Have you ever wondered where all your important files and cherished memories on your beloved device reside? In this article, we will delve into the intricate mechanics of where your iPhone stores its vast array of data and treasured memories without compromising your device's performance.
When it comes to mobile technology, the storage of information is a crucial aspect that directly impacts the overall user experience. Understanding how and where your iPhone stores data can empower you to make informed decisions on managing your device's internal memory efficiently.
Hidden within the depths of your iPhone's sleek external shell lies a complex labyrinth of integrated circuits and microchips. These minuscule electronic components work tirelessly to store and retrieve your personal information, seamlessly adapting to your usage patterns and preserving your memories, all while providing uninterrupted performance.
One of the key components responsible for storing your iPhone's data is the NAND flash memory. This remarkable technology allows your device to store vast amounts of information in a compact and durable form, enabling it to endure the rigors of everyday use.
So, as you navigate through your iPhone's interface, flipping through cherished photos, accessing important files, and enjoying your favorite apps, remember to appreciate the intricate infrastructure working tirelessly behind the scenes to safeguard and preserve your precious memories.
Understanding the Storage Mechanism of iPhone Data
In this section, we will delve into the intricate workings of the storage system employed by iPhones, shedding light on the fascinating process of how information is stored and accessed within these devices.
The Role of NAND Flash Memory in iPhones
NAND flash memory plays a crucial role in the functioning of iPhones, serving as a vital component for storing important information and data. This type of memory has a unique ability to retain data even when the power is turned off, making it highly efficient for storing and retrieving information on mobile devices like iPhones.
One of the key advantages of NAND flash memory is its non-volatile nature, which means that the stored data remains intact even in the absence of power. This makes it an ideal choice for storing the operating system, applications, and various other files in iPhones, ensuring quick access and consistent performance.
NAND flash memory is comprised of a series of memory cells arranged in grids, with each cell capable of storing multiple bits of data. These cells are organized into pages, which are further grouped into blocks. When information is saved on an iPhone, it is written into these blocks of NAND flash memory.
The process of writing data involves storing electrical charges in the memory cells through a series of floating-gate transistors. These electrical charges represent binary values (0 or 1) and are used to encode the information. When data needs to be accessed, the charges are read from the memory cells, allowing the information to be retrieved and displayed on the iPhone's screen.
Considering the limited physical space available in iPhones, NAND flash memory offers a compact yet high-capacity solution for storing vast amounts of data. This not only includes the operating system and pre-installed applications but also user-generated content like photos, videos, and documents.
- NAND flash memory provides the necessary foundation for the seamless functionality and storage capacity of iPhones.
- Its non-volatile nature ensures that critical data is preserved and accessible at all times.
- The organization of memory cells into pages and blocks enables efficient read and write operations.
- The ability to store multiple bits of data in each cell increases the storage capacity of iPhones.
- Overall, NAND flash memory plays an essential role in enhancing the performance and user experience of iPhones.
Exploring the Data Storage Hierarchy in iOS Devices
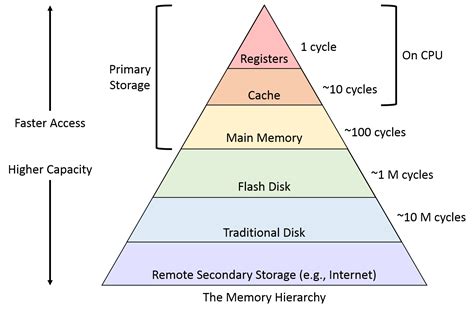
In the world of iOS devices, there exists a complex hierarchy of data storage systems that play a crucial role in facilitating the seamless functioning of these devices. Understanding this hierarchy is essential to comprehend how data is managed and stored within iPhones and other iOS devices, ensuring optimal performance and efficient utilization of memory resources.
1. NAND Flash Memory
At the heart of an iOS device's data storage hierarchy lies the NAND flash memory. It serves as the primary non-volatile storage medium for holding a vast array of data, including the operating system, applications, and user-generated content. Utilizing advanced technology, the NAND flash memory allows for high-speed read and write operations, ensuring responsive and efficient data handling.
2. File System
In iOS devices, the HFS+ (Hierarchical File System Plus) or the newer APFS (Apple File System) is employed to organize and manage the data stored within the NAND flash memory. These file systems define the structure and metadata associated with files, enabling efficient access, search, and modification of data. They also facilitate features like file encryption and compression to enhance data security and optimize storage utilization.
3. Data Storage Containers
Within an iOS device, data is further segregated into distinct storage containers, each serving a specific purpose. These containers include the app containers, which store the application bundle, user preferences, and other related resources. Additionally, there are system containers housing essential system-level files and libraries. This compartmentalization ensures data isolation, enhancing security and simplifying data management.
4. Databases
iOS devices utilize databases to efficiently organize and manage structured data. The most commonly used database engine in iOS is SQLite, offering a lightweight yet powerful solution. Applications leverage these databases to store and retrieve structured information, such as user profiles, settings, and cached data, enabling quick and efficient access to relevant data for various functionalities.
5. Caching Mechanisms
To enhance performance and optimize data retrieval, iOS devices incorporate various caching mechanisms. These mechanisms store frequently accessed data in a dedicated cache, reducing the need for repeated data retrieval from slower storage mediums. Caching also helps conserve battery life by minimizing data transfer activities, contributing to a seamless and responsive user experience.
6. Cloud Storage
Modern iOS devices have integrated cloud storage capabilities that enable seamless synchronization of data with remote servers. This allows users to access their files and media from multiple devices while providing a backup solution for ensuring data integrity and security. Cloud storage also facilitates collaboration and sharing of content, enhancing productivity and convenience.
7. Peripheral Devices
In addition to internal storage solutions, iOS devices can utilize external peripheral devices to expand their storage capacity. This includes options like external hard drives, flash drives, or wireless storage devices. These peripherals interface with the iOS device, providing additional storage space for storing large media files, backups, and other data, offering flexibility and scalability in data storage.
By gaining insights into the intricacies of the data storage hierarchy within iOS devices, users can make informed decisions to optimize storage utilization, enhance data security, and ensure efficient data management, ultimately maximizing the potential of their devices for various personal and professional purposes.
The Location of User Data on iPhones: Discovering the Digital Haven
In the vast realm of contemporary technology, the precise sanctuary harboring user data on iPhones remains a subject of fascination. As we delve into the intricate architecture of these devices, an exploration of the enigmatic abode where our personal information resides unfolds before us.
The Pandora's Box Within:
Deep within the intricate labyrinth of an iPhone's storage infrastructure lies a concealed chamber where user data finds its refuge. This digital haven, shielded from prying eyes, encloses a mesmerizing assortment of personal files, settings, and memories, all delicately ensconced within the device.
The Sentinels of Security:
Arsenal of robust security measures prowls to safeguard the sanctity of this clandestine domain. Encryption, a stalwart guardian, shelters the user's digital assets, rendering them impervious to unauthorized access. A complex tapestry of authentication mechanisms and layers of protection weave together, creating an impregnable fortress.
The Impressive Database Architecture:
Beneath the surface, a symphony of databases orchestrates the storage of user data. These repositories, artfully designed and meticulously organized, store a myriad of information. With each interaction the user has, whether capturing a photograph, sending a message, or downloading an application, these databases dutifully record and arrange the data, perpetuating the harmony of the iPhone's memory.
Introducing NAND Flash Memory:
At the heart of the iPhone's storage system lies the essential component known as NAND flash memory. This advanced technology, characterized by its non-volatile nature, allows for the retention of data even when the device powers down. Within this medium, user files are indexed and preserved, ready to be accessed at a moment's notice.
The Cloud Connection:
Beyond the physical confines of the device, a celestial bond is forged between our iPhones and the expansive realm of cloud storage. Through this interconnection, select user data is seamlessly synchronized and mirrored, ensuring its safety and accessibility across a multitude of devices.
In the intricate tapestry of an iPhone's architecture, user data finds its secure dwelling, sheltered by a formidable amalgamation of technology and innovation. Unlocking the secrets of this digital realm elucidates the ingenuity and precision with which our personal information is stored and guarded.
Unveiling the Backstage: How iPhones Handle Storage Infrastructure

Delving into the inner workings of Apple's beloved smartphones, this section explores the intricate mechanisms employed by iPhones to efficiently manage their storage ecosystem. With a focus on the concealed infrastructure behind data retention and organization, we unravel the behind-the-scenes operations that compose the foundation of iPhone storage.
iOS File System: A Closer Look at Its Organization
In this section, we will explore the intricate organization of the file system in iOS, taking a deeper dive into the way it manages and stores important information. By examining the structure of the file system, we can gain a better understanding of how data is stored and accessed in iOS devices.
When it comes to the organization of the iOS file system, it employs a hierarchical structure that allows for efficient management of files and directories. The file system is divided into various levels, with each level serving a specific purpose. At the topmost level, we have the root directory, which contains all other directories and files. These directories are further divided into various categories, such as system files, application files, and user-generated content.
System files play a crucial role in the functioning of the iOS ecosystem, as they contain important operating system components and configurations. They are carefully structured and organized in order to ensure a smooth operation of the device. On the other hand, application files are specific to each installed app and include all the necessary resources and data required by the app. These files are stored in dedicated directories, which are created for each individual app during its installation.
User-generated content, on the other hand, refers to any files or data that are created or modified by the users themselves. These can include documents, photos, videos, and other media files. They are typically stored in directories dedicated to each app or in the user's personal directories. This segregation allows for easy access and organization of user-generated content.
Furthermore, the iOS file system utilizes various techniques to ensure data security and privacy. One key aspect is the concept of sandboxing, which isolates each app within its own directory and restricts its access to other app directories. This separation prevents unauthorized access to sensitive data and enhances overall system security.
In conclusion, the organization of the iOS file system is carefully designed to ensure efficient file management and storage. With its hierarchical structure and segregation of system, application, and user-generated content, iOS provides a reliable and secure environment for data storage and retrieval.
Ensuring the Security of Your Valuable iPhone Data

In this section, we will discuss the crucial security measures that safeguard your valuable information stored within your iPhone, such as personal data, documents, and multimedia. By implementing these measures, you can prevent unauthorized access and potential data breaches.
Data Encryption: One of the fundamental security measures employed by iPhones is data encryption. Encryption involves the conversion of information into an unreadable format, which can only be deciphered with an authorized key or password. This ensures that even if someone gains physical access to your device or intercepts your data during transmission, it remains incomprehensible to them.
Secure Authentication Methods: To protect your iPhone data, Apple has integrated robust authentication methods. These include passcodes, Touch ID, and Face ID. Passcodes can be up to six digits or longer alphanumeric phrases, providing a personalized access code for your device. Touch ID relies on unique fingerprints, while Face ID utilizes facial recognition technology, ensuring that only authorized individuals can unlock your device.
Two-Factor Authentication: Apple provides an additional layer of security through two-factor authentication (2FA). By enabling this feature, you establish a trusted relationship between your iPhone and other devices (such as your iPad or MacBook), ensuring that only trusted devices can access your personal data. 2FA involves verifying your identity through a trusted device or phone number, providing enhanced protection against unauthorized access.
Secure Backup Options: Apple offers secure backup options, such as iCloud and encrypted iTunes backups. iCloud ensures that your data is regularly backed up and can be restored in case of device loss, damage, or data deletion. Encrypted iTunes backups protect your data by encrypting it with a unique password, ensuring that even if someone gains access to your backup, they cannot retrieve or view your data without the password.
App Permissions and Privacy Settings: To further safeguard your data, iPhone allows you to manage app permissions and privacy settings. You can control which apps have access to your personal information, such as contacts, location, photos, and more. By carefully reviewing and customizing these settings, you can minimize the risk of unauthorized access and protect your privacy.
Regular Software Updates: Apple consistently releases software updates that not only introduce new features but also address security vulnerabilities. Ensuring regular updates to your iPhone's operating system and apps is crucial to maintaining a secure environment for your data. These updates often include security patches that fix any identified vulnerabilities, keeping your data protected from external threats.
By following these security measures, you can have peace of mind knowing that your valuable iPhone data is well-protected and only accessible to authorized individuals. Remember to remain vigilant and proactive in managing your device's security settings to stay one step ahead of potential threats.
Ensuring the Safety and Retrieval of Vital Information on Your iPhone
In today's digital age, it is crucial to have a robust backup and recovery strategy in place for preserving essential data stored on your iPhone. By implementing effective measures, you can ensure the safeguarding and accessibility of valuable information, protecting it from unforeseen incidents and enabling effortless retrieval whenever needed.
Creating regular backups of your iPhone data is paramount in mitigating potential risks. Backing up your data entails making copies of important files, documents, contacts, photos, and other significant information stored on your device. This process involves storing these replicated files in secure locations, such as external hard drives, cloud services, or other trusted backup platforms.
One strategy for backing up your iPhone data is to utilize the iCloud service offered by Apple. iCloud provides seamless synchronization of your data across multiple devices, ensuring that your information is always up to date and readily available. By enabling the iCloud backup feature, you can automatically have your iPhone data backed up daily over a Wi-Fi connection, granting you peace of mind knowing that your vital information is securely stored.
Another alternative for safeguarding your iPhone data is to employ third-party backup solutions. These applications often offer additional features and customization options tailored to your specific needs. They allow you to schedule automatic backups, selectively choose the files to be backed up, and securely store your data in various locations, including external drives or cloud storage platforms.
- Investing in a reliable external hard drive is an excellent way to store your iPhone backups physically. These devices provide ample space to accommodate large amounts of data, ensuring that your information is readily accessible even without an internet connection. Moreover, external hard drives are portable and durable, making them a convenient option for maintaining your backups.
- Cloud storage services, such as Dropbox, Google Drive, or OneDrive, offer a secure and easily accessible location to store your iPhone backups. These platforms provide vast storage capacities and advanced encryption measures, guaranteeing the privacy and protection of your data. Additionally, cloud storage allows you to sync your files across multiple devices, enabling effortless retrieval and backup management.
In the unfortunate event of data loss or accidental deletion, having a reliable recovery strategy is essential. Regularly test your backup files to ensure their integrity and accessibility. Familiarize yourself with the recovery process specific to the backup method you have chosen, whether it involves restoring from an iCloud backup, recovering from an external hard drive, or utilizing a third-party backup solution.
To conclude, by implementing effective backup and recovery strategies, you can ensure the safety, accessibility, and seamless retrieval of vital information stored on your iPhone. Whether relying on iCloud, third-party applications, or a combination of both, regularly backing up your data and familiarizing yourself with recovery procedures are key steps in safeguarding your valuable information in today's technologically advanced world.
How To Clear System Data On iPhone and Free up Storage!
How To Clear System Data On iPhone and Free up Storage! by Fixed by Chaq 12,394 views 1 year ago 14 minutes, 40 seconds
Clear iPhone System Storage And Free iPhone Storage
Clear iPhone System Storage And Free iPhone Storage by Technical Wiz 118,349 views 6 months ago 6 minutes, 41 seconds
FAQ
Where is the data stored on an iPhone?
The data on an iPhone is stored in the device's internal memory, which includes both flash storage and RAM. Flash storage is where all the user data, such as apps, photos, videos, and documents, is stored. RAM, on the other hand, is used for temporary storage when apps are running.
Can I expand the storage capacity of my iPhone?
No, the storage capacity of an iPhone cannot be expanded. Unlike some Android devices that support expandable storage through external memory cards, iPhones have a fixed amount of internal storage that cannot be increased. Therefore, it is important to choose an iPhone with sufficient storage capacity when purchasing the device.
Is it possible to retrieve deleted data from an iPhone?
Yes, it is possible to retrieve deleted data from an iPhone, but it depends on various factors. If you have recently deleted the data and have a backup available, you can restore the data from the backup. However, if you do not have a backup, you might still be able to recover the data using specialized software or through the assistance of data recovery services. It is important to note that the chances of successful data recovery decrease with time, so it is recommended to act quickly if you need to recover deleted data.