As technology continues to advance and our daily lives become increasingly fast-paced, it is no wonder that wireless connectivity has become an essential part of our everyday routines. We rely on it for various tasks, from communicating with loved ones to streaming our favorite music and videos. However, while wireless headphones have become a popular choice for music enthusiasts, it is essential to acknowledge the limitations they may pose for traditional FM radio transmission.
In an era where wireless options dominate the market, it is crucial to explore why FM radio struggles to establish a seamless connection with wireless headphones.
FM radio, renowned for its crisp audio quality and wide coverage, has been a steadfast companion for decades, providing us with news, music, and entertainment. However, as we embrace the convenience and freedom of wireless headphones, it becomes clear that these two technologies do not always dovetail effortlessly. The intricate nature of FM radio transmission and the underlying mechanisms of wireless audio pose challenges that need to be understood to fully grasp why seamless compatibility is often elusive.
To comprehend this issue, we need to delve into the fundamentals of FM radio transmission and gain insight into how wireless headphones function.
Why FM Radio Signals Fail to Connect with Wireless Headsets

In the realm of wireless audio technology, there exists a perplexing quirk that prevents FM radio signals from seamlessly connecting to wireless headphones. This enigmatic phenomenon has puzzled many tech enthusiasts and left them wondering why this integration, which seems intuitive and logical, does not manifest as expected.
One possible explanation for this intricate puzzle lies in the unique nature of FM radio signals and the complex communication protocols employed by wireless headphones. Unlike other wireless audio technologies, such as Bluetooth or Wi-Fi, FM radio operates on a different frequency band and modulation technique. It relies on analog signals transmitted through airwaves, which undergo certain limitations and considerations that must be taken into account.
Wireless headphones, on the other hand, are designed to connect with audio sources using specific transmission protocols and frequencies. These devices typically rely on digital signals, utilizing advanced modulation techniques and compression algorithms to deliver high-quality audio wirelessly. Therefore, when attempting to pair wireless headphones with FM radio signals, incompatibilities arise due to the fundamental differences in the transmission and reception methods of the two systems.
The absence of a direct connection between FM radio signals and wireless headphones can also be attributed to the absence of a common language or protocol between the two. While FM radio signals are broadcasted in a standard format, wireless headphones operate through various proprietary protocols and codecs, requiring a compatible audio source to successfully transmit and receive audio signals.
Moreover, the design and functionality of wireless headphones prioritize mobility and versatility, often necessitating compact form factors and efficient power consumption. In contrast, FM radio signals are primarily intended for broadcast purposes, catering to a wide range of receivers. These disparities in intended usage and design further contribute to the lack of synergy between FM radio signals and wireless headphones.
In conclusion, the inability of FM radio signals to connect with wireless headphones can be attributed to the distinct characteristics and operational differences between the two systems. From the technical disparities in transmission and reception methods to the lack of a common language or protocol, these factors collectively present a barrier that hinders seamless integration. As technology advances, it remains to be seen whether future innovations will bridge this gap and enable a harmonious coexistence between FM radio and wireless headphones.
The Incompatibility between FM Radio and Bluetooth Technology
When it comes to the compatibility between FM radio and Bluetooth technology, there exists a significant challenge in achieving seamless integration. The fundamental differences in the audio transmission protocols utilized by these two technologies result in compatibility issues that hinder their simultaneous use.
One key factor that contributes to this incompatibility is the difference in frequency bands utilized by FM radio and Bluetooth. While FM radio operates in the frequency range between 87.5 and 108 MHz, Bluetooth technology operates within the 2.4 GHz frequency band. This discrepancy in frequency ranges makes it challenging for wireless headphones to support both FM radio reception and Bluetooth audio streaming simultaneously.
Additionally, the modulation techniques employed by FM radio and Bluetooth also diverge, further contributing to their incompatibility. FM radio uses frequency modulation, where the audio signal is encoded onto a carrier wave by varying its frequency. In contrast, Bluetooth employs a combination of frequency hopping spread spectrum and Gaussian frequency shift keying modulation techniques. These differences in modulation techniques make it difficult for wireless headphones to effectively receive and decode both FM radio signals and Bluetooth audio signals.
Another aspect to consider is the differing audio codecs used by FM radio and Bluetooth. FM radio broadcasts use analog signals, while Bluetooth relies on digital compression algorithms to transmit audio wirelessly. This discrepancy in audio encoding presents a hurdle for wireless headphones to decode and process both analog FM radio signals and digital Bluetooth audio signals concurrently.
- The contrasting frequency bands utilized by FM radio and Bluetooth
- The difference in modulation techniques employed by FM radio and Bluetooth
- The mismatch in audio codecs used by FM radio and Bluetooth
To overcome these compatibility challenges, manufacturers have started integrating FM radio receivers into wireless headphones specifically designed for this purpose. However, this solution limits the flexibility of using one's preferred wireless headphones with FM radio functionality. New advancements and innovations in wireless audio technology may eventually bridge the gap between FM radio and Bluetooth, enabling users to enjoy both seamlessly.
The Limitations of FM Radio Frequencies for Wireless Audio Transmission
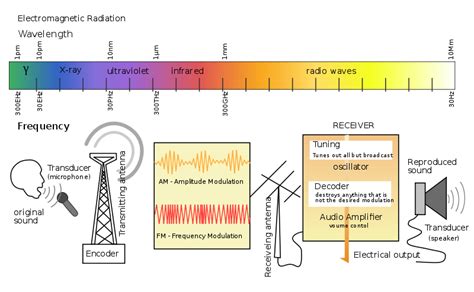
Wireless headphones have become increasingly popular as they offer freedom and convenience to the users. However, when it comes to the transmission of audio signals, FM radio frequencies have their limitations.
One of the main challenges with FM radio frequencies is signal interference. As FM frequencies operate within a limited range, they are susceptible to interference from various external factors. This interference can degrade the quality of the audio transmitted to wireless headphones, resulting in poor sound reproduction and disrupted listening experience.
Another limitation of FM radio frequencies for wireless audio transmission is the lack of bandwidth. FM frequencies have a limited bandwidth capacity, which restricts the amount of data that can be transmitted at a given time. This can lead to compression of audio signals, causing a loss in audio quality and clarity.
Furthermore, FM radio frequencies are also prone to signal dropout. As wireless headphones rely on a stable and consistent signal to receive audio, any drop in the FM signal can result in interruptions or complete loss of audio playback. This can be frustrating for users, especially when trying to enjoy their favorite music or engage in important phone conversations.
Additionally, FM radio frequencies may not provide the necessary range for wireless audio transmission. While FM signals can cover large distances for traditional radio broadcasting, the limited range for wireless headphones can result in the loss of audio when the user moves away from the transmission source. This can greatly limit the mobility and freedom offered by wireless headphones.
In conclusion, FM radio frequencies present several limitations for wireless audio transmission. The issues of signal interference, limited bandwidth, signal dropout, and restricted range hinder the ability of FM radio to deliver high-quality audio to wireless headphones. As a result, alternative transmission technologies such as Bluetooth have gained popularity to overcome these limitations and provide better wireless audio experiences.
The Challenges of Interference in FM Radio Signals for Wireless Headphone Connectivity
Interference poses significant challenges to the seamless connectivity between FM radio signals and wireless headphones. This phenomenon, characterized by the disturbance or disruption of signal transmission, can be caused by a variety of factors, including environmental conditions, signal strength, and competing wireless devices.
One of the main causes of interference is the presence of other wireless devices operating on similar frequencies. As wireless technology continues to advance, the airwaves have become increasingly crowded with various devices such as Wi-Fi routers, Bluetooth devices, and other wireless headphones. The overlapping frequencies can lead to signal collisions and result in degraded performance or complete loss of connectivity.
Another potential source of interference is the physical environment in which the wireless headphones and FM radio signals operate. Structures like buildings, walls, and even human bodies can obstruct or absorb radio waves, causing a significant reduction in signal strength. This attenuation often leads to a weakened FM radio signal and compromises the ability of wireless headphones to receive the signal effectively.
Furthermore, the quality of FM radio signals can also be affected by external factors such as atmospheric conditions and geographical location. For instance, regions with high levels of electromagnetic interference, such as urban areas with numerous electronic devices, may experience greater difficulties in maintaining a stable and clear FM radio signal for wireless headphone connectivity.
Addressing these interference challenges requires innovative solutions and technologies. One approach is the implementation of advanced signal processing algorithms and techniques to enhance the signal-to-noise ratio and mitigate the impact of interference. Additionally, the development of intelligent antenna designs and adaptive frequency hopping mechanisms can help minimize the effects of interference and improve the overall performance of FM radio signals in wireless headphone connectivity.
By understanding the various factors contributing to interference in FM radio signals, manufacturers and engineers can work towards developing robust wireless headphone systems that provide uninterrupted and high-quality audio experiences for users.
The Advantages and Disadvantages of FM Radio and Bluetooth for Wireless Listening

In this section, we will explore the advantages and disadvantages of two popular options for wireless listening: FM radio and Bluetooth. Both technologies offer unique features and capabilities that cater to different user preferences and needs.
Advantages of FM Radio:
FM radio has been a long-standing favorite for many enthusiasts due to its widespread availability, offering a wide range of stations and content to choose from. It provides a reliable and constant connection, ensuring uninterrupted playback. Additionally, FM radio does not require an internet connection, making it accessible in areas where internet access is limited or not available.
Disadvantages of FM Radio:
One of the main drawbacks of FM radio is its susceptibility to interference and signal quality issues, especially in crowded environments or areas with weak reception. Users may experience static, distortion, or fading signals, which can be frustrating when trying to enjoy high-quality audio. Another limitation is the limited range of FM signals, which can restrict the listener's ability to access stations in remote or distant areas.
Advantages of Bluetooth:
Bluetooth technology has revolutionized the wireless listening experience by providing convenience and versatility. With Bluetooth-enabled devices, users can have a seamless connection to their headphones without the need for any physical cables. This wireless capability allows for freedom of movement and eliminates the hassle of tangled cords. Bluetooth also offers a wider range of connectivity options, enabling users to pair their headphones with various devices, such as smartphones, tablets, or laptops.
Disadvantages of Bluetooth:
While Bluetooth offers many advantages, there are a few drawbacks to consider. One common concern with Bluetooth is the potential for audio quality degradation. Compression algorithms used in Bluetooth transmission can result in a loss of audio fidelity compared to a wired connection. Additionally, Bluetooth technology typically has a limited range, often around 30 feet, which means the user needs to maintain proximity to the audio source. Lastly, Bluetooth connectivity may drain the battery of both the audio source and the headphones at a faster rate compared to FM radio listening.
In conclusion, both FM radio and Bluetooth have their own set of advantages and disadvantages when it comes to wireless listening. Understanding these differences can help users make informed decisions based on their preferences, location, and desired audio quality.
[MOVIES] [/MOVIES] [/MOVIES_ENABLED]FAQ
Why can't I listen to FM radio with my wireless headphones?
FM radio requires a wired connection to receive the signal, and wireless headphones do not have a built-in FM radio receiver. Therefore, you cannot directly listen to FM radio with wireless headphones.
Can I use an adapter to connect my wireless headphones to FM radio?
No, it is not possible to use an adapter to connect wireless headphones to FM radio. The adapter would still require a wired connection, which wireless headphones lack.
Are there any wireless headphones that can receive FM radio signals?
No, currently there are no wireless headphones available that have a built-in FM radio receiver. If you want to listen to FM radio, you will need to use a device with a headphone jack or a separate FM radio receiver.
Why do wireless headphones not have FM radio receivers?
Wireless headphones focus on providing a wireless audio experience and are designed to connect to devices such as smartphones, tablets, and computers via Bluetooth or other wireless technologies. Including an FM radio receiver would add unnecessary complexity and cost to the headphones.
Are there any alternative ways to listen to FM radio with wireless headphones?
Yes, you can use a separate FM radio receiver that has a built-in headphone jack and connect your wireless headphones to it using an audio cable. This way, you can enjoy FM radio while still using your wireless headphones for audio playback.
Why can't I listen to FM radio using my wireless headphones?
Wireless headphones usually use Bluetooth technology to connect to the audio source, and FM radio operates on a different frequency range. Therefore, FM radio signals cannot be directly transmitted to wireless headphones using Bluetooth.
Is there any way to listen to FM radio with wireless headphones?
Yes, there are some solutions available. You can use FM radio adapters that connect to your audio source and transmit the FM radio signal wirelessly to your headphones using Bluetooth. Another option is to look for wireless headphones that have built-in FM radio receivers, although these are not as common as Bluetooth-only headphones.




