It can be an incredibly exasperating experience when your dependable personal computer is unable to initiate its operating system. We all rely on our devices for a multitude of purposes, be it work-related tasks or simply connecting with friends and family. However, there are moments when this reliable companion seems to have an unexpected hiccup, leaving us feeling helpless and perplexed.
When encountered with the enigma of a non-responsive computer system, fear not, for there are actionable steps you can take to rectify the situation. This guide is tailored to assist you in understanding and troubleshooting the underlying causes that prevent your device from initiating the familiar user interface you are accustomed to. Through a series of simple yet effective strategies, you can potentially breathe life back into your machine without having to seek professional assistance or resort to drastic measures.
Throughout this troubleshooting journey, we will explore an array of practical solutions, empowering you to become both a detective and a problem solver. By harnessing the power of logical thinking, combined with a little bit of patience, we will unravel the intricacies behind why your computer stubbornly refuses to start. Whether you are faced with an unresponsive screen, error messages, or infinite loading loops, this guide will equip you with the necessary knowledge to tackle each situation head-on.
Try Restarting in Safe Mode

If your Windows device is encountering difficulties starting up, one troubleshooting method you can try is restarting it in Safe Mode. Safe Mode is a diagnostic mode that enables you to access your computer with minimal drivers and software, allowing you to pinpoint and resolve any issues that may be preventing it from booting properly.
Restarting your device in Safe Mode is a useful technique to isolate software or driver-related problems. By temporarily disabling unnecessary programs and drivers, you can determine if the issue is caused by a recently installed application or driver conflict.
- To enter Safe Mode, start by shutting down your computer completely.
- Once it is powered off, press the power button to turn it on.
- As the device starts up, repeatedly press the F8 key until you see the Advanced Boot Options menu.
- Use the arrow keys to navigate to the "Safe Mode" option and press Enter.
Once you successfully boot into Safe Mode, you can troubleshoot various system issues, such as uninstalling recently installed programs, updating or rolling back drivers, or scanning for malware. If your computer functions properly in Safe Mode, it indicates that the problem lies with a particular software or driver, allowing you to take appropriate action to resolve it.
If Safe Mode doesn't resolve the booting problem, it may indicate a hardware issue or a more complex software problem that requires further troubleshooting steps. In such cases, it is recommended to consult a professional technician or refer to official support resources provided by the manufacturer of your Windows device.
Use a Recovery Disk or USB Drive
If your computer is experiencing difficulties starting up or booting properly, utilizing a recovery disk or USB drive can be a valuable solution. This method involves using external media to access various recovery options and repair tools. By employing a recovery disk or USB drive, you can effectively troubleshoot and resolve any issues preventing your system from booting and regain access to your computer.
One approach is to create a recovery disk or USB drive before encountering any problems. This way, you can have it readily available whenever needed. To create a recovery disk, you can use the built-in recovery options in your operating system or download a third-party tool. It is crucial to follow the specific instructions for your particular operating system to ensure the recovery media is created correctly.
Once you have your recovery disk or USB drive, you can use it to boot your computer. Start by inserting the recovery disk into the optical drive or connecting the USB drive to an available USB port. Then, restart your computer and access the boot menu. The key combination to access the boot menu may vary depending on the computer manufacturer, so consult the documentation or search online for the appropriate key combination for your device.
In the boot menu, select the option that corresponds to the recovery disk or USB drive. This action will initiate the booting process from the external media, bypassing the regular boot sequence. Once the system boots from the recovery disk or USB drive, you will have access to a range of recovery options.
These recovery options may include system repair tools, such as startup repair, system restore, and system image recovery. Startup repair scans your computer for any issues preventing it from booting correctly and attempts to fix them automatically. System restore allows you to roll back your system to a previous state when it was functioning correctly. System image recovery enables you to restore your computer using a previously created system image.
Furthermore, a recovery disk or USB drive may provide access to advanced troubleshooting options, such as the command prompt. The command prompt allows you to execute commands and perform manual repairs, such as fixing corrupted files or rebuilding the boot configuration data (BCD).
In summary, when your computer fails to boot, utilizing a recovery disk or USB drive can be an effective solution. By creating a recovery media beforehand and using it to access the recovery options, you can troubleshoot and resolve various issues preventing your system from booting normally, ultimately restoring the functionality of your computer.
Perform a System Restore
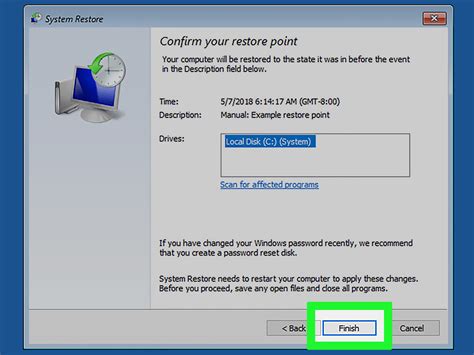
Resolve booting issues by utilizing the powerful tool of a system restore. If your computer is experiencing difficulties starting up properly, a system restore can help you revert your system to a previous working state. This process can aid in eliminating any software conflicts or changes that may be causing the booting problem, allowing you to regain access to your computer's functionality.
In the event that your device is displaying errors during boot or is stuck in a continuous loop, a system restore is a viable option for troubleshooting the issue without requiring technical expertise.
By performing a system restore, your computer will revert back to a point in time where it was functioning optimally, erasing any recently installed programs or system changes that could be causing the booting issue. It essentially serves as a time machine, restoring your computer's settings and configuration to a previous, stable state.
Remember that performing a system restore will not affect your personal files, such as documents or photos, but it is recommended to backup any important data before undertaking this process as a precautionary measure.
Accessing the system restore feature will vary depending on your specific operating system, but it is generally accessible through the advanced boot options or recovery environment. Follow the prompts and select a suitable restore point from the available options, taking note of the dates and descriptions to ensure you choose a point prior to the onset of the booting issue.
Once the system restore is initiated, it may take some time to complete. Your computer will restart to apply the changes, and upon completion, you should be able to boot into your operating system successfully.
Performing a system restore is a user-friendly solution to address booting problems and is often an effective troubleshooting step to resolve software-related issues that could be hindering the normal startup process of your computer.
FAQ
What are the possible reasons for a Windows computer not booting?
There can be several reasons for a Windows computer not booting. It could be due to a hardware issue, such as a faulty hard drive or RAM. It could also be caused by a software problem, like a corrupted operating system or a virus. Additionally, incorrect BIOS settings or a problem with the power supply could also prevent the computer from booting.
How can I determine if the problem is with my hardware or software?
To determine if the problem lies with your hardware or software, you can perform a few troubleshooting steps. Start by checking if any error messages or sounds are displayed when you try to boot up the computer. If there are, it could indicate a hardware issue. You can also try booting the computer in Safe Mode or using a bootable USB drive to see if it successfully boots. If it does, the problem is likely software-related.
What can I do if my Windows computer is stuck on the loading screen?
If your Windows computer gets stuck on the loading screen, you can try a few solutions. First, try restarting your computer and see if it resolves the issue. If not, you can try booting into Safe Mode and then performing a system restore to a previous point when the computer was working fine. Another option is to use the Advanced Startup Options to refresh or reset your PC.
Is it possible to fix a Windows computer that won't boot without losing my data?
Yes, it is possible to fix a Windows computer that won't boot without losing your data. If you have access to another computer, you can create a bootable USB drive or a bootable disk to troubleshoot and repair the computer. Additionally, you can also try connecting your hard drive to another computer and use data recovery software to retrieve your files before attempting any repair actions.
When should I consider seeking professional help to fix my computer?
If you have tried all possible troubleshooting steps and your computer still won't boot, it may be time to seek professional help. Additionally, if you are not comfortable with performing advanced troubleshooting tasks or accessing the internal components of your computer, it is advisable to consult a professional technician. They can diagnose the issue accurately and provide appropriate solutions to get your computer up and running again.
My Windows computer is not booting up. What should I do?
If your Windows computer is not booting up, there are a few troubleshooting steps you can try. First, check that all the cables are securely connected, including the power cable. If that doesn't solve the issue, try restarting your computer and pressing the F8 key repeatedly to access the Advanced Boot Options menu. From there, you can try options like Safe Mode or Last Known Good Configuration. If none of these solutions work, you may need to use a Windows installation disc or recovery drive to repair your computer's startup files.




