Are you constantly finding yourself frustrated with the rapid battery depletion and sluggish charging speed of your beloved tablet device? If so, you're not alone in this seemingly never-ending battle for a long-lasting and efficient power supply. In this article, we will explore the perplexing phenomenon behind the expeditious drainage of energy and the leisurely replenishment of your iPad's battery.
The Vanishing Energy
One of the most baffling aspects of the iPad's battery performance is the astonishing speed at which it drains. The moment you unplug your device from its charger, it feels as if a hidden energy vampire emerges, greedily siphoning off every ounce of power. What causes this enigmatic power-hungry behavior, leaving you frequently tethered to an electrical outlet?
Diving deeper into the labyrinth of technology, we find one dominant culprit: background applications. These seemingly innocent pieces of software quietly consume your battery life, even when you aren't actively using them. They operate surreptitiously, eagerly performing tasks and fetching data without your knowledge, ultimately placing an immense strain on your device's battery. From social media platforms continuously refreshing their feeds to location-based apps consistently tracking your whereabouts, these background applications demand a significant portion of your iPad's energy.
Reasons for the rapid battery drain on the iPad

In this section, we will explore the factors that contribute to the quick depletion of battery life on your iPad. While the iPad is known for its impressive performance and functionality, a few variables can affect the longevity of its battery. Understanding these aspects will help you optimize your usage and extend your iPad's battery life.
- Background Processes:
- Display Brightness:
- Network Connections:
- Push Email:
- Resource-Intensive Apps:
- Device Age and Battery Health:
iPads run various background processes, such as app updates, mail fetch, notifications, and location services. These activities consume power and can significantly contribute to the rapid battery drain. Minimizing the usage of these features or adjusting their settings can help conserve battery life.
The brightness of your iPad's screen affects the overall power consumption. Higher brightness levels require more energy, leading to faster battery drain. Adjusting the brightness to an optimal level can help prolong battery life.
iPads connect to the internet through Wi-Fi or cellular data, and both of these options consume power. Continuous use of network connections, especially in areas with weak signals, can strain the battery. Disconnecting from networks when not in use can help preserve battery life.
Enabling push email on your iPad means it will constantly check for new messages, resulting in frequent data fetching and battery usage. Switching to manual email fetching or extending the interval between fetches can reduce battery drain.
Some applications on the iPad are more resource-intensive than others. These apps utilize more processing power and drain the battery faster. Identifying and limiting the use of such apps can help maximize battery life.
Over time, batteries naturally degrade, leading to reduced capacity and faster battery drain. If your iPad is older or its battery health is deteriorating, it may require more frequent charging. Regularly checking and maintaining the battery health can optimize its performance.
By being conscious of these factors and implementing suitable adjustments, you can mitigate the rapid battery drain on your iPad and ensure a longer-lasting battery life.
Background applications consuming excessive power
In relation to the topic of the iPad's battery life and charging speed, one significant factor that can contribute to these issues is the presence of background applications consuming excessive power. These applications, which run in the background even when not actively used, can drain the battery at a faster rate and impede the charging process.
When background applications consume excessive power, it means that they are utilizing a significant amount of the iPad's resources, such as the processor and network connectivity, leading to increased power consumption. This can result in the battery losing its charge more quickly and the device taking a longer time to charge up.
Background apps may consume excessive power due to various reasons. Some applications may have poorly optimized code or are designed to constantly run in the background to provide real-time updates or notifications. Additionally, apps that require frequent syncing or data fetching can also contribute to power drain.
To mitigate this issue, it is essential to manage the background app activity on the iPad. Users can optimize their device's battery life by manually closing unnecessary background applications or disabling their background refresh functionality. By doing so, users can maximize their iPad's battery efficiency and potentially improve the charging speed.
It is also worth noting that regularly updating the iPad's software can help address and resolve any known issues related to background app power consumption. Software updates often include bug fixes and optimizations that can enhance battery performance and charging speed.
In conclusion, the presence of background applications consuming excessive power can negatively impact the battery life and charging speed of an iPad. By understanding and managing background app activity, users can optimize their device's battery efficiency and potentially improve the overall user experience.
Brightness Settings and Their Impact on Battery Life
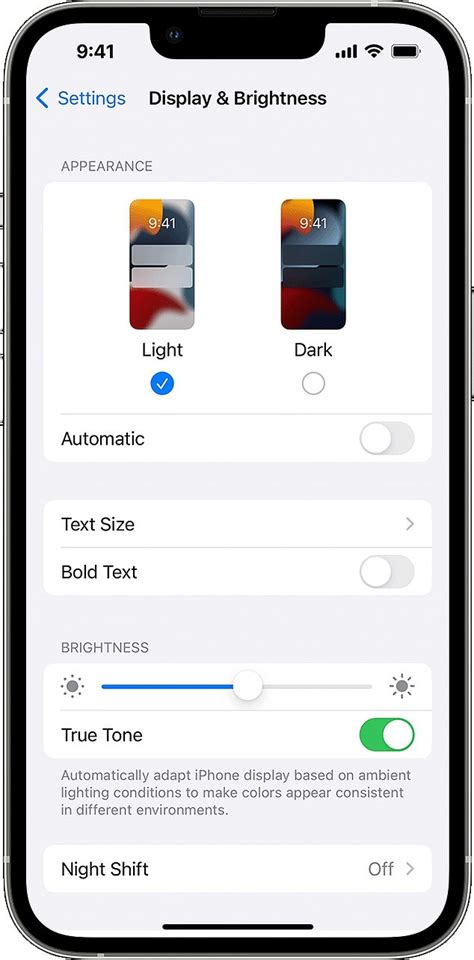
In the context of examining the factors that affect the battery life of an iPad, one important aspect to consider is the brightness settings. Adjusting the brightness level on your iPad screen can have a direct impact on the device's overall battery consumption. By understanding how brightness settings affect battery life, users can effectively manage their iPad's power usage and optimize its battery performance.
Effects of High Brightness:
When the brightness level is set to a higher value, the iPad's screen emits more light, resulting in increased energy consumption. This higher power usage leads to faster battery drain, causing the device to lose its charge more quickly. Therefore, it is advisable to keep the brightness at an appropriate level to conserve battery life.
Ways to Conserve Battery with Lower Brightness:
Lowering the brightness level of the iPad screen can significantly extend its battery life. By reducing the screen brightness, users can effectively decrease the power consumption of the device, mitigating the rate at which the battery depletes. Moreover, the impact of this adjustment on usability is minimal, and the benefits in terms of battery saving make it a worthwhile trade-off.
Optimizing Auto-Brightness:
The iPad offers an Auto-Brightness feature that automatically adjusts the screen brightness based on ambient light conditions. Enabling this feature can be beneficial for managing the device's power usage. By utilizing the built-in light sensor, the iPad can maintain an optimal brightness level that strikes a balance between usability and energy conservation. This way, the device can adapt to different lighting environments and reduce unnecessary battery drain.
In conclusion, managing the brightness settings on an iPad can have a significant impact on its battery life. By adjusting the brightness to appropriate levels, users can conserve battery power, extend usage time, and enhance the overall performance of their device.
Location services and GPS usage draining the battery
One of the factors that can potentially affect the battery life and charging speed of an iPad is the usage of location services and GPS. These features enable the device to determine its geographical location and provide location-based services, but they can also be power-intensive.
When location services are enabled on an iPad, the device constantly uses the GPS functionality to gather information about the user's location. This continuous tracking and data collection process can significantly consume battery power and contribute to a faster battery drain.
In addition to GPS, location services often utilize other technologies such as Wi-Fi, cellular data, and Bluetooth to enhance location accuracy. These technologies require the iPad to constantly search for and maintain connections, further straining the battery.
Apps that heavily rely on location services, such as navigation or mapping applications, can also contribute to battery drain. These apps constantly communicate with the GPS and make use of other location-related features, intensifying the power consumption even more.
If you notice that your iPad's battery is depleting quickly and it takes longer to charge, one of the potential culprits could be the excessive usage of location services and GPS. To optimize battery life, consider limiting the use of location services to only when necessary. You can check which apps have access to your location in the device settings and choose to disable or restrict location access for certain apps.
| Problems | Possible Solutions |
|---|---|
| Rapid battery drain | Limit the use of location services to necessary apps only. Disable or restrict location access for apps that don't require it. |
| Slow charging | Charge your iPad using a high-quality charger and cable. Close unnecessary apps and features while charging to minimize power usage. |
By managing the usage of location services and GPS on your iPad, you can help mitigate the impact on battery life and charging speed, ensuring a more efficient and longer-lasting device.
Push Email and Constant Data Syncing Leading to Rapid Battery Depletion

In today's fast-paced digital world, staying connected is essential. However, the convenience of push email and constant data syncing on the iPad can come at a cost – rapid battery depletion.
Push email, a feature that automatically delivers new email messages to your device as soon as they arrive, ensures that you are always up to date with your inbox. Unfortunately, this continuous data retrieval process requires a significant amount of power, resulting in a faster drainage of your iPad's battery.
Similarly, constant data syncing, which allows your iPad to synchronize data with various online services in real-time, is another culprit behind the device's quick battery drain. Whether it's syncing contacts, calendars, or files, these continuous background processes consume a substantial amount of energy.
Although push email and constant data syncing provide unparalleled convenience, they can impact your iPad's battery life and charging speed negatively. To mitigate these issues, it is advisable to review your email and data synchronization settings, prioritizing which accounts or services truly require real-time updates. By selectively enabling push for essential email accounts and adjusting the frequency of data synchronization for non-essential apps, you can strike a balance between staying connected and preserving battery life.
- Consider disabling push email for less critical accounts and manually checking them periodically to conserve battery power.
- Restrict background app refresh for apps that do not require up-to-the-minute data updates.
- Optimize the frequency of data syncing for apps that rely heavily on real-time updates.
By taking these steps to manage push email and data syncing settings effectively, you can extend your iPad's battery life and ensure it charges more efficiently, allowing you to stay connected without worrying about running out of power too quickly.
Intensive Usage of Graphic-Intensive Applications
When utilizing resource-demanding software and applications that heavily rely on graphics, certain factors can commonly contribute to the rapid battery drainage and slow charging of the iPad.
- The Power-Hungry Nature of Graphic-Intensive Applications:
- Continuous Utilization of CPU and GPU:
- Increased Screen Brightness:
- Background Processes and Network Connectivity:
- Battery Performance and Age:
Graphic-intensive applications, such as high-definition games or video editing software, typically consume a significant amount of battery power due to the processing requirements necessary to render complex graphics and animations.
When engaged in resource-intensive tasks, the central processing unit (CPU) and graphics processing unit (GPU) of the iPad have to work at full capacity, leading to increased energy consumption and subsequently causing the battery to drain more quickly than during regular usage.
To deliver an immersive visual experience, graphic-intensive applications often require a higher screen brightness. This raised brightness level, coupled with the prolonged periods of usage, can rapidly deplete the battery charge of the iPad.
Some graphic-intensive applications continue to run in the background, performing tasks that might require network connectivity or other system resources. These activities contribute to overall battery drain and slow down the charging process.
Over time, the efficiency of the iPad's battery may slightly deteriorate, resulting in reduced capacity and overall power management. Consequently, the device may discharge more rapidly during intensive usage and experience slower charging times.
Understanding the impact of intensive utilization of graphic-intensive applications on battery life and charging speed can help users optimize their iPad's performance and maximize usage time, especially when engaging in tasks that demand significant graphical processing power.
Faulty battery or hardware issues causing rapid power loss

A problematic battery or hardware malfunctions can result in the quick depletion of battery life and slow charging speed on an iPad. These issues can be attributed to various factors and can significantly impact the overall user experience and productivity.
One possible cause of the rapid power loss is a faulty battery. Over time, the battery may degrade and lose its ability to hold a charge efficiently. This can lead to the iPad draining power quickly, even with minimal usage. Additionally, a damaged or swollen battery can also contribute to the decreased battery life, as it may not be able to store and deliver power effectively.
Hardware issues can also be a culprit behind the rapid power loss and slow charging. For instance, a damaged charging port or cable can impede the proper flow of electricity, resulting in slower charging speeds. Similarly, a malfunctioning power management unit (PMU) or power-related components can disrupt the power distribution and utilization, leading to quick battery drain.
Furthermore, software glitches and background processes can occasionally cause the iPad to consume more power than expected, leading to faster battery depletion. This can occur due to poorly optimized apps or settings, excessive background activity, or outdated software. Identifying and resolving these software-related issues can help alleviate the rapid power loss.
In conclusion, a faulty battery or hardware issues can be the underlying cause of a fast-draining battery and slow charging on an iPad. It is essential to diagnose and address these problems promptly to optimize battery performance and ensure a seamless user experience.
Impact of Software and System Updates on Battery Performance
Software and system updates play a crucial role in the overall functioning of electronic devices. In the case of tablets like the iPad, these updates can significantly affect the performance and battery life. This section will delve into the relationship between software and system updates and their potential impact on the battery performance of iPads.
1. Operating System Optimizations: Software updates often introduce new optimizations to the operating system, aimed at improving the overall user experience. These optimizations may include performance enhancements, bug fixes, and power-saving features. However, certain updates may inadvertently result in increased power consumption, leading to a faster battery drain.
2. Background Processes: System updates can introduce changes in the way background processes are managed on the iPad. Background processes are essential for various functions, such as syncing data, updating apps, and fetching notifications. However, if these processes are not properly optimized, they can consume excessive power, resulting in a shortened battery life and slower charging times.
3. App Compatibility: Software updates often bring compatibility changes to ensure a seamless experience with the latest apps and features. However, these changes can also impact the efficiency of older apps, leading to increased power consumption. As a result, some apps may run in the background or utilize system resources inefficiently, contributing to faster battery drain and slower charging.
4. Power Management Algorithms: System updates can also introduce changes to the power management algorithms employed by the iPad. These algorithms determine how power is allocated to different components and processes based on user activity. If these algorithms are not properly calibrated, they can result in suboptimal power allocation, affecting battery performance and charging speed.
- Conclusion: It is essential to consider the impact of software and system updates on the battery performance of iPads. While updates often bring enhancements, they can also introduce unintended consequences that affect battery life and charging times. Understanding these factors can help users optimize their device usage and take necessary steps to mitigate any negative effects on battery performance.
Overcharging the iPad and its impact on battery capacity

One factor that significantly influences the lifespan and overall performance of an iPad's battery is overcharging. Over time, continuous overcharging can have adverse effects on the battery's capacity and its ability to hold a charge efficiently.
When an iPad is plugged in and kept on charge beyond its full capacity, the excess electrical energy causes the battery to undergo certain chemical reactions. These reactions generate heat, which can result in the degradation of the battery's internal components, including the electrolyte and electrodes.
As the battery capacity diminishes due to overcharging, the iPad's ability to retain a charge gradually declines. This can lead to the device discharging more quickly and requiring more time to recharge fully. Additionally, the battery may lose its ability to reach its maximum charge potential, resulting in a decreased battery life.
To mitigate the impact of overcharging on the iPad's battery, it is advisable to follow some best practices. These include avoiding leaving the device plugged in for prolonged periods once it reaches full charge, using the original charger and cable provided by Apple, and ensuring the iPad is not exposed to extreme temperatures.
By taking precautions to avoid overcharging and maintaining a healthy charging routine, users can help preserve the longevity and performance of their iPad's battery.
4G/LTE Connectivity Consuming Higher Power than Wi-Fi
In the realm of mobile devices, the choice between different connectivity options plays a crucial role in the overall battery performance. While both 4G/LTE and Wi-Fi enable users to stay connected, it is important to consider the power consumption associated with each option.
When using a 4G or LTE connection on your iPad, the device consumes more power compared to when it is connected to Wi-Fi. This higher power consumption is primarily due to the nature of 4G/LTE technology, which requires more energy to maintain a stable and strong connection with cellular networks.
- Network Signal Strength: 4G/LTE connectivity often requires the device to maintain a strong signal reception to ensure a reliable internet connection. This constant communication with nearby cellular towers utilizes more power than connecting to a Wi-Fi network, where the signal strength is generally better and requires less effort from the device.
- Data Transfer Speed: 4G/LTE networks are designed to provide faster data transfer speeds, allowing users to browse the internet, stream videos, and download large files swiftly. However, this enhanced performance comes at the cost of higher power consumption, as the device requires more energy to process and transmit data at these accelerated speeds.
- Background Processes: When connected to 4G/LTE, certain background processes, such as data synchronization, app updates, and push notifications, tend to be more active. These processes continuously interact with the network, consuming additional power compared to Wi-Fi, where such activities may be less frequent or optimized for efficient battery usage.
Therefore, if you notice that your iPad's battery drains faster and charges slower, it could be attributed to the use of 4G/LTE connectivity. To prolong battery life, it is advisable to connect to Wi-Fi whenever possible, especially when engaging in activities that do not require the high-speed capabilities provided by a cellular network.
Battery health degradation over time due to regular usage
One of the important factors that affects the performance of an iPad's battery is the gradual deterioration of its health over time, which is primarily a result of regular usage.
With the passage of time and regular utilization of the device, the iPad's battery undergoes natural wear and tear, ultimately leading to a decline in its overall performance. This degradation is inevitable and can be attributed to several factors related to the inner workings of the battery.
Factors such as chemical reactions within the battery, internal resistance, and the number of charge cycles it has gone through contribute to the gradual reduction in battery capacity. Chemical reactions occurring during charging and discharging activities gradually diminish the ability of the battery to hold a charge, resulting in decreased battery life.
Moreover, each time an iPad is charged and discharged, the battery's internal resistance increases slightly, further impacting its ability to retain a charge. Over time, this resistance continues to grow, causing the battery to drain more quickly and charge at a slower rate.
To mitigate the effects of battery degradation, manufacturers incorporate optimization techniques and algorithms within the iPad's operating system. These features attempt to optimize power consumption, enhance charging efficiency, and extend battery life. However, even with these measures in place, it is still crucial to take appropriate steps to minimize wear and tear on the battery.
- Refraining from excessive heat exposure, as high temperatures can accelerate battery degradation.
- Avoiding extremely low battery levels, as deep discharges can adversely affect battery health.
- Using original charging accessories and avoiding the use of unauthorized or counterfeit chargers.
- Implementing power-saving settings and reducing screen brightness can also help prolong battery life.
While battery degradation is an inevitable process, practicing proper charging habits and taking necessary precautions can slow down the decline and help maintain better performance and longer battery life for your iPad.
[MOVIES] [/MOVIES] [/MOVIES_ENABLED]FAQ
Why does my iPad's battery drain quickly?
There can be several reasons why your iPad's battery drains quickly. One common reason is that you have multiple apps running in the background, consuming energy. To fix this, you can close unnecessary apps or enable the "Background App Refresh" feature in settings to limit app refresh when not in use. Additionally, display brightness, push notifications, and location services can also impact battery life, so adjusting these settings can help extend the battery's duration.
Why does my iPad charge slowly?
There are several potential causes for slow charging on your iPad. Firstly, check if you are using the right charging adapter and cable, as using low-quality or third-party chargers may not deliver enough power. It is also possible that the charging port of your device is dirty or damaged, affecting the charging speed. In this case, gently clean the port or consult a technician for further assistance. Lastly, some iPad models are designed to charge at a slower rate to preserve battery health, so if you have an older iPad, this might be the reason for slow charging.
Can background app activities affect my iPad's battery life?
Yes, background app activities can significantly impact your iPad's battery life. Some apps continue to run in the background, even when you are not actively using them, consuming battery power. To address this issue, you can manually close unnecessary apps by swiping them off the multitasking screen or enable the "Background App Refresh" option. This feature allows you to control which apps can refresh their content in the background, helping to optimize battery usage.