Unraveling the perplexing puzzle surrounding the audible attenuation experienced in earbuds and headphones calls for a voyage into the intricate realm of sound transmission. This enigmatic phenomenon, whereby the intensity of auditory vibrations appears to dwindle, has attracted the curiosity of countless audio enthusiasts and scientists alike. In this contemplative exploration, we shall peel back the layers of this auditory riddle, delving into the underlying principles that elucidate the reasons behind the reduction in sound amplitude when we immerse ourselves in the world of personal audio devices.
Stepping into the realm of the auditory marvel that headphones symbolize, one is immediately besieged by this inquisitive quandary: why does the volume perceived through these diminutive devices seem to diminish in comparison to external sound sources? By venturing into the extraordinary domain of sound transmission, we begin to discern the subtle intricacies at play. As sound waves traverse through the labyrinthine channels within our earphones, their path is cloaked in a web of intricate factors.
Embedded deep within the core of this unraveling mystery are the elements of signal propagation, earphone design, and physiological nuances of human perception. The interplay between these intrinsic components intertwines to fashion the acoustic environment we experience within the confines of our earbuds. An assortment of phenomena, including diffraction, impedance mismatches, and psychoacoustic effects, converge to mold the idiosyncratic nature of sound reproduction in this miniature soundscape.
Understanding the Physics behind Sound Attenuation in Headphones
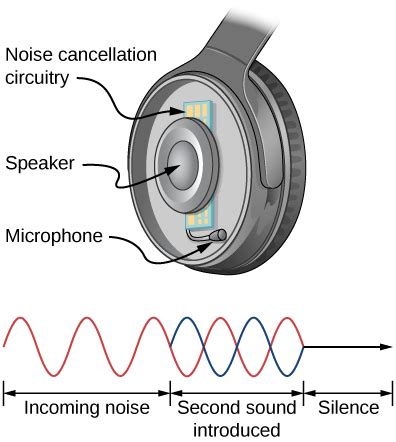
In this section, we will explore the fundamental principles underlying the reduction of sound intensity experienced when using headphones. By delving into the intricate workings of headphones and the physics of sound propagation, we can gain a deeper understanding of the mechanisms that contribute to sound attenuation in this context.
| Principle | Description |
|---|---|
| Acoustic Isolation | Headphones are designed to minimize the transfer of sound waves from the external environment to the ears. This is achieved through the use of materials that effectively block or absorb incoming sound waves, preventing them from reaching the ear canal. |
| Passive Noise Cancellation | Passive noise cancellation techniques, such as the design of the ear cups or the presence of earmuffs, can reduce the perceived loudness of external sounds. These components create a physical barrier that hinders sound waves from reaching the listeners' ears. |
| Sound Reflection | When sound waves encounter the internal surfaces of the headphone's ear cups, they can bounce off and reflect in different directions. This phenomenon causes a portion of the sound energy to be redirected away from the user's ears, resulting in a decrease in sound intensity. |
| Transducer Efficiency | The efficiency of the transducers, such as the speakers or drivers within the headphones, plays a crucial role in determining the overall sound attenuation. Higher efficiency transducers can convert electrical signals into sound waves more effectively, thereby compensating for any potential loss in sound intensity. |
| Wired or Wireless Connection | The type of connection used to transmit audio signals to the headphones can also impact sound attenuation to some extent. Wireless connections, for example, may introduce additional interference or loss of signal fidelity, leading to a potential decrease in sound quality and overall sound intensity. |
By understanding these foundational principles, we can appreciate the complex interplay between various factors that contribute to sound attenuation in headphones. This knowledge can help inform our choices when selecting headphones that meet our specific needs and preferences for sound quality and isolation.
Exploring the Different Types of Headphone Technologies
In this section, we will delve into an exploration of the various headphone technologies available in the market today. By understanding the different types of headphone technologies, we can gain insights into the factors that affect sound quality, as well as the potential reasons why sound may decrease when using headphones.
1. Wired Headphones
- Traditional headphones that rely on physical connections to audio devices.
- Often preferred for their high-quality sound reproduction and reliability.
- Can vary in terms of cable length, connector type, and overall design.
2. Wireless Bluetooth Headphones
- Utilize Bluetooth technology to connect wirelessly to compatible devices.
- Offer the convenience of freedom from tangled cables.
- May experience potential sound quality degradation due to data compression during wireless transmission.
3. Noise-Canceling Headphones
- Designed to reduce external noise using active or passive noise-canceling technology.
- Provide a more immersive audio experience by blocking unwanted sounds.
- May require additional power to operate the noise-canceling feature, reducing overall battery life.
4. In-Ear Monitors (IEMs)
- Specially designed to fit snugly inside the ear canal.
- Offer superior noise isolation compared to other headphone types.
- Can provide high-fidelity sound reproduction when properly sealed in the ear.
5. Open-Back and Closed-Back Headphones
- Open-back headphones allow some sound leakage, creating a more spacious and natural soundstage.
- Closed-back headphones provide better sound isolation and are suitable for noisy environments.
- Each type has its advantages and disadvantages, depending on the intended use.
By exploring these different types of headphone technologies, we can gain a better understanding of the factors that contribute to sound quality and potential issues that may arise, such as sound decrease. This knowledge can help us make informed decisions when selecting headphones and optimizing our audio experience.
How Noise-Canceling Technology Impacts Sound Intensity in Headphones
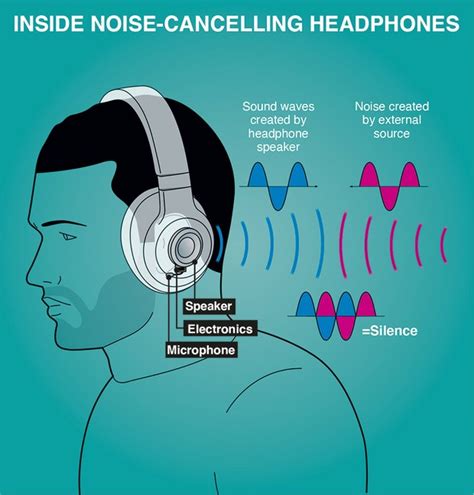
When it comes to the impact of noise-canceling technology on sound intensity in headphones, there are several factors at play that contribute to a unique listening experience. This section explores how noise-canceling headphones alter sound levels and offers insights into the mechanism behind this phenomenon.
1. Active Noise Cancellation:
- By actively analyzing external sounds, noise-canceling headphones generate anti-noise signals to counterbalance ambient noise.
- This process effectively reduces the overall noise level in the listener's environment.
- As a result, the perception of sound intensity is often enhanced, allowing users to enjoy their audio content without distractions.
2. Isolation and Passive Noise Reduction:
- Besides active noise cancellation, noise-isolating headphones create a physical barrier between the listener and the outside world.
- These headphones use materials such as foam or silicone to block external sounds from reaching the ear.
- As a consequence, the relative intensity of the desired audio signal increases in comparison to the surrounding noise.
3. Psychoacoustic Effects:
- Human psychoacoustic perception plays a significant role in understanding how noise-canceling headphones affect sound intensity.
- By reducing background noise, noise-canceling technology improves the signal-to-noise ratio and enhances the clarity of the audio signal.
- As a result, users may perceive the sound as more intense, even though the actual volume level remains consistent.
4. Customizability and Sound Profiles:
- Many noise-canceling headphones offer additional features that allow users to customize their sound experience.
- Equalizer settings, sound profiles, and other audio adjustments can influence the perceived intensity of different frequencies and audio effects.
- By tailoring the sound profile to personal preferences, users can further enhance their immersion and enjoyment of audio content.
In summary, noise-canceling technologies in headphones significantly impact the perception of sound intensity. Through active noise cancellation, isolation, psychoacoustic effects, and customizable sound profiles, users can elevate their audio experience and immerse themselves in their favorite content with reduced distractions.
The Role of Ear Pads in Sound Attenuation in Headphones
In the realm of audio devices, the magnitude of sound reduction experienced while using headphones is a phenomenon that has piqued the curiosity of many enthusiasts. One particular element that contributes significantly to this decrease in sound levels is the often overlooked component known as ear pads. These soft and cushioned structures, situated between the headphone speakers and the wearer's ears, play a crucial role in the overall sound attenuation experienced by the listener.
Enhanced Sound Isolation: The primary function of ear pads is to provide a barrier between the headphone speakers and the external environment. By creating a physical seal around the ears, the ear pads aid in preventing sound leakage and minimizing the interference of unwanted external noises. This enhanced sound isolation facilitates a more immersive audio experience, allowing the listener to focus on the intricacies of the sound being reproduced within the headphones.
Impact on Bass Response: The design and material composition of ear pads also have a notable impact on the perceived bass response. Thicker and denser pads tend to create a more sealed environment, effectively trapping low-frequency sounds within the headphone, resulting in a more pronounced and impactful bass representation. Conversely, thinner or less dense pads may allow some bass frequencies to escape, leading to a relatively weaker bass experience.
Comfort and Sound Leakage: In addition to their sound attenuating properties, ear pads also contribute to wearing comfort. By providing a soft and cushioned surface, they help distribute the pressure exerted by the headphones on the ears, reducing discomfort during prolonged listening sessions. Furthermore, the density and material composition of the ear pads can influence the level of sound leakage. Pads that are too porous or worn out may allow sound waves to escape, leading to reduced sound attenuation and potential disturbance to people in the vicinity.
Customization and Replacement: Ear pads are not a one-size-fits-all component. Manufacturers often offer a variety of ear pad options with different sizes, shapes, and materials to cater to individual preferences and optimize sound reduction. Additionally, over time, ear pads can wear out or deteriorate, negatively impacting their sound attenuating capabilities. Fortunately, many headphones provide the option to replace ear pads, allowing users to maintain optimal sound quality and comfort over an extended period.
In Conclusion: The significance of ear pads in sound reduction within headphones should not be underestimated. They not only contribute to enhanced sound isolation and bass response but also play a crucial role in wearer comfort and the prevention of sound leakage. Choosing the right ear pads and properly maintaining them can significantly enhance the overall audio experience provided by headphones.
Factors that Can Impact Sound Loss in Wireless Headphones

When using wireless headphones, there are several factors that can contribute to a decrease in sound quality. Understanding these factors can help users make informed decisions when purchasing and using wireless headphones.
1. Connectivity: The connection between the audio source and the wireless headphones is crucial for maintaining sound quality. Interference from other electronic devices, distance from the audio source, and the strength of the Bluetooth or Wi-Fi signal can all affect the quality of the sound transmitted to the headphones.
2. Compression: Most wireless headphones use compression algorithms to transmit audio wirelessly. While compression reduces the file size and enables faster transmission, it can also result in a loss of audio quality. Different compression algorithms have varying effects on sound quality, with some being more efficient but also more prone to quality degradation.
3. Codec Support: The audio codec used by the headphones and the audio source can also impact sound loss. Different codecs have different levels of compression and processing capabilities, which affect the fidelity of the sound transmitted wirelessly. Compatibility between the headphones and the audio source is important to ensure optimal sound quality.
4. Battery Life: Wireless headphones rely on built-in batteries to function. As the battery charge decreases, the power supplied to the headphones may also decrease, resulting in a decrease in sound volume and quality. It is necessary to regularly recharge wireless headphones to maintain optimal performance.
5. Physical Obstructions: The presence of physical obstructions between the audio source and the headphones can interfere with the wireless signal, leading to sound loss or distortion. Walls, furniture, and even the user's body can block or weaken the wireless signal, affecting the overall sound quality.
6. Environmental Factors: Environmental factors such as radio frequency interference, electromagnetic interference, and ambient noise can also impact sound loss in wireless headphones. These factors can introduce unwanted noise or disrupt the wireless signal, leading to a decrease in sound quality.
Understanding these factors can help users troubleshoot sound quality issues and make informed choices when selecting wireless headphones to suit their needs. By considering connectivity, compression, codec support, battery life, physical obstructions, and environmental factors, users can optimize their wireless headphone experience and enjoy high-quality sound reproduction.
Investigating the Relationship between Headphone Design and Sound Attenuation
In this section, we will delve into an in-depth analysis of the intricate connection between the design of headphones and the phenomenon of sound attenuation. With the aim of understanding the factors influencing sound reduction in headphones, we will explore various aspects of headphone design that contribute to this phenomenon.
- The Impact of Earcup Construction: The design and materials used in the construction of the earcups play a crucial role in sound attenuation. Different materials and shapes can affect the way sound waves interact with the headphone, resulting in varying levels of noise reduction.
- Sealing and Fit: The degree to which a headphone forms a tight seal against the wearer's ears is another significant factor influencing sound attenuation. A secure fit helps to minimize sound leakage, ensuring a more immersive audio experience.
- Noise Isolation Technology: Many modern headphones come equipped with specialized noise isolation technologies, such as active noise cancellation or passive noise isolation. We will explore the inner workings of these technologies and how they contribute to reducing external noise and enhancing audio quality.
- Open vs. Closed-Back Designs: Headphones can be categorized into open-back and closed-back designs, each with its own impact on sound attenuation. We will examine the differences between these designs and their respective effects on sound leakage and isolation.
- Headphone Design and Frequency Response: The design of the headphones can also affect the frequency response, leading to variations in sound attenuation across different frequency ranges. We will investigate how headphone design influences the overall audio experience and its relationship with sound reduction.
By exploring these various aspects of headphone design, we aim to gain a deeper understanding of the intricate relationship between design and sound attenuation. This knowledge can help both manufacturers and consumers make informed decisions when selecting headphones, ensuring optimal audio quality and noise reduction.
Can the Length of a Headphone Cable Impact the Quality of Sound?

When it comes to the quality of sound in headphones, one must consider various factors that might affect it. While many aspects can contribute to the overall sound experience, one important element under discussion is the length of the headphone cable.
Several studies and analyses have been conducted to determine if the cable length has an impact on sound quality. The consensus suggests that, yes, the length of the cable can indeed affect the sound produced by headphones.
Longer cables tend to introduce more resistance, which can lead to a decrease in sound quality. This resistance can affect the electrical signal that travels through the cable, resulting in an altered audio output. Additionally, longer cables are more prone to signal loss and interference, which further compromises the sound quality.
- Signal Loss: Longer cables have a higher chance of losing some of the signal as it travels through the length, resulting in a weaker and distorted sound.
- Interference: Extended cables are more susceptible to picking up external electrical and electromagnetic interference, which can introduce unwanted noise and disrupt the sound.
- Resistance: The longer the cable, the greater the resistance it possesses. Increased resistance can attenuate the audio signal and diminish the overall sound quality.
However, it is crucial to note that the impact of cable length on sound quality may vary depending on factors such as cable material, gauge, and the overall design and construction of the headphones. While shorter cables generally minimize these issues, selecting high-quality cables and headphones designed for longer lengths can help mitigate any negative effects.
In conclusion, the cable length of headphones can indeed affect the quality of sound. Understanding the potential drawbacks associated with longer cables allows users to make informed decisions when selecting headphones and cables, ultimately ensuring an optimal sound experience.
The Influence of Headphone Impedance on Sound Output
When it comes to the transmission of audio through headphones, there are various factors that can affect the sound quality and volume experienced by the listener. One such influential factor is the headphone impedance, which plays a significant role in determining the sound output.
Impedance can be described as the opposition or resistance that an electrical circuit presents to the flow of alternating current (AC). In the context of headphones, impedance refers to the resistance encountered by the audio signal as it passes through the headphone drivers.
The impedance of headphones is typically measured in ohms. Headphones can have varying impedance levels, ranging from low to high. Generally, headphones with lower impedance tend to be easier to drive and require less power to produce sound, while those with higher impedance demand more power to achieve the same volume level.
The influence of headphone impedance on sound output can be demonstrated through the concept of matching impedance. When the headphone impedance matches the output impedance of the audio source, maximum power transfer occurs and optimal sound output is achieved. Conversely, mismatching impedance levels can result in a decrease in sound volume and potentially affect the frequency response and overall audio quality.
It is important to note that while impedance is a significant factor, it is not the sole determinant of sound quality in headphones. Factors such as driver quality, frequency response, and headphone design also play crucial roles in shaping the listener's auditory experience. Therefore, a comprehensive understanding of headphone impedance and its impact on sound output is essential for audiophiles and individuals seeking the best possible audio experience.
Impact of Music Genres on Sound Perception in Headphones
In this section, we will examine the influence of different music genres on the way sound is perceived when listening through headphones. The type of music we listen to can have a significant impact on our overall auditory experience, including factors such as sound quality, immersion, and emotional response.
Music genres vary in terms of their characteristics, including tempo, rhythm, instrumentation, and production techniques. These elements can affect the audio dynamics and frequency range present in a particular genre, ultimately shaping the overall sound perception when listened to through headphones.
| Genre | Characteristics | Impact on Sound Perception |
|---|---|---|
| Classical | Orchestral arrangements, acoustic instruments | Provides a sense of depth and spatialization, highlighting nuances in instrumental performances |
| Rock | Heavy guitars, drums, powerful vocals | Emphasizes dynamic range and intensity, creating a more energetic listening experience |
| Electronic | Synthesized sounds, beats, electronic effects | Focuses on bass frequencies and intricate soundscapes, enhancing the overall rhythm and texture |
| Jazz | Improvisation, complex harmonies | Highlights individual instrument solos and musical interplay, providing a sense of intimacy and spontaneity |
| Pop | Catchy melodies, polished production | Emphasizes vocal clarity and infectious hooks, aiming for a more mainstream and accessible sound |
By understanding how different music genres influence sound perception in headphones, we can better appreciate the unique qualities and sonic experiences offered by each genre. This knowledge can also guide us in selecting the appropriate genres for specific listening preferences or mood settings, enhancing the overall enjoyment of our music listening sessions.
Tips to Optimize Sound Performance in Headsets
In this section, we will explore various strategies and techniques to enhance the efficiency of sound reproduction in headphones. By employing these tips, individuals can experience improved audio quality and maximize their overall listening experience.
1. Enhance the Fit: Ensuring a proper fit is crucial for optimal sound performance in headphones. Experiment with different sizes and types of ear tips or ear cups to find the most comfortable and secure fit. A proper fit creates a better seal, minimizing sound leakage and external noise interference.
2. Consider Noise Isolation: Noise isolation plays a significant role in sound efficiency. Headphones with effective noise isolation technology can block out external sounds, allowing users to focus solely on their audio content without any distractions. Consider investing in headphones specifically designed for noise isolation.
3. Positioning Matters: How you position the headphones on your ears can impact sound quality. Ensure that the ear cups fully cover your ears, creating a sealed environment. Improper positioning may result in sound leakage, compromising the overall audio experience.
4. Adjust Equalizer Settings: Explore the equalizer settings on your audio device or application to fine-tune the sound according to your preferences. Equalizer adjustments can enhance specific frequency ranges, enabling a customized audio experience tailored to your liking.
5. Optimize Source Audio Quality: The quality of the audio source directly affects the sound reproduction. Ensure that the music files or streaming services you use provide high-quality audio formats to achieve the best possible sound performance in your headphones.
6. Avoid Excessive Volume: While it may be tempting to crank up the volume to enjoy your favorite music, it is important to exercise caution. Listening to excessively high volume levels can not only degrade sound quality but also pose potential risks to your hearing health. Maintain a moderate volume level to preserve sound efficiency and protect your ears.
7. Keep Headphones Clean and Well-Maintained: Regularly cleaning your headphones can help maintain optimal sound quality. Keep them free from dust, debris, and earwax buildup, as these can affect the sound transmission and overall performance.
By following these tips, individuals can enhance their headphone sound efficiency, creating an immersive audio experience that brings their music, podcasts, and movies to life.
How to Improve Headphone Sound Quality For Free in Windows 10
How to Improve Headphone Sound Quality For Free in Windows 10 מאת Tropical Tech 473,687 צפיות לפני 3 שנים 8 דקות, 18 שניות
FAQ
Why does sound decrease in headphones?
The sound in headphones decreases due to a number of factors. One possible reason is the impedance mismatch between the headphone and the audio source. Another factor could be the limitations in the headphone's driver size, which affects their ability to reproduce sound accurately and at higher volumes. Additionally, the sound can decrease if the headphone cable is damaged or if there are issues with the audio device or the headphone jack.
What is impedance mismatch and how does it affect the sound in headphones?
Impedance mismatch refers to a difference in the electrical resistance between the audio source (such as a smartphone or computer) and the headphones. When the impedance of the source and the headphones do not match, it can result in a decrease in sound volume and quality. This is because the audio device may not be able to provide enough power to drive the headphones properly, leading to a decrease in sound output.
How can damaged headphone cables affect the sound quality?
When the headphone cables are damaged, it can lead to a decrease in sound quality. The damaged wires may cause interference or signal loss, resulting in lower volume or distorted sound. Additionally, if there is a partial break in the cable, it can affect one side of the headphones, causing an imbalance in sound output. In such cases, replacing or repairing the damaged cables can help restore the sound quality in headphones.




