In today's fast-paced digital landscape, businesses rely heavily on efficient and secure data management systems. One vital aspect of this is the utilization of network storage solutions on Windows Server. By leveraging the power of network drives, organizations can enhance collaboration, improve data accessibility, and ensure data redundancy, all while maintaining optimum productivity.
Network storage, also known as shared storage, enables multiple users to access and share files seamlessly across a network. It eliminates the need for physical storage devices connected directly to individual workstations, providing a centralized and organized data repository. This technology allows administrators to allocate and manage storage space effortlessly, offering flexibility and scalability as the business needs evolve.
Windows Server offers robust features and functionalities for managing network drives, making it a go-to solution for businesses of all sizes. With its intuitive administration tools, security measures, and seamless integration with other Microsoft applications, Windows Server provides a comprehensive and reliable platform for leveraging network storage. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of utilizing network drives on Windows Server, from setting up the initial configuration to optimizing performance and implementing backup strategies.
Understanding the Fundamentals of Network Drives
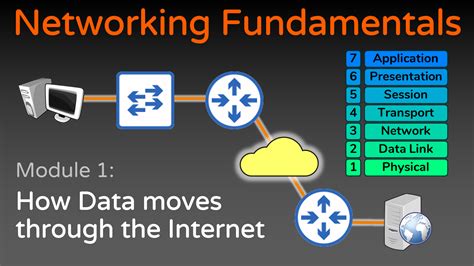
Network drives are an essential component of modern computer networks, facilitating efficient data storage and access for multiple users within an organization. This section aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of the underlying principles and functionality of network drives, without delving into specific technicalities.
A network drive can be likened to a virtual storage space that is accessible to authorized users connected to a network. It enables users to store, retrieve, and share files and folders in a centralized location, eliminating the need for individual storage devices and promoting collaboration and data consistency among team members.
One key feature of network drives is their ability to be mounted or mapped as a distinct drive letter on a user's workstation. By mapping a network drive, users can conveniently access and manage the shared resources as if they were stored locally on their own computers.
Network drives offer several advantages for organizations, including enhanced data security, centralized administration and management, improved data backup and recovery capabilities, and simplified file access and sharing procedures. By understanding the fundamentals of network drives, administrators can optimize their usage within a Windows Server environment and effectively harness their benefits.
| Benefits of Network Drives |
|---|
| Enhanced data security |
| Centralized administration and management |
| Improved data backup and recovery capabilities |
| Simplified file access and sharing procedures |
The Advantages of Utilizing Network Storage Devices
When it comes to data management in a corporate environment, the utilization of network storage devices brings numerous benefits for efficient and secure file storage and sharing.
Enhanced Collaboration: Network drives facilitate seamless collaboration among team members by allowing them to access and work on shared files from any location. This shared accessibility eliminates the need for individuals to physically transfer files, ensuring real-time updates and minimizing conflicts arising from multiple versions of a document.
Centralized Data Storage: By utilizing network drives, organizations can centralize their data storage, ensuring that all files and important data are stored in a single, secure location. This reduces the risk of data loss, improves data accessibility, and simplifies data backup and recovery procedures.
Improved Data Security: Network drives enable administrators to establish access controls, ensuring that only authorized personnel can view, edit, or delete files. This helps protect sensitive information and prevents unauthorized data tampering or accidental deletions.
Scalability and Flexibility: Network storage devices offer scalability, allowing organizations to expand their storage capacity as their data requirements grow. Additionally, these drives provide the flexibility to allocate and manage storage space based on specific department or user needs.
Efficient Backup and Disaster Recovery: Storing files on network drives simplifies the backup process, enabling organizations to schedule automatic backups and easily recover files in the event of data loss or system failure. This ensures continuity of operations and minimizes potential business disruption.
In conclusion, network storage devices offer numerous advantages, including enhanced collaboration, centralized data storage, improved data security, scalability, and efficient backup and disaster recovery. Incorporating network drives into your organization's infrastructure can greatly increase productivity, data management efficiency, and overall data security.
Setting Up Shared Storage on Windows Server
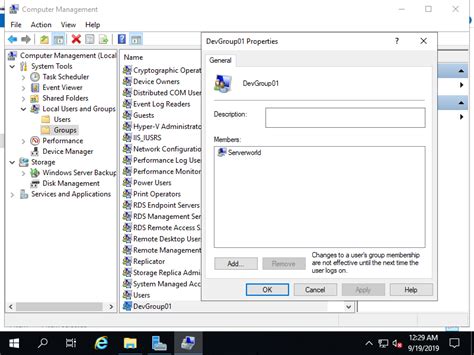
In this section, we will explore the process of configuring shared storage on a Windows Server environment. Shared storage plays a crucial role in enabling efficient collaboration and data accessibility across networked devices. By allocating network resources to create a centralized storage location, organizations can streamline data management and ensure seamless access to files and folders.
Firstly, we will delve into the prerequisites for setting up shared storage. This includes ensuring the availability of suitable hardware components such as network-attached storage (NAS) devices or storage area networks (SANs). Additionally, proper network configurations and permissions need to be established to facilitate secure access to the shared storage.
Next, we will outline the step-by-step process of setting up shared storage. This involves creating a shared folder on the Windows Server and configuring its permissions to control who has access to the shared files. We will explore various permission levels such as read, write, and modify, and discuss best practices for granting and managing these permissions.
Furthermore, we will cover advanced configuration options for shared storage, such as setting quota limits to manage storage usage, enabling encryption to enhance data security, and implementing versioning to maintain file integrity. These additional features offer organizations greater control and flexibility in managing their shared storage environment.
Lastly, we will discuss troubleshooting techniques and common challenges that may arise during the setup and maintenance of shared storage. We will provide insights into identifying and resolving issues related to file permissions, network connectivity, and storage device configuration. By understanding these troubleshooting strategies, administrators can effectively address any obstacles that may impede the smooth operation of shared storage.
Configuring Shared Folders
In this section, we will explore the process of setting up shared folders on your Windows Server environment. Shared folders allow multiple users or devices to access and modify files and data stored on a network. By configuring shared folders, you can enhance collaboration and streamline file sharing within your organization.
To begin, it is crucial to understand the importance and benefits of shared folders. Shared folders facilitate seamless access and sharing of information among team members, departments, or even across different locations. By granting appropriate permissions, you can control who can view, edit, or delete files within a shared folder.
When configuring shared folders, you need to consider certain factors such as the purpose of the shared folder, the level of security required, and the specific user or group permissions to be assigned. You can create new shared folders or modify existing ones, ensuring they align with the unique needs of your organization.
It is essential to select an appropriate naming convention for shared folders, making it easier for users to identify and locate relevant files. Additionally, you may want to consider implementing quotas to manage storage usage and prevent any single user from monopolizing the available disk space.
During the configuration process, you will have the option to enable offline access to shared folders, enabling users to access files and make modifications even when they are not connected to the network. This feature can significantly enhance productivity for remote or traveling team members.
In summary, this section will guide you through the process of configuring shared folders on your Windows Server ecosystem. By implementing shared folders effectively, you can optimize collaboration, simplify file sharing, and enhance productivity within your organization.
Assigning Permissions to Shared Storage Devices
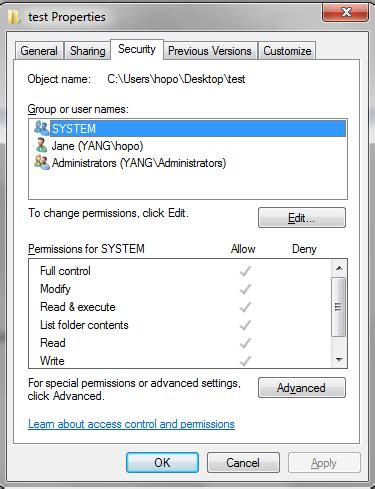
When using collaborative storage systems within a network environment, it is crucial to establish proper access control to ensure data security and maintain confidentiality. This section will explore the essential steps for assigning permissions to network drives, enabling administrators to fine-tune access levels for different users and groups.
| Permission Level | Description |
|---|---|
| Full Control | Allows users to perform all actions, including creating, modifying, and deleting files and folders, as well as changing permissions and taking ownership. |
| Read | Enables users to view files and folders, but not make changes or perform any other actions. |
| Write | Provides users with the ability to create, modify, and delete files and folders, but not change permissions or take ownership. |
| Modify | Allows users to make changes to existing files and folders, but not create new ones or change permissions. This permission is suitable for collaborative environments where users may need to update documents. |
| None | Denies all access to the network drive. Users with this permission level cannot view, modify, or delete any content in shared storage devices. |
To assign permissions to network drives, administrators should follow a systematic approach. Firstly, they should identify the users and groups that require access to the shared storage device. Once determined, the appropriate permission levels can be assigned to each user or group. It is important to ensure that permissions are granted based on the principle of least privilege, granting users only the necessary access needed for their specific roles.
Administrators can set permissions using the built-in security features provided by the operating system or by utilizing third-party tools specifically designed for managing network drive permissions. Regardless of the method chosen, regular review and maintenance of permissions is essential to address any changes in user roles or access requirements, effectively managing security risks and maintaining the integrity of the shared storage system.
Mapping Network Drives on Client Machines
Efficiently connecting external data storage to individual workstations is crucial for seamless collaboration and data accessibility. This section focuses on the process of establishing a connection between client machines and networked storage drives, facilitating uninterrupted file sharing and data retrieval.
Procedure for Mapping Network Drives:
Step 1: Start by identifying the desired network drive, which can be referred to as a remote storage location accessible over the network.
Step 2: Open the File Explorer on the client machine, locate the "Map network drive" option, and select it to initiate the mapping process.
Step 3: A new window will appear, prompting the user to specify the network drive's location. Enter the network path or browse through the available options to find the desired drive.
Step 4: Choose a drive letter that will be assigned to the network drive for easier identification and access. This letter will act as a shortcut to the network location.
Step 5: Optionally, enable the "Reconnect at sign-in" option to ensure that the mapped network drive automatically connects each time the user logs into their workstation.
Step 6: Authenticate by entering the appropriate credentials to gain access to the network drive. This is typically the username and password associated with the server hosting the drive.
Step 7: Click on "Finish" or a similar option to complete the mapping process. The network drive should now appear in the File Explorer, granting the client machine access to the shared storage.
By following these steps, client machines can easily map network drives, enabling seamless access to shared files and facilitating efficient collaboration within the networked environment.
FAQ
What are network drives and how do they work on Windows Server?
Network drives are storage spaces located on a network that can be accessed and utilized by users connected to the network. On Windows Server, network drives can be created and managed through the Server Manager or PowerShell, providing a centralized storage solution for multiple users.
Can network drives on Windows Server be accessed from different locations?
Yes, network drives on Windows Server can be accessed from different locations as long as the users have the necessary permissions and are connected to the network. This allows users to access their files and data from various devices and locations, providing flexibility and convenience.
What are the advantages of using network drives on Windows Server?
Using network drives on Windows Server offers several advantages. It provides a centralized storage solution, allowing for easy backup and data recovery. Network drives also enable secure access control, allowing administrators to manage user permissions and restrict access to sensitive data. Additionally, network drives facilitate collaboration and file sharing among users connected to the network.
How do I set up and configure network drives on Windows Server?
To set up and configure network drives on Windows Server, you can use the Server Manager or PowerShell. First, you need to ensure that the server has the File Server role installed. Then, you can create and configure shared folders, assign permissions to users or groups, and map the network drives on client machines. Detailed steps for each method can be found in the comprehensive guide mentioned in the article.
Are there any limitations or considerations when using network drives on Windows Server?
Yes, there are some limitations and considerations when using network drives on Windows Server. These include the maximum number of simultaneous connections allowed, the available storage capacity, and the network bandwidth. It is important to ensure that the server hardware and network infrastructure can handle the expected workload and provide adequate performance for all connected users.




