In today's ever-changing world, where connections are the backbone of progress and success, the significance of a compromised link cannot be undermined. This article delves into the intricacies of a disrupted connection, exploring the profound impact it can have on our lives and the elusive mirage it creates.
Imagine a scenario where the delicate bonds that bind our society together begin to disintegrate. With each fragment, a ripple effect ensues, spreading uncertainty and chaos. This intricate web of relationships, like an exquisite tapestry, interweaves our aspirations, ambitions, and aspirations into a complex fabric of existence. However, it is the unforeseen rupture, the moment when the chain breaks, that reveals the true price of such a rupture.
In this enigmatic pursuit, dreams hover just beyond reach, teasing us with their tantalizing allure. As the fragility of human connection becomes apparent, the value of our aspirations intensifies. With every fractured link, the once steadfast reality shatters, leaving behind shards of illusion. The power of what could have been becomes amplified, as our minds navigate through a labyrinth of missed opportunities and alternate futures.
The Effect of Disrupted Supply Systems on Global Economy
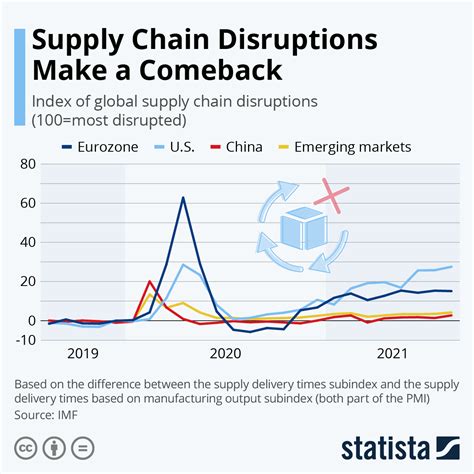
With the intricate web of interconnectedness between countries and industries, supply chains play a vital role in shaping the global economy. When disruptions occur in these supply systems, the consequences can be far-reaching and have substantial impacts on the economic landscape. In this section, we will explore how disruptions in the flow of goods, services, and resources can lead to ripple effects that affect various sectors and countries worldwide.
| Section | Subsection | Key Points |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Global Interconnectivity | a. Importance of Supply Chains | - The intricate network of supply chains |
| b. Globalization and Supply Chains | - How globalization has intensified supply chain dependencies | |
| 2. Disruptions in Supply Chains | a. Natural Disasters | - The impact of natural disasters on supply chains |
| b. Political and Economic Instability | - How political and economic instability affects supply chain operations | |
| 3. Economic Consequences | a. Loss of Productivity | - Decreased production and output due to disrupted supply chains |
| b. Financial Implications | - Economic losses and financial burdens on businesses and governments |
This section will delve into the interconnected nature of global supply chains, examining the importance of these chains in facilitating the movement of goods and services. Additionally, it will explore how globalization has intensified these dependencies, making disruptions in supply chains even more detrimental to the global economy.
We will then shift our focus towards various factors that can disrupt supply chains, ranging from natural disasters that can halt production and transportation, to political and economic instability that can disrupt trade flows and lead to the breakdown of supply systems.
Finally, we will discuss the economic consequences of disrupted supply chains. This includes a significant loss of productivity, as businesses struggle to obtain the necessary inputs for their operations, leading to reduced output and revenue. Additionally, we will analyze the financial implications of these disruptions, examining the economic losses incurred by businesses and the burden placed on governments to mitigate the impacts.
Impact of Supply Chain Breakdowns on Global Businesses and Economies
In the context of the theme, "The Price of a Broken Chain: A Dreamed Reality," this section explores the far-reaching consequences of disruptions in supply chains on businesses and economies at a global scale. By examining the various repercussions caused by breakdowns in the complex network of global supply chains, this article sheds light on the profound effects experienced by organizations and economies worldwide.
Supply chains form the backbone of modern businesses, connecting suppliers, manufacturers, distributors, and customers across different geographies. When supply chains break down due to unforeseen circumstances, such as natural disasters, political conflicts, or economic crises, businesses face numerous challenges that can have a significant impact on their operations and financial stability. These disruptions can lead to delayed or canceled orders, inventory shortages, increased costs, loss of customer trust, and damaged reputation.
The consequences of supply chain breakdowns are not limited to individual businesses; they reverberate throughout the global economy. Interruptions in the flow of goods and services can cause ripple effects across sectors and countries, impacting trade, employment, and economic growth. For instance, a shortage of key components from one region can affect the production capabilities of companies worldwide, leading to reduced output and lower consumer demand.
Moreover, supply chain disruptions can amplify vulnerabilities in global economies, exposing their heavy reliance on interconnected networks. As supply chains become increasingly complex and extended, the potential for vulnerability and disruption magnifies. The COVID-19 pandemic serves as a recent example, with lockdowns and travel restrictions causing significant disruptions in global supply chains, revealing the fragility of interconnected economies and underscoring the need for resilience and contingency planning.
| Impact on Businesses | Impact on Economies |
|---|---|
| Delayed or canceled orders | Trade disruptions |
| Inventory shortages | Economic contraction |
| Increased costs | Unemployment |
| Loss of customer trust | Reduced consumer spending |
| Reputational damage | Exposure of vulnerabilities |
Therefore, it is crucial for businesses and governments to address the risks associated with supply chain disruptions and develop strategies to enhance resilience. Collaborative efforts, supply chain diversification, technological advancements, and improved contingency planning can help mitigate the adverse effects of breakdowns in supply chains, ensuring the stability and sustainability of businesses and economies.
Environmental Impact of Global Production: Unanticipated Consequences of Unforged Links
Exploring the intricate web of global production unveils an astounding array of environmental repercussions. The intricately intertwined supply chains that span across continents and sectors contribute significantly to the growing ecological crisis we face today. This section delves into the far-reaching environmental consequences that emerge as a consequence of fractured links within this expansive network.
Global production, akin to a colossal tapestry delicately woven with countless threads, binds together nations, industries, and commodities. However, the inherent fragility of this interconnected system becomes evident as weak links are exposed. The disruption caused by these broken chains permeates various facets of the environment, leaving lasting scars on ecosystems, natural resources, and even human health.
One such consequence is the accelerated depletion of finite resources through increased extraction and manufacturing processes necessitated by disjointed supply chains. This relentless pursuit of efficiency and profit often neglects the impact on natural habitats and biodiversity. As chains fracture and new connections are forged, the extraction of raw materials intensifies, leading to deforestation, habitat destruction, and a loss of biodiversity that irreversibly alters ecosystems worldwide.
Exploring the Ecological Consequences of Fractured Supply Chains and Unsustainable Practices
In this section, we will delve into the wide-ranging environmental impacts that arise from the disruption of supply chains and the adoption of unsustainable practices. We will examine the interconnectedness of these factors and their profound implications for our ecosystems and natural resources.
The Ripple Effect of Supply Chain Disruptions
When supply chains break down or become inefficient, the consequences reverberate throughout the ecosystem. Disruptions can lead to increased waste, pollution, and resource depletion, causing irreparable damage to fragile environments. By analyzing the underlying causes and consequences of these fractures, we gain a deeper understanding of the urgency to foster resilient and sustainable supply chains.
The Unseen Price on Biodiversity
Unsustainable practices, such as overexploitation of natural resources or habitat destruction, have a lasting impact on biodiversity. Ecosystems are intricately interconnected, and when one species is affected, it sets off a domino effect that can lead to the destabilization of entire ecosystems. We will explore the implications of disregarding the delicate balance of nature and the potential loss of irreplaceable plant and animal species.
Unveiling the Plight of Climate Change
Broken supply chains and unsustainable practices contribute significantly to climate change. From carbon emissions resulting from inefficient transportation and energy usage to deforestation caused by unsustainable agricultural practices, the ecological consequences are vast. We will examine the intricate web of cause and effect between human activities, climate change, and the potential for irreversible damage to our planet.
| Potential Ecological Impacts | Examples |
|---|---|
| Erosion and Soil Degradation | Clear-cutting forests without proper reforestation leads to soil erosion, diminishing agricultural productivity. |
| Pollution | Discharge of toxic chemicals into bodies of water harms aquatic life and contaminates the surrounding ecosystem. |
| Loss of Biodiversity | The destruction of natural habitats forces species into smaller areas, increasing the risk of extinction. |
| Water Scarcity | Unsustainable water usage in agriculture and industrial processes depletes water sources, threatening ecosystems and human livelihoods. |
The Human Toll of Delicate Supply Networks in Emerging Economies

Supply chains are complex systems that connect various actors across the world, facilitating the movement of goods and services. However, in the context of developing countries, these supply chains often come at significant human costs. This section delves into the profound implications of fragile supply networks on the people living in emerging economies, shedding light on the challenges and vulnerabilities they face.
Vulnerable Labor Force: The fragility of supply chains in developing countries can lead to exploitative labor practices, putting the livelihoods of workers at risk. Faced with limited employment alternatives, individuals often find themselves in precarious working conditions, lacking proper job security and fair wages. This situation makes it difficult for workers to break out of the cycle of poverty, perpetuating a system that prioritizes profit over their well-being.
Fragile Health and Safety Standards: Inadequate implementation of health and safety regulations is another consequence of delicate supply chains in emerging economies. Without proper safeguards in place, workers are subjected to hazardous working conditions, risking their physical and mental well-being. The absence of comprehensive safety measures not only jeopardizes the lives of individuals but also negatively impacts their families and communities, leading to a spiral of health-related issues that further burden already strained healthcare systems.
Impacts on Local Communities: The human toll of fragile supply chains extends beyond the immediate workforce. Entire communities bear the brunt of these vulnerabilities, as the lack of stable job opportunities and reliable income sources creates a cycle of poverty and dependency. Local economies suffer as a result, with limited prospects for growth and development. The social fabric of these communities undergoes a transformation, as individuals face increased hardships and limited access to basic necessities, such as education and healthcare.
Gender Inequality: Fragile supply chains in developing countries often exacerbate existing gender inequalities. Women, in particular, face numerous challenges, including limited access to employment, unequal pay, and discrimination. The exploitation of female workers is prevalent in certain industries, perpetuating harmful stereotypes and hindering progress towards gender equality. Breaking the chains of these gender disparities requires transformative policies and empowerment initiatives that prioritize inclusivity and equal opportunities.
The human cost of fragile supply chains in developing countries is immense. It is crucial to address the systemic issues that perpetuate these vulnerabilities and work towards a more equitable and sustainable global supply network that prioritizes the well-being and rights of individuals.
Examining the Societal and Economic Ramifications Faced by Vulnerable Communities
In this section, we delve into the profound effects experienced by marginalized populations as a result of their vulnerable status within society. By exploring the social and economic consequences they encounter, we aim to shed light on the dire circumstances faced by these groups and highlight the urgent need for systemic change.
Social Consequences
- Dispossession of basic human rights
- Isolation and marginalization
- Stigmatization and discrimination
- Lack of access to quality education
- Breakdown of community cohesion
Economic Consequences
- Widespread poverty and financial insecurity
- Limited job opportunities and employment discrimination
- Inequality in income and wealth distribution
- Impediments to economic growth and development
- Increased reliance on social welfare programs
These social and economic consequences act as a cycle, perpetuating the vulnerability of individuals and communities. The lack of necessary resources, support systems, and opportunities trap vulnerable populations in a vicious cycle of disadvantages, making it exceedingly difficult for them to break free from their circumstances.
It is imperative that we recognize and address these consequences in order to cultivate inclusive societies that prioritize equity and justice for all. By understanding the complex web of challenges faced by vulnerable populations, we can work towards implementing policies and initiatives that uplift, empower, and ensure the well-being of all individuals within our society.
FAQ
What is the article "The Price of a Broken Chain: A Dreamed Reality" about?
The article explores the consequences and costs of a broken chain in achieving one's dreams and turning them into reality.
How does a broken chain affect one's ability to achieve dreams?
A broken chain hinders one's progress and prevents them from reaching their goals. It creates obstacles and setbacks that can be costly in terms of time, effort, and even personal growth.
What are some examples of a broken chain mentioned in the article?
The article mentions examples such as lack of motivation, self-doubt, external distractions, and fear of failure as common factors that contribute to a broken chain.
How can one repair a broken chain and regain focus?
Repairing a broken chain requires self-reflection, determination, and taking proactive steps to overcome the obstacles. This may involve seeking support, setting specific goals, and developing a resilience mindset.
What is the importance of maintaining a strong chain in achieving dreams?
Maintaining a strong chain is crucial as it ensures consistency, progress, and resilience in the pursuit of dreams. It provides a foundation for success and helps individuals stay on track even in the face of challenges.




