Have you ever wondered how sound manages to penetrate our digital devices and into our ears? Have you ever marveled at the seamless harmonization between your headphones and your phone, creating a symphony of rhythm and melody that captivates your senses? It is indeed an enchanting phenomenon, one that is both technically intricate and intellectually stimulating. As we embark on this auditory journey, let us explore the phenomenon behind the transmission of sound through our pocket-sized musical companions.
Embarking on this journey of discovery, it is essential to unravel the intricate web of electrical and audio engineering that underlies this process. Our quest will encompass the realms of electrical signals, intricate circuitry, and the transformative power of digital information. Whether you are equipped with the latest state-of-the-art headphones or simply using the standard-issue earbuds, the principles at play remain consistent, even as the technological landscape continues to evolve. Brace yourself for an exploration into the fascinating world of acoustics and electronic connectivity!
As we delve deeper into this intellectual abyss, it becomes evident that the union between our headphones and our phones encompasses more than meets the eye. Behind the seamless synchronization of sound lies a meticulously crafted system designed to channel the complex nuances of auditory bliss. The path taken by the soundwaves as they traverse from device to device is a complex interplay of physics and engineering. It is a journey of vibrations and oscillations, transforming from electrical impulses to audible sensations.
How do headphones function in conjunction with smartphones?
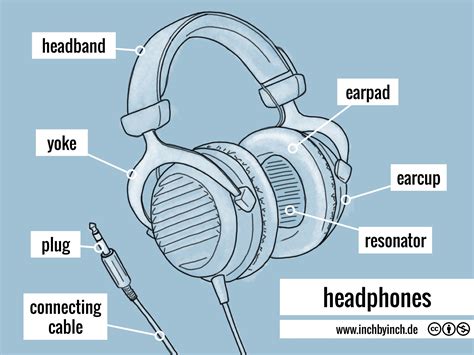
When headphones are connected to a smartphone, they allow users to experience audio content in a more private and immersive manner. This section will explore the mechanisms behind how headphones work with smartphones, highlighting the various components and processes involved.
One fundamental component of headphones is the driver. A driver is a small device that converts electrical signals into audible sound waves, allowing users to hear audio content. It consists of a magnet and a diaphragm, which vibrates in response to the electrical signals from the smartphone. This vibration creates sound waves that are subsequently transmitted to the user's ears.
Headphones feature a connector, typically a 3.5mm audio jack or a USB-C port, which allows them to be connected to smartphones. The connector enables a reliable electrical connection between the headphones and the smartphone, facilitating the transfer of audio signals.
To ensure a high-quality audio experience, headphones often incorporate sound insulation features. These features include over-ear or in-ear designs, as well as the use of noise-canceling technology. Over-ear headphones cover the entire ear, creating a physical barrier that blocks out external noise. In-ear headphones fit snugly inside the ear canal, providing a more direct path for sound to enter the ear while minimizing external interference.
In addition to delivering sound, headphones also commonly include built-in controls and microphones. These controls allow users to adjust volume, play or pause audio content, and answer phone calls without needing to interact directly with the smartphone. The microphone enables users to make voice calls or use voice commands.
| Components of Headphones | Functions |
|---|---|
| Driver | Converts electrical signals into sound waves |
| Connector | Establishes an electrical connection between the headphones and smartphone |
| Sound Insulation Features | Blocks external noise to enhance audio experience |
| Built-in Controls | Allows users to adjust audio settings and answer calls |
| Microphone | Enables voice calls and voice commands |
Exploring the Fundamentals of Headphone Technology
When we connect headphones to our mobile devices, we're able to experience an immersive audio environment. Understanding the basics of headphone technology can enhance our appreciation for the quality of sound we enjoy.
Headphones consist of various components that work together to produce sound. A transducer is a key component responsible for converting electrical signals into sound waves. It consists of a diaphragm, voice coil, and a magnet. When an electrical signal passes through the voice coil, it interacts with the magnet, causing the diaphragm to vibrate and produce sound.
The type of headphone technology used can greatly impact the sound quality. There are two popular types: dynamic and electrostatic headphones. Dynamic headphones, also known as moving-coil headphones, rely on a magnetic field to produce sound. They are commonly used due to their durability and ability to produce excellent bass response.
On the other hand, electrostatic headphones use an incredibly thin, electrically-charged diaphragm suspended between two plates. When an audio signal is applied, the diaphragm is attracted to one plate while repelled by the other, resulting in sound vibrations. Electrostatic headphones are known for their exceptional detail and accuracy in sound reproduction.
Another critical factor in headphone technology is the frequency response range. This range determines the ability of headphones to reproduce various frequencies accurately. The wider the frequency response range, the more precise and balanced the sound reproduction will be across different genres of music.
Additionally, the impedance of headphones plays a significant role in their compatibility with audio devices. Impedance is a measure of the resistance to the flow of electrical current. Headphones with higher impedance require more power to drive, making them well-suited for studio use or high-end audio systems.
To ensure a comfortable listening experience, headphone design also matters. Over-ear headphones enclose the entire ear, providing excellent noise isolation and delivering immersive sound. On the other hand, in-ear headphones fit directly into the ear canal, making them portable and convenient for daily use.
Overall, understanding the fundamental components and technologies used in headphones allows us to make informed choices when selecting the right headphones for our needs. By considering factors such as transducer type, frequency response range, impedance, and design, we can enhance our audio experience and enjoy our favorite music to the fullest.
Exploring the wiring connections between headphones and smartphones
In this section, we will delve into the intricate network of electrical connections that exist between headphones and smartphones. By analyzing the underlying wiring setup, we can better understand how these two devices communicate and deliver audio efficiently.
Throughout the exploration, we will examine the intricate connections without focusing on the specific reasons behind the sound transmission or the phone's role in the process. Instead, our primary objective will be to understand the technical mechanisms that enable sound to pass from the smartphone to the headphones when they are connected.
To begin, we will investigate the physical connections between the headphones and the headphone jack on the smartphone. This connection serves as the primary pathway for sound transmission. We will explore the types of connectors commonly used, such as the 3.5mm audio jack or USB-C connectors, and highlight their unique features and functionalities.
Next, we will dissect the headphone cable, a crucial component responsible for transmitting electrical signals from the smartphone to the headphones. We will explore the different wire configurations used in headphone cables, including the number of wire strands and their specific functions. Additionally, we will examine the role of shielding in minimizing interference and ensuring high-quality audio transmission.
The internal wiring of both the headphones and the smartphone will be another point of focus in our exploration. We will uncover the intricate pathways through which electrical signals travel within the headphones and the smartphone, including the circuits and connections involved in delivering sound to the user's ears.
Finally, we will touch upon the role of additional features, such as built-in microphones and remote controls, in the wiring connections between headphones and smartphones. These added functionalities further enhance the user experience and require additional wiring and connections to operate seamlessly.
By exploring the wiring connections between headphones and smartphones, we will gain a deeper understanding of the complex mechanisms at play behind the transmission of sound. This knowledge can not only satisfy our curiosity but also equip us with a better understanding of how to troubleshoot any issues that may arise with our audio devices.
Understanding the Transmission of Audio Signals through Connected Headphones
When headphones are plugged into a mobile device, they serve as a vital intermediary to facilitate the transfer of audio signals into audible sound waves that can be perceived by the listener. This process involves the conversion and amplification of electrical signals into recognizable audio tones, allowing for an immersive audio experience.
1. Transduction: Within the headphones, there are built-in transducers that convert the electrical signals from the mobile device into sound waves. These transducers, commonly known as speakers or drivers, consist of a diaphragm, voice coil, and magnet. The electrical current flowing through the voice coil interacts with the magnet, causing the diaphragm to vibrate and produce sound waves.
2. Signal Amplification: To ensure that the sound produced is audible and clear, the headphones include an amplifier. This component strengthens the electrical signal received from the mobile device, increasing its power to a level suitable for driving the speakers. The amplifier plays a crucial role in maintaining sound quality and controlling volume levels.
3. Audio Quality Enhancement: Headphones may also incorporate additional technologies to enhance the audio quality. Some headphones use digital signal processing (DSP) algorithms to adjust the sound frequency response, creating a more balanced and accurate representation of the original audio. Noise cancellation technology can also be utilized to reduce unwanted background noise, providing a more immersive listening experience.
4. Cable Transmission: The cable connecting the headphones to the mobile device serves as the pathway for transmitting the electrical signals. It consists of conductive materials, usually copper or silver, that efficiently carry the electrical current from the audio source to the headphones. The cable is designed to minimize signal loss and interference, ensuring that the sound remains faithful to the original audio source.
5. Compatibility: It is important to note that not all headphones are compatible with every mobile device. Different headphone jacks or connectors can vary in size, shape, and electrical configuration. Therefore, it is crucial to ensure that the headphones and mobile device are compatible to establish a proper connection for audio transmission.
In conclusion, when headphones are connected to a mobile device, they act as an interface for transducing and amplifying electrical signals into audible sound waves. Their components, such as speakers, amplifiers, and signal processing technologies, work together to deliver an immersive audio experience. Understanding the process behind this audio transmission can help in selecting suitable headphones and optimizing the overall sound quality.
The Role of Audio Jacks and Ports in Sound Transmission

In the realm of modern technology, audio jacks and ports play a vital role in the seamless transmission of audio signals. These connectors serve as the essential link between devices, facilitating the transfer of sound from a source to an output medium. Understanding the mechanisms behind audio jacks and ports can shed light on how sound travels through headphones when connected to a phone.
Connectors and Compatibility: Audio jacks and ports come in various shapes and sizes, depending on the intended purpose and device architecture. The most common types include the 3.5mm TRS (Tip-Ring-Sleeve) jack, USB-C, and Lightning ports. These connectors establish a physical connection between the audio source, such as a phone, and the headphones, ensuring compatibility and efficient sound transmission.
Signal Transmission: When headphones are connected to a phone via an audio jack or port, the audio signal is transmitted from the phone through the wiring within the cable. The jack or port acts as the interface that allows the transfer of electrical signals between the two devices. The sound information is then converted into analog signals, which are subsequently amplified and delivered to the headphones' speakers.
Role of Male and Female Connectors: Audio jacks and ports are designed with either male or female connectors. The male connector, typically found on the audio cable, features a protruding pin or set of pins that perfectly align with the corresponding holes or slots in the female connector of the receiving device. This precise alignment ensures a secure connection and minimizes signal loss, enabling clear and uninterrupted sound reproduction.
Importance of Quality Equipment: The quality of audio jacks and ports, as well as the headphones themselves, significantly impacts sound transmission. Inferior connectors may introduce noise, distortions, or poor contact, resulting in reduced audio quality or even a complete loss of sound. Therefore, investing in reputable and well-made audio equipment can enhance the overall audio experience and ensure optimal sound transmission.
Evolution of Audio Connectivity: With the continuous advancements in technology, audio connectivity options have evolved. Traditional audio jacks are progressively being replaced by wireless audio transmission methods, such as Bluetooth and NFC, eliminating the need for physical connections. However, audio jacks and ports still remain widely used for their reliability and compatibility across a variety of devices.
In conclusion, understanding the critical role of audio jacks and ports in sound transmission helps explain why sound travels through headphones when connected to a phone. These connectors form the foundation of audio connectivity, ensuring efficient signal transmission and maintaining the integrity of sound reproduction.
Analog vs. digital signals: Understanding their impact on sound transmission in headphones
When it comes to the transmission of sound through headphones, it is essential to consider the distinction between analog and digital signals. These two types of signals play a crucial role in determining the quality and fidelity of the audio experience. Proper comprehension of the differences between analog and digital signals can shed light on why sound can be transmitted through headphones when connected to a phone.
Analog signals are continuous, representing an exact replica of the original sound wave. They are often used in traditional audio systems and older headphone models. Analog signals are characterized by their ability to capture the subtle nuances and details in the audio, resulting in a potentially richer and more natural sound experience. In the context of headphones connected to a phone, analog signals are converted from the digital audio files present in the phone into electrical signals that are then sent through the headphone cable. This conversion process ensures that the analog sound can be transmitted and reproduced by the headphones.
In contrast, digital signals represent sound in numerical form, with discrete values that can be processed by electronic devices. Digital signals rely on sampling and quantization techniques to convert sound waves into a series of binary numbers, allowing for efficient storage, transmission, and manipulation of the audio data. The conversion of analog sound into digital signals occurs within the phone itself, typically through an analog-to-digital converter (ADC). These digital signals are then sent to the headphones, where they are converted back into analog form using a digital-to-analog converter (DAC) to produce audible sound.
The impact of analog and digital signals on sound transmission in headphones lies in the way they handle the audio data. Analog signals maintain the integrity of the original sound wave, retaining its natural characteristics. On the other hand, digital signals may introduce some level of quantization and sampling errors during the conversion process, potentially affecting the accuracy and fidelity of the reproduced sound. However, advancements in digital signal processing and DAC technology have significantly minimized these errors, allowing for high-quality sound reproduction in modern digital audio systems and headphones.
In conclusion, the ability of sound to go through headphones when connected to a phone is made possible by the conversion of digital audio signals into analog form and their transmission through the headphone cable. Understanding the differences between analog and digital signals and their impact on sound transmission can help us appreciate the advancements in audio technology and why headphones are capable of delivering immersive and high-fidelity audio experiences.
Common troubleshooting tips for headphone connectivity issues

When using headphones with your smartphone, it is not uncommon to encounter sound connectivity issues. These issues can manifest in various ways, such as no sound being played through the headphones, distorted audio, or intermittent sound interruptions.
Fortunately, there are several troubleshooting tips that can help you resolve these common sound connectivity issues with your headphones.
1. Check the headphone connection: Start by ensuring that the headphones are properly and securely connected to your smartphone. Gently plug them into the headphone jack or the designated port, depending on the type of headphones you are using.
2. Inspect the headphone cable: Examine the cable connecting your headphones to the smartphone for any signs of damage or wear. A frayed or damaged cable can lead to poor sound connectivity. Consider using a different cable or replacing it if necessary.
3. Clean the headphone jack: Sometimes, dust, dirt, or debris can accumulate in the headphone jack, causing poor connection and resulting in sound issues. Use a clean, dry cotton swab to carefully clean the inside of the jack. Be gentle and avoid applying excessive force.
4. Adjust the volume settings: It is possible that the volume settings on your smartphone are not optimized for headphone usage. Ensure that the volume is turned up and not muted. Additionally, check if any equalizer or sound enhancement settings are affecting the headphone output.
5. Update software and firmware: Outdated software or firmware on your smartphone can sometimes lead to sound connectivity problems. Check for any available updates for your device and install them to ensure compatibility and stability.
6. Test with different headphones: If possible, try using a different pair of headphones to determine if the issue is specific to your current headphones or the smartphone itself. This can help pinpoint the source of the sound connectivity problem.
7. Restart your smartphone: Sometimes, a simple restart can resolve temporary software glitches or conflicts that may be causing sound connectivity issues with your headphones. Turn off your smartphone, wait a few seconds, and then turn it back on.
By following these troubleshooting tips, you can resolve common sound connectivity issues with headphones and enjoy uninterrupted audio playback on your smartphone.
[MOVIES] [/MOVIES] [/MOVIES_ENABLED]FAQ
Why does sound come out of the phone speakers instead of the headphones when I connect them to my phone?
The sound comes out of the phone speakers instead of the headphones because the audio output settings on your phone might not be configured to automatically switch the audio to the connected headphones. You can manually change the audio output settings in the phone's settings menu to ensure that sound is routed to the headphones.
Why can I hear sound from both the headphones and the phone speakers simultaneously?
If you can hear sound from both the headphones and the phone speakers simultaneously, it could be due to a faulty headphone jack or connection. Check if the headphones are properly plugged in and try a different pair of headphones to eliminate any issues with the headset. If the problem persists, there might be a hardware issue with the phone's audio jack or circuitry, and it would be best to seek professional assistance or contact the manufacturer for support.
How can I troubleshoot the issue of no sound coming through the headphones when connected to my phone?
If you are experiencing the issue of no sound coming through the headphones when connected to your phone, there are a few steps you can take to troubleshoot the problem. Firstly, ensure that the headphones are securely plugged into the phone's audio jack. You can also try using different headphones or testing the headphones on another device to eliminate any issues with the headphones themselves. Additionally, check the volume settings on your phone and make sure they are not muted or set too low. If none of these steps solve the problem, there may be an issue with the audio jack or circuitry of the phone, and you may need to contact a professional or the manufacturer for further assistance.
Why do I sometimes experience a loss of sound in one side of the headphones when connected to my phone?
If you are experiencing a loss of sound in one side of the headphones when connected to your phone, there could be a few reasons for this issue. Firstly, check if the headphones are properly inserted into the audio jack and ensure that they are securely connected. The problem could also be due to a faulty headphone cable or connector, in which case, you might need to replace the headphones or have them repaired. Additionally, check the audio balance settings on your phone to ensure that the sound is not biased towards one side. If the issue persists, there may be a hardware problem with the audio jack or circuitry of the phone, and it is advisable to seek professional help or contact the manufacturer for assistance.
Is it possible to listen to sound exclusively through the headphones when connected to my phone?
Yes, it is possible to listen to sound exclusively through the headphones when connected to your phone. Most phones have audio output settings that allow you to choose where the sound is routed. You can typically find these settings in the sound or audio section of your phone's settings menu. By selecting the headphones as the audio output, you can ensure that all sound is directed through the headphones and not the phone speakers. However, it is worth noting that some phones may have limitations or compatibility issues with certain headphones, so it is always a good idea to check the user manual or contact the manufacturer for specific instructions regarding your phone model.
Why does sound come through the phone even when headphones are connected?
When headphones are connected to a phone, the sound still comes through the phone because the audio output is not automatically redirected to the headphones. This allows the user to choose whether they want to listen to audio through the headphones or the phone's speakers.




