Have you ever experienced that peculiar occurrence when listening to music through your headphones, only to hear inexplicable sounds that seem to originate from the microphone? This phenomenon, known as audio feedback, can be quite perplexing, leaving us questioning the technical intricacies behind its occurrence.
Audio feedback in personal audio devices occurs when the sound from the microphone is inadvertently looped back into the headphones, resulting in an unexpected blend of incoming audio and captured sound. This can manifest as echoes, high-pitched squeals, or a muffled distortion that can significantly deteriorate the quality of our listening experience.
The root cause of this phenomenon lies in the intricate interplay between the microphone and the headphones. When our headphones are equipped with an integrated microphone or if we are using an external microphone while wearing our headphones, a feedback loop can be inadvertently created. This loop is initiated when the sound captured by the microphone enters the audio input, gets processed and amplified, and then accidentally gets played back through the headphones.
To put it simply, the feedback loop occurs when the microphone picks up the sound from the headphones and sends it back into the device, where it is amplified and then fed back into the headphones. This repetitive cycle can create an unsettling experience where we find ourselves hearing sounds that are not supposed to be there.
Understanding the mechanisms behind audio feedback can help us take preventive measures to minimize or eliminate this phenomenon. By familiarizing ourselves with the factors that contribute to feedback, such as microphone sensitivity, headphone volume levels, and the distance between the microphone and the headphones, we can ensure a more seamless and uninterrupted audio experience.
Understanding the Phenomenon of Sound Leakage from the Microphone to Headphones

In this section, we explore the intriguing phenomenon of sound escaping from the microphone and reaching the headphones. This occurrence, which encompasses the transmission of auditory signals from the microphone to the headphones, has attracted considerable attention due to its impact on the overall sound experience. By delving into the intricate workings behind this phenomenon, we aim to shed light on the factors contributing to the leakage of sound and the implications it holds for users.
The transmission of sound from the microphone to the headphones, commonly referred to as sound leakage, occurs when an unintended pathway allows a portion of the acoustic signal to bypass its intended route. This unexpected transfer introduces an additional element to the auditory experience, as the listener perceives sound not only from the desired source but also from the microphone itself. It is crucial to comprehend the underlying mechanisms that enable this phenomenon to better understand its implications and potential solutions.
- Acoustic feedback: One common cause of sound leakage from the microphone to the headphones is the occurrence of acoustic feedback. Feedback arises when the sound emitted from the headphones is inadvertently picked up by the microphone, creating a loop where the captured audio is then replayed through the headphones. This feedback loop amplifies the original sound and can result in distortion or unwanted echoes.
- Microphone sensitivity: The sensitivity of the microphone plays a significant role in the extent of sound leakage. A highly sensitive microphone is more prone to capturing ambient noise and unintentional audio signals, which can reach the headphones. This sensitivity can be affected by factors such as the quality of the microphone and its positioning relative to the sound source.
- Headphone design: The design of the headphones themselves can also contribute to sound leakage. Open-back headphones, for instance, are designed with small openings or perforations on the outer ear cups, allowing sound to escape intentionally. However, in some cases, these openings may allow unintended sound from the microphone to reach the listener's ears.
Understanding the phenomenon of sound escaping from the microphone to the headphones involves a comprehensive examination of acoustic feedback, microphone sensitivity, and headphone design. By gaining insight into these factors, users can make informed decisions regarding their audio setup and explore potential solutions to mitigate sound leakage. The subsequent sections of this article delve further into these factors, providing a deeper understanding of the mechanisms at play.
How Sound Travels Between the Microphone and Headphones
In this section, we will explore the fascinating journey of how sound travels between the microphone and headphones. We will delve into the intricate mechanisms and pathways that enable the transmission and reception of audio signals, creating an immersive experience for our ears.
- Capturing Sound: The process begins with the microphone, a device that converts sound waves into electrical signals. When a sound wave reaches the microphone, it causes a diaphragm or a similar component to vibrate, creating fluctuations in the electrical current. These fluctuations represent the captured sound and serve as the initial step in transmitting it.
- Transmission Via Cables or Wireless Connections: The electrical signals produced by the microphone are then transported to the headphones. This transfer commonly occurs through cables or wireless connections, depending on the audio setup. Cables act as conductors, carrying the signals' electrical currents, while wireless technologies employ radio waves to transmit the audio data.
- Amplification and Processing: Upon reaching the headphones, the electrical signals are amplified to achieve an appropriate audio level for listening. Within the headphones, various components and circuits process the incoming signals, shaping and equalizing them to enhance the sound quality according to the preferences or specifications set by the user.
- Conversion to Sound Waves: After amplification and processing, the headphones convert the electrical signals back into sound waves. This transformation involves the displacement of tiny transducers, such as dynamic drivers or balanced armature receivers, which generate vibrations that correspond to the electrical fluctuations. These vibrations produce audible sound waves that can then be perceived by our ears.
- Delivery to the Ears: Finally, the generated sound waves are delivered to the ears through the headphones' earcups or earbuds. By transmitting the sound directly into the ear canal, the headphones allow the listener to enjoy the audio content while minimizing external noise interference. This immersive experience enables us to fully immerse ourselves in music, podcasts, calls, or any other audio content.
Understanding the journey of sound from the microphone to the headphones provides us with valuable insights into the intricate process that allows us to enjoy rich and vibrant audio experiences. By harnessing the power of technology and intricate mechanisms, sound is seamlessly converted and delivered, bringing us closer to the captivating world of audio.
Common Reasons for Experiencing Audio Playback from the Microphone in Headphones
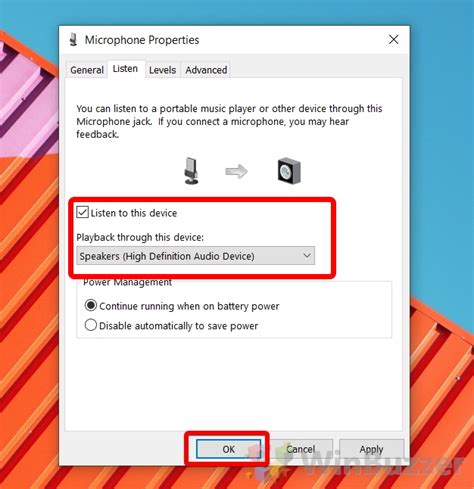
Discovering the underlying causes for the occurrence of audio playback from the microphone in headphones can provide valuable insights into troubleshooting and resolving this perplexing issue. By understanding the common factors contributing to this phenomenon, users can effectively address and rectify the audio interference experienced during microphone use with their headphones.
1. Feedback Loop: A potential reason for hearing audio playback from the microphone in headphones is the presence of a feedback loop. Feedback loops occur when sound from the headphones is picked up by the microphone, creating a continuous loop of sound amplification. This can lead to an unpleasant and distracting audio experience.
2. Inadequate Isolation: Another possible cause is insufficient physical isolation between the microphone and the headphones. If they are placed too closely or lack appropriate shielding, sound vibrations from the headphones can leak into the microphone, resulting in audio feedback or unintended audio capture.
3. Input and Output Configuration: Incorrect input and output configurations within the audio settings of the device can also lead to sound being transmitted from the microphone to the headphones. Misalignments in these settings may cause the sound signals to be inadvertently routed back to the headphones instead of being solely recorded by the microphone.
4. Faulty Hardware Connections: Issues with hardware connections, such as loose cables or faulty connectors, can contribute to audio leakage from the microphone into the headphones. These physical faults can disrupt the intended audio signals, resulting in unwanted sound playback.
5. Echo and Ambient Noise Enhancements: Some devices have features or settings that enhance ambient noise or create an echo effect during audio recordings or communications. These enhancements, while potentially enhancing overall sound quality, can inadvertently lead to the perception of microphone audio being played back through the headphones.
Identifying the common reasons behind the occurrence of audio playback from the microphone in headphones assists users in effectively troubleshooting and resolving this issue. By addressing feedback loops, ensuring proper isolation, configuring input and output settings correctly, checking hardware connections, and adjusting device settings, users can regain the intended audio experience when using their headphones and microphone together.
The Role of Audio Leakage in Transmitting Sound via the Microphone to Headphones
Audio leakage plays a crucial role in the transmission of sound from the microphone to the connected headphones. This phenomenon involves the unintentional escape of sound signals, resulting in their reproduction through the headphone speakers. Understanding the mechanisms behind audio leakage is crucial in comprehending the factors that contribute to this occurrence and finding effective solutions to mitigate its impact.
One significant aspect of audio leakage is the unintentional transmission of sound waves picked up by the microphone. These waves can include background noise, ambient sounds, or even one's own voice. Through various means, such as inadequate sound insulation or poorly designed microphone placement, these captured audio signals can leak into the headphone output, interfering with the intended audio playback and possibly causing distractions.
Furthermore, audio leakage can be influenced by several factors, including the quality and design of the microphone and headphones themselves. A low-quality microphone or headphones may lack proper shielding or insulation, allowing sound to leak more easily. Additionally, the physical distance between the microphone and headphones, as well as the volume or intensity of the sound captured by the microphone, can also impact the extent of audio leakage.
- Improperly fitting headphones can contribute to audio leakage. When the headphones do not create a proper seal around the ears, sound can escape both from the headphones to the surroundings and from the surroundings to the headphones.
- The positioning of the microphone can affect the amount of audio leakage. If the microphone is placed too close to the headphone speakers, the likelihood of sound escaping from the microphone to the headphones increases.
- Inadequate sound isolation in the microphone or headphone cables can also contribute to audio leakage. These cables can act as conduits for sound signals, allowing them to flow between the microphone and headphones more easily.
Overall, understanding the role of audio leakage in the transmission of sound from the microphone to the headphones is crucial in addressing and preventing the unintended reproduction of sound signals. By considering the various factors that contribute to audio leakage, such as the microphone quality, headphone fit, and cable insulation, effective measures can be implemented to minimize these occurrences and enhance the overall audio experience.
Tips and Solutions to Minimize Sound Leakage from the Microphone to Headphones

When using headphones with a microphone, it is common to experience sound leakage, where audio picked up by the microphone is played back through the headphones. This can be distracting and affect the audio quality during voice or video calls. Fortunately, there are several solutions and tips to help prevent sound from escaping the microphone and interfering with your headphone experience.
- Adjust the microphone position: Try repositioning the microphone away from the headphone speakers to reduce the likelihood of picking up audio from the headphones. Experiment with different placements to find the optimal distance that minimizes sound leakage.
- Use a headset with noise-canceling technology: Consider investing in a headset that features active noise-canceling technology. These headsets typically have built-in microphones designed to block out external sounds, including any audio coming from the headphones.
- Use a microphone with directional pickup: Instead of using a microphone that captures sound from all directions, opt for a unidirectional or cardioid microphone. These types of microphones are more focused and primarily pick up audio from the front, reducing the chances of sound leakage from the headphones.
- Reduce the volume: Lowering the volume of your headphones can help prevent sound leakage. By keeping the volume at a reasonable level, the microphone is less likely to pick up audio from the headphones and transmit it back to your ears.
- Enable microphone noise gate: Many audio software and communication applications include a feature called a noise gate. With this feature enabled, the microphone will only pick up sound above a certain threshold, effectively filtering out any lower volume sounds, such as the audio from your headphones.
- Use headphones with better isolation: Consider using headphones that offer better noise isolation. Closed-back headphones, for example, have ear cups that fully enclose your ears, helping to prevent sound leakage both from the environment and the microphone.
By implementing these tips and utilizing the appropriate equipment, you can significantly reduce sound leakage from the microphone to your headphones, enhancing your audio experience during calls, recordings, or any other activities where headphone usage is vital.
🔈How to fix “No Sound from Headphones🎧” issue in Windows 10
🔈How to fix “No Sound from Headphones🎧” issue in Windows 10 by CoolTechtics 442,856 views 3 years ago 4 minutes, 54 seconds
FAQ
What could be the possible reasons for hearing sound from the microphone in my headphones?
There can be several reasons behind this issue. One possibility is that the microphone and headphone jacks are incorrectly connected, leading to sound leakage. Another reason could be a faulty headphone or microphone cable. Additionally, the issue might be caused by incorrect audio settings on your device or an incompatible audio driver.
How can I fix the problem of hearing my own voice in the headphones?
To fix this issue, first, check the connections between the microphone and headphone jacks to ensure they are properly plugged in. If the connections are secure, try using a different set of headphones or microphone to see if the issue persists. Adjusting the audio settings on your device, such as reducing the microphone levels or turning off audio monitoring, might also solve the problem. Updating or reinstalling the audio drivers can sometimes resolve compatibility issues that cause sound leakage.
Is it possible that the microphone itself is faulty and causing the sound leakage?
Yes, it is possible for a faulty microphone to cause sound leakage in your headphones. If you have tried all the troubleshooting steps mentioned earlier and the issue still persists, the problem might lie with the microphone itself. Consider getting it checked or replaced by a professional if necessary.
Are there any software solutions to eliminate the sound from the microphone in my headphones?
Yes, there are software solutions that can help eliminate the sound from the microphone in your headphones. You can try using audio editing software to reduce or remove the microphone audio from the headphone output. Additionally, some communication software and applications offer settings to control the audio monitoring levels or disable it altogether.




