In the vast and ever-expanding realm of open-source operating systems, a group of Linux distributions have emerged as pioneers in adopting the revolutionary systemd. This groundbreaking init system, with its robust feature set and enhanced system management capabilities, has sparked debates, ignited passions, and reshaped the way Linux enthusiasts perceive the future of their beloved operating system.
With each passing year, more and more distros embraced systemd, entrusting their systems to its promising potential. Emphasizing efficient boot times, flexible service management, and advanced logging, these Linux distributions embody the spirit of progress and strive to provide users with a seamless and reliable computing experience.
Among the selected distros that have unequivocally espoused systemd is a diverse range of options, each with its unique strengths and community support. From the stalwart leaders in the Linux community to newly established players, these distros have made a conscious choice to embrace systemd, spurred by a collective desire to streamline system administration, enhance compatibility, and bolster the overall user experience.
However, while systemd has garnered widespread adoption, it has not gone without criticism. Some argue that its extensive feature set and centralized control expose systems to potential vulnerabilities, while others contend that it strips away the Unix philosophy of simplicity and modularity that Linux distributions have long been known for. Nevertheless, systemd enthusiasts remain steadfast in their belief that this innovative init system is a necessary evolution in the Linux ecosystem.
Overview of Linux distributions with systemd
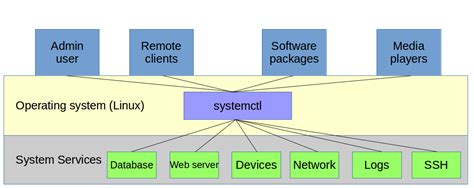
The increasing demand for efficient and modern operating systems has led to the adoption of systemd as the default init system in several Linux distributions. This article provides an overview of various Linux distributions that have embraced systemd, highlighting their key features and advantages.
| Distribution | Description |
|---|---|
| Ubuntu | Ubuntu, one of the most popular Linux distributions, integrates systemd to enhance the boot process and manage system services effectively. It offers a user-friendly experience and extensive community support. |
| Debian | Debian, known for its stability and reliability, includes systemd as the default init system starting from Debian 8 (Jessie). It simplifies system management tasks and ensures efficient resource utilization. |
| Fedora | Fedora, a cutting-edge Linux distribution backed by Red Hat, has been an early adopter of systemd since Fedora 15. It leverages systemd's features to improve boot speed, service management, and troubleshooting capabilities. |
| Arch Linux | Arch Linux, a lightweight and flexible distribution, has embraced systemd as its init system. Its philosophy of simplicity and comprehensive package management is complemented by systemd's advanced service control and dependency management. |
| SUSE Linux Enterprise | SUSE Linux Enterprise, designed for enterprise environments, incorporates systemd as the default init system to ensure reliable and consistent system startup. It offers enterprise-level support and integrates well with other SUSE technologies. |
These are just a few examples of Linux distributions that use systemd. Each distribution brings its unique strengths and focuses on catering to different user needs, ranging from home users to large corporations. By adopting systemd, these distributions have embraced a modern approach to system initialization and management, paving the way for improved performance and efficiency in the Linux ecosystem.
Understanding systemd: A Key Component in Many Linux Distributions
In the realm of various Linux operating systems, there exists a crucial element known as systemd. This pivotal technology plays an integral role in the functioning and management of numerous popular Linux distributions, serving as the foundation for their operational processes. Appreciating the significance and intricacies of systemd is essential for anyone seeking a deeper understanding of these Linux systems.
systemd is a sophisticated initialization system that provides a range of functionalities and services to enhance the overall performance and reliability of a Linux distribution. It replaces the traditional System V init system and offers advanced features such as parallel startup processes, on-demand service activation, advanced logging capabilities, and dependency-based boot ordering.
With systemd, administrators gain powerful tools for managing and controlling various system components and services, enabling efficient resource utilization and streamlined operations. By embracing systemd, Linux distributions can benefit from improved boot times, simplified management of system services, and enhanced monitoring and troubleshooting capabilities.
Furthermore, systemd offers declarative configuration files that enable administrators to define and control the behavior of system services through simple and intuitive descriptions. These configuration files, along with systemd's extensive logging functionality, contribute to efficient system diagnostics and troubleshooting, facilitating the identification and resolution of issues.
Notably, systemd has become the default choice for many major Linux distributions, including but not limited to Ubuntu, Fedora, Debian, CentOS, and Arch Linux. Its widespread adoption reflects its reliability, flexibility, and the robust feature set it offers. Understanding the role and functionalities of systemd in these diverse distributions is therefore crucial for system administrators, developers, and Linux enthusiasts in general.
In summary, systemd stands as a fundamental component of many Linux distributions, providing a comprehensive suite of features and services that optimize system performance and management. Through its advanced capabilities and widespread usage, systemd plays a significant role in shaping the modern Linux ecosystem.
Popular Linux distributions utilizing systemd
In the world of open-source operating systems, numerous well-known and widely used distributions take advantage of the powerful systemd software suite for managing system services and processes. These distributions have embraced systemd as a reliable and efficient init system, benefiting from its extensive features and enhanced system performance. Let's explore some of the popular Linux distributions that have adopted systemd as their preferred init system.
Choosing the Ideal Linux Distribution with systemd
When it comes to selecting a suitable Linux distribution, there are numerous factors to consider. One critical aspect to take into account is the choice of init system, as it significantly impacts the functionality and performance of your system. Systemd, a powerful init system, has gained widespread adoption and is utilized by several popular Linux distributions. In this section, we will explore the advantages and characteristics of various Linux distributions that incorporate systemd.
- Ubuntu: Ubuntu, a widely recognized Linux distribution, utilizes systemd as its default init system. With its focus on user-friendliness and stability, Ubuntu is an excellent choice for beginners and those seeking a reliable operating system.
- Debian: As one of the oldest and most influential Linux distributions, Debian also embraces systemd. Renowned for its stability, Debian offers a vast repository of software packages and is suitable for both desktop and server environments.
- Fedora: Fedora is a cutting-edge Linux distribution that maintains a close relationship with the upstream projects. With systemd as its default init system, Fedora provides the latest software releases, making it an excellent option for developers and enthusiasts seeking the latest features.
- OpenSUSE: OpenSUSE, known for its flexibility and robustness, also adopts systemd. This distribution offers two different editions: Leap, which focuses on stability and longevity, and Tumbleweed, which boasts a rolling release model with the latest software updates.
- Arch Linux: Arch Linux follows a minimalist approach, allowing users to customize their system from the ground up. Systemd is supported in Arch Linux, making it a popular choice for advanced users who desire a lightweight and highly configurable distribution.
These are just a few examples of Linux distributions that employ systemd as their init system. Each distribution has its own strengths and target audience, so it is essential to consider your specific needs and preferences when selecting the right Linux distribution based on systemd.
FAQ
Which Linux distributions use systemd?
Many popular Linux distributions have adopted systemd as their init system. Some of the notable ones include:
Why do many Linux distributions use systemd?
Systemd has gained popularity in the Linux community due to its advanced features and benefits it offers over traditional init systems. Some of the reasons why many Linux distributions have adopted systemd include:
Are there any Linux distributions that do not use systemd?
Yes, there are some Linux distributions that have chosen not to use systemd as their init system. These distributions often provide alternative init systems or aim to maintain compatibility with sysvinit. Some examples of Linux distributions without systemd include:
Can I switch from a Linux distribution with systemd to one without systemd?
Yes, it is possible to switch from a Linux distribution with systemd to one without systemd. However, this process can be complex and may require a complete reinstallation of the operating system. Additionally, compatibility issues may arise when switching init systems, so it is advisable to thoroughly research and plan the switch before proceeding.
What are some alternative init systems to systemd?
There are several alternative init systems to systemd, which are used by various Linux distributions. Some popular alternative init systems include:
Which Linux distributions use systemd?
Systemd is the default init system in many popular Linux distributions, including Debian 8 and later, Ubuntu 15.04 and later, Fedora, CentOS 7 and later, Arch Linux, and openSUSE.
Why do some Linux distributions use systemd?
Systemd offers several advantages over traditional init systems, including faster boot times, parallel service startup, improved service management, and better logging and debugging capabilities. Additionally, systemd provides a uniform interface across distributions, making it easier for developers to create and maintain software that runs on multiple Linux distributions.




