Human beings have long been captivated by the complexity and enigma of brain tumors, intrinsically intertwined with our very existence. These neoplasms, which emerge within the delicate realm of our brain matter, continue to perplex both scientists and medical professionals alike. Understanding the intricate causes, diverse set of symptoms, and the vast array of treatment modalities available for brain tumors has become a paramount quest in contemporary medical research.
Substantiating a comprehensive comprehension of the intricate web of factors that give rise to brain tumors is pivotal in our pursuit of effective diagnostics and therapies. Multiple causal factors, such as genetic predispositions, environmental influences, and the intricate interplay of various cellular mechanisms, contribute to the development of brain tumors. Despite remarkable advancements in diagnostic imaging techniques, there still remains a dearth of clarity surrounding the precise etiologies involved.
Exploring the presentation of symptoms: The manifestations of brain tumors can be elusive, often presenting as vague symptoms that may overlap with various neurological disorders. Some commonly observed symptoms encompass persistent headaches, seizures, cognitive impairments, and motor abnormalities. However, it is important to acknowledge that these symptoms may vary depending on the location, size, and specific type of tumor present within the intricate network of the brain.
Unfolding the realm of treatment options: The treatment landscape for brain tumors spans a wide spectrum, incorporating various approaches tailored to the specific characteristics of each individual case. Conventional treatment methods, such as surgical resection, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy, are commonly employed, oftentimes in combination, to combat these cellular aberrations. Moreover, recent advancements in targeted therapies and immunotherapy have sparked newfound hope in the realm of brain tumor treatment, offering alternative avenues for patients.
Understanding Brain Tumors: An Overview
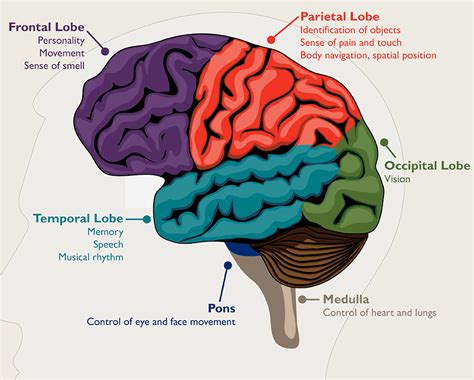
When it comes to the intricate workings of the human brain, certain abnormalities can arise that pose significant health risks. These abnormalities, which can occur in various forms and sizes, are commonly referred to as brain tumors.
Brain tumors, though diverse in nature, share a common characteristic: the abnormal growth of cells within the brain. These cells can multiply and form masses, or tumors, that can interfere with the normal functioning of the brain.
- Brain tumors can occur in different regions of the brain, such as the cerebrum, cerebellum, or brain stem.
- They can be either malignant, meaning cancerous and capable of spreading to other parts of the body, or benign, non-cancerous and localized.
- The causes of brain tumors remain largely unknown, although certain genetic conditions and exposure to radiation have been linked to their development.
Brain tumors can manifest in a variety of ways, resulting in a wide range of symptoms. These symptoms can include headaches, seizures, changes in vision, or difficulties with speech and coordination. The specific symptoms experienced largely depend on the size and location of the tumor.
Once diagnosed, treatment options for brain tumors may involve surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, or a combination of these approaches. The choice of treatment depends on several factors, including the type and grade of the tumor, its size, and the patient's overall health.
It is important to note that early detection and prompt treatment play a crucial role in improving the prognosis for individuals with brain tumors. Regular check-ups, awareness of potential symptoms, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle can all contribute to early intervention and better outcomes.
Different Types of Brain Tumors
In this section, we will explore the various types of tumors that can affect the brain. Understanding the diversity of brain tumors is crucial in identifying the appropriate treatment approach and predicting the prognosis for patients. Let's delve into the distinct categories of these growths within the intricate network of our brain.
Gliomas:
Gliomas refer to a group of tumors that originate from glial cells, which provide support and protection to nerve cells in the brain. These tumors can form in different areas of the brain and can be further classified into several subtypes, including astrocytomas, oligodendrogliomas, and ependymomas. Each subtype has its unique characteristics and requires specific treatment strategies.
Meningiomas:
Meningiomas are typically noncancerous (benign) tumors that develop from the meninges, which are the protective membranes covering the brain and spinal cord. These tumors tend to grow gradually and may not cause immediate symptoms. However, they can still pose a significant threat if they exert pressure on vital brain structures or obstruct the normal flow of cerebrospinal fluid.
Pituitary Tumors:
Pituitary tumors originate in the pituitary gland, a small gland located at the base of the brain. These tumors can be either benign or malignant and affect the gland's hormone production, leading to hormonal imbalances and various symptoms. Pituitary tumors are often manageable through medication, hormone replacement therapy, or surgical intervention, depending on their size and characteristics.
Medulloblastomas:
Medulloblastomas are rapidly growing tumors that primarily affect children and arise in the lower back part of the brain, called the cerebellum. Despite being relatively rare, they are the most common malignant brain tumors in children. Prompt diagnosis and treatment are crucial for achieving optimal outcomes in patients with medulloblastomas.
Metastatic Brain Tumors:
Metastatic brain tumors, also known as secondary brain tumors, occur when cancer cells from other parts of the body spread to the brain through the bloodstream or lymphatic system. These tumors are not derived from brain tissue but rather represent the spread of cancer from another organ. The primary focus of treatment for metastatic brain tumors is often to control the spread of the primary cancer while providing palliative care for the brain metastases.
By understanding the different types of brain tumors and their characteristics, healthcare professionals can tailor treatment plans to address the specific needs of patients. Early detection, accurate diagnosis, and personalized treatment approaches play pivotal roles in increasing survival rates and improving the quality of life for individuals affected by brain tumors.
Exploring the Factors Behind Brain Tumors
The origin of brain tumors is a complex and intricate subject that requires an in-depth examination. By delving into the factors that contribute to the development of these conditions, we can gain a deeper understanding of their nature and potential causes. This section aims to explore the various components that play a role in the onset of brain tumors, shedding light on the interplay between genetic predisposition, environmental factors, and lifestyle choices.
Genetic Predisposition:
A significant aspect to consider when studying the causes of brain tumors is the influence of genetic predisposition. Certain inherited conditions and gene mutations have been linked to an increased likelihood of developing brain tumors. Researchers have identified specific genes that, when mutated, can contribute to the development of these tumors. Understanding the genetic factors involved can provide invaluable insights into the origin and mechanisms of brain tumors.
Environmental Factors:
While genetics play a role, environmental factors also contribute significantly to the development of brain tumors. Exposure to certain environmental elements, such as radiation, chemicals, and other pollutants, has been associated with an increased risk of developing brain tumors. Examining these external influences and their potential effects on brain health is crucial in understanding the causes of these conditions.
Lifestyle Choices:
In addition to genetic and environmental factors, an individual's lifestyle choices can contribute to the development of brain tumors. Factors such as diet, physical activity levels, smoking, and alcohol consumption have been correlated with the risk of developing certain types of brain tumors. Analyzing the impact of these lifestyle choices on tumor formation can provide insights into preventative measures and potential treatment approaches.
Conclusion:
By considering the intricate interplay between genetic predisposition, environmental factors, and lifestyle choices, we can begin to unravel the causes of brain tumors. Understanding these factors is crucial in the development of effective prevention strategies and treatment approaches. With ongoing research and advancements in medical science, we can strive towards a world where the causes of brain tumors are thoroughly understood, leading to improved outcomes for individuals affected by these conditions.
Recognizing the Common Symptoms
In this section, we will explore the typical signs and indications that can help individuals identify the presence of brain tumors. By understanding these symptoms, individuals may be able to seek prompt medical attention and diagnosis.
| 1. Cognitive changes | -> Alterations in mental processes and abilities, such as difficulty concentrating, memory problems, or changes in behavior. |
| 2. Headaches | -> Persistent and often severe headaches that may worsen over time or become more frequent. |
| 3. Vision problems | -> Blurred or double vision, loss of peripheral vision, or visual disturbances. |
| 4. Motor skills difficulties | -> Weakness in limbs, poor coordination, muscle twitching, or difficulty with balance and walking. |
| 5. Seizures | -> Sudden, uncontrolled electrical activity in the brain leading to seizures, which can range from mild to severe. |
| 6. Nausea and vomiting | -> Persistent feelings of nausea or the urge to vomit, which may be unrelated to food intake. |
| 7. Speech and language difficulties | -> Problems with speaking, slurred speech, difficulty finding words, or understanding language. |
| 8. Fatigue | -> Excessive tiredness or lack of energy that is not improved with rest or sleep. |
| 9. Mood changes | -> Unexplained changes in mood, such as irritability, depression, or sudden outbursts of anger. |
| 10. Sensory alterations | -> Changes in the senses, including tingling or numbness in the arms or legs, altered sense of taste or smell, or decreased hearing ability. |
It is important to note that individuals may experience a combination of these symptoms or exhibit different ones depending on the location and size of the brain tumor. If any of these signs persist or worsen over time, it is crucial to consult a healthcare professional for further evaluation and appropriate management.
The Significance of Early Diagnosis

Recognizing the presence of brain tumors at the earliest stage is of utmost importance. Identifying these abnormal growths in the brain before they progress significantly can have a significant impact on the overall outcome and treatment options. A speedy and accurate diagnosis plays a crucial role in offering timely medical intervention and improving the chances of successful treatment.
Prompt identification of brain tumors allows healthcare professionals to initiate the appropriate medical procedures promptly. Detecting the presence of these neoplasms as early as possible enables the medical team to make informed decisions regarding treatment plans and the best course of action. Quick diagnosis can potentially minimize the risks associated with the tumor's growth and lead to more effective treatment options.
An early diagnosis also provides the opportunity for patients to receive the necessary support and care from their loved ones and the medical community. With the knowledge of the condition at an early stage, patients can take steps to address the tumor's impact on their daily lives and mental well-being. Moreover, early diagnosis empowers individuals to take an active role in their treatment journey, fostering a sense of control and understanding.
Emphasizing the significance of early diagnosis helps raise awareness about the importance of regular health check-ups and prompt reporting of specific symptoms. Encouraging individuals to prioritize their well-being and seek medical attention at the earliest signs of potential brain tumors can potentially save lives and improve the overall prognosis.
Diagnostic Tests for Brain Tumors
Assessing the presence of abnormal growths within the brain requires a series of comprehensive diagnostic tests. These tests aim to identify and understand the underlying causes, indications, and extent of these tumors. Through a combination of non-invasive and invasive techniques, medical professionals can gather crucial information to appropriately diagnose brain tumors.
Imaging Methods: Specialists employ various imaging techniques to visualize the brain and detect any abnormalities. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI), computed tomography (CT) scans, and positron emission tomography (PET) scans are commonly used methods. These imaging tests provide detailed and multi-dimensional images that help identify the specific location, size, and characteristics of the brain tumor.
Cerebrospinal Fluid Analysis: The examination of cerebrospinal fluid through a procedure called lumbar puncture helps in diagnosing certain types of brain tumors. This analysis assists in detecting the presence of abnormal cells, proteins, or other substances that may indicate the presence of a brain tumor.
Biopsy: To obtain a definitive diagnosis, a biopsy is often necessary. During this procedure, a small sample of the tumor tissue is removed either surgically or with a needle. The sample is then examined under a microscope by a pathologist to determine the tumor type, grade, and other important characteristics. Biopsies can be performed as open surgeries or through minimally invasive techniques such as stereotactic biopsy or endoscopic biopsy.
Genetic Testing: In some cases, genetic testing may be conducted to determine specific genetic mutations or abnormalities associated with certain types of brain tumors. This testing can provide crucial information about the tumor's behavior, response to treatments, and potential genetic predispositions.
Electroencephalography (EEG): EEG measures the electrical activity of the brain and can help identify abnormalities that may be caused by the presence of a brain tumor. This non-invasive test involves placing electrodes on the scalp to detect and record brain wave patterns.
Neurological Examination: A comprehensive neurological examination is necessary to assess the overall function and health of the brain. This examination involves assessing motor skills, reflexes, sensory abilities, balance, coordination, and other cognitive functions. Deviations from normal neurological function can provide valuable clues about the presence, location, and effects of a brain tumor.
Accurate and timely diagnostic testing plays a critical role in understanding brain tumors. The combination of these tests allows healthcare professionals to accurately diagnose and develop appropriate treatment strategies tailored to each patient's specific situation.
Available Treatment Options
In the journey towards combating this condition affecting the human brain, multiple options have emerged to address the numerous facets that contribute to its development and growth. These treatment alternatives provide individuals with a range of choices in managing and potentially overcoming this medical challenge.
Medical Interventions: The advancements in medical science have paved the way for various interventions aimed at targeting and shrinking the abnormal growth in the brain. These interventions utilize cutting-edge techniques and modern technologies to deliver precise and effective treatments.
Surgical Procedures: Surgeons skilled in the intricacies of neurological surgery employ their expertise in performing intricate operations to remove brain tumors. Through meticulous planning and careful execution, surgeons aim to eliminate the tumor and preserve essential brain functions.
Radiation Therapy: By employing high-energy radiation, this treatment option aims to destroy or shrink brain tumors non-invasively. By precisely targeting the tumor cells, radiation therapy works to halt their growth and potentially eradicate them altogether.
Chemotherapy: Chemical-based treatments play a vital role in combating brain tumors by targeting the abnormal cells that contribute to their formation. This therapeutic approach aims to weaken and destroy these cells, impeding their ability to multiply and invade healthy brain tissue.
Targeted Therapies: These innovative treatments rely on specific agents that directly target the molecular abnormalities present in brain tumors. By focusing on these specific genetic or cellular factors, targeted therapies aim to interrupt tumor growth and minimize damage to surrounding brain tissue.
Palliative Care: In cases where complete eradication of brain tumors is not feasible, palliative care emerges as a crucial treatment approach. This holistic method aims to provide relief from symptoms, manage pain, and improve the overall quality of life for individuals facing this challenging condition.
It is important to note that the selection of a specific treatment option depends on the individual's specific case, including the type, size, location, and stage of the brain tumor, as well as overall health and personal preferences.
Advances in Research on Brain Tumor Progression and Treatment
As scientists continue to explore the intricate workings of the human brain, remarkable progress has been made in understanding the complex nature of brain tumors. Ongoing research has shed new light on the underlying causes, identification of early warning signs, and development of effective treatment strategies for these formidable conditions.
1. Improved Imaging Techniques: Revolutionary advancements in imaging technology, such as functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) and positron emission tomography (PET), are instrumental in providing detailed insights into brain tumor characteristics, including their size, location, and growth patterns. These enhanced imaging techniques enable medical professionals to make more accurate diagnoses and develop individualized treatment plans.
2. Molecular Profiling: Through the utilization of sophisticated genetic analysis methods, scientists have been able to identify specific genetic abnormalities and mutations associated with various types of brain tumors. By deciphering the molecular profiles of tumors, researchers can gain a better understanding of their underlying mechanisms, facilitating the development of targeted therapies that effectively disrupt tumor growth.
3. Immunotherapy Breakthroughs: Recent research has focused on harnessing the power of the immune system to combat brain tumors. Immunotherapy treatments, such as immune checkpoint inhibitors and adoptive cell therapies, have shown promising results in enhancing the body's natural defenses against tumor cells. These innovative approaches are paving the way for more effective and less invasive treatment options for patients with brain tumors.
4. Advancements in Surgical Techniques: Surgeons are benefiting from advancements in minimally invasive procedures, allowing for more precise tumor removal and reduced risk to surrounding healthy brain tissue. Innovations like neuro-navigational systems and intraoperative imaging are enhancing the accuracy and safety of brain tumor surgeries, resulting in improved patient outcomes and reduced complications.
5. Nanotechnology in Drug Delivery: Nanotechnology-based drug delivery systems offer promising opportunities in brain tumor treatment. By utilizing nanoparticles, drugs can be selectively targeted to tumor cells while minimizing damage to healthy surrounding tissues. This approach improves drug effectiveness and reduces side effects, ultimately enhancing patient tolerability and treatment outcomes.
These exciting advancements in brain tumor research are revolutionizing our understanding of these complex conditions and opening doors to more effective and personalized treatment options. Continued exploration and collaboration among scientists, clinicians, and patients remain critical in advancing our knowledge and ultimately finding a cure for brain tumors.
Coping with Intracerebral Lesions: Aid and Rehabilitation
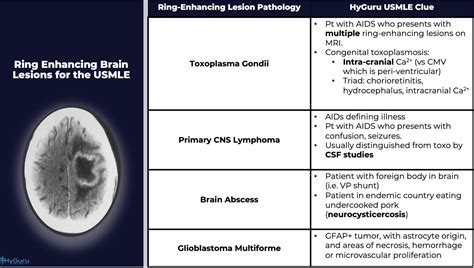
Adjusting to the challenges presented by intracerebral lesions can be an arduous journey. This section offers guidance on how to cope with the emotional, physical, and cognitive impact associated with such conditions. By providing support and exploring rehabilitation options, individuals affected by these lesions can enhance their quality of life and regain a sense of control.
Emotional Support: Facing a diagnosis of intracerebral lesions may trigger a range of emotions. It is essential to recognize and address these feelings in order to promote emotional well-being. Connecting with support groups or seeking counseling can provide a platform to share experiences, gain insight, and receive guidance from others who have encountered similar challenges. Additionally, family and friends can play a vital role in offering understanding, empathy, and encouragement throughout the recovery process.
Physical Rehabilitation: Intracerebral lesions can often result in physical impairments, such as muscle weakness, coordination difficulties, or changes in mobility. Engaging in physical therapy under the guidance of qualified professionals can help individuals regain strength, improve coordination, and restore physical functionality. These specialists tailor exercises and techniques to the specific needs and capabilities of each patient, facilitating a safe and effective recovery.
Cognitive Rehabilitation: Intracerebral lesions may impact cognitive functions, such as memory, attention, and problem-solving abilities. Cognitive rehabilitation involves a variety of techniques, including specialized exercises and activities, to improve cognitive skills and minimize the impact of these impairments. Occupational therapists and neuropsychologists often collaborate to develop personalized rehabilitation plans, helping individuals regain independence and optimize cognitive functioning.
Alternative Therapies: In addition to traditional rehabilitation approaches, alternative therapies can complement the recovery process. These may include acupuncture, massage therapy, meditation, and yoga. While their effectiveness varies from person to person, these holistic approaches aim to reduce stress, promote relaxation, and enhance overall well-being. It is important to consult healthcare professionals before integrating alternative therapies into a treatment plan to ensure they align with individual circumstances.
Support for Caregivers: Caring for individuals with intracerebral lesions can be demanding and emotionally taxing. Caregivers should prioritize self-care, seek support from their own networks, and consider joining caregiver support groups. These resources provide a platform to share experiences, exchange valuable advice, and alleviate feelings of isolation. By nurturing their own well-being, caregivers can better support and advocate for their loved ones throughout the challenging journey.
FAQ
What causes brain tumors?
Brain tumors can be caused by a variety of factors, including genetic mutations, exposure to radiation, certain inherited conditions, and a weakened immune system. However, in many cases, the exact cause of a brain tumor is unknown.
What are the common symptoms of brain tumors?
The symptoms of brain tumors can vary depending on the location and size of the tumor, but common symptoms include headaches, seizures, memory problems, changes in personality or behavior, problems with balance and coordination, and changes in vision, hearing, or speech.
How are brain tumors diagnosed?
Brain tumors are typically diagnosed through a combination of imaging tests, such as MRI or CT scans, and a biopsy, which involves removing a small sample of the tumor tissue to examine it for cancerous cells.
What are the treatment options for brain tumors?
The treatment for brain tumors depends on factors such as the type, size, and location of the tumor, as well as the overall health of the patient. Treatment options may include surgery to remove the tumor, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, targeted drug therapy, or a combination of these methods.
What is the prognosis for someone with a brain tumor?
The prognosis for a brain tumor can vary depending on factors such as the type and stage of the tumor, the age and overall health of the patient, and the response to treatment. Some brain tumors can be successfully treated, while others may have a poorer prognosis, but advancements in medical technology and treatment options have improved outcomes for many patients in recent years.
What are the common causes of brain tumors?
Brain tumors can be caused by genetic factors, exposure to radiation, certain inherited conditions, and rarely, certain viruses. However, in most cases, the exact cause of brain tumors is unknown.




