Imagine a world where you effortlessly navigate between operating systems, merging your digital realm without a hitch. In today's fast-paced technological landscape, the need for versatility and adaptability is paramount. When it comes to switching from one operating system to another, it can be a daunting task to ensure a smooth transfer of your precious data. To help you accomplish this task with ease, we present a comprehensive guide on how to seamlessly migrate your files and documents from one environment to another.
Change is a constant in the world of technology, and moving your data is no exception. Whether you are migrating from a familiar Windows system to a Linux platform or looking to diversify your digital experience, this guide will equip you with the essential knowledge and tools to ensure a successful transition. Discover the most effective methods and techniques to securely transfer your files, ensuring that nothing is left behind.
With the ever-expanding capabilities of technology, it is increasingly common for individuals and businesses to explore alternative operating systems. However, the fear of losing valuable information often hinders this exploration. By following the guidance provided in this article, you will be able to embrace the advantages of both Windows and Linux, confidently moving your files with minimal disruption to your workflow. No longer should the fear of data loss hold you back from experiencing the best of both worlds.
Prepare yourself for a journey of discovery as we delve into the intricacies of migrating your files and documents. From understanding the unique file systems of both Windows and Linux to utilizing robust tools and techniques, we will empower you to begin your transition with confidence. Unlock the hidden potential that lies within both operating systems and expand the horizons of your digital universe. Let us embark on this transformative journey together!
Understanding the Differences Between Windows and Linux
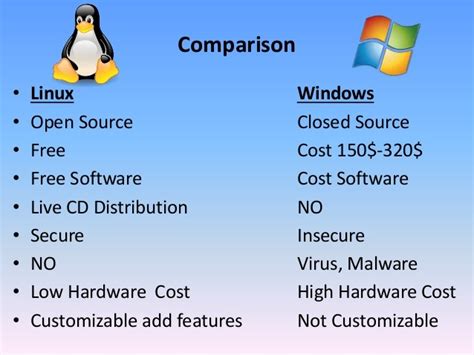
When it comes to operating systems, Windows and Linux are two distinct platforms that cater to different needs and user preferences. While both offer solutions for various computing tasks, it is crucial to understand their inherent differences to make an informed choice.
Windows, developed by Microsoft, has long been synonymous with user-friendly interfaces and widespread accessibility. It dominates the personal computer market, providing a comprehensive suite of applications and a vast library of software programs. In contrast, Linux, an open-source operating system, offers unparalleled flexibility and customization options.
One significant difference between Windows and Linux lies in their underlying architecture. Windows relies on a proprietary codebase, ensuring compatibility with a wide range of hardware and software options. Conversely, Linux adopts the Unix-like system structure, which promotes stability, security, and efficient resource allocation.
Moreover, the two operating systems vary in terms of their file systems. Windows primarily uses the New Technology File System (NTFS), known for its journaling capabilities, advanced permissions management, and support for large file sizes. On the other hand, Linux predominantly utilizes the Extended File System (EXT), renowned for its robustness, reliability, and support for file compression.
While Windows boasts a vast selection of commercial software and popular video games, Linux emphasizes open-source software and community-driven development. Additionally, Windows users tend to rely on graphical user interfaces (GUIs) for most tasks, whereas Linux offers a command-line interface (CLI) alongside GUI options, making it a preferred choice among tech-savvy users and system administrators.
Understanding the fundamental distinctions between Windows and Linux is essential when considering data transfer between the two platforms. By recognizing their unique characteristics, users can employ appropriate techniques and tools to ensure a smooth transition and maintain data integrity.
The fundamental variances in the operating systems
When moving data between two distinct operating systems, it is crucial to understand the fundamental variances that exist between them. While both operating systems aim to provide a user-friendly interface and efficient performance, they adopt different approaches and structures. These differences encompass various aspects ranging from the basic file system organization to software compatibility and command execution.
File System Organization: One of the primary variances lies in how the operating systems organize and manage data. Windows primarily utilizes the File Allocation Table (FAT) or New Technology File System (NTFS), whereas Linux adopts their own structures such as the Extended File System (ext4) or XFS. These differences in file system organization impact the way data is stored, accessed, and managed, making direct compatibility between the two systems challenging.
Software Compatibility: Another crucial difference is the availability and compatibility of software applications. Windows operating system boasts a vast range of software options, widely used across various industries. On the other hand, Linux offers a more open-source ecosystem with a considerable number of free applications developed by the community. However, the compatibility of software designed for Windows might not be straightforward on Linux, as it requires alternative versions, emulators, or virtualization techniques.
Command Execution: Windows and Linux differ significantly in the way commands are executed and interacted with. Windows predominantly employs a graphical user interface (GUI), allowing users to perform tasks through visually intuitive elements. Meanwhile, Linux emphasizes the command-line interface (CLI), enabling users to execute commands using text-based input. This variance in command execution methods can impact the workflow and the skills required to operate efficiently within each system.
Diverse User Communities: Both operating systems have distinct user communities and support networks. Windows, being a widely adopted operating system, has extensive technical support available from both the Microsoft team and third-party developers. Linux, being an open-source platform, boasts a passionate community that actively contributes to software development and provides support through forums and online communities. Understanding the diversity in user communities is essential when exploring data transfer options between the two systems.
By acknowledging and comprehending these fundamental variances in operating systems, users can better appreciate the challenges and intricacies involved in transferring data from Windows to Linux. With careful planning and utilization of appropriate tools and techniques, successful data migration can be achieved, ensuring a smooth transition between the two powerful operating systems.
Why Transferring Data is Essential for Migrating Between Operating Systems

Efficiently transitioning between different operating systems requires careful consideration and planning. When moving from one operating system to another, such as shifting from a Windows environment to a Linux environment, it is crucial to understand the significance of transferring data seamlessly. This process ensures that valuable information, files, and settings are not left behind, enabling a smooth and uninterrupted transition.
Recognizing the importance of transferring data from one operating system to another involves understanding the distinctive characteristics and functionalities of both Windows and Linux. By comprehending the unique features of each operating system, individuals can identify the specific data that needs to be transferred and ensure its compatibility with the new system.
Transferring data allows users to retain crucial information, such as documents, presentations, spreadsheets, and multimedia files, ensuring that valuable data is available and accessible on the new Linux platform. Additionally, transferring settings, preferences, and personal configurations permits users to maintain a familiar computing experience, reducing the learning curve typically associated with adopting a new operating system.
Moreover, the process of transferring data from Windows to Linux enables the preservation of user accounts, including usernames, passwords, and associated profiles. By replicating these accounts on the Linux platform, individuals can seamlessly transition their online identities and access critical resources, email accounts, and web services without disruption.
In conclusion, understanding the importance of transferring data from Windows to Linux is essential when undergoing a transition between these distinct operating systems. It ensures the preservation of valuable information, enables a smoother user experience, and allows continuity in accessing critical resources. By recognizing the significance of this process, individuals can effectively migrate their data and seamlessly adapt to the new Linux environment.
Exploring the Motivations for Migrating Information
In order to successfully navigate the transition from one operating system to another, it is crucial to understand the motivations behind transferring data.
When embarking on the journey of migrating information, individuals and organizations encounter a variety of driving factors that push them to seek alternative solutions. These motivations can be rooted in the desire to enhance system performance, streamline operations, or reduce costs. Additionally, the urge to embrace new technological advancements, improve security measures, or capitalize on the benefits of open-source software often fuels the decision to migrate data.
Exploring these motivations in greater depth allows us to gain a better understanding of the underlying reasons why individuals and organizations choose to migrate data from one operating system to another. By delving into the specifics of each motivation, we can assess the potential benefits and challenges involved in the process of transferring information. This understanding is essential for devising an effective data migration strategy that addresses the unique needs and goals of each entity.
| Motivation | Description |
|---|---|
| Enhanced Performance | Migration may be driven by the desire to optimize system efficiency, improve response times, and boost overall performance. |
| Operational Streamlining | The need to simplify and streamline operations, by leveraging the features and capabilities of the target operating system, is a common motivation for data migration. |
| Cost Reduction | Migrating to an alternative operating system may provide opportunities to reduce licensing fees, software costs, and infrastructure expenses. |
| Technological Advancements | The desire to leverage the latest advancements in technology, such as improved hardware compatibility or enhanced software capabilities, can be a driving force behind data migration. |
| Security Enhancement | Individuals and organizations may choose to migrate data in order to strengthen cybersecurity measures, protect sensitive information, and mitigate potential risks. |
| Open-Source Software Benefits | Capitalizing on the advantages of open-source software, such as customization options, flexibility, and community-driven development, can motivate the decision to transfer data to a Linux-based system. |
Understanding the motivations behind data migration is essential for a successful transition, as it allows individuals and organizations to align their objectives with the potential benefits offered by an alternative operating system. By comprehending these driving factors, stakeholders can confidently embark on the process of transferring data while maximizing the potential for success.
Preparing for the Transition

In order to successfully migrate your files and important documents from one operating system to another, it is crucial to adequately prepare for the data transfer process. This section will guide you through the necessary steps to ensure a smooth transition, allowing you to seamlessly move your valuable information.
Evaluating File Compatibility: Start by considering compatibility between file systems. You will need to determine if the file formats used in your current Windows environment can be seamlessly opened and accessed within a Linux system. This evaluation will help you identify any potential challenges or limitations and enable you to take the necessary precautions.
Organizing and Categorizing Data: Before transferring your data, it is vital to organize and categorize it effectively. Review your files and documents, dividing them into appropriate categories or folders to maintain a structured and easily accessible record. This step will save you time and effort during the migration process, ensuring a more efficient transfer.
Backing Up Your Data: Prior to initiating any transfer, it is imperative to create a backup of your data. Accidental deletion or unforeseen errors can occur during the transition, and having a backup will provide a safety net. Make sure to store the backup in a secure location, whether it be an external storage device or a cloud-based service.
Researching Linux Tools and Applications: Familiarize yourself with Linux-specific tools and applications that can facilitate the data transfer process. Take the time to assess their compatibility, features, and user-friendliness, ensuring that they meet your specific requirements. This knowledge will allow you to make an informed decision on the most suitable tools for a successful migration.
Preparing Hardware and Network: Check the hardware requirements and compatibility for Linux on your devices. Ensure that your computer or laptop has adequate storage space, memory, and processing power to accommodate the new operating system. Additionally, verify that your network settings are properly configured to establish a stable connection during the data transfer.
Taking Security Measures: As you prepare to transfer your data, it is essential to prioritize security. Implement necessary measures to protect your files and sensitive information during the migration process. This may involve encrypting files, using secure connections, or employing other security protocols to maintain data integrity and confidentiality.
Documenting the Transfer Process: It is advisable to keep a record of the steps and procedures undertaken during the data transfer process. This documentation will serve as a reference in case any issues arise post-migration and will aid in troubleshooting. Having a comprehensive record will also facilitate future data transfers if the need arises.
By thoroughly preparing for the data transfer process, you will minimize the risks associated with migrating from one operating system to another. Following the guidelines outlined in this section will ensure that your transition from Windows to Linux is successful and that your valuable data is securely transferred.
Gathering the necessary tools and resources
In order to successfully transition your data from a Windows operating system to a Linux operating system, it is essential to gather all the necessary tools and resources to ensure a smooth and efficient transfer process. This section will provide an overview of the various tools and resources you will need, without specifically referring to the Windows-to-Linux data transfer.
One of the crucial tools you will require is a reliable external storage device. This can include a USB flash drive, an external hard drive, or even cloud storage solutions. These storage devices will serve as a temporary repository for your data while you transition from one operating system to another.
In addition to external storage, it is important to equip yourself with compatible software programs for data migration and file compatibility. These programs may vary depending on the specific file formats and applications you have used on Windows. Researching and identifying the appropriate software tools for your specific needs can greatly facilitate the data transfer process.
Another resource that can prove invaluable during the transition is access to a helpful online community or forum. These platforms provide an opportunity to seek guidance, troubleshoot issues, and learn from others who have successfully made the switch from Windows to Linux. Engaging with the community can offer valuable insights and tips that can enhance your data transfer experience.
- Acquire a reliable external storage device
- Research and obtain compatible software programs
- Connect with online communities or forums for support
By gathering these essential tools and resources, you will be well-equipped to undertake the process of transferring your data from a Windows environment to a Linux environment. The next section will delve into the specific steps involved in the data transfer process.
Strategies for Transferring Files and Folders

When migrating between different operating systems, one crucial aspect to consider is the smooth transition of your data. In this section, we will explore effective strategies for easily and securely transferring files and folders from one environment to another.
1. Organizing your Data: Before initiating the transfer process, it is essential to organize your data in a structured manner. Categorize your files and folders based on their type, purpose, or relevance, making it easier to locate and transfer specific data sets.
2. Compression and Archiving: Compressing files and folders before transferring can significantly reduce the overall size and facilitate faster data transfer. Consider using popular compression formats like ZIP or GZ to create archives of multiple files, ensuring a more efficient transfer process.
3. File Transfer Protocols: Several file transfer protocols exist that facilitate data migration between different operating systems. The choice of protocol depends on factors such as the size of the files, network security, and the operating systems involved. Common protocols include FTP (File Transfer Protocol), SFTP (SSH File Transfer Protocol), and SCP (Secure Copy Protocol).
4. Cloud Storage Services: Utilizing cloud storage services can simplify the transfer process, allowing you to conveniently upload your files and folders from one operating system and then download them to another. Popular cloud storage options include Dropbox, Google Drive, and OneDrive.
5. Network Sharing: If the computers are connected within the same local network, transferring data can be accomplished using network sharing features. Enable file and folder sharing on both the Windows and Linux systems, granting access to the desired files and folders for a seamless transfer process.
6. Compatibility Considerations: Before initiating the transfer, ensure compatibility between file systems and formats. Windows primarily uses NTFS, while Linux often relies on ext4 or other filesystems. Verify that both operating systems can efficiently read and write to the file systems involved.
7. Verification and Testing: Once the transfer process is complete, it is crucial to verify the integrity and completeness of the transferred data. Compare file sizes, conduct random file checks, and verify that the transferred files can be successfully accessed and opened in the new environment.
8. Migration Tools: Numerous migration tools are designed specifically to facilitate data transfer between different operating systems. Research and utilize reliable tools that can automate and simplify the transfer process, ensuring a smoother transition and minimizing the chances of data loss or corruption.
By employing these strategies, you can confidently and efficiently transfer your files and folders between Windows and Linux environments, allowing for a seamless transition without the loss of valuable data.
Step-by-step guide for a successful Migration
When transitioning your digital files and important documents from one operating system to another, it is essential to follow a carefully laid out plan to ensure a smooth and successful transfer. In this section, we will provide you with a step-by-step guide that will help you navigate through the migration process without any hassle or data loss.
1. Preparing for Migration
Before beginning the migration process, it is crucial to gather all the necessary information and tools you will need for a seamless transfer. This includes identifying the specific data you want to migrate, such as documents, photos, or software installations, and making sure you have ample storage space available for the transfer.
2. Backing up Your Data
Prior to the actual migration, it is highly recommended to create a backup of all your data to ensure its safety in case of any unforeseen circumstances. Backing up your data will act as an insurance policy in case of accidental data loss during the transfer process.
3. Transferring Files
Once you have completed the necessary preparations and backed up your data, it is time to initiate the actual transfer process. This step involves selecting the appropriate transfer method, such as using an external hard drive, cloud storage services, or a local network connection, and following the instructions specific to your chosen method.
4. Verifying Data Integrity
After the transfer is complete, it is crucial to verify the integrity of the transferred data to ensure that no files were lost or corrupted during the migration process. This step involves cross-checking the transferred data with the original files and running integrity checks using available tools to ensure the accuracy and completeness of the transferred data.
5. Adjusting Settings and Applications
Upon successful data transfer, it is essential to review and adjust settings and applications to ensure optimal performance and compatibility with the new operating system. This step might include reinstalling software, configuring preferences, and updating drivers to maximize functionality on your new Linux system.
By following these step-by-step instructions, you will be able to smoothly transfer your data to Linux without any loss or inconvenience. Be sure to take your time, follow the provided guidelines carefully, and enjoy the benefits of using Linux as your new operating system!
[MOVIES] [/MOVIES] [/MOVIES_ENABLED]FAQ
What are the different ways to transfer data from Windows to Linux?
There are several ways to transfer data from Windows to Linux. One way is to use a USB drive or an external hard drive to transfer the files. Another way is to use a network file transfer protocol like FTP or SFTP. Additionally, you can use cloud storage services like Google Drive or Dropbox to upload the files from Windows and then download them on your Linux machine.
Can I transfer my files using a network cable?
Yes, you can transfer files from Windows to Linux using a network cable. This method is known as a direct network transfer, where you connect the two computers with a crossover Ethernet cable. Once connected, you need to configure the network settings on both Windows and Linux machines and then transfer the files using file transfer protocols like FTP or SFTP.
Is it possible to transfer installed applications from Windows to Linux?
No, it is not possible to directly transfer installed applications from Windows to Linux. Windows and Linux are two different operating systems with different file structures and compatibility requirements. Therefore, you will need to reinstall the applications on your Linux machine using Linux-compatible versions or alternatives of the same applications.




