When it comes to computer operating systems, there exists a multitude of options available that can cater to diverse user needs and preferences. In this article, we will delve into the various flavors of Linux-based operating systems, each with its unique characteristics and functionalities. Additionally, we will explore the diverse techniques one can employ to install these versatile operating systems efficiently.
Unveiling the Array of Linux Distributions and Their Features
Linux distributions, commonly referred to as "distros," are essentially variants of the Linux operating system. These distros are built around the Linux kernel and come bundled with a selection of software packages, utilities, and desktop environments. Each distro is designed with a specific target audience, purpose, or level of expertise in mind, offering a degree of flexibility and customization that appeals to a wide range of users, from novices to seasoned professionals.
Embracing User-Friendly Installation Techniques for Linux Distros
Setting up a Linux distribution is a straightforward process, with various installation methods available depending on the user's preferences. Whether you are keen on dual-booting with an existing operating system, upgrading from an older Linux version, or even trying it out through virtualization, there are installation methods to accommodate every situation. Moreover, many distros provide user-friendly graphical installers that simplify the setup process, eliminating the need for technical expertise or cumbersome command-line interventions.
The Variety of Linux Distributions
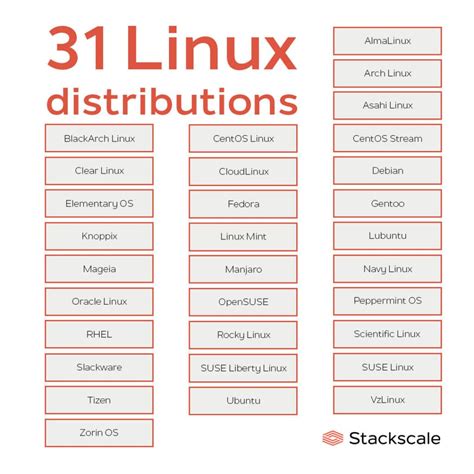
In the realm of software operating systems, there exists a plethora of diverse distributions that harness the power of the Linux kernel. These unique variations of Linux offer users a multitude of options when it comes to selecting an operating system that aligns with their specific needs and preferences.
One distinguishing feature of Linux distributions is the assortment of user interfaces they offer. Some distributions opt for a sleek and streamlined graphical interface, while others prefer a more minimalist approach. Additionally, the level of customization available varies from one distribution to another, allowing users to tailor their Linux experience to suit their individuality.
Furthermore, these distributions exhibit dissimilar approaches to software management. While some Linux distributions employ package managers that simplify the process of installing, updating, and removing software, others require users to manually compile and install applications themselves. This divergence in software management methods allows users to choose a system that aligns with their technical proficiency and preferences.
Moreover, each Linux distribution caters to different user communities, fostering a sense of belonging and collaboration. Whether users are developers, artists, educators, or enthusiasts, there is a Linux distribution that caters to their specific interests and requirements. This promotes a vibrant ecosystem where users can share their knowledge and contribute to the ongoing development of their chosen distribution.
In conclusion, the wide array of Linux distributions ensures that there is a Linux operating system for every individual, characterized by unique user interfaces, software management methods, and targeted user communities. This diversity underscores the open-source nature of Linux, empowering users to embrace their individuality and find a Linux distribution that resonates with their needs and preferences.
Debian: A Reliable and Versatile Linux Distribution
Debian, a highly regarded and versatile distribution, stands as a testament to the power and flexibility of Linux. With a strong emphasis on stability and reliability, Debian offers users a robust operating system that can be customized to suit a wide range of needs.
Unlike some other distributions, Debian does not limit users to a particular environment or package manager, allowing for greater freedom and flexibility. It provides a wide array of software packages, ensuring compatibility with various hardware configurations.
Renowned for its rock-solid stability, Debian offers long-term support and regular updates to ensure users have access to the latest software advancements while maintaining the security and reliability of their systems. Furthermore, Debian's massive community of contributors and developers ensures that support and assistance are readily available for any issues that may arise.
One of Debian's notable features is its package management system, which streamlines the process of installing, upgrading, and removing software. With its advanced package manager, users can easily install thousands of software packages with just a few simple commands, making it a favored choice for both novice and experienced Linux users alike.
Whether you're a student, developer, or server administrator, Debian offers a powerful and flexible platform that can cater to your specific requirements. Its extensive software repository, stability, and community support make it an ideal choice for those seeking a reliable and versatile Linux distribution.
Introduction to Ubuntu

In this section, we will explore Ubuntu, a popular and widely used open-source operating system. Ubuntu offers a range of features and benefits that make it an attractive choice for individuals and organizations seeking a reliable and user-friendly computing experience.
User-friendly Interface: Ubuntu provides a user-friendly interface that is easy to navigate and understand. Its intuitive design allows both novice and experienced users to quickly adapt and start using the system.
Software Availability: Ubuntu offers a vast selection of free and open-source software through its Software Center, allowing users to easily download and install a variety of applications for their specific needs.
Stability and Security: Ubuntu is known for its stability and security measures. Regular and timely updates ensure that the system remains up-to-date and protected against potential vulnerabilities.
Community Support: Ubuntu has a strong and active community of users and developers who provide support and assistance through forums, documentation, and online resources. This vibrant community ensures that users can easily find solutions to any issues they may encounter.
Customization and Flexibility: Ubuntu offers a high level of customization, allowing users to personalize their desktop environment and tailor it to their preferences. Users can choose from a variety of themes, icons, and extensions to create a unique and personalized computing experience.
Choice of Editions: Ubuntu offers several editions, each catered to specific needs and preferences. Whether you are a developer, a casual user, or a business professional, Ubuntu has an edition that suits your requirements.
Ecosystem Integration: Ubuntu seamlessly integrates with various cloud-based services and platforms, allowing users to sync and access their files and data across multiple devices easily.
Conclusion: Ubuntu is a versatile and reliable operating system that provides a user-friendly experience, a wide range of software options, and a strong community support system. Whether you are an individual or an organization, Ubuntu offers a compelling choice for your computing needs.
Fedora: An Overview
Fedora, an open-source operating system, is a prominent member of the Linux family, renowned for its versatility and user-friendly interface. This section will delve into the distinctive features, functionalities, and benefits of Fedora, shedding light on why it is a preferred choice for many individuals and organizations alike.
| 1. Robust Package Management | Fedora provides a comprehensive package management system, which allows users to effortlessly install, update, and remove software packages. The extensive repository of packages ensures access to a plethora of applications and tools, catering to diverse requirements and preferences. |
| 2. Cutting-Edge Software | As a leading-edge distribution, Fedora prides itself on offering the latest software versions. It serves as a platform for testing and showcasing emerging technologies, making it an ideal choice for tech enthusiasts and developers seeking to stay at the forefront of technological advancements. |
| 3. Community-Driven Development | Fedora is developed by a passionate community of contributors who actively collaborate in its evolution. This vibrant community fosters innovation, encourages transparency, and welcomes user feedback, inspiring continuous improvement and refinement of the operating system. |
| 4. Security and Stability | Fedora places a strong emphasis on security and stability, implementing robust security measures to safeguard user data and privacy. Regular updates, security audits, and proactive vulnerability management contribute to maintaining a secure environment, ensuring peace of mind for users. |
| 5. Customizability and Flexibility | With its extensive range of desktop environments and flexible configuration options, Fedora allows users to tailor their system according to their specific requirements and preferences. This level of customization empowers users to create a personalized computing experience. |
In summary, Fedora stands out among Linux distributions for its robust package management, commitment to cutting-edge software, community-driven development model, focus on security and stability, as well as its customizable nature. These factors contribute to its widespread popularity and make it a compelling choice for both individuals and organizations seeking a powerful and adaptable operating system.
Introduction to CentOS

CentOS is a popular open-source operating system that offers a reliable and secure platform for various applications and services. This section will provide an overview of CentOS, highlighting its features, benefits, and its role in the Linux ecosystem.
Diving into the world of CentOS, you will discover a robust and stable operating system that is derived from the source code of Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL). CentOS's main focus is to provide a free and community-supported alternative to RHEL, making it an excellent choice for individuals and organizations looking for a trustworthy and cost-effective solution.
One of the notable features of CentOS is its long-term support, allowing users to enjoy security updates and bug fixes over an extended period. This stability and reliability make CentOS particularly suitable for server environments and critical applications where downtime can have a significant impact.
With CentOS, you can leverage the power of a Linux operating system that is backed by a committed and vibrant community. This vibrant community ensures regular updates and continuous development, offering users access to a vast repository of software packages and tools.
Whether you are a seasoned Linux professional or a beginner, CentOS provides a user-friendly experience, allowing easy installation and configuration. Additionally, CentOS offers excellent compatibility with a wide range of software applications and hardware platforms, making it a versatile choice for various use cases.
In conclusion, CentOS stands as a prominent member of the Linux family, providing users with a reliable, secure, and community-supported operating system. Whether you are setting up a server, developing applications, or exploring the vast world of Linux, CentOS is a worthy choice that combines stability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness.
Installation Techniques
In this section, we explore various approaches that can be employed to install different versions of the versatile and highly-customizable open-source operating system known for its flexibility, security, and wide range of hardware compatibility.
Discovering the most suitable methods to deploy Linux on your device is imperative for successful installation and smooth operation. This section offers insights into the diverse techniques available, empowering you to select the optimal approach for your specific requirements.
Dual Boot with Windows
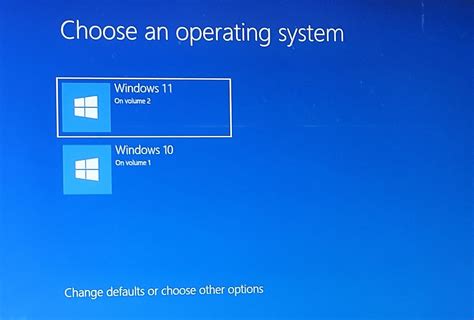
In this section, we will explore the concept of running two operating systems, Linux and Windows, on a single computer through the practice of dual booting. This method allows users to experience the benefits of both Linux and Windows simultaneously, without the need for separate machines or virtualization.
Understanding Dual Booting:
Dual booting refers to the process of installing and configuring multiple operating systems on a single computer, allowing users to select the preferred operating system to load upon system startup. One of the most common scenarios for dual booting is combining Linux and Windows, which provides users with the flexibility to utilize the advantages of both systems.
When setting up a dual boot configuration with Linux and Windows, it is important to plan the installation process carefully. The user must allocate adequate disk space for both operating systems, ensuring that each system has its own dedicated partition. This partitioning allows for the independent storage and management of files and applications for each operating system.
The Benefits of Dual Booting:
By dual booting Linux and Windows, users can take advantage of the unique features and software offered by each operating system. Linux, known for its customizability, open-source nature, and robust security, appeals to developers, tech enthusiasts, and those seeking a more flexible computing experience. On the other hand, Windows provides a user-friendly interface and compatibility with a wide range of software, making it ideal for everyday users and those dependent on specific Windows-only applications.
Furthermore, dual booting allows users to switch between Linux and Windows seamlessly, based on their specific needs and preferences. For example, users can utilize Linux for programming and development tasks and then switch to Windows for gaming or running certain proprietary software. This flexibility eliminates the need for separate machines or virtualization solutions, streamlining the workflow and providing a more efficient computing experience.
Installing Linux and Windows in Dual Boot:
The process of setting up a dual boot configuration with Linux and Windows involves several steps. Firstly, the user must install Windows on their machine, ensuring that adequate disk space is allocated for the subsequent Linux installation. After setting up Windows, the next step involves installing the chosen Linux distribution, such as Ubuntu or Fedora, onto a separate partition.
Throughout the installation process, users must follow the prompts, making choices such as partitioning the hard drive, configuring boot options, and selecting the default operating system for startup. Once the installation is complete, users can switch between Linux and Windows by selecting the desired operating system at system startup, as prompted by a boot menu.
Note: It is crucial to make regular backups and exercise caution when modifying the system's partitioning or boot configuration, as errors can lead to data loss or system instability.
By following the appropriate installation procedures and understanding the benefits of dual booting, users can leverage the power of both Linux and Windows, creating a versatile computing environment tailored to their individual needs.
Virtual Machine Installation
Exploring alternative methods of utilizing different versions of Linux, one way of achieving this is through the installation of virtual machines. This section delves into the process of setting up virtual machines for running Linux operating systems, offering a flexible and efficient approach to experimentation and multi-platform setups.
Virtual machine installation involves the creation of virtual computing environments within an existing operating system. These virtual environments, commonly referred to as virtual machines, are capable of running their own isolated instances of an operating system, offering users the ability to install and use a variety of Linux distributions without affecting their primary operating system or hardware.
One popular virtual machine software is Oracle's VirtualBox. This software provides a user-friendly interface and comprehensive features for setting up and managing virtual machines. The installation process typically involves downloading and installing the VirtualBox software, creating a new virtual machine, and selecting the desired Linux distribution to install within the virtual environment.
Another option for virtual machine installation is VMware Workstation. Similar to VirtualBox, VMware Workstation allows users to run multiple virtual machines simultaneously, providing additional flexibility for testing different Linux distributions and configurations. The installation process for VMware Workstation involves downloading and installing the software, configuring the virtual machine settings, and then proceeding with the Linux distribution installation within the virtual environment.
Aside from VirtualBox and VMware Workstation, there are also other virtualization solutions available, each with its own advantages and features. These include KVM (Kernel-based Virtual Machine), Xen, and QEMU (Quick Emulator), among others. Depending on the specific requirements and preferences, users can choose the most suitable virtual machine software for their Linux installation needs.
Virtual machine installation offers numerous benefits, such as the ability to test and evaluate different Linux distributions, applications, and configurations without affecting the main operating system. It also provides a convenient way to create isolated development environments and facilitates software compatibility testing. Additionally, virtual machines enable seamless migration, backups, and snapshots, making it easier to manage and maintain multiple Linux installations.
| Virtual Machine Software | Main Features |
|---|---|
| Oracle VirtualBox | User-friendly interface, comprehensive features |
| VMware Workstation | Simultaneous running of multiple virtual machines |
| KVM (Kernel-based Virtual Machine) | Open-source, fast and efficient virtualization |
| Xen | High-performance, open-source virtualization |
| QEMU (Quick Emulator) | Supports a wide range of architectures |
In conclusion, virtual machine installation offers a flexible and efficient method of exploring and utilizing different Linux distributions without disrupting the primary operating system. With a variety of virtual machine software options available, users can easily set up and manage virtual environments, enabling seamless experimentation and multi-platform setups.
Live USB/DVD Installation
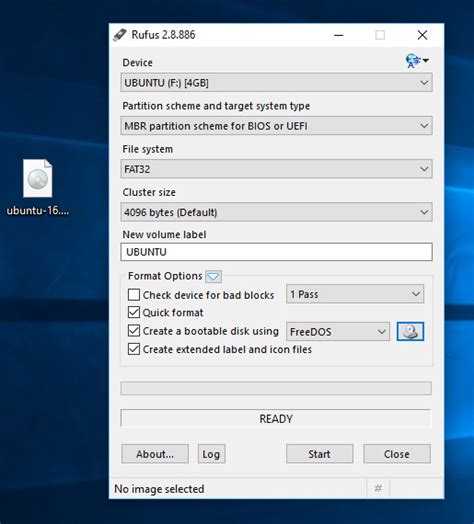
In this section, we will explore the process of installing a Linux operating system using a live USB or DVD. This method allows you to test and experience the Linux environment without making any changes to your computer's existing operating system.
One of the advantages of using a live USB or DVD is the ability to carry your Linux operating system with you anywhere. With a live USB, you can simply plug it into a computer, boot from the USB, and have access to your personalized Linux environment. Similarly, a live DVD allows you to boot directly from the disc and access the Linux system without installing it on the computer.
Setting up a live USB or DVD involves creating a bootable media with the Linux operating system of your choice. You can download a Linux distribution ISO file from the official website and use software like Rufus or Etcher to create a bootable USB. Alternatively, you can burn the ISO file onto a DVD using disc burning software.
Once you have your bootable media ready, you need to restart your computer and access the boot menu. This can usually be done by pressing a specific key (such as F12 or Esc) during the computer's startup process. From the boot menu, select the USB or DVD drive as the primary boot device.
When the Linux live system loads, you have the option to explore the operating system's features, applications, and user interface. You can experience the performance, compatibility, and functionality of the Linux distribution firsthand before deciding to install it on your computer. Keep in mind that any changes made during the live session will not be saved, ensuring that your computer's existing operating system remains intact.
If you decide to install the Linux operating system from the live session, most distributions provide an easy-to-use installation wizard. This allows you to choose the installation options, such as partitioning the hard drive, setting up a dual boot with another operating system, or performing a clean installation. Follow the on-screen instructions to complete the installation process.
Overall, the live USB/DVD installation method provides a convenient and risk-free way to try out different Linux operating systems. It allows you to test their compatibility with your hardware and evaluate their features before committing to a full installation. Whether you're a beginner or an experienced Linux user, the live installation method is a valuable tool for exploring the diverse world of Linux.
FAQ
What are the different types of Linux operating systems?
There are various types of Linux operating systems available, such as Ubuntu, Fedora, CentOS, Debian, and Arch Linux. Each of these distributions has its own set of features, packages, and user interfaces.
How do I install Linux on my computer?
There are multiple installation methods for Linux. You can either create a dual-boot setup with an existing operating system, install Linux alongside Windows or macOS, or perform a clean installation by erasing the existing operating system. The exact steps depend on the specific distribution you choose, but usually involve creating a bootable USB drive or DVD and following the on-screen instructions.
What is the recommended Linux distribution for beginners?
Ubuntu is often recommended for beginners due to its user-friendly interface, extensive documentation, and large community support. It provides an easy-to-use graphical installer and a wide range of pre-installed software. Additionally, there are numerous online resources and forums available to assist beginners with any questions or issues they may encounter.




