In the vast realm of operating systems, passionate Linux users are constantly on the lookout for the ultimate solution that harmonizes seamlessly with their creative endeavors. With numerous intuitive graphical interfaces available, each possessing its own distinctive charm, it becomes a captivating exploration to seek the most suitable one that resonates with individual preferences.
Delving into the realm of Linux, one embarks on an exhilarating journey where endless possibilities unfold. Embracing the art of customization, users take delight in shaping their digital experiences. From dynamic widgets to elegant icons, the Graphical Interface invigorates the otherwise solitary interactions that take place on the screen, gradually transforming it into an extension of personal expression.
Within this dynamic realm, the quest to discover the perfect Graphical Interface becomes an undeniably tantalizing pursuit. By connecting the dots between form and function, enthusiasts find themselves meticulously navigating through a labyrinth of options. Each offering a unique blend of efficiency, fluidity, and aesthetic appeal, the Graphical Interface transforms the way users perceive and interact with their Linux operating system.
Thus, a journey begins – a journey to unknot the intricacies of diverse Graphical Interfaces, and to decipher the rich tapestry of features they encapsulate. As we embark on this exploration, we invite you to delve into the nuances of each Interface, understanding their strengths, weaknesses, and the distinctive experiences they bestow upon Linux enthusiasts.
Different Linux graphical interfaces and their features
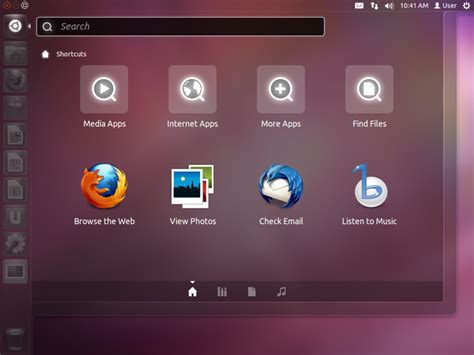
In the realm of Linux, there exists a fascinating array of graphical interfaces that offer diverse and unique features to enhance the user experience. These interfaces, known for their visually appealing designs and efficient functionality, cater to the specific needs and preferences of individual users.
1. GNOME: This popular interface has an elegant and modern design, focusing on simplicity and user-friendliness. It offers an intuitive interface with minimal distractions, allowing users to navigate seamlessly. GNOME provides various built-in applications and extensive customization options to personalize the user experience.
2. KDE Plasma: Known for its exceptional visual aesthetics and versatility, KDE Plasma offers a highly configurable and feature-rich environment. With its customizable panels, widgets, and desktop effects, users can create a personalized workspace. The interface supports multiple workflows, making it suitable for both new and experienced users.
3. Xfce: Designed to be lightweight and resource-efficient, Xfce caters to users seeking a fast and responsive interface. It provides a traditional desktop layout with a clean and customizable interface. Xfce prioritizes performance without compromising essential features, making it ideal for older hardware or those desiring a minimalistic approach.
4. Cinnamon: Built on the foundations of GNOME, Cinnamon offers a familiar and traditional desktop experience. It combines visual elegance with productivity-enhancing features, providing users with a comfortable and efficient interface. Cinnamon emphasizes ease of use and stability, making it an excellent choice for users transitioning from other platforms.
5. MATE: Inspired by the classic GNOME 2, MATE aims to deliver a straightforward and traditional desktop environment. It focuses on simplicity, stability, and compatibility, providing users with a familiar interface reminiscent of older versions of Linux. MATE offers a lightweight and resource-friendly option without compromising essential functionality.
6. LXDE: Aimed at users seeking an incredibly lightweight and efficient graphical interface, LXDE offers a minimalistic design with low resource requirements. It prioritizes speed and simplicity, making it ideal for older hardware or those looking for a fast and distraction-free environment. Despite its lightweight nature, LXDE still provides essential features and customization options.
Each Linux graphical interface mentioned above possesses its own distinct set of features, catering to different user preferences and requirements. Whether prioritizing aesthetics, performance, simplicity, or a combination of factors, Linux provides a diverse range of graphical interfaces to suit every individual's needs.
Comparison of Linux GUIs based on user experience
Exploring the realm of Linux operating systems, it becomes essential to evaluate the graphical user interfaces (GUIs) available to users. This comparison delves into the user experience offered by various Linux graphical interfaces, presenting an objective analysis of their merits and drawbacks.
In assessing the user experience of Linux GUIs, several key factors come into play. One such factor is the intuitiveness of the interface, encompassing the ease with which users can navigate through menus, access applications, and interact with the system. Additionally, the visual appeal and aesthetics of the GUI contribute to the overall satisfaction of the user. A smooth and responsive interface can significantly enhance the user experience, and therefore, performance is another vital aspect to consider.
Another crucial aspect to evaluate is the availability and versatility of customization options offered by the GUI. The extent to which users can tailor the interface to suit their preferences, whether through personalized themes, window managers, or other customization features, greatly influences the overall user experience.
Furthermore, the integration and compatibility with various hardware components and software applications also play a significant role in determining the user experience. A Linux GUI that seamlessly interacts with peripherals, audio/video drivers, and other software packages can offer a smoother and hassle-free experience.
Lastly, the stability and reliability of the GUI throughout the user's journey impact their overall satisfaction. A robust and resilient Linux graphical interface can minimize system crashes, freezes, or unexpected errors, ensuring a more enjoyable experience for users.
By considering these user-centric factors, this comparison aims to provide an insightful evaluation of Linux graphical interfaces, enabling individuals to make informed decisions based on their specific requirements and preferences.
Factors to Consider When Selecting the Ideal Linux User Interface

When it comes to choosing the most suitable user interface for your Linux system, several important factors should be taken into consideration. These considerations will ensure a seamless and efficient experience, tailored to your specific needs and preferences. In this section, we explore the essential aspects to weigh before making your decision.
1. Customizability: A key factor to consider is the level of customization available within the user interface. Look for a UI that offers flexibility in terms of layout, color schemes, and functionality. This will allow you to create an environment that aligns with your workflow and personal aesthetic.
2. Resource Efficiency: Another crucial consideration is the user interface's impact on system resources. Linux offers a wide range of user interfaces, each with varying levels of resource consumption. Evaluate your hardware capabilities and choose a UI that strikes a balance between functionality and resource efficiency.
3. Intuitiveness: The user interface should be intuitive and user-friendly, allowing for effortless navigation and ease of use. Consider the UI's design principles, such as the placement of menu options, icons, and navigation tools. A well-designed interface will enhance your productivity and overall user experience.
4. Community Support: The Linux community plays a significant role in the development and support of user interfaces. Consider opting for a UI that has an active and supportive community behind it. This ensures consistent updates, bug fixes, and access to a vibrant community forum for troubleshooting and assistance.
5. Application Compatibility: Compatibility with your preferred applications is another crucial factor to account for. Ensure that the user interface supports the software you frequently use, especially if you depend on specific applications for your workflow. This will prevent potential compatibility issues and ensure a seamless integration between the UI and your applications.
6. Documentation: Adequate documentation and online resources play a vital role in learning and troubleshooting a user interface. When making your decision, consider the availability of tutorials, user guides, and forums dedicated to the UI you are interested in. This will assist you in quickly familiarizing yourself with the interface and resolving any potential issues.
By carefully considering these factors, you can make an informed decision when choosing the Linux user interface that best suits your needs and enhances your overall computing experience.
FAQ
Which Linux graphical interface is the best to use for beginners?
For beginners, the best Linux graphical interface to use is usually Ubuntu with its default interface called Unity. Ubuntu is known for its user-friendly interface and extensive online documentation, making it easier for newcomers to navigate and learn Linux.
What Linux graphical interface is recommended for advanced users looking for customization?
For advanced users seeking customization options, the Linux graphical interface that is highly recommended is GNOME. GNOME provides a powerful and flexible environment, allowing users to easily tailor their desktop according to their preferences and workflow. It offers a range of extensions and themes that can transform the interface into a personalized and efficient workspace.
Which Linux graphical interface is known for its lightweight and efficient performance?
LXDE (Lightweight X11 Desktop Environment) is well-known for its lightweight and efficient performance. It is designed to be resource-friendly and works exceptionally well on older or less powerful hardware. LXDE offers a simple and intuitive interface without sacrificing functionality, making it a popular choice among users who prioritize performance over advanced features.




