years, the challenge of latency remains an ongoing issue. Manufacturers continuously work to reduce latency through advancements in signal processing, improved data compression algorithms, and optimization of wireless transmission protocols.
As technology evolves, it is expected that future wireless headphones will offer even lower latency, providing users with a seamless and synchronized audio experience.
Compression Codecs: The Impact of Audio Coding on Sound Fidelity
In the realm of audio transmission, the efficiency of wireless protocols is contingent upon the implementation of compression codecs. These codecs play a critical role in determining the overall sound fidelity experienced by users of wireless headphones. By employing various encoding techniques, compression codecs aim to reduce the size of audio files for seamless wireless transmission without compromising the perceptible audio quality. However, the extent to which compression codecs affect sound reproduction remains a topic of significant debate and scrutiny.
Compression codecs refer to algorithms that compress audio data before transmission and decompress it upon receipt. By employing complex mathematical models, these codecs exploit inherent limitations of human auditory perception, enabling the reduction in file sizes without noticeable loss in audio quality. The algorithms achieve this through the elimination of redundant or inaudible data, resulting in a smaller data packet size that can be efficiently transmitted over wireless networks.
The choice of a compression codec has a direct impact on the sound fidelity experienced by wireless headphone users. While some codecs offer higher compression ratios, enabling greater amounts of data to be transmitted in a given bandwidth, they may result in perceptible compromises in audio quality. Other codecs prioritize maintaining the original sound quality, necessitating larger file sizes and potentially limiting the number of audio streams that can be transmitted simultaneously.
The debate over the impact of compression codecs on sound quality revolves around the trade-off between preserving audio fidelity and optimizing bandwidth utilization. Critics argue that the lossy nature of many compression algorithms leads to the removal of subtle audio details, resulting in a degradation of the listening experience. Proponents, on the other hand, highlight the necessity of compression to enable wireless transmission and emphasize the continued advancements in codec technology, which minimize perceptible compromises in sound quality.
Ultimately, understanding the impact of compression codecs on sound quality requires a nuanced evaluation of their advantages and limitations. While compression is necessary for efficient wireless audio transmission, the choice of codec should be carefully considered to strike a balance between maximizing data compression and preserving audio fidelity. Ongoing advancements in compression codec technology, coupled with improvements in wireless protocols, hold promise for further enhancing the sound quality of wireless headphones in the future.
Battery Life vs. Sound Quality: The Trade-Off in Wireless Headphones

In the world of wireless headphones, finding the perfect balance between battery life and sound quality is a delicate task. When it comes to choosing a pair of wireless headphones, users often face a trade-off between these two critical aspects of performance. The longer the battery life, the more compromises might be made in terms of sound quality, and vice versa.
Battery life plays a pivotal role in a user's overall headphone experience. It determines how long one can enjoy their favorite tunes, podcasts, or calls without interruption. A longer battery life ensures extended usage without the need for frequent recharging. However, aiming for a prolonged battery life often leads to design decisions that may impact sound quality.
Sound quality is the holy grail of every audio enthusiast. It encompasses factors such as clarity, depth, and fidelity. While technological advancements have allowed wireless headphones to achieve impressive sound quality, there are still inherent limitations compared to their wired counterparts. Manufacturers face challenges in reproducing a rich and immersive audio experience due to the constraints imposed by the wireless communication and power management systems.
The trade-off between battery life and sound quality lies in the engineering decisions made during the design and manufacturing of wireless headphones. To prioritize and optimize battery life, manufacturers may implement power-saving techniques that limit the headphone's audio capabilities. These techniques can include utilizing lower-power audio codecs, reducing amplifier power, or employing wireless transmission protocols with lower bandwidth.
Conversely, prioritizing sound quality may result in reduced battery life. Manufacturers may choose to use higher-power audio codecs, more powerful amplifiers, or codecs that provide higher audio fidelity. While these choices contribute to an enhanced sound experience, they also require more significant power consumption, leading to shorter battery life.
This trade-off poses a challenge for both manufacturers and consumers. Manufacturers strive to strike the right balance between these two aspects, catering to the varying preferences and needs of users. Consumers must consider their priorities, whether they value long-lasting battery life or exceptional sound quality, when selecting the perfect pair of wireless headphones.
In conclusion, the interplay between battery life and sound quality in wireless headphones highlights the complexity of engineering truly exceptional audio devices. As technology continues to evolve, manufacturers will undoubtedly push the boundaries to provide longer battery life without sacrificing sound quality, but until then, users must carefully consider their preferences and expectations when making their wireless headphone purchase.
Build Quality and Material: How it Affects the Overall Sound Experience
The design and construction of wireless headphones play a crucial role in determining the quality of the sound they produce.
When it comes to audio devices, the build quality and the choice of materials used directly impact the overall sound experience. From the choice of plastic or metal for the housing to the quality of internal components, every aspect contributes to the final audio output.
The build quality of wireless headphones can affect the clarity, detail, and overall balance of sound reproduction.
Headphone casings made from high-quality materials, such as durable metals or sturdy plastics, can significantly minimize vibrations and resonance that can distort the sound. These materials provide a robust and stable platform for the drivers, ensuring accurate sound reproduction without any unwanted interference.
The choice of materials can also impact the comfort and fit of the headphones, ultimately affecting the overall sound experience.
While comfort may not be directly related to sound quality, it does play a crucial role in the overall experience. The materials used for the headband and ear cup padding can affect how the headphones fit on the head and how they seal against the ears. Proper fit and seal are essential for excellent sound isolation, preventing sound leakage and external noise interference, resulting in a more immersive sound experience.
The quality of internal components, such as drivers and circuitry, can significantly impact the overall sound performance of wireless headphones.
Wireless headphones with high-quality drivers can deliver accurate sound reproduction, with clear highs, rich mids, and deep lows. The quality of the circuitry, including amplifiers and digital signal processors, also plays a role in enhancing the sound quality and overall audio performance.
In conclusion, the build quality and choice of materials, as well as the quality of internal components, are crucial factors that affect the overall sound experience of wireless headphones. By investing in headphones with excellent build quality and high-quality materials, users can enjoy a more immersive and satisfying sound performance.
Equalization Settings: The Importance of Adjusting Audio Preferences
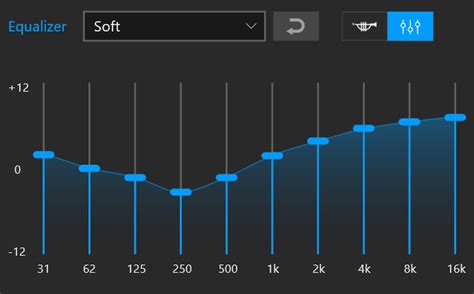
Optimizing audio preferences is a critical aspect of enhancing the overall listening experience. Fine-tuning equalization settings allows users to personalize their audio output according to their unique preferences, ensuring optimal clarity and a balanced sound profile.
By adjusting the equalization settings on wireless headphones, individuals can effectively modify the frequency response of the audio output. This allows for the enhancement or reduction of specific ranges, such as bass or treble, to suit personal preferences or compensate for varying audio sources.
Equalization settings play a vital role in addressing the limitations and characteristics of audio playback equipment. Every individual's hearing profile differs, and their perception of sound frequencies may vary. Therefore, customizing the equalization settings helps overcome any potential shortcomings in sound reproduction and ensures a more accurate representation of the original audio content.
Additionally, adjusting audio preferences through equalization settings can compensate for ambient noise or room acoustics. By boosting or cutting certain frequency ranges, users can mitigate the impact of external disturbances and achieve a more immersive sound experience.
However, it is important to note that the excessive modification of equalization settings can sometimes result in an unnatural or unbalanced audio output. Therefore, it is essential to exercise caution and make subtle adjustments that enhance the listening experience without compromising the overall sound quality.
In conclusion, understanding the significance of equalization settings and their ability to tailor audio preferences is imperative for maximizing the potential of wireless headphones. By customizing the frequency response and adapting to individual hearing profiles, users can enjoy a more personalized and immersive audio experience.
[MOVIES] [/MOVIES] [/MOVIES_ENABLED]FAQ
Why do wireless headphones typically have poor sound quality?
Wireless headphones often have poor sound quality due to the limitations of wireless technology. The audio signal needs to be compressed and transmitted wirelessly, which can result in data loss and reduced audio fidelity.
Are there any specific factors that contribute to the poor sound quality of wireless headphones?
Yes, there are several factors that contribute to the poor sound quality of wireless headphones. These include signal interference, limited bandwidth for audio data transmission, and the use of lossy audio compression algorithms.
Do all wireless headphones have poor sound quality?
No, not all wireless headphones have poor sound quality. Some high-end wireless headphones are designed to overcome the limitations of wireless technology and provide excellent sound quality. However, these headphones tend to be more expensive compared to average wireless headphones.
What alternatives are available for those who want better sound quality than wireless headphones?
If you are looking for better sound quality than wireless headphones, you may consider wired headphones or earphones. Wired connections can deliver uncompressed audio signals, resulting in higher fidelity sound. Additionally, some audiophiles prefer using dedicated headphone amplifiers to further enhance audio quality.




