In today's fast-paced and highly competitive manufacturing industry, optimizing operational processes is crucial for success. One key aspect of achieving operational excellence is effective management of manufacturing process systems. Innovation and efficiency are vital for staying ahead of the competition, and technology plays a significant role in enabling companies to streamline their processes.
One powerful tool that has gained popularity among manufacturing companies is open source software. Open source solutions provide a cost-effective and flexible alternative to proprietary software, allowing businesses to customize their systems to meet their specific needs. This article explores the benefits of utilizing open source software in the configuration of manufacturing process management systems, highlighting its potential to enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and increase productivity.
Open source software offers manufacturers the freedom to modify and adapt their process management systems according to the unique requirements of their production lines. This flexibility enables companies to optimize their operations by tailoring the software to fit their specific workflows and procedures. By integrating open source solutions into their manufacturing processes, organizations can eliminate the limitations often imposed by proprietary software and gain greater control over their systems.
Overview of Manufacturing Process Control Solutions
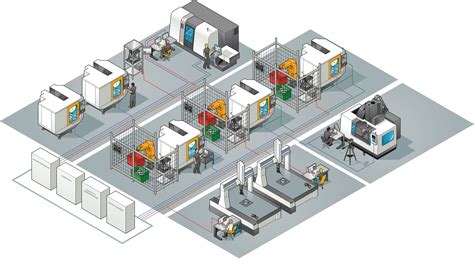
Manufacturing process control solutions play a pivotal role in optimizing and streamlining production operations. These systems encompass a range of integrated software and hardware components that enable businesses to manage and control every aspect of their manufacturing processes efficiently.
A comprehensive manufacturing process control solution provides real-time visibility into production activities, facilitating better decision-making, reducing production downtime, and enhancing overall operational efficiency. It enables manufacturers to monitor and control key process parameters, ensuring consistent quality, adherence to regulatory requirements, and compliance with industry standards.
These systems employ various automation technologies, including industrial robots, programmable logic controllers (PLCs), supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA) systems, and human-machine interfaces (HMIs). They leverage data analytics and predictive maintenance algorithms to identify potential issues and optimize production schedules, leading to increased productivity and reduced costs.
Furthermore, manufacturing process control solutions often integrate with enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems, providing seamless data exchange and synchronization between shop floor operations and business management functions. This integration enables manufacturers to achieve end-to-end visibility and control over their entire production and supply chain processes.
| Key Features of Manufacturing Process Control Solutions |
|---|
| Real-time monitoring and control of production parameters |
| Automated data collection and analysis |
| Integration with other manufacturing and business systems |
| Intuitive user interfaces for easy operation |
| Alerts and notifications for proactive issue resolution |
| Advanced analytics for performance optimization |
| Support for regulatory compliance and quality standards |
Manufacturing process control solutions offer a robust framework for managing and optimizing manufacturing operations. With their ability to provide real-time visibility, automation, and integration capabilities, these systems empower businesses to achieve higher productivity, improved quality control, and cost-effectiveness in their manufacturing processes.
Advantages of Linux for Streamlining Manufacturing Operations
In today's constantly evolving industrial landscape, it is crucial for companies to optimize their manufacturing processes to stay competitive. Utilizing an efficient operating system can play a pivotal role in this endeavor. Linux, renowned for its flexibility, reliability, and open-source nature, stands out as a valuable tool for managing and improving manufacturing process management systems.
Enhanced Security: Linux offers robust security features that safeguard manufacturing operations from potential cyber threats. Its open-source nature enables quick identification and mitigation of vulnerabilities, ensuring a secure environment for critical data and sensitive manufacturing information.
Customizability and Flexibility: Linux provides unparalleled customization capabilities, allowing manufacturers to tailor their process management systems to meet their unique requirements. With a vast array of user-friendly tools, developers can easily modify and optimize software solutions to streamline manufacturing operations.
Reliability and Stability: Linux is renowned for its stability, with long uptimes and minimal downtime, making it an ideal choice for mission-critical manufacturing processes. Its ability to withstand high workloads and efficiently handle large data volumes ensures smooth and uninterrupted operations throughout the manufacturing workflow.
Cost-Efficiency: Linux eliminates the need for costly licensing fees associated with proprietary operating systems. Its open-source nature allows businesses to reduce software expenses while still benefiting from a robust and feature-rich platform for managing manufacturing process management systems.
Open-Source Community: The Linux community comprises millions of developers worldwide, constantly striving to improve the operating system. This global collaboration fosters innovation and ensures a steady stream of updates and enhancements to meet the evolving needs of manufacturing process management.
Interoperability: Linux supports a wide range of hardware architectures, making it compatible with various manufacturing equipment and devices. This flexibility enables seamless integration of diverse components within the manufacturing process, promoting interoperability and enhancing overall efficiency.
In conclusion, leveraging the benefits of Linux in manufacturing process management offers companies a powerful solution for optimizing their operations. From enhanced security to customization and flexibility, Linux empowers manufacturers to meet industry demands efficiently and effectively.
Implementation of Linux in Manufacturing Process Management Systems
In this section, we will explore the integration of the powerful open-source operating system into the realm of Manufacturing Process Management Systems (MPMS). By leveraging the versatility and flexibility offered by Linux, organizations can optimize their manufacturing processes, enhance productivity, and streamline operations.
Linux, being an open-source platform, provides businesses with the freedom to tailor MPMS solutions to their specific needs. Utilizing Linux as the foundation for MPMS enables companies to leverage a wide range of customizable tools and applications, facilitating seamless integration with existing systems and processes. Furthermore, the extensive community support and constant updates ensure that manufacturers can adapt to evolving industry requirements and technological advancements effortlessly.
When it comes to managing complex manufacturing processes, Linux offers a robust and secure environment. Its inherent stability and scalability make it an ideal choice for large-scale manufacturing operations that demand precision, reliability, and real-time data analysis. By leveraging Linux's capabilities, organizations can effectively monitor, control, and optimize their manufacturing workflows, ensuring efficient resource allocation, minimized downtime, and improved overall productivity.
Furthermore, Linux brings cost-effectiveness to the realm of MPMS. The absence of licensing fees and the availability of a vast array of open-source software enable organizations to significantly reduce their IT investment while still achieving superior functionality and performance. By leveraging Linux, manufacturers can allocate saved resources towards other critical aspects of their production processes, such as research and development or employee training, thus fostering continuous improvement and innovation.
Overall, the implementation of Linux in Manufacturing Process Management Systems offers organizations the opportunity to enhance their manufacturing capabilities, streamline operations, and achieve sustainable growth. The inherent flexibility, security, and cost-effectiveness of Linux make it an indispensable tool for manufacturers seeking to optimize their processes and remain competitive in an ever-changing global market.
Choosing the Appropriate Linux Distribution
In the context of configuring manufacturing process management systems, it is essential to select the most suitable Linux distribution for optimal performance and compatibility. This section aims to provide guidance on how to make an informed decision about choosing the right Linux distribution for your specific needs.
- Consider the requirements: Before selecting a Linux distribution, it is crucial to evaluate the requirements of the manufacturing process management system. Assess factors such as hardware specifications, software compatibility, security features, and ease of integration. Identifying these essential requirements will help narrow down the options and ensure a successful implementation.
- Evaluate stability and support: A key consideration when choosing a Linux distribution is its stability and the level of support offered. Look for distributions with a reliable track record of stability in industrial environments. Additionally, consider the availability of community support or professional services that can assist with troubleshooting and maintenance.
- Assess customization capabilities: Manufacturing process management systems often require customization to meet specific business needs. Therefore, it is important to assess the level of customization offered by different Linux distributions. Look for distributions that provide ample flexibility and allow for easy configuration and adaptation to accommodate the unique requirements of the manufacturing processes.
- Consider software availability: Another crucial aspect to consider is the availability of software packages and tools that are compatible with the chosen Linux distribution. Ensure that the necessary software for managing manufacturing processes, such as production scheduling, quality control, or inventory management, is readily accessible and supported by the chosen distribution.
- Review security features: Manufacturing process management systems deal with sensitive data and require robust security measures. When selecting a Linux distribution, thoroughly assess its security features and the availability of security updates and patches. Look for distributions with a strong focus on security, including features such as secure boot, data encryption, and access control.
- Consider long-term support and compatibility: It is vital to select a Linux distribution that offers long-term support and compatibility to prevent disruption in the manufacturing process. Look for distributions with established release cycles, extended support options, and a commitment to compatibility with future hardware and software technologies.
By carefully considering the requirements, stability, customization capabilities, software availability, security features, and long-term support and compatibility, selecting the right Linux distribution for configuring manufacturing process management systems becomes a well-informed decision that can contribute to the success and efficiency of the overall system implementation.
Customization and Integration of Linux for Streamlining Manufacturing Operations

In this section, we will explore the various ways in which Linux can be tailored and seamlessly incorporated into manufacturing processes, resulting in enhanced efficiency and productivity. By customizing and integrating Linux, businesses can optimize their operations and better adapt to the specific needs and requirements of their manufacturing environment.
Enhancing Flexibility and Adaptability: Linux offers a wide array of customizable features and components, allowing manufacturing organizations to configure the operating system according to their unique specifications. This level of flexibility enables businesses to align their manufacturing processes with changing market demands and technological advancements, ensuring smooth operations within dynamic production environments.
Integrating Open Source Solutions: One of the key advantages of Linux is its compatibility with open-source software and tools. By integrating open-source solutions with Linux-based manufacturing process management systems, organizations can leverage the power of collaborative development and benefit from a diverse range of specialized applications. This integration provides access to innovative functionalities, facilitates process automation, and promotes cost-effective solutions for manufacturing operations.
Streamlining Communication and Collaboration: Linux-based platforms offer robust communication and collaboration tools that can be seamlessly integrated into manufacturing processes. These tools allow different stakeholders, such as designers, engineers, and production personnel, to easily exchange information, share updates, and collaborate on projects in real-time. By streamlining communication, Linux enhances coordination across teams, reduces errors, and promotes efficient decision-making, ultimately leading to optimized manufacturing operations.
Ensuring Security and Stability: Linux is renowned for its robust security infrastructure and stability, making it an ideal choice for critical manufacturing environments. Customizing and integrating Linux enables businesses to implement stringent security measures, protecting sensitive manufacturing data and mitigating the risk of unauthorized access or system vulnerabilities. Furthermore, the stability of Linux ensures uninterrupted operation of manufacturing processes, minimizing downtime and optimizing overall productivity.
Ensuring Security and Reliability with Linux
In the realm of deploying Linux for the implementation of Manufacturing Process Management systems, one area that warrants significant emphasis is the assurance of security and reliability. The undeniably robust nature of Linux, coupled with its inherent security features, makes it an ideal choice for safeguarding critical manufacturing processes. This section delves into the various measures and best practices that can be adopted to ensure the security and reliability of Linux-based systems.
1. Implementing stringent access controls: One of the fundamental aspects of ensuring security and reliability is to enforce strict access controls. This involves implementing user authentication mechanisms, role-based access controls, and granular permissions, thereby restricting unauthorized access to sensitive data and system resources.
2. Regular system updates and patch management: Keeping the Linux system up-to-date with the latest security patches and updates is crucial for defending against potential vulnerabilities. By regularly applying patches and updates, manufacturers can address security loopholes and enhance the overall reliability of the system.
3. Utilizing firewalls and network security measures: Deploying firewalls and implementing appropriate network security measures is essential for protecting manufacturing process management systems. This includes configuring firewall rules, establishing secure network connections, and implementing intrusion detection and prevention systems to detect and mitigate potential threats.
4. Encrypting data in transit and at rest: Data encryption is a vital component in ensuring the confidentiality and integrity of sensitive information. By utilizing encryption techniques, both for data in transit (such as communication between system components) and data at rest (such as stored files and databases), manufacturers can significantly enhance the security of their Linux-based systems.
5. Regular system monitoring and auditing: Continuous monitoring and auditing of the Linux system is paramount to detect any suspicious activities or security breaches in a timely manner. Implementing centralized log management, intrusion detection system alerts, and real-time monitoring tools can provide manufacturers with valuable insights and enable immediate action to address security incidents.
By implementing these security and reliability measures, manufacturers can leverage the robustness and inherent security features of Linux to safeguard their Manufacturing Process Management systems from potential threats, ensuring uninterrupted operations and safeguarding sensitive data throughout the manufacturing process.
Manufacturing Management
Manufacturing Management by Tutorialspoint 28,571 views 5 years ago 7 minutes, 15 seconds
Session-26 | Process Management in Linux | Manage Processes in RHEL | Nehra Classes
Session-26 | Process Management in Linux | Manage Processes in RHEL | Nehra Classes by Nehra Classes 2,607 views 3 years ago 30 minutes
FAQ
What are the benefits of using Linux for configuring manufacturing process management systems?
Using Linux for configuring manufacturing process management systems brings several advantages. Firstly, Linux is an open-source operating system, which means it is highly customizable and adaptable to specific needs. This flexibility allows for easy integration with other systems and software tools used in the manufacturing process. Additionally, Linux is known for its stability and reliability, making it suitable for managing critical manufacturing operations. Furthermore, Linux offers robust security features, protecting sensitive manufacturing data from potential cyber threats.
Can Linux be used with existing manufacturing process management systems?
Yes, Linux can be seamlessly integrated with existing manufacturing process management systems. Its open-source nature ensures compatibility with various hardware and software components, enabling smooth communication and data exchange between different systems. Whether the manufacturing process management system is based on proprietary software or other operating systems, Linux can be employed as a powerful tool for configuring and managing the system, enhancing efficiency and productivity.
Are there any specific Linux distributions recommended for configuring manufacturing process management systems?
There is no specific Linux distribution recommended for configuring manufacturing process management systems as the choice depends on various factors such as specific requirements, hardware compatibility, and the expertise of the IT team. However, some popular Linux distributions commonly used in industrial settings include Ubuntu, CentOS, and Debian. These distributions offer long-term support, frequent security updates, and extensive community support, making them suitable choices for configuring manufacturing process management systems.
How can Linux enhance the security of manufacturing process management systems?
Linux provides several features and tools to enhance the security of manufacturing process management systems. Firstly, it offers built-in security mechanisms such as access control lists (ACLs), file system permissions, and user management, allowing administrators to enforce strict access controls and limit privileges. Additionally, Linux has a robust firewall system (such as iptables) and supports various encryption protocols, safeguarding sensitive data from unauthorized access. Regular security updates and patches further strengthen the security of Linux-based manufacturing process management systems.




