Have you ever experienced the strange phenomenon of hearing sounds through your headphones even though they are not physically connected to any device? It's an enigma that has puzzled audiophiles and technology enthusiasts alike. The presence of audio emanating from these non-existent headphones continues to baffle researchers, sparking intriguing discussions and hypotheses.
The inexplicable occurrence of sound appearing to originate from headphones that are not actually present raises intriguing questions about the nature of our perception. This auditory illusion challenges our understanding of how sound waves travel and how our brains interpret them. It is a captivating conundrum that invites us to explore the intricate workings of our auditory system.
While the phenomenon can be perplexing, it also serves as a testament to the incredible capabilities of our brains. Our brains are finely tuned machines, constantly processing sensory information and constructing our perception of reality. This remarkable ability to fill in the gaps in our sensory experience allows us to perceive sound in ways that may seem impossible at first glance.
The Mystery of Auditory Hallucinations Unveiled

In the realm of auditory perception lies a phenomenon that has fascinated scientists and researchers for decades - auditory hallucinations. These perplexing experiences, often referred to as "hearing voices," involve the perception of sound without any external auditory stimuli. While commonly associated with certain mental health conditions, the science behind auditory hallucinations goes far beyond mere psychological explanations.
The Complex Interplay of Perception and Cognition
The human auditory system is a marvel of complexity, capable of processing a wide range of sounds and discerning subtle differences, enabling us to communicate and interact effectively with our environment. However, this intricate system is not immune to occasional misfires. Auditory hallucinations, in some cases, can arise due to a disruption in the integration of sensory input and cognitive processes.
Neurological Signatures of Auditory Hallucinations
Neuroscientists have delved deep into the neural correlates of auditory hallucinations, aiming to unravel the underlying mechanisms at play. Findings suggest that abnormalities in specific brain regions, such as the auditory cortex and the network responsible for language processing, may contribute to the manifestation of auditory hallucinations. These irregularities can stem from a variety of factors, including genetic predispositions, neurological disorders, or even substance abuse.
Exploring the Role of Expectations and Beliefs
Not simply confined to neurological factors, auditory hallucinations also exhibit a fascinating interplay with individual beliefs and expectations. Research has shown that a person's preconceived notions and internal schema regarding hallucinatory experiences can significantly influence the nature and content of their auditory hallucinations. Furthermore, social and cultural influences can shape the interpretation of these auditory perceptions, giving rise to a wide spectrum of experiences across different societies and cultures.
Unlocking the Mysteries for Better Understanding
As our understanding of auditory hallucinations advances, so does the potential for improved diagnostics and therapeutic interventions. By combining neuroscientific investigations with psychological and sociological perspectives, researchers aim to develop comprehensive models that can elucidate the intricate nature of auditory hallucinations. Such advancements could pave the way for tailored treatments and interventions that address the underlying causes and alleviate the distress caused by this enigmatic phenomenon.
Understanding the Role of the Brain in Perception
Exploring the intricate workings of our brain and how it contributes to our perception is a fascinating yet complex subject. By delving into this topic, we aim to unravel the enigmatic processes that occur within our minds, shedding light on the mechanisms through which we make sense of the world around us.
The brain acts as a remarkable interpreter, orchestrating the reception and interpretation of sensory input from our environment. It processes the signals received through our senses, such as sound, touch, and sight, transforming them into meaningful perceptions that shape our understanding of reality.
One key aspect of perception is the brain's ability to fill in gaps and make predictions based on available information. Our brain constantly integrates sensory signals from various sources, utilizing past experiences and learned knowledge to construct a coherent and meaningful representation of the world. This process involves complex neural networks and cognitive processes, allowing us to recognize objects, identify sounds, and navigate our surroundings.
However, the brain's role in perception is not limited to the integration of sensory information alone. It also plays a crucial role in shaping our subjective experience and influencing how we interpret and respond to stimuli. Our emotions, motivations, and attention can all affect the way we perceive the world, highlighting the intricate interplay between our brain and our perception.
Understanding the brain's involvement in perception is not only of scientific interest but also has practical implications. Insights gained from this research can help enhance our understanding of sensory disorders, such as auditory hallucinations or visual illusions, and develop innovative approaches to improve sensory perception in various contexts, from virtual reality technologies to assistive devices.
In conclusion, exploring the brain's role in perception leads us to appreciate the complexity and adaptability of our cognitive processes. By unraveling the mysteries of perception, we hope to gain a deeper understanding of our own experiences and pave the way for advancements in neuroscience and the ways in which we interact with the world.
The Impact of External Elements on Auditory Perception
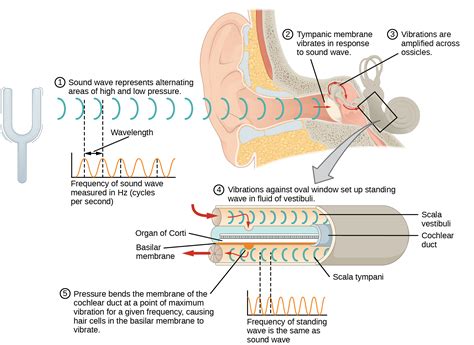
In the realm of auditory sensation, the way we perceive sound can be influenced by a multitude of external factors. These factors, which include various environmental and situational elements, have the potential to affect our overall auditory experience in unique ways.
1. Ambient Noise: The presence of background noise can significantly impact our perception of sound. Whether it is the hum of a bustling city, the sound of traffic, or the gentle rustle of leaves in a serene park, ambient noise can either enhance or interfere with the clarity and quality of auditory stimuli.
2. Room Acoustics: The characteristics of a particular space, such as its size, shape, and the materials used in its construction, can greatly influence the way sound behaves within it. Different room acoustics can lead to variations in sound reflection, absorption, and reverberation, which ultimately affect our perception of the auditory stimuli present in that environment.
3. Personal Listening Devices: The utilization of personal listening devices, such as headphones or earphones, can have a profound impact on auditory perception. These devices, when used correctly, can provide an immersive and individualized listening experience. However, improper usage, such as excessively high volume levels or prolonged exposure, can lead to detrimental effects on hearing health and overall auditory sensation.
4. Psychological Factors: Our mental and emotional state can also play a significant role in how we perceive sound. Factors such as attention, focus, mood, and cognitive biases can all influence our auditory perception and interpretation of the soundscape around us.
- The Influence of Sound Source Location: The spatial location from which a sound originates can affect our perception of its direction, distance, and intensity. This phenomenon, known as the "ventriloquist effect," can sometimes lead to the misplacement of sound sources in our auditory perception.
- Effects of Sound Frequency: Different frequencies of sound vibrations can evoke varying emotional and physiological responses in individuals. For example, low-frequency sounds may create a sense of depth or power, while high-frequency sounds may elicit feelings of brightness or sharpness.
- Social and Cultural Influences: Our auditory perception is also heavily influenced by social and cultural factors. These can include language, musical preferences, and the social norms and expectations surrounding sound perception within a particular community or society.
It is important to recognize and understand the impact of these external elements on auditory perception in order to optimize our overall listening experience. By acknowledging and considering these factors, we can enhance our communication, music enjoyment, and appreciation of the acoustic world around us.
Unraveling the Phenomenon of "Musical Ear Syndrome"
Delving into the enigmatic world of auditory perception, "Musical Ear Syndrome" unveils a captivating phenomenon that challenges our understanding of sound and its relationship with the human mind. This intriguing occurrence, often labeled as MES for brevity, refers to the perception of music or other sounds without external auditory stimuli like headphones or speakers.
One fascinating aspect of Musical Ear Syndrome is its ability to transcend traditional auditory pathways and create a unique sensory experience within the mind of the individual. The perception of melodies, harmonies, and even lyrics can manifest spontaneously, seemingly arising out of thin air. While the underlying mechanisms of MES remain largely elusive, exploring this phenomenon opens doorways to understand the intricate workings of the human brain and its profound connection with music.
- Various Factors Influencing MES
- The Role of Auditory Memory in Musical Ear Syndrome
- Psychological and Emotional Implications of MES
- Exploring the Phenomenon through Case Studies
- Techniques for Managing and Embracing Musical Ear Syndrome
Understanding the intricate interplay of factors that contribute to the occurrence of Musical Ear Syndrome is crucial in unraveling this captivating phenomenon. This section examines various potential influences, such as neurological conditions, medication side effects, and even musical exposure, that may contribute to the manifestation of MES. By exploring the multifaceted nature of these factors, researchers strive to shed light on the underlying reasons behind the spontaneous perception of music.
A crucial component of MES lies in the intricate workings of auditory memory. This section delves into the role of memory in the phenomenon, investigating how past musical experiences, including familiar tunes or songs, can resurface in the absence of external auditory stimulation. By unraveling the complex neural mechanisms involved in auditory memory retrieval, researchers hope to unravel the mysteries behind the recurrence of musical perception in individuals with MES.
The psychological and emotional implications of Musical Ear Syndrome are profound, and this section seeks to delve into their significance. Examining the emotional impact of MES on individuals and exploring potential connections with mental health conditions offers valuable insights into the interplay between perception, cognition, and emotional well-being. Shedding light on these implications can not only enhance our understanding of MES but also guide the development of therapeutic interventions for those affected.
Investigating the phenomenon of Musical Ear Syndrome through the lens of real-life cases provides valuable anecdotes and insights into the first-hand experiences of individuals living with MES. This section presents compelling case studies that explore the diversity of musical perceptions, the contexts in which MES manifests, and the subjective nature of these auditory experiences. By examining these cases, researchers and individuals alike can gain a deeper appreciation for the nuances and personal significance associated with MES.
Finally, acknowledging the challenges and potential distress that MES can present, this section offers techniques and strategies for managing and embracing this phenomenon. From seeking medical guidance to engaging in sound therapy and harnessing the power of music, various methods can empower individuals with MES to navigate their unique auditory landscape with confidence and ease. This section aims to provide practical tips and resources to support individuals living with MES, fostering a sense of empowerment and acceptance.
Psychological Explanations for Perceiving Imaginary Sounds

In the realm of auditory perception, there exists a mysterious phenomenon where individuals claim to hear sounds despite the absence of any external auditory stimuli. Without the presence of headphones or any other visible source, these individuals experience the auditory sensation of sounds that seem to manifest from thin air.
Researchers and psychologists have delved into this intriguing phenomenon, seeking to unravel the enigma surrounding non-existent sounds. Many theories have emerged, offering psychological explanations that help shed light on why some individuals perceive imaginary sounds when there is no apparent source. These theories highlight the complex interplay between one's mind, perception, and underlying cognitive processes.
- Cognitive Dissonance: One possible explanation for hearing non-existent sounds lies in the phenomenon of cognitive dissonance. When there is a conflict between what one expects to hear and what is actually heard, the brain attempts to reconcile this incongruity by generating sounds that align with the individual's preconceived notions. This cognitive process can result in the perception of non-existent sounds, as the brain tries to make sense of the discordant information.
- Attentional Bias: Another psychological explanation revolves around the concept of attentional bias. Individuals with a heightened sensitivity to auditory stimuli may be more prone to perceiving sounds that are not present. This bias can be influenced by various factors, such as anxiety, stress, or previous experiences, which can amplify their perception of auditory cues, even when there are none.
- Neurological Factors: It is also plausible that certain neurological factors contribute to the perception of non-existent sounds. Brain abnormalities or dysfunctions in the auditory processing areas could result in the generation of spontaneous auditory signals, leading to the illusion of hearing sounds that do not exist in reality. Further research is required to fully understand the precise nature of these neurological mechanisms.
- Sensory Deprivation: Sensory deprivation, whether due to complete silence or the absence of external auditory stimuli, can trigger the brain to compensate by generating imaginary sounds. In a state of sensory deprivation, the brain may produce auditory hallucinations as a way to fill the void, stimulating the auditory system and preventing complete sensory monotony.
- Psychological Priming: Lastly, psychological priming, or the activation of specific mental frameworks, can influence the perception of non-existent sounds. Individuals who have been primed with auditory-related cues or suggestions may be more susceptible to perceiving sounds that are not actually present. This priming effect can create an internal perception of sounds, even in the absence of any external stimuli.
In conclusion, the phenomenon of hearing non-existent sounds without the presence of headphones or any visible source is a fascinating subject within the field of auditory perception. Psychological explanations, such as cognitive dissonance, attentional bias, neurological factors, sensory deprivation, and psychological priming, offer valuable insights into the complex processes underlying this intriguing phenomenon. Exploring these psychological explanations brings us closer to understanding the extraordinary ways in which our minds perceive and interpret the world around us.
How Stress and Anxiety Can Trigger Auditory Perceptions
When individuals experience high levels of stress and anxiety, their brain's auditory processing mechanisms can sometimes exhibit unusual behavior, leading to the perception of sounds that are not actually present. These auditory illusions, also known as auditory hallucinations or phantom sounds, can take various forms and significantly impact a person's overall well-being.
Stress and anxiety have the potential to influence the brain's sensory processing centers, including those responsible for auditory perception. When a person is under significant emotional strain, the heightened activation of stress-related neural pathways can disrupt the normal functioning of these auditory areas, resulting in the misinterpretation of auditory stimuli or the creation of entirely new sounds.
Symptoms of auditory illusions triggered by stress and anxiety vary widely among individuals, with some reporting hearing music, voices, or buzzing sounds, while others may perceive non-existent ringing, hissing, or pulsating noises. These phantom sounds can be temporary or persistent, intermittent or continuous, and their intensity can range from barely noticeable to extremely bothersome.
Research suggests that the occurrence of auditory illusions can be influenced by several factors, including genetic predispositions, environmental stressors, and pre-existing mental health conditions. However, the exact mechanisms underlying these phenomena are still not fully understood and require further investigation.
Coping with stress and managing anxiety can play a crucial role in reducing the frequency and intensity of auditory hallucinations. Techniques such as relaxation exercises, mindfulness meditation, and cognitive-behavioral therapy have been found helpful in alleviating stress-related auditory perceptions and improving overall mental well-being.
In conclusion, the impact of stress and anxiety on auditory processing can lead to the manifestation of auditory illusions. Understanding the connection between these psychological states and the brain's auditory mechanisms can contribute to better management strategies and treatment approaches for individuals experiencing such symptoms.
The Link between Chronic Illness and Auditory Hallucinations

A curious phenomenon that has intrigued researchers and medical professionals alike is the connection between chronic illness and auditory hallucinations. This intriguing relationship suggests that there may be a complex interplay between the physical and mental aspects of these conditions, leading to the manifestation of auditory hallucinations in individuals affected by chronic illnesses.
Understanding Auditory Hallucinations
Auditory hallucinations, commonly referred to as hearing voices, are perceptions of sound that occur without any external stimuli. They can range from simple sounds like ringing or buzzing to more complex experiences, such as hearing voices or music. Traditionally associated with mental health conditions like schizophrenia, recent studies have shown that auditory hallucinations can also occur in individuals with chronic illnesses.
The Intricate Relationship
The underlying mechanisms and precise causes of auditory hallucinations in individuals with chronic illnesses are still unclear. However, it is believed that various factors contribute to the development of these hallucinations. These factors may include the impact of chronic pain or medication side effects on brain functioning, altered sensory processing, or psychological distress associated with living with a chronic illness.
Exploring Potential Explanations
One hypothesis suggests that chronic illness-related stressors, such as prolonged pain or physical discomfort, may disrupt the brain's normal functioning and lead to auditory hallucinations. Another possibility is that certain medications used in the treatment of chronic illnesses could directly influence the neural pathways associated with auditory processing, causing hallucinations to occur.
Unraveling the Mystery
Further research is necessary to fully understand the underlying mechanisms behind the link between chronic illness and auditory hallucinations. Studying the experiences of individuals with chronic illnesses who also experience auditory hallucinations can provide valuable insights into the relationship between physical and mental health. With a deeper understanding of this connection, medical professionals can develop tailored interventions to support individuals living with chronic illnesses and alleviate the burden of auditory hallucinations.
Exploring the Association between Specific Drugs and Phantom Sounds
This section delves into the intriguing relationship between certain medications and the occurrence of phantom sounds, or auditory hallucinations.
While a myriad of factors can contribute to the experience of phantom sounds, recent research has found a potential link between the use of specific drugs and the manifestation of this phenomenon. These medications, which will be examined in detail in the following subsections, have been associated with cases where individuals report hearing sounds that are not present in their environment.
| Medication | Phantom Sounds Reported |
|---|---|
| Antidepressants | Whispering, buzzing, or music-like sounds |
| Antibiotics | Tinnitus-like ringing or high-pitched tones |
| Anticonvulsants | Pulsing or rhythmic sounds |
It is important to note that the occurrence of phantom sounds may vary greatly among individuals, and not everyone who takes these medications will experience such auditory hallucinations. However, understanding the potential association can contribute to more informed discussions between patients and healthcare providers about potential side effects and treatment options.
Further research is needed to elucidate the precise mechanisms through which these medications may influence auditory perception, and to identify risk factors that contribute to the development of phantom sounds in certain individuals. This knowledge can lead to improved management strategies for patients who experience these unsettling sensations.
Coping Strategies for Managing Auditory Sensations

Living with the experience of auditory sensations that are not grounded in external stimuli can be challenging and distressing for individuals. It is important to develop coping strategies that help navigate and manage these hallucinatory experiences. By implementing effective techniques, individuals can gain a sense of control and improve their overall well-being.
- Practice relaxation techniques: Engaging in relaxation exercises such as deep breathing, meditation, or progressive muscle relaxation can help reduce stress and anxiety associated with auditory hallucinations. These techniques promote a calm and focused state of mind, allowing individuals to better cope with their experiences.
- Seek support from trusted individuals: Sharing experiences with a supportive network of friends, family, or therapists can provide a sense of understanding and validation. Talking about auditory hallucinations can help individuals gain clarity and reduce feelings of isolation.
- Establish a routine: Maintaining a structured daily routine can help individuals maintain a sense of stability and control. By incorporating activities that promote mindfulness, physical exercise, and hobbies, individuals can distract themselves from the auditory sensations.
- Engage in reality testing: Encouraging the use of reality testing techniques can help individuals differentiate between genuine external sounds and auditory hallucinations. This can be done by asking trusted individuals for confirmation, using additional sensory input, or engaging in grounding exercises.
- Utilize distraction techniques: Engaging in activities that capture attention and divert focus away from auditory sensations can be helpful. Listening to calming music, practicing a hobby, or engaging in physical exercise can redirect attention and alleviate distress.
- Explore medication options: Depending on the severity and impact of auditory hallucinations, medication may be considered as part of a comprehensive treatment plan. Working closely with a healthcare professional can help determine the most suitable medication options and guide the individual through the process.
It is important to remember that coping strategies may vary for each individual, and finding the most effective techniques may require some trial and error. By actively exploring and implementing strategies that address their unique needs, individuals can enhance their ability to cope with auditory hallucinations and improve their overall quality of life.
iPhone 6s/6s Plus Stuck in Headphones Mode & Here's How To Fix!
iPhone 6s/6s Plus Stuck in Headphones Mode & Here's How To Fix! by AppleTricks 167,995 views 1 year ago 1 minute, 40 seconds
FAQ
Why do headphones show up as connected even when they're not physically connected?
There can be several reasons why headphones show up as connected even when they're not physically connected. One common reason is a software glitch or bug in the device or operating system. In such cases, the device mistakenly detects a headphone connection even though there is none. Another reason could be a hardware issue, such as a faulty headphone jack or a short circuit. In some cases, the headphone connector might be dirty or damaged, causing the device to interpret it as a constant connection.
What can I do if my headphones keep showing up as connected even though they're not?
If your headphones keep showing up as connected even though they're not, there are a few troubleshooting steps you can try. First, try cleaning the headphone jack using a soft brush or a compressed air canister to remove any debris or dust that might be causing an incorrect connection. If that doesn't work, you can try restarting your device or resetting the device's network settings. If the problem still persists, you might need to contact the manufacturer or seek professional help to diagnose and fix the issue.
Can a software update fix the issue of headphones showing up when they're not connected?
Yes, a software update can potentially fix the issue of headphones showing up when they're not connected. Often, such problems are caused by software glitches or bugs, which can be addressed and resolved in the software update. It is recommended to keep your device's software up to date to ensure optimal performance and compatibility.
Is it possible to disable the headphone detection feature on a device?
In most cases, it is not possible to disable the headphone detection feature on a device. The headphone detection feature is a built-in functionality that helps the device automatically switch the audio output from the built-in speakers to the connected headphones. However, some devices may allow for manual control over this feature through settings or third-party applications. It is worth exploring your device's settings or checking with the manufacturer to see if there is an option to disable the headphone detection feature.
Why is it important for devices to accurately detect headphone connections?
Accurate detection of headphone connections is important for devices because it ensures seamless audio playback and user experience. When the device correctly detects that headphones are connected, it automatically switches the audio output from the device's speakers to the headphones. This allows users to enjoy their audio content privately without disturbing others. Additionally, accurate detection helps in automatically pausing or resuming audio playback when headphones are plugged in or unplugged, providing convenience and ease of use.
Why do headphones show up on my device even when they're not physically connected?
There could be several reasons for headphones showing up on your device when they're not physically connected. One possibility is that there is a software glitch or bug causing the device to incorrectly detect the presence of headphones. Another reason could be that the headphone jack or port is damaged or malfunctioning, causing false detection. In some cases, it could also be due to a compatibility issue between the device and certain headphone models.
How can I fix the issue of headphones showing up when they're not there?
If you're experiencing the problem of headphones showing up on your device even when they're not physically connected, there are a few steps you can try to resolve the issue. First, try restarting your device to see if it can correct any software glitches. If that doesn't work, you can try cleaning the headphone jack or port with compressed air or a soft brush to remove any debris that may be causing false detection. If the issue persists, you may need to contact technical support or bring your device to a professional for inspection and possible repair.




