Embark on a captivating exploration into the wondrous realm of reproduction in the diverse inhabitants of our planet. This comprehensive compendium serves as a cornerstone of knowledge, shedding light on the intricate and awe-inspiring phenomenon of animal pregnancy.
Discover the mysteries of conception, the delicate intricacies of fetal development, and the astonishing adaptations that occur during the gestational period. Dive into an abyss brimming with fascinating facts and extraordinary tales, where each species unveils its own astonishing journey towards bringing new life into the world.
Delve into the secrets of maternal care, as we unravel the remarkable strategies adopted by various animal mothers to safeguard the well-being of their unborn young. Witness the tireless efforts and selflessness exhibited by these expectant mothers, as they chart their path towards ensuring the survival of their offspring.
Exploring the Physiology of Animal Gestation

In the following section, we will delve into the intricate workings of the reproductive processes that occur within various living organisms. By examining the physiological aspects of animal gestation, we can gain a deeper understanding of the remarkable mechanisms that drive these miraculous journeys of life.
Embarking on a Journey of Creation and Nurturing
The intricate physiology of animal pregnancy involves a series of complex events and processes that pave the way for the creation and nurturing of life. From the initial fertilization of gametes to the development and growth of the fetus, each stage brings its own set of unique challenges and adaptations.
The Miracle of Conception: Fertilization and Implantation
The journey begins with the union of a male and female gamete, resulting in fertilization. This captivating process sets in motion a cascade of events, leading to the implantation of the fertilized egg into the uterus or another site suitable for development. Various factors influence the successful attachment of the embryo, including hormonal signaling and uterine receptivity.
Organogenesis: The Marvels of Development
During the period of organogenesis, the developing embryo undergoes a remarkable transformation. Specialized cells differentiate, forming the foundation for the various organs and systems that will sustain and support life. A delicate balance of genetic programming, environmental cues, and maternal support shapes the intricate structures and functions that will define the offspring as it grows.
Pregnancy Adaptations: Nurturing and Protecting Life
In preparation for nurturing the growing fetus, various adaptations occur in the pregnant animal's body. These adaptations help maintain the appropriate environment for optimal development, providing necessary nutrients, immunological protection, and hormonal regulation. From the expansion of the uterus to accommodate the growing fetus to hormonal shifts that regulate various physiological processes, the mother's body tirelessly supports the thriving life within.
Parturition: The Magical Moment of Birth
After months of growth and development, the time arrives for the culmination of the pregnancy journey – parturition. This awe-inspiring event involves a series of intricate hormonal and physical changes that initiate labor and facilitate the safe delivery of the newborn. From contractions to the rupture of the amniotic sac, every step is orchestrated to ensure a smooth transition from the womb into the world.
By exploring the fascinating physiology behind animal pregnancy, we can gain a newfound appreciation for the intricate processes that bring life into existence. Each species presents its own unique adaptations and strategies, ensuring the survival and continuation of its kind. Understanding these physiological components allows us to marvel at nature's brilliance and appreciate the diverse miracles of life.
Diverse Approaches to Animal Reproduction
In the natural world, the creation of new life takes on myriad forms and strategies across different species. From the mountains to the depths of the oceans, animals employ a wide array of reproductive techniques to ensure the survival of their kind. This section delves into the fascinating world of animal reproduction, exploring the various methods employed by different creatures to procreate.
Variations in Reproductive Structures
One of the key factors that differentiates animal reproduction is the diversity in reproductive structures. While many species rely on the classic male-female pairing for reproduction, others exhibit intricate differences in their reproductive anatomy. Some possess specialized organs, such as the avian oviduct or the mammalian uterus, that play crucial roles in the reproductive process. On the other hand, certain creatures have developed unique adaptations, like the egg-laying capabilities of monotremes or the asexual reproduction seen in certain invertebrates.
Mating Rituals and Behavior
Another interesting aspect of animal reproduction is the wide range of mating rituals and behavior exhibited by different species. From elaborate courtship displays to complex mating dances, animals have developed ingenious strategies to attract and select mates. Some species engage in fierce competition among males, while others rely on intricate sensory signals and pheromones to communicate their reproductive readiness. Understanding these diverse behaviors not only sheds light on the complexity of animal courtship, but also provides insights into the evolution of reproductive strategies.
Reproductive Success and Strategies
The ultimate goal of all reproduction is to ensure the survival and propagation of offspring. Different species employ varied reproductive strategies in order to maximize their chances of reproductive success. Some animals produce large numbers of offspring, relying on sheer numbers to increase the likelihood of survival. In contrast, others invest significant time and energy into nurturing a smaller number of offspring, ensuring their survival through parental care. By examining these diverse reproductive strategies, we gain a deeper appreciation for the remarkable adaptations and behaviors that support the continuation of life across the animal kingdom.
As we explore the different types of animal reproduction, it becomes clear that nature's ingenuity knows no bounds. The wide range of reproductive techniques observed in the animal kingdom showcases the immense diversity and resilience of life on Earth.
The Duration of Gestation in Popular Domesticated Creatures
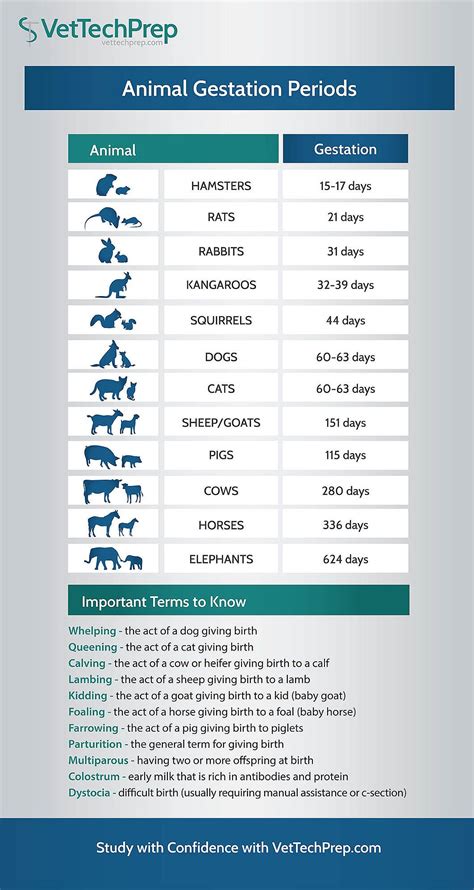
Within the realm of companions that dwell within our human abodes, a fascinating aspect of their reproductive journey is the length of time they carry their young within them. This section delves into the diverse range of gestation periods observed in various well-loved domestic creatures, providing an insight into the wonders of nature's reproductive workings.
1. The Canine Cohort:
- Dogs, our faithful four-legged friends, carry their developing pups for approximately 58 to 68 days.
- Our playful feline companions, known as cats, undergo a gestation period of approximately 63 to 65 days as they nurture their precious kittens.
- Equines, the majestic horses, embody patience as their gestational period spans from 320 to 370 days, paving the way for the birth of a strong foal.
- In the world of bovines, cows graciously harbor their future calves for approximately 279 to 290 days, a testament to their nurturing spirit.
2. The Avian Family:
- As feathered wonders, chickens entrust the incubation of their eggs to the world for a span of 21 days before adorable chicks emerge.
- In contrast, the enigmatic ostriches engage in a lengthier gestation period, spanning approximately 42 to 46 days, leading to the hatching of their magnificent offspring.
3. The Small Mammal Cohort:
- Rabbits, known for their prolific breeding, go through a relatively short gestation period, lasting about 28 to 32 days, preparing for the arrival of an energetic litter.
- Rodents such as mice and rats display swift reproductive cycles, with gestation periods ranging from 19 to 23 days, ensuring a continuous presence of their tiny offspring.
- Guinea pigs, cherished for their gentle nature, encounter a journey of around 59 to 70 days before welcoming their endearing pups.
4. The Loyal Cattle:
- Gentle giants like elephants bear an incredible gestation period, extending between 630 to 660 days, highlighting their astonishing dedication as they await the arrival of their majestic calves.
- Comparatively, the attentive giraffes traverse a gestation period of approximately 400 to 460 days before greeting their long-necked offspring.
Understanding the varying durations of gestation among popular domesticated creatures not only deepens our appreciation for the intricate wonders of nature but also enables us to witness the beauty and diversity of life's creation.
Unique Challenges of Pregnancy in Marine Mammals
Pregnancy presents distinctive hurdles for marine mammals, who reside in an aquatic environment and belong to a diverse group of species. These challenges differ from those faced by land-dwelling animals due to the specific adaptations required for reproduction in water.
- Water-based adaptations: Marine mammals must navigate the complexities of gestation and birth in a fluid environment, which necessitates specialized adaptations to ensure the survival of offspring.
- Birthing strategies: Unlike some terrestrial animals, marine mammals usually give birth to live young rather than laying eggs. This requires distinct anatomical and physiological adaptations to facilitate the successful birth and immediate care of newborns in water.
- Thermoregulation: Maintaining the appropriate body temperature is crucial for both the mother and developing fetus in the marine environment, which presents its own challenges due to the thermal properties of water.
- Nutrition and energy requirements: Pregnancy in marine mammals necessitates efficient energy transfer from the mother to the developing fetus. The unique diet and feeding behaviors of these animals further complicate the nutritional aspects of pregnancy.
- Migratory patterns and habitats: Many marine mammals undertake extensive migrations or inhabit specific ecological niches during pregnancy, which can introduce additional challenges related to finding suitable breeding grounds and avoiding predation.
- Impact of human activities: The presence of human activities such as pollution, noise, and climate change poses additional risks and challenges for pregnant marine mammals, potentially affecting their reproductive success and the overall population dynamics.
Understanding and addressing the unique challenges faced by marine mammals during pregnancy is crucial for the conservation and management of these remarkable creatures in their natural habitats.
Exploring Adaptations to Pregnancy in Challenging Environments

Surviving and thriving during pregnancy is a remarkable feat for animals across the globe, but those residing in extreme environments face even greater challenges. This section delves into the fascinating adaptations that enable animals to carry and nurture their young in environments that push the boundaries of what seems possible.
1. Adapting to Harsh Climate: In extreme cold or hot environments, animals have evolved unique strategies to protect their developing offspring. From insulating fur and blubber in Arctic mammals to increasing blood flow near the skin's surface in desert dwellers, diverse adaptations ensure the survival of both mother and fetus.
2. Navigating Food Scarcity: Pregnancy in environments with limited resources presents a formidable obstacle. Some animals have developed remarkable abilities to conserve energy, adjust metabolic rates, and efficiently extract nutrients from scarce food sources, allowing them to sustain both themselves and their growing offspring.
3. Overcoming Altitude Challenges: High altitudes pose distinctive challenges to animals during pregnancy, including reduced oxygen levels. Certain species have ingenious adaptations, such as increased red blood cell production, larger lungs, and efficient oxygen utilization, enabling them to cope with the demanding conditions and successfully reproduce at great heights.
4. Enduring Water Scarcity: Pregnancy in environments devoid of water presents significant hurdles. Various animals possess extraordinary water-saving mechanisms, such as efficient kidneys and the ability to extract moisture from their food, enabling them to endure extended periods without access to water while ensuring the development of their young.
Understanding how animals adapt to pregnancy in extreme environments not only reveals the wonders of natural selection but also provides valuable insights into the limits of reproductive success. By adapting to these challenging conditions, these animals demonstrate the remarkable resilience and adaptability of life itself.
The Importance of Hormones in Animal Gestation
Understanding the intricate mechanisms behind animal gestation involves delving into the pivotal role that hormones play throughout the reproductive process. Hormones, the chemical messengers of the body, orchestrate a complex symphony of events and transformations necessary for successful pregnancy in various species.
One of the key hormones involved in animal gestation is progesterone, which is responsible for preparing and maintaining the uterine environment. It assists in thickening the lining of the uterus, creating an ideal environment for implantation and nourishment of the developing fetus. Progesterone also helps suppress the maternal immune response, ensuring the embryo is not rejected as a foreign entity.
| Hormone | Function | Effects on Pregnancy |
|---|---|---|
| Estrogen | Stimulates uterine growth | Supports fetal development |
| Relaxin | Loosens ligaments and pelvic muscles | Prepares the birth canal for delivery |
| Prolactin | Promotes milk production | Nurtures the offspring after birth |
Other hormones, such as estrogen, contribute to the growth and development of the uterus, facilitating the expansion necessary for accommodating the growing fetus. Estrogen also plays a role in initiating labor by stimulating uterine contractions.
Additionally, relaxin, a hormone predominantly found in pregnant females, helps to relax ligaments and pelvic muscles, allowing for easier passage of the offspring through the birth canal during delivery.
Prolactin, yet another hormone, triggers the production of milk in the mammary glands, enabling the mother to provide vital nourishment to her young after birth, ensuring their survival and growth.
Understanding the functions and effects of these hormones can provide invaluable insights into the physiology and behavior of animals during the miraculous journey of pregnancy. By unraveling the intricacies of hormonal regulation, scientists and animal caretakers alike can better support and monitor the well-being of pregnant animals, ultimately contributing to the conservation and welfare of various species.
Common Health Issues and Concerns During Animal Gestation

Throughout the course of animal reproduction, various health issues and concerns may arise that require attention and care. The well-being of both the expectant mother and her developing offspring is of utmost importance. This section aims to explore some common challenges that animals may face during pregnancy and offer guidance on how to address them.
1. Nutritional Needs: Proper nutrition is crucial for a healthy pregnancy in animals. The dietary requirements of expectant mothers can vary depending on the species, breed, and stage of gestation. It is essential to provide a balanced and nutrient-rich diet to support the mother's growth and meet the needs of her developing offspring.
2. Hormonal Imbalances: Hormonal changes are an integral part of pregnancy, but imbalances can lead to complications. These imbalances may manifest as fertility issues, irregular cycles, or difficulty with fetal development. Understanding the hormonal fluctuations and identifying any abnormalities can help in managing and resolving these concerns.
3. Gestational Diseases: Just like humans, animals are susceptible to specific diseases during pregnancy. These may include infections, such as uterine infections or sexually transmitted diseases, which can potentially harm both the mother and her unborn offspring. Timely detection, appropriate treatment, and preventive measures are vital in minimizing the risk of gestational diseases.
4. Maternal Stress: Stressors during pregnancy can negatively impact an animal's well-being. Factors such as environmental changes, transportation, and excessive physical exertion can induce stress, leading to complications. Providing a calm and stable environment, regular veterinary check-ups, and ample rest can help alleviate maternal stress and promote a healthy pregnancy.
5. Congenital Defects: Congenital abnormalities can occur in animal pregnancies, affecting the normal development of the offspring. These defects can range from minor to severe and may be genetic or caused by external factors. Proper breeding practices, genetic screenings, and early detection can play a significant role in managing congenital defects and ensuring the health of the offspring.
By being aware of these common health issues and concerns during animal pregnancy, responsible caretakers can take proactive measures to optimize the reproductive journey and ensure the well-being of both the expectant mother and her unborn offspring.
The Fascinating Strategies of Species for Nurturing their Offspring
In the natural world, various species have developed extraordinary strategies to care for and protect their young. These remarkable approaches go beyond the traditional notions of parenting, showcasing the diverse and innovative ways animals nurture their offspring.
1. Maternal Dedication: Some species exhibit astonishing levels of maternal dedication, carrying their unborn young for an extended period. This period often involves intricate physiological adaptations, ensuring the survival and development of the offspring. These remarkable mothers invest substantial time and energy, demonstrating a profound commitment to nurturing their young.
2. Cooperative Parenting: In certain social species, the responsibility for raising the young extends beyond the mother. Cooperative parenting systems, where males and other group members contribute to the care of offspring, have evolved. These cooperative efforts demonstrate the power of communal support and highlight the success achieved through shared responsibilities.
3. Protective Strategies: Many animal species have developed ingenious ways to protect their offspring from predators and environmental hazards. Some construct elaborate nests, while others employ camouflage techniques or utilize physical defenses. These protective strategies help ensure the survival of the vulnerable young, providing a fascinating glimpse into the intricate mechanisms of nature.
4. Extended Education: Some species go beyond basic parental care and offer extended education to their offspring. Through intricate behavioral patterns, young animals learn crucial skills and gain valuable knowledge from their parents. This extended education period paves the way for successful adaptation to their environment, equipping the next generation with essential tools for survival.
5. Unique Nurture Techniques: Nature never ceases to amaze when it comes to nurturing strategies. From specialized milk production in mammals to symbiotic relationships and unique feeding methods, each species has developed its own distinctive ways to provide nourishment to their young. Exploring these various techniques offers insights into the exceptional adaptability and resilience of different animal species.
By examining these fascinating strategies of nurturing and care within the animal kingdom, we gain a deeper appreciation for nature's ingenuity and the remarkable diversity of parental approaches. Understanding these extraordinary behaviors enriches our knowledge of the natural world and enhances our understanding of the complex bond between parents and offspring across species.
FAQ
What are the different stages of pregnancy in animals?
Pregnancy in animals typically has three stages: the pre-implantation stage, the embryonic development stage, and the fetal development stage. During the pre-implantation stage, the fertilized egg travels to the uterus and implants itself. The embryonic development stage involves the formation of organs and tissues, while the fetal development stage focuses on growth and maturation.
How long is the gestation period in different animal species?
The gestation period varies significantly among different animal species. For example, in dogs, the gestation period ranges from 58 to 68 days, while in cats, it is typically around 63 days. In elephants, the gestation period can be as long as 22 months, while rabbits have a gestation period of about 31 days. It is important to note that these are just general estimates and can vary depending on various factors.
What are some common signs of pregnancy in animals?
There are several common signs of pregnancy in animals. These can include changes in behavior, appetite, and weight gain. Some animals may also experience morning sickness or exhibit nesting behaviors. Physical changes such as enlarged mammary glands or a swollen belly can also indicate pregnancy in certain species. However, it is always best to consult a veterinarian for an accurate diagnosis of pregnancy in animals.




