As technology continues to evolve at an astonishing pace, it is no surprise that the realm of audio devices has witnessed a significant transformation. With convenience and portability becoming key factors in our modern lifestyle, it is natural to crave a seamless audio experience that complements our on-the-go routines. However, when navigating through the vast array of choices, one might wonder why Bluetooth headphones are conspicuously absent from the top-performing options.
Delving into this intriguing question, it becomes apparent that the absence of Bluetooth headphones is not indicative of their inferior quality or technical capabilities. In fact, these wireless audio devices have garnered immense popularity over the years, offering unprecedented freedom and versatility to users. The decision to exclude them from the favored list stems from a multitude of reasons that go beyond their wireless nature.
One of the primary considerations that result in the omission of Bluetooth headphones lies in the realm of sound quality. While Bluetooth technology has undoubtedly made significant strides in recent years, purists and audiophiles often argue that it still falls short when compared to traditional wired headphones. The nuances and intricacies of a meticulously produced audio track may not be fully conveyed through Bluetooth transmission, resulting in a compromised listening experience.
Compatibility Issues with Certain Devices

When it comes to using wireless audio devices, such as headphones, with different devices, there can sometimes be challenges and limitations in terms of compatibility. Various factors may affect the ability of Bluetooth headphones to connect and work effectively with certain devices, hindering a seamless audio experience.
One of the primary compatibility issues arises from the diversity of Bluetooth versions and profiles available in different devices. While Bluetooth technology continues to evolve, not all devices are equipped with the latest Bluetooth version or support the same profiles. This can result in incompatibility between Bluetooth headphones and devices that do not have matching specifications.
Another compatibility factor is the operating system on the device. Different operating systems may have varying levels of support for Bluetooth headphones. For instance, older versions of operating systems may lack the necessary drivers or software updates to fully utilize the features and functionalities of Bluetooth headphones. As a result, users may encounter issues such as limited control options or reduced audio quality.
| Compatibility Issue | Impact |
|---|---|
| Codec Support | Some Bluetooth headphones utilize advanced audio codecs, such as aptX or LDAC, to enhance sound quality. However, not all devices support these codecs, leading to a downgrade in audio performance. |
| Pairing and Connection Stability | Certain devices may experience difficulties in establishing a stable connection with Bluetooth headphones. Pairing issues or frequent disconnections can disrupt the listening experience. |
| Functionality Limitations | Some devices may have limitations regarding the use of specific features of Bluetooth headphones, such as microphone support or playback controls. This can limit the overall convenience and functionality of the headphones. |
In summary, compatibility issues can arise when attempting to connect Bluetooth headphones with certain devices due to differences in Bluetooth versions, profiles, and operating system support. It is important for users to consider the specifications and capabilities of their devices to ensure a seamless and satisfying wireless audio experience.
Limitations of Bluetooth Technology and Device Compatibility
Bluetooth technology has its own set of limitations and challenges in terms of device compatibility.
One of the primary limitations is the range of Bluetooth connectivity, which is typically limited to around 30 feet. While this may be sufficient for many scenarios, it can become problematic in larger spaces or when there are obstacles between devices.
Another limitation is the potential for interference from other electronic devices operating on similar frequencies. This can lead to signal degradation or even complete loss of connection.
Additionally, Bluetooth technology has evolved over the years with different versions and profiles, which can result in compatibility issues between older and newer devices. For example, a Bluetooth device using an older version of the technology may not be compatible with a device using a newer version.
Device compatibility can also be influenced by the supported profiles and codecs. Different devices may support different audio codecs, such as SBC, AAC, or aptX, which can affect the audio quality and compatibility between devices.
- Range limitations, especially in larger spaces or with obstacles
- Interference from other electronic devices operating on similar frequencies
- Compatibility issues between devices using different versions of Bluetooth
- Variations in supported profiles and codecs affecting audio quality and compatibility
These limitations and compatibility challenges need to be considered when using Bluetooth headphones or other Bluetooth devices to ensure optimal performance and functionality.
Limited Battery Life and Charging Constraints
One of the aspects that may prevent Bluetooth headphones from being included in the given list is their limited battery life and the associated charging constraints.
These headphones typically rely on a built-in battery to power their wireless functionality, and this battery has a finite capacity. As a result, Bluetooth headphones may have a shorter battery life compared to their wired counterparts.
Furthermore, the need to recharge Bluetooth headphones can be a hassle for users. Unlike wired headphones that can operate as long as they are connected to a compatible device, Bluetooth headphones require regular charging to maintain their functionality. This can be inconvenient, especially when users are on the go and do not have immediate access to charging ports or outlets.
Additionally, the charging process itself can pose constraints. Depending on the specific model, Bluetooth headphones may require a specific type of charging cable or dock, which may not be readily available or compatible with other devices. This can limit the flexibility and convenience of charging options for users.
Given these limitations and constraints associated with limited battery life and charging requirements, Bluetooth headphones may not be included in the list due to the potential inconvenience and usability issues they may present for users.
The Limitations of Wireless Headphones in Terms of Battery Consumption
When discussing the disadvantages of using wireless headphones, one significant aspect that can't be ignored is their battery usage. While Bluetooth technology offers the convenience of cord-free listening, it also comes with certain drawbacks.
1. Limited Battery Life: One of the key concerns with Bluetooth headphones is their limited battery life. Due to the continuous transmission of wireless signals, these headphones tend to drain the battery quickly. Users often find themselves needing to recharge the headphones more frequently, especially during long periods of use.
2. Dependency on Battery Level: Another drawback of Bluetooth headphones is their dependence on battery levels. If the battery is not sufficiently charged, the headphones may experience reduced sound quality or even disconnect from the connected device altogether. This dependence on battery levels can be quite inconvenient, especially during travel or when battery charging options are limited.
3. Incompatibility with Older Devices: Some older devices may not be equipped with Bluetooth functionality or may have outdated Bluetooth versions. This can prevent users from using Bluetooth headphones with their devices, forcing them to resort to alternative options or purchasing new devices that are compatible with the headphones.
4. Additional Power Consumption for Bluetooth Connectivity: In order to establish and maintain a connection with the audio source, Bluetooth headphones require additional power. This means that not only do the headphones consume power to deliver sound, but also additional power to support the wireless connection. This can further contribute to the battery drain and reduce the overall battery life of the headphones.
5. Interference and Connection Issues: Bluetooth connections can sometimes be unreliable due to interference from other wireless devices or physical obstructions. In such cases, the headphones may struggle to maintain a steady connection, resulting in dropped audio or disrupted listening experience. These connectivity issues can be particularly frustrating, especially when users are in environments with a high concentration of wireless signals.
- Overall, while Bluetooth technology offers the freedom from tangled wires, it does come with certain drawbacks in terms of battery consumption.
- Bluetooth headphones tend to have limited battery life, may have compatibility issues with older devices, and require additional power for the wireless connection.
- Furthermore, dependence on battery levels and the potential for interference and connection issues can create inconvenience and frustration for users.
Drawbacks of Wireless Headphones: Audio Quality Deterioration in Comparison to Wired Alternatives

When it comes to the realm of wireless audio devices, certain compromises are to be expected. While Bluetooth headphones offer convenience and mobility, one significant drawback is the decreased audio quality compared to their wired counterparts.
The reliance on wireless transmission introduces various factors that can negatively impact the audio fidelity. Bluetooth headphones utilize compression algorithms to transmit audio data wirelessly, which can result in a loss of sonic details and a reduction in dynamic range. This compression process, although necessary for efficient transmission, may lead to a somewhat compressed and flattened sound representation.
Moreover, wireless technology is susceptible to interference from external sources, causing potential disruptions in the transmitted audio signal. Interference from other electronic devices, such as Wi-Fi networks or microwaves, can introduce static, dropouts, or distortion, further compromising the overall audio quality. These potential interruptions can be especially noticeable in crowded urban areas or environments with a high density of electronic devices.
Additionally, wireless headphones are prone to audio latency issues, referred to as "audio lag." This delay occurs due to the time it takes for the audio signal to be transmitted wirelessly and processed by the headphones, leading to a slight delay in sound reproduction. Although this latency is typically minimal, it can be perceptible during certain activities that require precise audio synchronization, such as gaming or watching videos.
While advancements in Bluetooth technology continue to improve audio quality, it is important to acknowledge that wired headphones still maintain an edge in terms of audio fidelity. Their direct analog or digital connection to the audio source ensures the transmission without any loss or compression, resulting in a more accurate and faithful representation of the original sound. Therefore, for those seeking the highest possible audio quality, wired headphones remain a preferred choice.
- Compression algorithms used in Bluetooth transmission can compromise audio quality
- Wireless headphones are prone to interference, affecting the transmitted audio
- Audio latency issues may arise with wireless headphones, leading to slight delays
- Wired headphones offer superior audio quality due to their direct connection to the audio source
Factors That Impact the Audio Experience of Wireless Headphones
In the realm of wireless audio devices, it is important to consider various factors that may affect the quality of sound reproduction. While Bluetooth technology is commonly used for transmitting audio wirelessly, it is essential to recognize that certain aspects can influence the audio experience when using Bluetooth headphones.
| Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Codec | The choice of audio codec, such as SBC, AAC, or aptX, affects the quality of sound transmission and potential latency issues. |
| Source Audio | The original audio file quality and encoding can have an impact on the final sound reproduction when using Bluetooth headphones. |
| Interference | Wireless interference from other devices or environmental factors can cause signal degradation, resulting in audio quality loss. |
| Battery Life | As the battery depletes, the performance of Bluetooth headphones may be compromised, affecting the audio experience. |
| Connection Stability | The stability of the Bluetooth connection can influence the audio quality, with intermittent drops or interruptions affecting the overall experience. |
| Ergonomics | The design and fit of Bluetooth headphones can impact the audio experience, as an improper fit or discomfort may affect sound perception. |
| Audio Processing | The quality of the built-in audio processing within the headphones can greatly influence how the audio is reproduced and perceived. |
Considering these various factors, it becomes clear that Bluetooth headphones may not always deliver the same audio experience as wired headphones. While Bluetooth technology offers convenience and flexibility, it is important to carefully evaluate these aspects when choosing wireless headphones to ensure optimal audio performance.
Interference and Connectivity Problems

When it comes to wireless audio devices, a common challenge users encounter is the issue of interference and connectivity problems. This section delves into the various factors that can affect the seamless operation of Bluetooth headphones, exploring the potential pitfalls that users may face.
In the realm of wireless audio transmission, interference can disrupt the signal between the headphones and the source device. This can result in a range of issues, such as audio skips, sudden drops in quality, or even complete disconnections. Understanding the underlying causes of interference is crucial in troubleshooting and finding suitable solutions.
One key factor that can contribute to interference is the presence of other wireless devices operating in the same frequency band. The ever-growing number of wireless technologies, including Wi-Fi routers, cordless phones, and other Bluetooth devices, can all create a crowded and congested environment, leading to signal interference. The proximity of such devices to the headphones and the source device can greatly impact the audio performance.
Another factor to consider is the physical environment in which the Bluetooth headphones are being used. Obstacles like walls, furniture, or even human bodies can obstruct the signal transmission, resulting in weaker connections or outright signal loss. Understanding how these physical barriers affect Bluetooth connectivity is vital in optimizing performance in different settings.
Furthermore, other electronic devices, such as microwave ovens and fluorescent lights, can generate electromagnetic radiation that interferes with Bluetooth signals. These devices emit radio waves on similar frequency ranges, potentially causing disruptions in audio transmission. Identifying potential sources of electromagnetic interference and minimizing their impact can greatly improve the overall connectivity experience.
In summary, interference and connectivity problems are inherent challenges when using wireless audio devices like Bluetooth headphones. Understanding the factors that contribute to interference and being aware of the surrounding environment can help users troubleshoot and optimize their listening experience.
The challenges of Bluetooth connectivity and potential signal interference
In the realm of wireless audio devices, the seamless connectivity and uninterrupted streaming experience are essential factors that users seek. However, the path to achieving flawless Bluetooth connectivity poses considerable challenges due to various factors that can potentially interfere with the signal transmission.
One of the primary challenges revolves around the issue of signal interference. Bluetooth technology operates in the 2.4 GHz frequency range, which is shared with other wireless devices such as Wi-Fi routers, cordless phones, and microwaves. This shared frequency band can lead to signal congestion and result in reduced signal strength and quality.
Furthermore, physical barriers and environmental factors can impede the Bluetooth signal. Walls, furniture, and other obstacles present in the surroundings can weaken the signal and create dead zones. Additionally, the presence of electromagnetic interference from nearby electronic devices can further disrupt the signal transmission.
Another factor that contributes to potential signal interference is the increasing number of Bluetooth-enabled devices in use. As the popularity of wireless audio devices grows, so does the number of devices concurrently attempting to connect to Bluetooth networks. This congested Bluetooth spectrum can lead to interference and connection issues.
To combat these challenges, advancements in Bluetooth technology have been made, such as the incorporation of frequency hopping and adaptive frequency hopping techniques. These techniques allow Bluetooth devices to switch between different frequencies within the 2.4 GHz band, minimizing interference and improving signal reliability.
However, despite these advancements, occasional signal interference and connectivity issues can still occur, affecting the overall user experience. It is crucial for users to be aware of these potential challenges and take necessary precautions, such as ensuring a clear line of sight between the Bluetooth device and its source, and avoiding crowded areas with an abundance of wireless devices.
Latency Issues Impacting Real-Time Audio/Video Sync

Unwanted delays in real-time audio/video synchronization caused by latency issues have become a significant concern in modern technology. These delays can result in frustrating experiences for users, making it essential to understand the factors contributing to latency and find effective solutions to mitigate its impact.
Latency refers to the delay between the transmission and reception of data in a digital system. In the context of audio/video sync, latency occurs when there is a noticeable time lag between the audio and video components. This delay can lead to lip-sync issues, where the audio does not match the corresponding visuals, negatively affecting user experience.
Several factors contribute to latency in audio/video transmission, including wireless transmission protocols, signal processing, encoding/decoding algorithms, and hardware limitations. In wireless communication technologies like Bluetooth, latency can be influenced by the distance between devices, signal interference, and the version of the protocol used.
The use of compression algorithms and codecs, while necessary for efficient data transmission and storage, can also introduce latency. These algorithms aim to reduce the size of audio/video data without significantly compromising quality. However, the encoding and decoding processes can introduce processing delays that impact real-time synchronization.
To address latency issues, various techniques and technologies are being developed. Low-latency codecs and protocols, such as aptX Low Latency and LDAC, aim to minimize the delay in audio transmission. Additionally, advancements in hardware and signal processing algorithms contribute to reducing latency and improving real-time audio/video synchronization.
- Optimizing signal strength and minimizing interference is important to reduce latency in wireless communication.
- Using newer versions of Bluetooth that support lower latency can improve real-time synchronization.
- Employing adaptive streaming techniques, where data is transmitted in small, manageable chunks, can help mitigate latency issues.
- Continued research and development in the field of audio/video synchronization aim to overcome the challenges posed by latency, resulting in a seamless user experience.
In conclusion, latency issues affecting real-time audio/video sync are a significant concern in modern technology. Factors such as wireless transmission protocols, signal processing, encoding/decoding algorithms, and hardware limitations contribute to latency. However, advancements in codecs, protocols, signal processing, and adaptive streaming techniques are continuously being developed to minimize latency and ensure seamless synchronization for users.
Audio and Video Synchronization Challenges Caused by Wireless Headphones
Wireless headphones, which utilize Bluetooth technology for audio transmission, can introduce certain challenges in maintaining synchronization between audio and video content. These synchronization issues arise from the inherent nature of Bluetooth communication and the limitations it presents in real-time data transmission.
One of the primary causes of audio and video synchronization problems is the latency introduced during data transmission over Bluetooth. Latency refers to the delay between the audio signal being sent from the source device and its reception on the wireless headphones. Due to the wireless transmission process, there is a small but noticeable delay, commonly referred to as audio lag, which can cause the audio to be slightly out of sync with the corresponding video.
Additionally, the quality of the Bluetooth connection can also affect audio and video synchronization. Factors such as distance from the source device, physical obstacles, and interference from other wireless devices can degrade the quality of the Bluetooth connection. This degradation can lead to further delays in audio transmission, amplifying the synchronization issues.
Furthermore, different Bluetooth headphone models may have varying levels of audio and video synchronization problems. While some headphones may exhibit minimal synchronization issues, others may experience more significant delays, resulting in noticeable audio lag. Factors such as the Bluetooth version used, the codec employed for audio transmission, and the headphone's internal processing capabilities can contribute to these variations.
To illustrate the impact of synchronization problems, consider a scenario where a user is watching a video with wireless headphones that suffer from audio lag. As the video progresses, the audio playback may not align perfectly with the corresponding on-screen actions, creating an incongruent viewing experience. This discrepancy can be particularly noticeable in situations that rely heavily on accurate audio cues, such as watching movies or playing video games.
To address these audio and video synchronization challenges, manufacturers continuously work on improving Bluetooth technology and its capabilities for real-time data transmission. Whether through advancements in Bluetooth standards, development of low-latency codecs, or enhancements in wireless headphone hardware, efforts are being made to minimize these issues and deliver an optimal audiovisual experience.
| Key Points |
|---|
| - Latency introduced in Bluetooth transmission can cause audio and video synchronization problems. |
| - Quality of Bluetooth connection, including distance and interference, can further degrade synchronization. |
| - Different headphone models may exhibit varying degrees of synchronization issues. |
| - Synchronization problems can impact viewing experiences, especially in scenarios reliant on accurate audio cues. |
| - Ongoing advancements in Bluetooth technology aim to minimize synchronization challenges. |
Concerns for Health and Potential Risk of Radiation Exposure
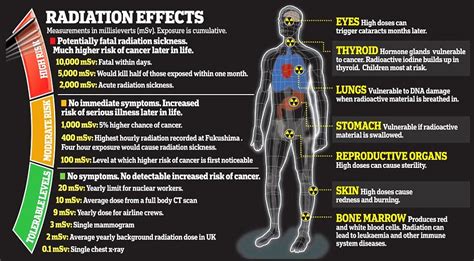
In the realm of wireless audio technologies, it is crucial to examine the potential risks associated with prolonged usage and exposure, specifically in relation to health concerns and radiation exposure.
With the growing popularity and convenience of wireless headphones, it is vital to explore the potential impact they may have on human health. While these devices provide a seamless listening experience without the hassle of tangled wires, concerns have been raised regarding the potential harmful effects of the radio frequency (RF) radiation they emit.
Exposure to RF radiation, also referred to as electromagnetic radiation, has been a topic of debate and research in recent years. It is important to note that RF radiation is not unique to Bluetooth headphones, but it is a fundamental aspect of their functionality. RF radiation is emitted by various wireless devices like smartphones, Wi-Fi routers, and even microwave ovens.
The potential risk associated with RF radiation lies in its ability to penetrate the body's tissues and interact with biological cells. Although extensive research is still being conducted, some studies suggest a possible link between long-term, high-level exposure to RF radiation and adverse health effects such as increased risk of brain tumors, neurological disorders, and disruptions to reproductive health.
It is important to emphasize that the effects of RF radiation exposure are still a matter of ongoing scientific investigation and debate. Some international guidelines exist to limit exposure levels, such as those issued by the International Commission on Non-Ionizing Radiation Protection (ICNIRP) and the Federal Communications Commission (FCC). These guidelines aim to provide a framework for manufacturers to ensure their devices do not emit excessive levels of radiation that may pose a risk to users.
While Bluetooth headphones fall within the scope of these guidelines, it is recommended for individuals to limit their exposure to RF radiation by practicing safe usage habits. This may include using headphones in moderation, taking regular breaks, and considering wired alternatives in situations where wireless connectivity is not necessary.
While wireless audio technology continues to evolve, it is imperative to stay informed about potential risks and make informed decisions to safeguard our health and well-being.
[MOVIES] [/MOVIES] [/MOVIES_ENABLED]FAQ
Why aren't Bluetooth headphones included in the list?
Bluetooth headphones are not on the list because the article specifically focuses on wired headphones. The author likely wanted to highlight the advantages and features of wired headphones, such as better audio quality and compatibility with various devices.
Are Bluetooth headphones not as good as wired headphones?
Bluetooth headphones have made significant advancements in recent years, offering excellent audio quality and convenience. However, wired headphones still have some advantages, such as lower latency and the ability to deliver higher-quality audio. The article focuses on these advantages but does not imply that Bluetooth headphones are inferior.
Can I use Bluetooth headphones with devices that do not have Bluetooth capabilities?
No, Bluetooth headphones require devices with built-in Bluetooth functionality to connect wirelessly. If your device does not have Bluetooth, you won't be able to use Bluetooth headphones with it. However, you can use wired headphones with any device that has a headphone jack or an adapter.




