In today's fast-paced and ever-evolving industrial landscape, businesses are constantly seeking ways to enhance efficiency, minimize costs, and achieve maximum productivity. One crucial aspect of achieving these goals lies in the effective management and control of production processes.
Traditionally, businesses have relied on various operating systems to configure and manage their production process management systems. However, in recent years, Linux has emerged as a powerful and versatile solution, offering unparalleled flexibility and functionality.
Linux, renowned for its stability and security, provides an array of tools and resources that enable businesses to tailor their production processes to meet specific needs and achieve optimal performance. Its open-source nature fosters constant innovation and collaboration among developers, resulting in a vast selection of applications and software solutions.
With Linux, businesses can harness the power of a robust and customizable operating system to configure and fine-tune their production process management systems. From monitoring equipment performance to automating critical tasks, Linux offers a wide range of features that empower businesses to streamline their operations and achieve peak productivity.
By leveraging Linux's extensive library of software applications, businesses can effectively optimize their production process control systems, ensuring seamless coordination and synchronization across all stages of the production cycle. Whether it's managing inventory, tracking production schedules, or analyzing performance metrics, Linux provides the tools and capabilities to drive efficiency, consistency, and quality.
In this article, we will explore the various benefits of using Linux to configure a production process management system, delve into real-world success stories, and provide a comprehensive guide for businesses looking to adopt this robust operating system. Join us as we unravel the power of Linux in revolutionizing process control systems and discover how it can empower your business to achieve unparalleled success.
Advantages of Utilizing Linux in Production Process Oversight

Linux, a widely embraced open-source operating system, offers numerous benefits when employed in the realm of production process management. By harnessing the power and versatility of Linux, organizations can achieve enhanced efficiency, heightened security, and greater scalability in their production operations. This section delves into the notable advantages of integrating Linux into the monitoring and control of production processes.
- Flexibility: One key advantage of Linux in production process management lies in its flexibility. Linux allows for the customization and tailor-fitting of systems based on specific production requirements. This adaptability empowers organizations to efficiently configure their production processes, ensuring optimal performance and resource utilization.
- Stability: With its renowned stability, Linux provides a solid foundation for managing and controlling production operations. The robust architecture of Linux minimizes the risk of system failures, ensuring uninterrupted monitoring and oversight of critical processes. This stability fosters a secure and reliable production environment, boosting overall productivity.
- Cost-effectiveness: Linux, being an open-source platform, eliminates the need for costly licensing fees associated with proprietary operating systems. By choosing Linux for production process management, organizations can allocate their financial resources more efficiently, freeing up funds for other areas of development and improvement.
- Security: Utilizing Linux for production process management establishes a strong security framework. Linux's inherent security features and community-driven development ensure prompt identification and mitigation of vulnerabilities. Additionally, the availability of robust security tools and constant updates contributes to safeguarding critical production data and assets.
- Scalability: The scalability offered by Linux makes it highly suitable for handling diverse production environments. Whether dealing with small-scale operations or large industrial processes, Linux can seamlessly adapt to varying production complexities. Its scalability enables efficient management of resources, promotes growth, and facilitates the expansion of production capabilities.
In summary, the integration of Linux into production process management provides organizations with a flexible, stable, cost-effective, secure, and scalable solution. These advantages empower businesses to optimize their production processes, enhance productivity, and ensure a competitive edge in the ever-evolving industrial landscape.
Enhanced Security
In this section, we explore the various measures and techniques that can be implemented to strengthen the security of the production process management system. By employing robust security measures, organizations can safeguard their sensitive information, prevent unauthorized access, and mitigate potential risks and vulnerabilities.
- Implementing multi-factor authentication: By requiring multiple forms of identification, such as passwords, biometrics, and tokens, the system can ensure that only authorized individuals have access to critical resources.
- Enforcing strong password policies: By implementing policies that promote the use of complex and unique passwords, organizations can reduce the risk of password-related vulnerabilities, such as brute-force attacks or password guessing.
- Regularly updating and patching software: Keeping the production process management system up to date with the latest security patches and updates can help address known vulnerabilities and protect against emerging threats.
- Adopting encryption technologies: Encrypting data both at rest and in transit can provide an additional layer of protection, ensuring that even if unauthorized individuals gain access to the system, the data remains unreadable and unusable.
- Implementing access controls and permissions: By assigning specific roles and permissions to users, organizations can limit access to sensitive information and functionalities, reducing the risk of accidental or intentional data breaches.
- Conducting regular security audits and assessments: Periodic evaluations of the production process management system can help identify potential weaknesses and vulnerabilities, allowing organizations to take proactive measures to address them.
- Implementing intrusion detection and prevention systems: By monitoring network traffic and identifying suspicious activities, these systems can detect and mitigate potential security breaches in real-time, helping to prevent unauthorized access or data compromise.
By implementing these enhanced security measures, organizations can significantly enhance the overall security posture of their production process management system, ensuring the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of critical business information and operations.
Flexibility and Customizability

In the realm of implementing a versatile and adaptable production process management solution, it is crucial to explore the inherent flexibility and customizability provided by Linux. This section delves into the capabilities offered by Linux for tailoring and configuring a system that meets the unique requirements of any production process.
- Adaptability: Linux offers a vast array of open-source tools and frameworks that enable users to customize their production process management system to suit specific needs. With its modular nature, Linux allows for the integration of various software components, enabling users to tailor the system to their desired level of complexity.
- Scalability: Linux provides extensive scalability options, allowing the production process management system to grow alongside the evolving needs of the organization. Whether it is adding new functionalities, accommodating increased workloads, or expanding the user base, Linux offers the flexibility to scale the system without major disruptions.
- Freedom of Choice: Linux empowers users with the freedom to select the most suitable tools and applications for their production process management system. This freedom of choice extends to the selection of programming languages, software libraries, and user interfaces, enabling organizations to align their system with their existing technology stack and development preferences.
- Interoperability: Linux fosters interoperability by supporting a wide range of open standards, protocols, and communication interfaces. This interoperability allows the production process management system to seamlessly integrate with other systems and devices, facilitating data exchange and enabling a cohesive workflow across the organization.
- Security and Stability: Linux is renowned for its robust security features and stability. By leveraging the inherent security mechanisms and regularly updated patches, organizations can build a production process management system that meets stringent security requirements and ensures uninterrupted operations.
In conclusion, Linux provides a solid foundation for configuring a production process management system that is highly customizable and flexible. The inherent adaptability, scalability, freedom of choice, interoperability, and security features of Linux lay the groundwork for designing a system that aligns precisely with the specific needs and preferences of any organization.
Stability and Reliability
In the context of the topic "Using Linux for Configuring a Production Process Management System," this section focuses on the crucial aspect of stability and reliability in the management system. It delves into ensuring the consistent and dependable performance of the system, emphasizing its importance for smooth and efficient production processes.
The stability and reliability of the production process management system are key factors that contribute to productive operations. A stable system ensures that the processes and procedures implemented will consistently and reliably deliver the desired outcomes. It minimizes the occurrence of errors, glitches, and downtime, providing a robust foundation for the overall system's functionality.
- Consistency: A stable production process management system guarantees consistent performance by maintaining a uniform approach across all operations. It ensures that each step is executed reliably, without any variations or deviations.
- Dependability: The reliability of the system ensures that it functions as intended without unexpected failures or disruptions. It provides a trustworthy platform for managing the production processes, allowing businesses to rely on it without concerns about interruptions.
- Efficiency: A stable and reliable management system optimizes efficiency by eliminating unnecessary downtime or delays. It streamlines the workflow, reduces errors, and enhances productivity, enabling businesses to achieve their production goals effectively.
- Continuous Improvement: Ensuring stability and reliability in the production process management system enables continuous improvement efforts. By minimizing inconsistencies and identifying areas for enhancement, organizations can implement refinements and optimizations to further enhance their processes and overall performance.
- Risk Mitigation: A stable and reliable system reduces the risks associated with operational disruptions, errors, and data loss. It establishes a secure and dependable environment, safeguarding critical production data and minimizing the potential for costly setbacks or failures.
Ultimately, stability and reliability form the core foundation of a robust production process management system. By prioritizing these aspects, businesses can build an infrastructure that consistently delivers efficient, error-free, and dependable production processes.
Key Features of Linux for Effective Process Control
In this section, we will explore the distinctive characteristics and functional advantages that Linux brings to the table when it comes to streamlining and optimizing production process management. Linux, renowned for its robustness and flexibility, offers a highly reliable and versatile platform for ensuring seamless control and monitoring of industrial operations.
1. Stability and Reliability: Linux provides a stable and dependable foundation for managing production processes, ensuring minimal downtime and reducing the risk of system failures. Its robust architecture and efficient task scheduling mechanisms enable reliable operation even under demanding conditions, contributing to uninterrupted workflow.
2. Open Source Nature: Linux's open-source nature not only signifies its wide availability but also empowers organizations to customize and adapt the system according to their specific process management requirements. This flexibility enables businesses to create tailored solutions that align precisely with their unique production needs and scale as their operations grow.
3. Wide Range of Tools and Packages: Linux boasts a vast ecosystem of tools, libraries, and packages that facilitate process control automation, data analysis, and monitoring. From powerful command-line utilities to graphical interface applications, Linux offers a comprehensive collection of resources that can be leveraged for seamless integration with production systems.
4. Security and Access Control: Linux prioritizes security, making it an ideal choice for managing critical production processes. Its robust access control mechanisms and built-in security features, such as user and group permissions, help safeguard sensitive data, prevent unauthorized access, and protect against potential cyber threats.
5. Scalability and Performance: Linux's scalability ensures that production process management systems can expand and adapt as business requirements evolve. With its efficient resource utilization and optimized performance, Linux enables organizations to efficiently handle increasing workloads, ensuring smooth operations even during periods of high demand.
6. Collaborative Community Support: The Linux community comprises passionate developers and experts who are always ready to provide support and share knowledge. This collaborative community fosters a culture of continuous improvement, enabling businesses to tap into a vast pool of expertise and obtain assistance when configuring or troubleshooting their production process management systems.
To sum up, Linux offers a stable, customizable, secure, and scalable environment with an abundance of tools and community support. These key features position Linux as a reliable choice for effectively managing and enhancing production process control systems.
Command-Line Interface
In the context of the topic "Using Linux for Configuring a Production Process Management System", the command-line interface plays a crucial role in enabling efficient and flexible management of various processes within the system. This section will explore the command-line interface and its significance in the configuration and operation of the production process management system.
The command-line interface, also known as the CLI, is a text-based interface that allows users to interact with the operating system or software through commands. It provides a powerful and efficient way to control and manipulate the system, offering a wide range of functionalities and options.
One of the key advantages of the command-line interface is its ability to automate tasks and processes. By utilizing command-line commands and scripts, users can create automated workflows, reducing manual effort and ensuring consistency in the management of the production process.
- The command-line interface provides a wide range of commands that can be used to perform various operations such as file and directory management, process monitoring, network configuration, and system administration.
- With the command-line interface, users have direct access to powerful tools and utilities that are essential in managing the production process. These tools enable tasks such as process scheduling, performance monitoring, and resource allocation.
- Furthermore, the command-line interface allows users to execute commands and retrieve results quickly, making it an efficient choice for managing time-sensitive production processes.
In summary, the command-line interface is a fundamental component when utilizing Linux for configuring a production process management system. Its versatility, automation capabilities, and direct access to essential tools make it an invaluable tool for efficient and effective system management.
Package Management System
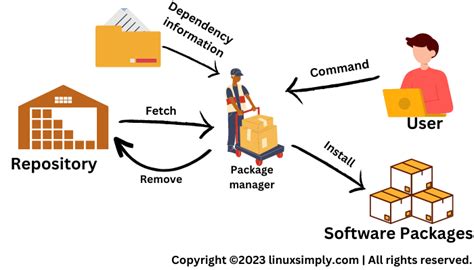
In the context of the topic "Using Linux for Configuring a Production Process Management System," this section explores the essential component of a package management system. A package management system plays a critical role in efficiently organizing and distributing software packages, ensuring the smooth operation of a production process management system. It enables users to install, update, and remove software packages, ensuring dependency resolution and version control.
The Importance of Package Management System
Effective package management is vital for maintaining a reliable and secure production process management system. It simplifies the installation and management of software packages by handling dependencies, resolving conflicts, and ensuring compatibility. With a robust package management system, administrators can efficiently deploy, update, and monitor the software stack required for their production environment.
Dependency Resolution and Version Control
A package management system ensures that all the necessary dependencies for a software package are installed, resolving any conflicts that may arise. It keeps track of the versions of installed packages, facilitating easy upgrades and downgrades when needed. By managing dependencies and version control, it guarantees the stability and integrity of the production process management system.
Centralized Repository
A key feature of a package management system is the presence of a centralized repository. This repository serves as a centralized hub where software packages are stored, categorized, and made available for installation. By accessing the repository, users can easily search and retrieve the required packages for their production process management system, ensuring consistency and reliability.
Package Installation and Removal
With a package management system, installing and removing software packages becomes a straightforward and standardized process. Administrators can quickly deploy new packages, update existing ones, or remove unnecessary packages, all through a user-friendly interface or command-line tools. This streamlined process saves time, reduces errors, and keeps the production process management system up to date.
Community Support and Integration
Open-source package management systems often come with robust community support. Users can benefit from a vast collection of packages contributed by the community, ensuring a wide range of software options for their production process management system. Furthermore, integration with other tools and systems is made easier through well-established package management systems, fostering compatibility and interoperability.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a reliable package management system is an indispensable component in configuring a production process management system. It provides efficient software package organization, installation, and removal, ensuring dependency resolution and version control. By leveraging a centralized repository, administrators can easily access and manage the required packages. The seamless integration and community support offered by package management systems further enhance their effectiveness in optimizing the production process management system.
Automation and Scripting Capabilities
The ability to automate tasks and create custom scripts is fundamental in the efficient management of a production process. By harnessing the power of automation, businesses can streamline repetitive tasks, improve productivity, and reduce the potential for human error. In this section, we will explore the various automation and scripting capabilities available in the context of Linux, empowering organizations to optimize their production process management system.
- Flexible Command-Line Interface: Linux provides a robust command-line interface that allows users to interact with the system through command-line commands. This flexibility enables the automation of complex tasks and the integration of various software components in the production process.
- Shell Scripting: Shell scripting is a powerful tool for automating repetitive tasks within a Linux environment. By combining commands and creating scripts, users can automate tasks, schedule them to run at specific times, and process large volumes of data efficiently.
- Task Scheduling: Linux offers various tools for scheduling tasks, such as cron and systemd timers. These tools enable users to automate the execution of scripts and commands, ensuring that critical processes in the production system run at predetermined intervals without manual intervention.
- Pipeline and Stream Processing: Linux provides robust support for pipeline and stream processing, allowing users to efficiently process and manipulate data in real-time. By leveraging commands such as awk, grep, and sed, businesses can automate data transformations and extract valuable insights from their production process.
- Application Programming Interfaces: Linux offers extensive APIs that allow developers to interact with the system and integrate custom software solutions into the production process. This capability enables the creation of tailored automation solutions that align with specific business requirements.
By harnessing the automation and scripting capabilities of Linux, businesses can achieve enhanced efficiency, scalability, and reliability in their production process management system. The diverse range of tools available empowers organizations to customize automation workflows, streamline operations, and ultimately optimize their production processes.
Implementing Linux to Streamline Production Operations

In this section, we will explore the process of integrating Linux into a production environment to enhance efficiency and streamline operations. By leveraging the power and flexibility of Linux, businesses can optimize their production process management and achieve higher levels of productivity. Let's delve into the key strategies and benefits of implementing Linux in the production workflow.
Enhanced Stability and Reliability: Linux provides a robust and stable operating system foundation, ensuring minimal downtime and improved reliability for critical production processes. With its solid architecture and efficient resource management, Linux offers a dependable platform that can withstand complex production tasks.
Seamless Integration with Existing Infrastructure: The flexibility of Linux allows for seamless integration with existing production systems and technologies. Whether it's connecting to industrial automation equipment, monitoring sensors, or managing databases, Linux offers extensive compatibility and adaptability, enabling businesses to easily incorporate it into their current infrastructure.
Customization and Scalability: Linux provides a vast array of customization options, allowing businesses to tailor their production process management system to meet their specific requirements. From configuring specialized applications to adapting user interfaces and workflows, Linux empowers organizations to create an optimal environment that aligns with their unique production needs.
Open-Source Community and Continuous Innovation: Leveraging the power of the open-source community, Linux benefits from continuous development and innovation. Regular updates and bug fixes ensure the system's security and efficiency, while the availability of a wide range of open-source tools and software allows for the implementation of cutting-edge technologies in the production process management system.
Cost-Effectiveness: Linux is renowned for its cost-effectiveness, with many distributions being freely available. By implementing Linux for production process management, businesses can reduce licensing fees associated with proprietary software and allocate their resources towards improving other aspects of their operations.
| Key Benefits of Implementing Linux for Production Process Management |
|---|
| Enhanced stability and reliability |
| Seamless integration with existing infrastructure |
| Customization and scalability |
| Open-source community and continuous innovation |
| Cost-effectiveness |
Choosing the Appropriate Linux Distribution
In the context of implementing a system for managing production processes, it is crucial to select the right Linux distribution for optimal performance and efficiency. The choice of Linux distribution can significantly impact the overall functionality and stability of the production process management system. This article explores key considerations and factors to be taken into account when selecting the appropriate Linux distribution.
Evaluating Hardware and System Requirements:
One of the primary considerations in choosing the right Linux distribution is evaluating the hardware and system requirements of the production process management system. Different distributions have varying hardware support and system resource utilization, which can impact the overall performance and reliability. It is essential to carefully analyze the system specifications and compare them with the recommended requirements of different distributions to ensure compatibility and optimal utilization of resources.
Considering Desktop Environment:
Another aspect to consider when choosing a Linux distribution is the desktop environment. The desktop environment defines the user interface and its functionality, including the appearance, organization, and accessibility of system features and applications. It is crucial to select a desktop environment that aligns with the requirements and preferences of the users who will interact with the production process management system. Factors such as ease of use, customization options, and workflow efficiency should be taken into account to ensure a seamless user experience.
Examining Package Management:
The package management system of a Linux distribution plays a vital role in software installation, updates, and maintenance. Different distributions have different package managers, such as APT, Yum, or Zypper, each with its unique features and capabilities. It is important to evaluate the package management system of each distribution to ensure compatibility with existing software requirements, availability of required packages, and the ease of managing and updating the system and applications.
Weighing Security and Stability:
Security and stability considerations should not be overlooked when selecting a Linux distribution for a production process management system. It is essential to choose a distribution that emphasizes security measures such as regular security updates, robust user management settings, and a strong community support system. Additionally, the stability of the distribution, as indicated by its release schedule and long-term support options, should also be considered, particularly for long-term production process management deployment.
Taking Community and Support into Account:
Last but not least, the community and support surrounding a Linux distribution can greatly aid in resolving issues, getting assistance, and staying updated with latest developments. It is advisable to choose a distribution that has an active and knowledgeable community, readily available support channels, and extensive documentation. The strength of the community and support can contribute to the overall success and smooth operation of the production process management system.
[MOVIES] [/MOVIES] [/MOVIES_ENABLED]FAQ
What is the advantage of using Linux for configuring a production process management system?
Linux offers several advantages for configuring a production process management system. Firstly, it is an open-source operating system, which means that it is freely available and customizable. This allows businesses to tailor the system to their specific needs and modify it as necessary. Secondly, Linux is known for its stability and reliability, making it an ideal choice for mission-critical systems. Additionally, Linux has a large and active community of developers and users, providing extensive support and resources for troubleshooting and updates. Lastly, Linux has a modular architecture, allowing businesses to choose and integrate only the necessary components for their production process management system, reducing unnecessary overhead and complexity.
Can I use Linux for a small-scale production process management system?
Absolutely! Linux is a versatile operating system that can be used for both small-scale and large-scale production process management systems. Its flexibility and scalability make it suitable for a wide range of applications. Even for a small-scale system, Linux offers benefits such as cost-effectiveness, customization options, and stability. Businesses can choose a lightweight distribution of Linux, optimized for minimal resource usage, to run on lower-spec hardware. This allows them to efficiently configure and manage their production processes while keeping costs down.
Are there specific Linux distributions recommended for configuring a production process management system?
There are several Linux distributions that are commonly recommended for configuring a production process management system. Some popular choices include Ubuntu, CentOS, and Fedora. Ubuntu is known for its user-friendly interface and extensive package repositories, making it a good choice for businesses new to Linux. CentOS, on the other hand, is based on the stable and highly reliable Red Hat Enterprise Linux. It is often favored for its long-term support and security updates. Fedora, although more cutting-edge, provides the latest software versions and features, suiting businesses that require the latest technologies. Ultimately, the choice of Linux distribution depends on the specific requirements and preferences of the business.
Is it challenging to migrate an existing production process management system to Linux?
Migrating an existing production process management system to Linux can present certain challenges, but it is certainly achievable with proper planning and execution. One of the main challenges is ensuring compatibility of the existing system with Linux. This involves assessing the software applications, databases, and hardware components used in the current system and finding suitable alternatives or ensuring Linux compatibility. Data migration and system configuration can also be complex, requiring careful planning and testing to ensure a smooth transition. However, with the right expertise and support from experienced Linux administrators, businesses can successfully migrate their production process management system to Linux and benefit from its advantages.




