In the intricate labyrinth of a modern computer network, where information constantly flows like an intricate dance, one cannot undermine the importance of an organizational framework that seamlessly connects and manages all the elements. The concept of a digital ecosystem that houses integral resources, from user accounts to shared files, has given birth to a powerful tool known as directory services. This remarkable technology, deeply interwoven into the fabric of a Windows-based domain, acts as a central nerve center, orchestrating the harmonious collaboration between various network components.
Similar to a conductor who effortlessly guides an orchestra, directory services provide a rich assortment of capabilities that revolutionize the way organizations handle users, devices, and assets. With its unassuming yet commanding demeanor, directory services ensure the smooth functioning of a network domain by offering a secure repository for essential information. By establishing a comprehensive directory structure, organizations can create a hierarchical arrangement that not only simplifies management but also enables efficient and precise access control to vital resources.
Intertwined within the digital DNA of a directory service lies the potential to enhance productivity and streamline operations. By leveraging a myriad of features, such as user authentication, permissions management, and seamless integration with other enterprise systems, these services empower administrators to effortlessly execute critical tasks. Whether it is the creation of user accounts with a mere stroke of a key or the enforcement of finely-grained security policies, the versatility of directory services uplifts the efficiency of system administrators to new heights.
The Significance of Active Directory in the Management of a Windows Domain
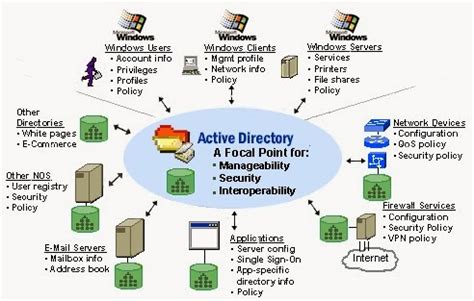
In the realm of IT infrastructure, an essential component plays a pivotal role in the effective administration of a network of computers operating on a specific operating system. This crucial element, characterized by its efficient organization and seamless coordination, holds an immense influence on the successful management of a network or a system.
Recognized for its indispensable impact, Active Directory serves as the cornerstone of a Windows domain management, facilitating the integration and synchronization of multiple resources within a network. Its fundamental purpose revolves around centralizing and organizing the vast range of data, user accounts, and network resources, all in one unified directory system. This consolidation enables administrators to efficiently manage and regulate access, ensuring seamless connectivity and secure operations.
Streamlined Administration: Active Directory simplifies network administration by providing a centralized platform that empowers administrators to efficiently control access, supervise user accounts, allocate network resources, and standardize configurations. This streamlined approach eliminates the need for individual management of each component, reducing complexity and enhancing overall efficiency.
Seamless Resource Access: Through Active Directory's robust access control mechanisms, network resources can be allocated and made available to authorized users conveniently. By imposing security policies, administrators can regulate access levels based on user profiles, granting permissions to specific resources and limiting unauthorized access. This ensures the seamless availability of resources while safeguarding the network against potential vulnerabilities.
Enhanced Security: Active Directory serves as a robust security mechanism, implementing various authentication and authorization protocols to ensure data integrity and prevent unauthorized access. By enforcing password policies, encryption standards, and two-factor authentication, it fortifies the authentication process, reducing the risk of security breaches and safeguarding sensitive information within the Windows domain.
Efficient Collaboration: Active Directory promotes effective collaboration among network users by facilitating the creation and management of shared resources. Features such as group policies and distribution lists enable efficient communication and enable users to collaborate seamlessly, fostering productivity and teamwork within the Windows domain.
Overall, the importance of Active Directory in managing a Windows domain cannot be overstated. Its versatility, security enhancements, centralized administration, and seamless resource access enable organizations to optimize their network management, increase productivity, and uphold a secure and efficient IT infrastructure.
Understanding Active Directory: A Centralized Directory Service
To comprehend the essence of Active Directory, it is essential to gain insight into its fundamental architecture and core functionality. Active Directory serves as a centralized and interconnected directory service that plays a pivotal role in organizing and managing a network's resources, facilitating user authentication, and enabling seamless access to various network services.
The Essence of Centralization: Active Directory embodies the concept of centralization, acting as a central repository that stores and maintains vital information about network resources, including users, computers, printers, and other network objects. By consolidating this information into a single location, Active Directory simplifies network administration, improves security, and enhances collaboration among network entities.
Paving the Path for Efficient Resource Management: Active Directory enables efficient resource management by providing a hierarchical structure that organizes objects into logical containers, such as domains, organizational units (OUs), and sites. This hierarchical organization enables systematic administration and delegation of responsibilities, ensuring efficient resource allocation, and reducing administrative burdens.
Authentication and Access Control: Active Directory serves as the cornerstone for user authentication and access control. It verifies the identity of users, ensuring secure access to network resources and services based on user permissions and policies. By establishing a centralized authentication mechanism, Active Directory enhances network security and simplifies user management.
Seamless Integration with Network Services: In addition to its core functions, Active Directory seamlessly integrates with various network services, including DNS (Domain Name System) and DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol). This integration ensures efficient and reliable name resolution, IP address assignment, and other essential network functionalities, promoting seamless communication and connectivity within the network environment.
Empowering Collaboration and Exchange: By providing a global address list and supporting features like email distribution groups and calendars, Active Directory enables effective collaboration and exchange within an organization. It fosters communication and streamlines workflows, enhancing productivity and facilitating seamless information sharing among network users.
The Power of Active Directory Federation Services (ADFS): Active Directory Federation Services expands the reach of Active Directory beyond organizational boundaries, facilitating secure single sign-on authentication and authorization for external users. ADFS enables organizations to extend their Active Directory services to partner organizations, allowing seamless access to shared resources without compromising security.
In summary, Active Directory serves as a centralized directory service that offers efficient resource management, robust authentication and access control, seamless integration with network services, and enhanced collaboration capabilities. Understanding the core functionality and significance of Active Directory is crucial in comprehending its role and impact within a Windows domain.
Advantages of utilizing Active Directory in a Windows Domain Environment

In today's interconnected digital landscape, the implementation of a robust and efficient directory service can prove to be an invaluable asset for any organization. Active Directory, as a fundamental component of a Windows domain environment, offers a multitude of benefits that enhance the security, scalability, and management of an organization's network resources.
Enhanced Security: Active Directory provides a secure and centralized authentication mechanism, ensuring that only authorized individuals can access the network resources. By enforcing strong password policies, implementing multi-factor authentication, and granting access based on individual roles and responsibilities, Active Directory helps safeguard sensitive data and mitigate security risks.
Streamlined User Management: Active Directory simplifies the management of user accounts and access permissions across the Windows domain environment. Administrators can efficiently create, modify, or disable user accounts, assign group memberships, and control access rights. This centralized approach saves time, reduces the potential for errors, and ensures consistent user management practices.
Scalability and Flexibility: Active Directory supports the seamless expansion of the Windows domain environment as an organization grows. With the ability to manage thousands of objects, such as users, computers, and resources, Active Directory enables efficient scalability without sacrificing performance. Additionally, its flexible organizational structure allows for the customization and adaptation of directory services to suit specific business requirements.
Integrated Resource Management: Active Directory consolidates the administration of network resources by providing a structured and hierarchical framework. It enables centralized management of shared folders, printers, applications, and other network services. This integration simplifies the deployment, maintenance, and tracking of resources, resulting in increased efficiency and productivity.
Group Policy Management: Active Directory's Group Policy feature enhances the control and management of Windows-based desktops and servers within a domain environment. It allows administrators to define and enforce policies, such as security settings, software installations, and remote management configurations, across multiple computers. This centralized control ensures consistent configurations and reduces the complexity of managing individual systems.
Audit and Reporting Capabilities: Active Directory offers comprehensive auditing and reporting features that enable organizations to monitor and track user activities, changes to directory objects, and security events. These capabilities assist in complying with regulatory requirements, identifying security breaches, and troubleshooting issues within the Windows domain environment.
In summary, Active Directory in a Windows domain environment provides numerous advantages including enhanced security, streamlined user management, scalability and flexibility, integrated resource management, group policy management, and audit and reporting capabilities. By leveraging these benefits, organizations can establish a robust and efficient network infrastructure that facilitates secure access, simplified management, and improved productivity.
Centralized User Management with Active Directory
In the realm of network administration, streamlining user management can prove to be a challenging task. However, by leveraging the power of Active Directory, organizations can effectively centralize all aspects of user management, resulting in increased efficiency and improved security.
With Active Directory's centralized user management capabilities, administrators can easily create, modify, and revoke user accounts. This eliminates the need for manual updates on individual machines, thereby saving time and reducing the likelihood of errors. Additionally, the use of Active Directory enables administrators to implement consistent security policies across the entire network, ensuring that user access rights are appropriately assigned and regularly reviewed.
Active Directory offers a hierarchical structure, allowing organizations to group users based on various criteria such as departments, locations, or job roles. This hierarchical organization simplifies user management by enabling administrators to make changes at the appropriate level, propagating them down to all relevant users and devices. Furthermore, Active Directory's support for organizational units allows for granular delegation of administrative tasks, offering greater control and flexibility to different teams within the organization.
Another key feature of Active Directory is its integration with other Windows services and applications. This integration enables seamless user authentication and authorization across the network, eliminating the need for users to remember multiple sets of credentials. By leveraging Active Directory, organizations can achieve a single sign-on experience, enhancing user productivity and reducing the risk of password-related security incidents.
In summary, Active Directory plays a vital role in centralized user management within a Windows domain. By providing a consolidated platform for user administration, security enforcement, and integration with other services, Active Directory simplifies user management, enhances security, and improves overall network efficiency.
Enhancing Authentication and Authorization Processes with Active Directory
In this section, we will explore the vital role played by Active Directory in simplifying and improving the way authentication and authorization processes are handled within a Windows-based network environment. We will delve into how Active Directory streamlines user management, centralizes access control, and enhances security within the organization.
- Streamlining User Management: Active Directory enables organizations to efficiently manage user accounts and their associated permissions. By centralizing this process, it eliminates the need for multiple user profiles and simplifies the task of granting or revoking access to various resources within the network.
- Centralized Access Control: With Active Directory, administrators can implement a unified access control system that covers all Windows domain resources. This centralized approach allows for consistent application of security policies and ensures that access privileges are managed effectively across the network.
- Enhanced Security: Active Directory provides robust security features that contribute to a secure network environment. It offers authentication protocols, such as Kerberos, that authenticate user identities and prevent unauthorized access. Additionally, Active Directory supports the encryption of sensitive data, ensuring confidentiality and integrity during transmission.
- Simplified Integration: Active Directory seamlessly integrates with various Microsoft services, such as Exchange Server and SharePoint, resulting in a streamlined authentication and authorization experience for users. This integration eliminates the need for separate authentication mechanisms and simplifies the management of user accounts and access rights across different platforms.
By leveraging the capabilities of Active Directory, organizations can optimize their authentication and authorization processes, leading to increased efficiency, stronger security, and a more streamlined network environment.
Simplifying Configuration Management with Group Policy and Active Directory
In the world of enterprise IT environments, efficient configuration management is crucial for maintaining the stability and security of systems and networks. Group Policy, a powerful feature of Active Directory, offers a simplified approach to managing configuration settings across Windows domains.
By leveraging the capabilities of Group Policy within Active Directory, organizations can centrally manage and enforce various configuration settings, policies, and security controls for their networked computers and users. The group policy framework provides a flexible and scalable platform that enables administrators to define and apply specific settings to different organizational units, groups, or users, streamlining the overall configuration management process.
With Group Policy, organizations can enforce security policies, control user access, manage application installations and updates, and configure various system settings, such as network configurations, power options, and desktop preferences. This centralized approach eliminates the need for manual configuration changes on individual machines, reducing administrative overhead and ensuring consistency across the network.
Furthermore, Group Policy enables administrators to create and manage custom templates called Group Policy Objects (GPOs), which contain specific configuration settings and policies. These GPOs can be linked to different Active Directory containers to target specific sets of users or computers, providing granular control over configuration management. Changes made to GPOs are automatically propagated to the targeted computers or users, ensuring efficient and consistent enforcement of policies.
In addition to simplifying configuration management, Group Policy offers enhanced security by allowing administrators to enforce security policies, such as password complexity requirements, account lockout policies, and software restriction policies. These security controls help organizations protect against unauthorized access, malware, and other potential threats.
In summary, Group Policy's integration with Active Directory simplifies the process of configuration management by providing a centralized platform for defining and enforcing configuration settings, policies, and security controls. With its ability to manage and apply settings at various levels of granularity, Group Policy offers organizations a powerful tool for maintaining consistency, security, and efficiency in their Windows domains.
Scalability and Interoperability Through Active Directory Domain Services
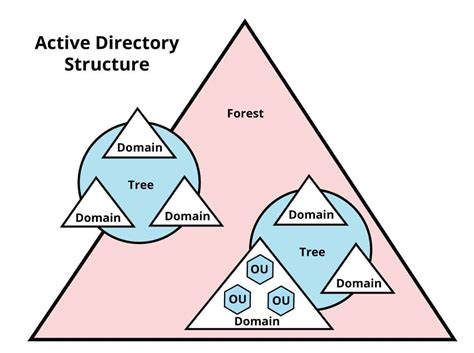
Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) plays a crucial role in empowering organizations with the ability to efficiently expand their network infrastructure and ensure seamless integration between different systems and platforms.
| Enhanced Scalability | Improved Interoperability |
|---|---|
| With AD DS, businesses can effortlessly scale their network environment by adding or removing resources, such as users, computers, and servers, without disturbing the overall system functionality. This scalability ensures that enterprises can easily adapt to changing requirements and accommodate future growth. | AD DS facilitates interoperability by providing a standardized platform for integrating diverse applications and services. It offers a common authentication and authorization mechanism, allowing various systems to seamlessly communicate and share resources securely. This promotes interoperability between different software applications and devices, streamlining business processes and promoting collaboration. |
By harnessing the features of AD DS, organizations can build a robust and scalable network infrastructure that enables them to efficiently manage resources while ensuring seamless interoperability between different systems and platforms.
Ensuring High Availability and Redundancy in Active Directory Replication
In this section, we will explore the significance of maintaining high availability and redundancy in the replication process of the versatile Active Directory system. We will delve deep into the crucial role of replication in ensuring the smooth functioning of organizational networks and the importance of implementing advanced strategies to guarantee seamless data synchronization among domain controllers.
- Importance of Active Directory Replication
- Replication Topology Design
- Implementing Redundancy for Disaster Recovery
- Utilizing Failover Mechanisms
- Monitoring and Troubleshooting Replication
Active Directory replication serves as the backbone of a reliable and efficient network infrastructure, facilitating the distribution of crucial directory data across multiple domain controllers. It plays a pivotal role in maintaining seamless user authentication, access control, and resource management processes within a diverse organizational ecosystem.
Designing an optimized replication topology is essential to ensure efficient data transmission, balancing network traffic, and reducing latency. The correct configuration of replication partners, connection objects, and replication schedules helps establish a robust framework for data synchronization while efficiently utilizing available network resources.
To safeguard against potential disruptions or failures, implementing redundancy measures is crucial. Taking advantage of redundant domain controllers and Active Directory sites allows organizations to mitigate risks and ensure continuous availability of directory services even in the face of unexpected events or natural disasters.
Failover mechanisms provide further resilience to the replication process by automatically routing traffic to alternative domain controllers in case of primary server failures. Employing failover strategies, such as site link bridging, enables uninterrupted communication between replication partners and enhances overall network reliability.
Continuous monitoring and proactive troubleshooting of replication issues are vital to maintaining a healthy Active Directory environment. Employing monitoring tools, analyzing replication logs, and implementing effective problem-solving techniques help diagnose and resolve potential replication errors, ensuring the integrity and consistency of directory data.
By understanding the significance of high availability and redundancy in Active Directory replication and implementing advanced strategies, organizations can create a resilient and secure network infrastructure to meet the evolving needs of modern-day IT environments.
Data Security in a Windows Domain: Active Directory's Crucial Role

Ensuring the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data is a paramount concern for organizations operating in a Windows domain. Active Directory, a fundamental component of the domain infrastructure, plays a vital role in safeguarding sensitive information and maintaining a secure environment. In this section, we will explore the essential elements of Active Directory's contribution to data security.
- Enhanced Authentication Mechanisms: Active Directory implements robust authentication protocols and mechanisms to verify the identity of users and computers within the domain, preventing unauthorized access attempts.
- Centralized Access Control: Through role-based access control and permission management, Active Directory grants or denies access to resources based on predefined policies, effectively limiting data exposure and minimizing potential security breaches.
- Data Encryption: Active Directory facilitates the encryption of data transmission and storage, ensuring that sensitive information remains protected from interception or unauthorized disclosure.
- Secure Group Policy Implementation: Active Directory's Group Policy feature enables administrators to enforce security configurations, manage user privileges, and set restrictions, thereby enforcing consistent security practices throughout the domain.
- Efficient Auditing and Monitoring: Active Directory offers comprehensive auditing capabilities, allowing organizations to track and review user activities, changes to security settings, and other events, crucial for detecting and mitigating potential security incidents.
By leveraging the powerful functionalities of Active Directory, organizations can establish a robust security framework within their Windows domain, safeguarding critical data from external threats and internal vulnerabilities. The next section will delve deeper into specific strategies and best practices for maintaining data security within the domain environment.
FAQ
What is Active Directory?
Active Directory is a directory service provided by Microsoft that stores information about objects on a network and makes this information available to users and administrators.
Why is Active Directory important in a Windows domain?
Active Directory plays a crucial role in a Windows domain as it provides centralized management and authentication for users, computers, and resources within the network. It simplifies administration tasks and enhances security.
What are the benefits of using Active Directory?
Using Active Directory offers several advantages such as a single sign-on capability, secure access to network resources, easy management of users and groups, efficient delegation of administration tasks, and the ability to implement group policies for consistent settings across the domain.
How does Active Directory work?
Active Directory is based on a hierarchical structure called a directory tree. It uses the Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) to communicate and replicate data between domain controllers. Domain controllers store information about objects in a domain, including users, groups, computers, and organizational units.
Can Active Directory be used in environments other than Windows?
No, Active Directory is a Microsoft technology designed specifically for Windows operating systems. However, there are alternative directory services available for other platforms, such as OpenLDAP for Linux.




