Have you ever wondered why, in the world of audio technology, we sometimes encounter unpleasant and disruptive sounds instead of the harmonious melodies we seek? It is a perplexing phenomenon that has puzzled experts and enthusiasts alike for decades. Perhaps it is time to uncover the secrets behind the discordant noise that headphones occasionally emit, and to shed light on the factors that contribute to this peculiar issue.
When we immerse ourselves in the world of music or any other form of audio pleasure, we anticipate a pristine auditory experience devoid of any disturbances. However, despite our utmost efforts to maintain audio purity, there are instances when our ears are met with an unwelcome array of intrusive sounds. These unwarranted noises often come in the form of static crackles, buzzing frequencies, or intermittent hums, which tarnish our listening enjoyment.
The culprit behind this unfortunate occurrence lies within the intricate mechanisms and delicate components that bring our headphones to life. Just like any technological device, headphones are not invincible to imperfections and external interference. From the circuitry within the speakers to the wires that transmit signals, every element plays a role in either enhancing or degrading the audio quality. Consequently, any slightest flaw or disruption can result in the generation of unwanted noise, disrupting our music sessions and steering us away from auditory bliss.
The Mechanics Behind the Generation of Sound in Headphones
When we put on a pair of headphones, we enter a world of audio, enveloped by the symphony of our favorite songs, podcasts, or movies. But have you ever wondered about the fascinating physics that allow these devices to transform electrical signals into audible sound?
At the heart of the headphone's sound generation lies a complex interplay of various components and principles. One of the main elements is the driver, which can be thought of as the engine responsible for converting electrical signals into sound waves that travel through the air and reach our ears. This remarkable mechanism relies on the principles of electromagnetism and acoustics to create the music and audio experiences we love.
- Electromagnetic Induction: Headphones use a phenomenon called electromagnetic induction to generate sound. Within the driver unit, there is a magnet surrounded by a coil of wire. When an electrical signal passes through this coil, it creates a fluctuating electromagnetic field. This changing field interacts with the magnet and causes the coil to move back and forth, vibrating the diaphragm.
- Vibrations and Sound Waves: The diaphragm is a thin, flexible membrane located at the front of the driver. As the coil moves in response to the changing electromagnetic field, it pushes and pulls the diaphragm, creating vibrations. These vibrations generate changes in air pressure, which propagate as sound waves. The frequency and amplitude of these waves determine the pitch and volume of the sound produced.
- Transducers and Frequency Response: The diaphragm acts as a transducer, converting electrical energy into mechanical energy and then into acoustic energy. Different headphones have different diaphragm designs, sizes, and materials, which affect their frequency response. The frequency response indicates how well a headphone reproduces sound across the audible spectrum, from low to high frequencies.
- Enclosures and Acoustic Design: Another crucial factor in headphone sound generation is the enclosure or ear cup design. The shape, materials, and acoustic properties of the ear cups influence the way sound waves interact with the drivers. Enclosures often feature damping materials and chambers designed to enhance specific frequency ranges, improve sound isolation, and reduce unwanted resonances.
Understanding the physics behind headphone sound generation allows us to appreciate the intricate engineering and craftsmanship that goes into these audio devices. From the electromagnetic interactions to the vibration of the diaphragm and the careful acoustic design, each component plays a vital role in delivering the captivating soundscapes that enrich our daily lives.
Common issues that result in unwanted sound distortion in headphones
When using headphones, it is not uncommon to experience certain disturbances in the audio quality that can be described as noise or unwanted sound distortion. These problems can arise due to a variety of reasons and understanding these issues can help us identify and resolve them effectively.
| Issue | Description |
| Electromagnetic interference | External electromagnetic waves can interfere with headphone signals, leading to noise or distorted sound. This can be caused by proximity to electronic devices such as smartphones, tablets, or even power cables. |
| Poor cable connections | Loose or damaged cable connections can result in intermittent audio disruptions or a constant buzzing sound. A faulty connection between the headphones and the audio source may also contribute to this problem. |
| Impedance mismatch | If the impedance of the headphones and the connected audio device do not match, it can lead to audio irregularities. This can cause both low volume levels and excessive noise in the headphones. |
| Audio source quality | The quality of the audio source being played through the headphones can also play a role in noise issues. Low-quality recordings, improperly encoded files, or streaming services with low bitrates can introduce unwanted artifacts or noise into the audio. |
| Worn-out or damaged components | Over time, various components of the headphones, such as the speakers or the audio jack, can degrade or become damaged. This can lead to distortions or unwanted noise when using the headphones. |
These are just a few examples of the common issues that can cause noise or unwanted sound distortion in headphones. By identifying and addressing these problems, users can enhance their listening experience and enjoy high-quality audio without any disturbances.
The Impact of Electrical Interference on Distorted Audio in Headphones

When listening to audio through headphones, many users may experience the frustrating phenomenon of distorted sound, commonly referred to as noise. This issue arises due to a variety of factors, one of which is the presence of electrical interference. Electrical interference can cause disruptions in the signal transmission, resulting in compromised audio quality.
Electrical interference refers to the disruption or distortion of an electrical signal caused by the presence of external electromagnetic fields. These fields can emanate from various sources, including power lines, electronic devices, and even wireless signals. When these fields interact with the electrical circuitry within headphones, they can induce unwanted electrical currents or voltages, which interfere with the accurate reproduction of sound.
One of the primary contributors to this interference is electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) issues. To ensure proper functioning, electronic devices must meet specific EMC standards, which regulate their ability to emit and withstand electromagnetic interference. If the headphones or their associated components do not comply with these standards, they may be more susceptible to electrical interference and subsequently produce distorted audio.
Furthermore, inadequate shielding within the headphone design can also exacerbate the effects of electrical interference. Shielding is a protective layer that surrounds the internal components of the headphones, preventing external electromagnetic fields from entering the circuitry. Insufficient shielding or gaps in the shielding can allow these fields to penetrate the headphones, leading to increased electrical interference and compromised sound quality.
| Factors Contributing to Electrical Interference | Impact on Headphone Noise |
|---|---|
| Power lines | Induces unwanted currents, leading to distorted audio |
| Electronic devices | Produces electromagnetic fields that disrupt signal transmission |
| Wireless signals | Interferes with headphone circuitry, resulting in compromised audio |
| Electromagnetic compatibility issues | Non-compliance leads to increased susceptibility to interference |
| Inadequate shielding | Allows external fields to penetrate, amplifying electrical interference |
To mitigate the effects of electrical interference, manufacturers employ various techniques such as improving shielding materials, implementing better circuit designs, and conforming to stringent EMC standards. By addressing these factors, headphone manufacturers strive to provide users with an enhanced audio experience, free from the disruptive noise caused by electrical interference.
How headphone design impacts sound quality
The quality of sound produced by headphones is influenced by various factors related to their design. These design elements play a crucial role in determining the overall audio experience and can greatly enhance or compromise the sound quality.
- Headphone Drivers:
- Enclosure Design:
- Ear Cup and Ear Pad Construction:
- Cable Construction:
- Connectivity:
The type and quality of drivers used in headphones greatly affect the sound output. Different drivers, such as dynamic, planar magnetic, or electrostatic, have their own unique characteristics that influence the frequency response, clarity, and accuracy of the sound. Manufacturers carefully select and tune the drivers to achieve a specific sound signature.
The design of the headphone enclosures, including their shape, size, and materials, impacts the sound reproduction. The enclosure's ability to effectively isolate the sound from external noise and prevent sound leakage can significantly enhance the audio experience. Moreover, certain materials may introduce unwanted resonances, affecting the overall sound quality.
The design of the ear cups and ear pads also affects the sound quality. The shape and size of the ear cups can impact the soundstage and imaging, while the material and thickness of the ear pads influence comfort and the seal around the ears, which directly affects bass response and noise isolation.
The construction and quality of the cable connecting the headphones to the audio source can impact the sound transmission. Factors such as cable length, gauge, shielding, and connectors can introduce interference, signal loss, or distortion if not designed and implemented properly.
The method of connecting the headphones to the audio source can also affect the sound quality. Wired connections generally provide more stable and reliable audio transmission compared to wireless connections, which may introduce latency or signal degradation.
Overall, the design of headphones encompasses a variety of factors, each of which can significantly impact the sound quality. Manufacturers carefully consider these design elements to achieve the desired audio performance and provide users with an immersive and enjoyable listening experience.
The Influence of Headphone Cable Quality on Disturbance Generation

In the realm of audio devices, the quality of the cable connecting headphones to their source plays a significant role in the occurrence of unwanted disturbances. These disturbances, commonly referred to as noise, are the result of various factors related to the cable itself. Understanding the relationship between headphone cable quality and noise production is crucial for both manufacturers and consumers seeking optimal audio experiences.
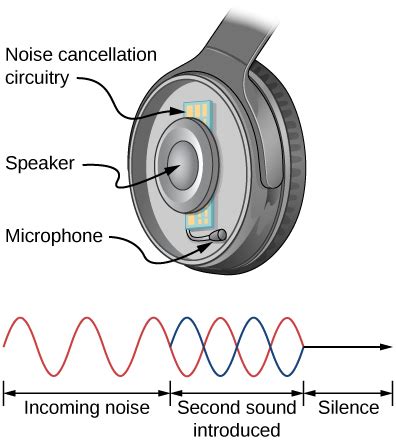
Noise-canceling technology: Minimizing unwanted sounds
Unwanted sounds can often disrupt the listening experience when using electronic audio devices. To address this issue, advanced noise-canceling technology has been developed to reduce the presence of these undesirable sounds. By employing innovative techniques, this technology aims to enhance audio quality and eliminate distractions caused by external noise.
One effective method used in noise-canceling technology is signal processing. This technique involves the analysis of incoming sound waves and the creation of counteractive sound waves. By producing these counteractive waves, the technology actively combats and cancels out unwanted noise, allowing the listener to focus on the desired audio content.
Another approach employed in noise-canceling technology is passive noise cancellation. This technique utilizes physical barriers or materials to passively block out external sounds. By using sound-absorbing or sound-reflecting materials in the design of headphones, unwanted noise is naturally attenuated, minimizing its impact on the audio experience.
- Active noise canceling: This method actively measures the external noise and generates sound waves to counteract it, effectively eliminating unwanted sounds. It can be particularly effective in environments with constant background noise, such as airplanes or trains.
- Passive noise cancellation: This technique relies on physical barriers or materials to block out external sounds. By using acoustic isolation and insulation, unwanted noise is reduced, providing a quieter listening experience.
- Hybrid noise cancellation: Some headphones combine both active and passive noise cancellation methods to provide a comprehensive solution. These headphones often use a combination of microphones, speakers, and specialized materials to achieve optimal noise reduction.
Noise-canceling technology has revolutionized the audio industry by significantly improving the listening experience. Whether it is reducing the constant hum of an airplane engine during travel or eliminating background chatter in a busy office, this technology allows users to enjoy their audio content without distractions, enabling a more immersive and enjoyable experience.
The Interplay between Headphone Resistance and Disturbance
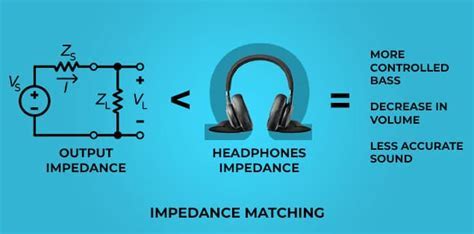
One of the key factors affecting the quality of sound reproduction in headphones is the impedance, or electrical resistance, of the device. The impedance of headphones plays a significant role in determining the extent to which unwanted noise interferes with the sound experience. Understanding the relationship between headphone impedance and noise is essential for achieving optimal audio performance.
Impedance as a Protective Shield
Headphone impedance serves as a barrier against external disturbances that can degrade the audio signal. The higher the impedance, the more effectively it attenuates unwanted electrical noise present in the environment. This shielding effect reduces the impact of interference, ensuring a cleaner and more accurate sound reproduction.
Inadequate Impedance and Noise Amplification
When headphones have low impedance, they become more susceptible to picking up electrical noise. This vulnerability can result in the amplification of interference, leading to a compromised audio experience characterized by static, buzzing, or hissing sounds. The interaction between low impedance and external noise sources highlights the importance of impedance matching in headphone selection to avoid such disturbances.
Headphone Impedance and Audio Source Compatibility
The impedance of headphones should also be considered in relation to the audio source being used. Mismatched impedance between the headphones and the source can introduce distortion and degrade the sound quality. Therefore, it is crucial to select headphones with an impedance range that is compatible with the output impedance of the audio device to achieve optimal sound reproduction.
Impedance Variations within Headphone Models
Even within the same model of headphones, there can be variations in impedance. This variation occurs due to manufacturing tolerances and design considerations. It is important to be aware of these impedance differences, as they can affect the overall audio performance and the susceptibility of headphones to noise interference. Checking the specifications or consulting with experts can aid in choosing headphones with desired impedance characteristics.
By understanding the intricate relationship between headphone impedance and noise interference, users can make informed decisions when selecting headphones that produce high-quality sound with minimal disruptions. Proper impedance matching, along with other audio considerations, can enhance the overall listening experience and ensure a more immersive soundstage.
Common Causes of Distorted Audio in Headphones
When using headphones, it is not uncommon to experience distorted or noisy audio. However, this issue may not always be attributed to a fault with the headphones themselves. Instead, improper usage or external factors can contribute to the production of unwanted noise. In this section, we will explore the various reasons why headphones can produce noise due to improper usage.
| Potential Cause | Description |
|---|---|
| Incorrect Volume Levels | One common mistake that can result in noisy audio is setting the volume levels too high. When the volume is turned up excessively, it can overload the headphones' drivers, leading to distortion and noise. It is important to find the right balance to ensure clear and crisp sound. |
| Poor Cable Connections | Another reason for noise in headphones can be attributed to poor cable connections. If the cables are not securely plugged into the audio source or the headphone jack, it can result in intermittent connections, causing static or crackling sounds. Ensuring a snug fit and proper cable management can minimize this issue. |
| Interference from External Devices | External electronic devices, such as smartphones, tablets, or even wireless routers, can introduce interference when used near headphones. This interference can manifest as buzzing, popping, or hissing sounds. Keeping headphones away from such devices can help reduce the noise caused by interference. |
| Worn-out or Damaged Headphone Components | Over time, headphone components, such as the ear cushions, cables, or drivers, can wear out or become damaged. This wear and tear can lead to irregular audio performance and produce unwanted noise. Regular maintenance and replacing worn-out parts can help restore optimal sound quality. |
| Compatibility Issues | Incompatibility between the headphones and the audio source can also result in distorted or noisy sound. Different headphones have different impedance levels, and using headphones with impedance that is not suitable for the audio source can lead to improper sound reproduction. Checking the compatibility specifications can help avoid such issues. |
In conclusion, while headphones are designed to deliver high-quality sound, improper usage can contribute to the production of noise instead. By understanding and addressing the common causes mentioned above, users can optimize their headphone experience and enjoy clear and immersive audio.
Addressing misconceptions about unwanted sounds in headphones

Often, we may encounter the phenomenon of distractions in our headphones that are not harmonious melodies or clear audio signals, but rather unwelcome noises. It is essential to distinguish between the misconception that headphones intentionally generate noise instead of sound, and the reality that these unwanted sounds may arise due to various factors. In this section, we will debunk several misconceptions surrounding headphone noise, shedding light on the true causes behind these disturbances.
The myth of intentional noise:
Firstly, it is important to dispel the notion that headphones are intentionally designed to produce noise instead of producing sound. Headphones are created to provide a medium for audio transmission, allowing us to enjoy music, receive phone calls, or immerse ourselves in other audio experiences. The primary purpose of headphones is to faithfully reproduce the intended sound signals, without introducing additional noise or distortions. Consequently, any noise observed during headphone usage can be attributed to underlying factors that affect the audio quality.
Environmental factors:
One significant factor contributing to unwanted sounds in headphones is the environment in which they are used. External noises, such as traffic, conversations, or background music, can find their way into the headphones, mixing with the desired audio and reducing overall sound quality. Additionally, electromagnetic interference from nearby electronic devices or wireless signals can disrupt the audio transmission, resulting in unwanted noise. These environmental factors must be taken into account when assessing the quality of sound produced by headphones.
Quality of headphones:
The quality of headphones plays a vital role in the occurrence of unwanted noise. Inferior or damaged headphones may produce crackling sounds, static noise, or distortions due to poor construction or faulty components. Furthermore, headphones that do not fit properly or have loose connections can create audio interruptions or introduce additional noise. It is crucial to invest in well-built, reputable headphones to minimize the chance of experiencing disruptive noises.
Internal electronic factors:
Internal electronic components within the headphones can also contribute to the generation of noise. For instance, inadequate shielding within the device can allow electrical signals to interfere with the audio circuitry, resulting in unwanted sounds. In addition, electrical grounding issues or poor signal processing can introduce noise into the audio output. Manufacturers must address these internal factors to ensure a high-quality sound experience for users.
Solutions and troubleshooting:
To address headphone noise issues, several troubleshooting steps can be taken. This includes selecting headphones with noise-canceling capabilities or using ear cups that provide better isolation from external noise. Additionally, regularly cleaning headphone connectors and ensuring a secure connection can reduce audio disruptions caused by loose connections. Furthermore, keeping headphones away from strong electromagnetic sources can minimize interference and improve audio clarity.
In conclusion, understanding the complexities behind headphone noise is crucial in dispelling misconceptions about intentional noise production. By acknowledging the impact of environmental factors, quality of headphones, and internal electronic components, we can identify and address the true causes of unwanted sounds. Taking appropriate steps to mitigate these factors and employing troubleshooting techniques can enhance our overall audio experience and provide a clearer, noise-free sound.
Tips for reducing unwanted sounds in your listening devices
Do you ever find that your headphones emit unwanted sounds when you're trying to enjoy your favorite music or podcasts? If you're tired of dealing with distracting noises, here are some helpful tips to minimize those unwanted sounds and enhance your audio experience.
1. Check your connections: Ensure that your headphones are properly plugged into your device and that the connection is secure. Loose or faulty connections can contribute to unwanted noise.
2. Keep your cables untangled: Tangled or damaged cables can introduce interference and result in crackling or buzzing sounds. Make sure to keep your headphone cords organized and avoid excessive twisting or bending.
3. Choose a quiet environment: Background noise can easily be amplified by headphones, so try to listen in a quiet setting whenever possible. Avoid crowded or noisy areas to minimize distractions and optimize your sound quality.
4. Adjust the volume: High volume levels can often lead to distortion and unwanted noise. Experiment with different volume settings to find a comfortable and clear sound level that minimizes any unnecessary disruptions.
5. Clean your headphones: Over time, dirt, debris, and earwax can accumulate on the surfaces of your headphones, affecting sound quality. Regularly clean your headphones with a soft, lint-free cloth or a mild cleaning solution to maintain optimal performance.
6. Use noise-cancelling headphones: Consider investing in noise-cancelling headphones, which are specifically designed to reduce external distractions. These headphones use advanced technology to actively block out ambient noise, providing a more immersive listening experience.
7. Consult a professional: If you've tried various troubleshooting methods and are still experiencing significant noise issues, it may be helpful to consult an audio professional or the manufacturer for further assistance. They can diagnose any underlying problems and provide specialized solutions.
By following these tips, you can minimize unwanted noise and enjoy crystal-clear sound from your headphones. With a little extra care and attention, your listening experience can be greatly improved.
🔴 Box Fan - Low Speed, Black Screen 💨⬛ • Live 24/7 • No mid-roll ads
🔴 Box Fan - Low Speed, Black Screen 💨⬛ • Live 24/7 • No mid-roll ads by DJ Grossman 1,056,873 views
How Do Noise Canceling Headphones Work?
How Do Noise Canceling Headphones Work? by Branch Education 952,972 views 3 years ago 6 minutes, 12 seconds
FAQ
Why do headphones sometimes make a buzzing or static noise?
Headphones can produce buzzing or static noise due to a variety of reasons. One common reason is electrical interference. If the headphones are not properly shielded, they can pick up electromagnetic signals from nearby electronic devices, such as smartphones or Wi-Fi routers. Another reason could be a loose or damaged connection between the headphone cable and the audio source, causing interference. Additionally, if the headphones are old or low-quality, they may not have good insulation, resulting in unwanted noise.
What causes the hissing sound in headphones?
The hissing sound in headphones is often caused by the electronic components inside the headphones, particularly the amplifier. The amplifier amplifies the audio signal to a level that can be heard through the headphones. However, due to imperfections in the amplifier circuitry, such as high resistance or poor grounding, a hissing noise can be introduced. Additionally, if the audio file being played is of low quality or has a low signal-to-noise ratio, it can contribute to the hissing sound.
Why do noise-canceling headphones sometimes produce a strange humming sound?
Noise-canceling headphones usually work by using a microphone to detect external sounds and then producing an inverse sound wave to cancel out the noise. However, this process can introduce a strange humming sound. The humming can be caused by the internal circuitry of the noise-canceling system, which generates the inverse sound wave. This circuitry can create a residual hum that is audible, especially in quiet environments. Some noise-canceling headphones may also produce a humming sound when the battery is low or when the noise-canceling feature is turned off.




