When it comes to creating captivating melodies, producing awe-inspiring sounds, and unleashing your musical genius, there exists an operating system that not only empowers but also elevates the art of music creation. We're not talking about your run-of-the-mill software, though. Today, we delve into a world where freedom meets innovation, and where limitless possibilities intertwine harmoniously. Enter a realm where musicians, producers, and sound engineers alike find solace in a versatile and robust platform: the unbridled realm of Linux.
Linux, often dubbed as the guardian of technophiles and the playground of open-source enthusiasts, is a powerful force quietly revolutionizing the music production landscape. With its lineage tracing back to the depths of computing history, Linux bestows developers and users alike with the ability to shape their creative destinies. By harnessing the collective wisdom and collaborative endeavors of the open-source community, Linux presents a unique set of advantages that transcend barriers and redefine traditional music production norms.
Leave behind the limitations imposed by conventional, closed-source software; Linux serves as a gateway to a world of limitless experimentation and customization. Embrace the raw potential, the untapped innovation, and the inexhaustible creativity that awaits at your fingertips.
Choosing the optimal Linux distribution to enhance your music production experience

When venturing into the world of music production using the powerful operating system known for its open-source nature, it's crucial to align your creative needs with the right Linux distribution. With a plethora of options available, selecting the suitable distribution becomes a critical decision for optimizing your music production workflow.
- Consider your preferred audio software: Different Linux distributions offer compatibility with various audio software packages. Determine the specific audio software you rely on or plan to use for your music production, and research which distributions provide optimal support for those tools.
- Evaluate hardware compatibility: Not all Linux distributions are created equal when it comes to hardware compatibility. Ensure your chosen distribution supports your audio hardware seamlessly, avoiding any potential compatibility issues that may hinder your music production process.
- Assess the community and user support: The Linux community embodies a collaborative spirit, and having a strong user base and extensive online resources can be invaluable when encountering challenges or seeking guidance. Look for distributions backed by supportive communities that can provide assistance along your music production journey.
- Consider system resources and stability: Music production often requires running multiple resource-intensive applications simultaneously. Evaluate the system requirements and stability of different Linux distributions, ensuring they can handle your specific workload reliably without compromising performance or causing crashes.
- Explore customization options: Each Linux distribution comes with its own set of customization options, allowing you to tailor your system to your preferences. Consider the flexibility and ease of customization offered by different distributions to optimize your music production environment.
By carefully considering these factors and aligning them with your music production goals and preferences, you can select the Linux distribution that provides the ideal foundation for your creative endeavors.
Understanding the Varied Distributions and Their Distinctive Attributes
When it comes to exploring the vast realm of Linux for music production, gaining a comprehensive understanding of the diverse distributions available can be immensely beneficial. Linux, being an open-source operating system, boasts a wide range of distributions with unique features and tools tailored to specific needs. This section aims to provide an overview of the distinctive attributes of various Linux distributions, enabling artists and producers to choose the most suitable option for their music production endeavors.
Considering Compatibility and System Requirements
When delving into the realm of music production on Linux, it is crucial to consider the compatibility of your hardware and the system requirements of the software you intend to use. By ensuring that your hardware is compatible and meets the necessary specifications, you can optimize your music production experience.
Firstly, it is essential to assess the compatibility of your hardware components with the Linux operating system. This includes ensuring that your audio interface, MIDI controllers, and other peripherals are supported by Linux drivers or have appropriate workarounds available. Compatibility issues can lead to functionality limitations and potential frustrations during your music production endeavors.
Furthermore, understanding the system requirements of the software you plan to use is vital for a smooth music production workflow. Be aware of the minimum and recommended specifications outlined by the software developers, such as the required processor speed, RAM capacity, and storage space. Meeting or surpassing these requirements will ensure optimal performance and minimize possible software crashes or latency issues.
Alongside hardware compatibility and system requirements, it is also beneficial to consider your own specific needs and preferences. Different music production techniques or genres may require varying levels of hardware power or specific features. Researching and understanding the specific requirements for your preferred music production style will enable you to tailor your setup accordingly.
In conclusion, when embarking on your music production journey with Linux, taking into account hardware compatibility and system requirements is essential. Ensuring that your hardware components are compatible and meet the required specifications, as well as considering your individual needs, will contribute to a successful and fulfilling music production experience.
Preparing Your Linux System for Crafting Musical Masterpieces
When it comes to unleashing your creativity in the realm of sound and melody, having a properly set up Linux system can be crucial. In this section, we will delve into the essential steps you need to take to optimize your Linux environment for music production. From choosing the right audio interface to configuring your software, we've got you covered.
- Selecting the Perfect Audio Interface: The first step in setting up your Linux system for music production is to choose a reliable audio interface. A high-quality audio interface acts as the bridge between your instruments or microphones and your computer, ensuring pristine sound quality and minimal latency. We'll explore some popular options and key considerations to help you make an informed decision.
- Installing the Necessary Audio Drivers: Installing the correct audio drivers is essential for optimal performance. Linux supports a range of drivers, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. We'll guide you through the process of identifying, installing, and configuring the appropriate drivers for your setup.
- Optimizing System Settings for Low Latency: Achieving low latency is vital for music production, as it ensures that there is no noticeable delay between your actions and the output. We'll provide you with practical tips and tricks to minimize latency by tweaking various system settings, such as adjusting buffer sizes and prioritizing audio processes.
- Utilizing Specialized Music Production Software: Linux offers an impressive array of music production software, ranging from digital audio workstations (DAWs) to virtual instruments and effects. We'll showcase some top-notch options and help you identify the tools that align with your specific needs and preferences.
- Setting up MIDI Devices and Controllers: If you plan to incorporate MIDI devices and controllers into your music production workflow, proper configuration is necessary. We'll walk you through the process of connecting and configuring MIDI devices to unleash their full potential in your Linux system.
By following these steps and harnessing the power of Linux, you'll be well on your way to creating captivating tunes and pushing the boundaries of your musical creativity. Are you ready to unleash your sonic potential?
Setting up the Essential Software for Audio Production on Linux
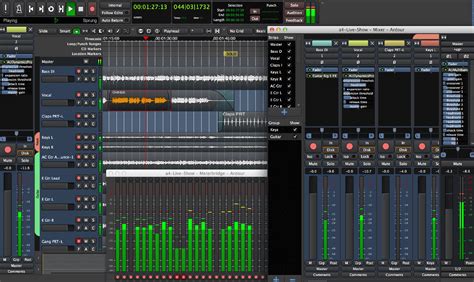
When immersing yourself into the world of music creation on a Linux operating system, it is crucial to have the right set of software tools at your disposal. This section focuses on guiding you through the installation process of the necessary audio production software, allowing you to unleash your creative prowess.
1. Digital Audio Workstation:
Begin by installing a robust and feature-rich digital audio workstation (DAW) on your Linux machine. A DAW is the heart of your music production setup, providing you with a diverse range of tools for recording, editing, mixing, and arranging your musical creations. Look for reputable options such as Ardour, Qtractor, or Tracktion T7.
Example: Installing Ardour on your Linux system will empower you with a versatile and professional-grade DAW.
2. Audio Plugins:
Enhance your audio production capabilities by installing various plugins that offer a multitude of effects and virtual instruments. These plugins can add depth, variety, and creativity to your musical compositions. Explore popular plugins like LADSPA, LV2, or VST plugins, which seamlessly integrate with your chosen DAW.
Example: The extensive range of LADSPA plugins grants you access to an array of audio effects, including compressors, equalizers, and reverbs.
3. MIDI Controller Support:
To enrich your music creation experience, ensure that your Linux system seamlessly supports MIDI controllers. Installing the necessary software drivers and configurations will allow you to connect and control a MIDI-enabled device, whether it's a keyboard, drum pad, or a MIDI controller surface. Check documentation or online forums for details on how to set up MIDI support for your specific Linux distribution.
Example: Establishing MIDI support will enable you to play virtual instruments using a physical keyboard, granting you a more tactile and expressive connection to your music.
By following these steps, you will have successfully set up the essential software and tools required for audio production on your Linux system. With a powerful DAW, a plethora of audio plugins, and MIDI controller support, you are one step closer to expressing your musical ideas and bringing them to life.
Optimizing System Performance for Minimal Delay in Music Creation
In the realm of sound production on Linux, achieving optimal system performance is crucial to ensure minimal latency during music creation. Fine-tuning your system settings and optimizing various components can significantly enhance real-time audio processing, resulting in a seamless and responsive music production workflow.
1. Kernel Configuration: Begin by customizing your kernel settings to prioritize low-latency performance. This involves enabling real-time preemption and adjusting the timer frequency to reduce system interrupt latency. Additionally, consider utilizing a real-time kernel variant specifically designed for audio production, such as the PREEMPT-RT patch.
2. CPU Management: Efficient CPU management is essential to minimize audio processing delays. Utilize CPU governor tools to prioritize performance mode over power-saving modes, ensuring consistent processing power during music production. Additionally, disabling CPU frequency scaling mechanisms can prevent potential glitches caused by varying processor frequencies.
3. System Services and Background Processes: Disable unnecessary system services and background processes that consume CPU resources or generate interrupts. Close any unnecessary applications running in the background to free up system resources, reducing the chances of audio dropouts or glitches.
4. Real-time Audio Libraries: Employ real-time audio libraries and tools, such as JACK (Jack Audio Connection Kit), to facilitate low-latency audio connections between applications and audio interfaces. Configure JACK with appropriate buffer sizes and sample rates to achieve optimal performance without compromising audio quality.
5. Hardware Considerations: Ensure your hardware components are compatible and well-suited for low-latency audio production. Invest in high-quality audio interfaces with stable drivers that offer direct monitoring capabilities. Furthermore, optimizing system memory and utilizing solid-state drives can significantly improve overall system performance and reduce access times for audio data.
6. Latency Monitoring: Monitor and measure system latency using tools like a2jmidid or latencyTOP. By regularly monitoring latency levels, you can identify and address any potential bottlenecks or problematic areas within your system setup.
7. Experimentation and Optimization: Fine-tuning your system for low-latency performance may involve trial and error. Experiment with various system configurations, kernel parameters, and software settings to find the optimal balance between latency and stability for your specific music production requirements.
By implementing these optimization techniques and keeping your system fine-tuned for low-latency performance, you can unleash the full power of Linux for music production, enabling a seamless and immersive musical experience.
Recording and editing audio on an open-source operating system

In this section, we will explore the versatile capabilities of an open-source operating system for recording and editing audio, providing a powerful and cost-effective solution for music enthusiasts and professionals alike.
1. Free and open-source audio software:
- Discover a wide range of free and open-source audio software options available for Linux, offering robust features for recording and editing audio.
- Explore popular digital audio workstations (DAWs) such as Ardour and Tracktion T7, which provide a comprehensive environment for recording, mixing, and mastering music.
- Dive into high-quality audio editors like Audacity and Ocenaudio, offering precise waveform editing and advanced effects capabilities.
2. Audio interfaces and hardware compatibility:
- Learn about the compatibility of Linux with various audio interfaces and hardware, enabling seamless integration for recording and playback purposes.
- Discover the advantages of using Linux-compatible audio interfaces, including low-latency performance, multiple input/output channels, and support for professional-grade audio equipment.
- Explore the process of setting up and configuring audio interfaces on Linux, ensuring optimal performance and compatibility.
3. Plugins and virtual instruments:
- Explore the world of plugins and virtual instruments available for Linux, expanding your audio production capabilities.
- Discover a variety of plugin formats supported on Linux, including LV2, VST, and LADSPA, allowing you to enhance your audio recordings with a wide range of effects and instruments.
- Learn how to install and configure plugins and virtual instruments on Linux, harnessing their power within your DAW or audio editor.
4. Workflow and project management:
- Optimize your workflow and project management strategies when using Linux for audio production.
- Explore various software options for project organization, file management, and collaboration, making it easier to navigate and keep track of your audio projects.
- Discover efficient techniques for organizing and labeling audio files, creating backups, and maintaining version control throughout the production process.
By leveraging the capabilities of an open-source operating system, Linux, for recording and editing audio, you can realize your musical vision while enjoying the freedom, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness that this platform provides.
Exploring popular digital audio workstations (DAWs) on Linux
In this section, we will delve into the diverse range of digital audio workstations (DAWs) available for the Linux operating system. DAWs are powerful software tools specifically designed for professional music production, offering a comprehensive array of features and functionalities.
Linux users seeking to create and produce music can choose from various popular DAWs tailored to their specific needs. Each DAW comes with its own unique interface, workflows, and plugins, providing artists and producers with the flexibility to explore and experiment with different tools for their music projects.
Ardour: Ardour is a full-featured digital audio workstation that offers extensive capabilities for recording, editing, and mixing music. It boasts a user-friendly interface and supports a wide range of audio file formats, making it a popular choice among musicians and audio engineers.
Bitwig Studio: Bitwig Studio is a professional-grade DAW packed with innovative features and workflows. It combines advanced editing and customization options with a modular approach, allowing users to shape their music production environment to suit their creative desires.
Ableton Live (via Wine): While not originally designed for Linux, many music producers use the renowned Ableton Live software on their Linux machines by utilizing compatibility layers such as Wine. Ableton Live offers a wide range of features for composing, recording, and performing music, making it a popular choice among electronic music artists.
These are just a few examples of the DAWs available on Linux, and each one brings its own unique strengths and capabilities. By exploring the wide selection of DAWs tailored for Linux, musicians and producers can discover the perfect tool to bring their musical vision to life.
Exploring Music Production Capabilities with Advanced Plugins and Effects
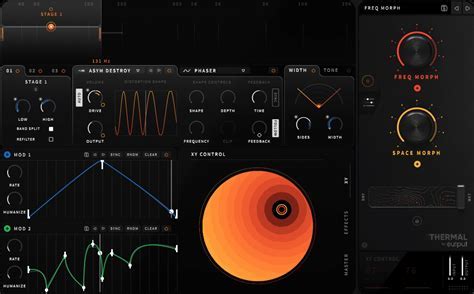
Enhancing the quality and creativity of music production is an essential aspect of the professional sound production process in Linux-based environments. Leveraging an array of powerful plugins and effects can elevate your music to new heights, enabling you to achieve professional-level results.
With the wide range of plugins and effects available for Linux, you can effortlessly transform ordinary sounds into captivating compositions. These tools offer a plethora of options, allowing you to shape and mold your music with precision. From virtual instruments that replicate the sounds of real instruments to dynamic effects that add depth and texture, the possibilities are virtually endless.
One of the significant advantages of using plugins and effects in Linux-based music production is the diverse collection of open-source options. These plugins not only offer exceptional functionality but also allow for customization and flexibility, enabling you to tailor the sound to your specific needs. Whether you're a beginner or a seasoned professional, you can find plugins and effects suitable for your level of expertise and musical style.
Another essential aspect of using plugins and effects is the seamless integration with digital audio workstations (DAWs). Linux-friendly DAWs have extensive plugin support, providing a user-friendly interface for managing and manipulating these tools. This integration streamlines your workflow, allowing you to focus on the creative process without additional technical complexities.
Moreover, plugins and effects often provide presets, giving you a starting point for experimenting with different sounds and effects. These presets offer valuable insights into the potential uses of each plugin, helping you unlock new possibilities and push the boundaries of your creativity. By combining multiple plugins and effects, you can create layers of complexity and richness that bring your music to life.
Ultimately, harnessing the power of plugins and effects in Linux for music production offers a gateway to professional sound quality and limitless sonic exploration. With the right set of tools at your disposal, you can take your music production skills to new heights and produce captivating and innovative compositions.
Mixing and Mastering Your Music on a Linux Platform
Optimizing the sonic quality of your musical creations is a crucial aspect of the music production process. In this section, we will explore the techniques and tools available on the Linux platform for achieving professional-grade mixing and mastering results.
- Utilizing a Digital Audio Workstation (DAW): Linux offers a wide range of DAW options designed specifically for music production. These software packages provide a comprehensive set of features for recording, editing, and processing audio tracks.
- Implementing Audio Effects and Plugins: Enhancing the sound of your music involves the strategic use of audio effects and plugins. Linux-based DAWs support a vast array of plugins that provide capabilities such as EQ, compression, reverb, and delay, among others.
- Understanding Signal Flow and Routing: To achieve optimal mixing, it is important to have a solid understanding of signal flow and routing within your DAW. Linux-based DAWs offer flexible routing options, allowing you to direct audio signals through desired channels and effects processors.
- Applying EQ and Compression: Equalization (EQ) enables you to shape the frequency response of individual tracks, while compression helps control dynamics and ensures a balanced mix. Linux-based DAWs provide intuitive tools for precise EQ and compression adjustments.
- Creating Spatial Depth with Reverb and Delay: Adding depth and dimension to your music can be achieved using reverb and delay effects. Linux-based DAWs deliver a wide range of reverb and delay plugins that allow you to experiment with different virtual spaces and create immersive sonic environments.
- Balancing Levels with Automation: Automation is a powerful tool for achieving dynamic and expressive mixes. Linux-based DAWs enable you to automate various parameters such as volume, panning, and effect parameters, ensuring smooth transitions and precise control over the mix.
- Mastering Your Music: Once your mix is perfected, the final step is mastering. Linux offers dedicated mastering software, which provides tools for enhancing the overall loudness, clarity, and coherence of your music, ensuring it sounds polished and professional across different playback systems.
By leveraging the available tools and techniques on the Linux platform, you can effectively mix and master your music, showcasing your creativity and achieving professional-level results.
[MOVIES] [/MOVIES] [/MOVIES_ENABLED]FAQ
What is Linux?
Linux is an open-source operating system that is popular among computer enthusiasts and professionals. It is known for its stability, flexibility, and security.
Can Linux be used for music production?
Absolutely! Linux offers a variety of powerful tools and software for music production, including digital audio workstations (DAWs), plugins, synthesizers, and effects.
Why would someone choose Linux for music production?
There are several reasons why Linux is favored by some music producers. First, it is highly customizable, allowing users to tailor their system to their specific needs. Second, Linux is known for its stability and low-latency performance, which is crucial in music production. Lastly, Linux provides a cost-effective solution as it is free and doesn't require expensive proprietary software.
What are some popular music production software available on Linux?
There are several well-regarded music production software available for Linux, such as Ardour, Bitwig Studio, Qtractor, and Tracktion T7. Each of these provides a range of features and capabilities to suit different production needs.
Are there any limitations to using Linux for music production?
While Linux has made significant strides in the field of music production, it may not have the same extensive library of plugins and virtual instruments as some proprietary platforms. However, many popular plugins can now be used on Linux through compatibility layers or dedicated versions. Additionally, some specific hardware may have limited driver support on Linux, so it's important to research compatibility before making hardware choices.




