In the ever-evolving landscape of mobile technology, two giants stand out: Apple and Google. Each company has developed its own proprietary operating system, catering to their unique philosophies and user experiences. These distinctive software platforms, known as iOS and Android, offer users a diverse range of features and functionalities.
Individually designed, yet competitively vying for market dominance, iOS and Android present users with distinct advantages and trade-offs. Both operating systems strive to provide seamless performance, intuitive interfaces, and a wide variety of applications. However, each has its own distinct approach towards achieving these goals.
At the core of iOS lies Apple's vision for a tightly controlled and harmonious ecosystem. By integrating hardware and software at a deep level, iOS devices offer a seamless user experience. Apple prioritizes consistency and uniformity across its devices, resulting in a cohesive ecosystem that extends from smartphones to tablets and beyond. This attention to detail and focus on user experience has solidified iOS as a preferred choice for many.
In contrast, Android's ethos revolves around openness and customization. Developed by Google, Android operates on a wider range of devices, allowing for greater flexibility and choice. This open-source approach enables smartphone manufacturers and developers to modify the software, resulting in a vast ecosystem of devices with varying designs, features, and user interfaces. Android's adaptability has garnered it a loyal following among tech enthusiasts and those seeking greater control over their device.
The Evolution of iOS and Android

Over the years, both the iOS and Android platforms have undergone significant transformations, reflecting the constant pursuit of innovation and improvement by their respective developers. This section explores the remarkable journey of both operating systems, tracing their evolution through various versions and highlighting the key milestones along the way.
- Introduction of Revolutionary Features: Both iOS and Android have strived to introduce groundbreaking features that enhance user experience. From the early versions, they have continuously added new functionalities, such as voice assistants, augmented reality capabilities, and biometric authentication.
- Interface Enhancements: The visual appeal and user interface of both platforms have experienced remarkable advancements. Through the years, iOS and Android have evolved from simple and static interfaces to dynamic and intuitive designs, incorporating elements like fluid animations, customizable home screens, and streamlined navigation.
- App Ecosystem Development: The app ecosystems of iOS and Android have expanded exponentially, providing users with a vast range of applications to choose from. Developers have been empowered with tools and frameworks to create sophisticated and feature-rich applications, transforming smartphones into powerful devices capable of fulfilling diverse needs.
- Improved Performance and Efficiency: Both operating systems have continuously worked towards optimizing performance and efficiency, allowing for smoother multitasking, faster app loading times, and better battery management. Through advancements in hardware integration and software optimization, iOS and Android have aimed to deliver superior performance with each new release.
- Security Enhancements: With the growing concerns around data security and privacy, both iOS and Android have invested heavily in fortifying their operating systems. Regular security updates, enhanced encryption mechanisms, and robust permissions management have become integral components of their evolution, safeguarding user information from emerging threats.
The evolution of iOS and Android has revolutionized the way we interact with our mobile devices. From the introduction of new features to the development of expansive app ecosystems, these operating systems have consistently innovated to meet the evolving needs of users. Through continuous improvements in performance, user interface design, and security, iOS and Android have shaped the modern smartphone landscape, enriching our digital experiences and integrating seamlessly into our daily lives.
A Glimpse into the Evolution of Apple's Mobile Operating System
Exploring the trajectory of Apple's renowned mobile software illuminates the path that has led to the development of the popular iOS we know today. Delving into the past of this influential operating system unveils a captivating story of innovation, evolution, and user-centric design. Let's embark on a journey to trace the brief but remarkable history of iOS.
1. iOS 1: The Pioneering Phase
- Origins as iPhone OS
- Revolutionary introduction in 2007
- Innovative touch-based interface
- Emphasis on simplicity and intuitive user experience
2. iOS 2: Expanding Possibilities
- Arrival of the App Store
- Third-party apps revolutionize device functionality
- Push notifications enhance user engagement
- Introduction of the App Store ecosystem
3. iOS 3: Multitasking and Refinements
- Introduction of multitasking capabilities
- Enhanced performance and stability
- Copy and paste functionality
- Expanded language support
4. iOS 4: Transformational Features
- Facetime enables video calling
- Enhanced organization with folders
- Multitasking enhancements
- Introduction of iBooks and Game Center
5. iOS 5: The Era of Integration
- Notification Center unifies alerts and updates
- iCloud introduces seamless data synchronization
- Siri, the voice-controlled intelligent assistant
- Introduction of iMessage for easy messaging
6. iOS 6: Sleek Design and Enhanced Maps
- Refreshed user interface with a modern look
- Apple's proprietary mapping application
- Passbook revolutionizes digital ticketing
- Facebook integration for seamless sharing
7. iOS 7: Flat Design and Expanded Utilities
- Redesigned interface with flat design elements
- Control Center for easy access to settings
- Airdrop enables quick file sharing
- Enhanced camera features and photo organization
8. iOS 8: Interactive and Cross-Device Compatibility
- Widgets and interactive notifications
- Continuity features for seamless device integration
- Health app tracks fitness and health data
- Introduction of Apple Pay for secure payments
9. iOS 9: Enhanced Intelligence and Multitasking
- Proactive Siri suggestions
- Improved multitasking with Split View
- Enhanced security features
- Performance enhancements for older devices
10. iOS 10 and Beyond: Advancing with Evolution
- Revamped lock screen and notification experience
- Enhanced messaging capabilities with iMessage
- Intelligent Photos app with advanced search
- Continual innovation and refinement in subsequent releases
Reflecting upon the remarkable journey of iOS reveals Apple's unwavering commitment to elevating the mobile experience. The history of iOS exemplifies how Apple has consistently strived to bring innovation, simplicity, and seamless integration to its users, solidifying its position as a leading player in the ever-evolving landscape of mobile operating systems.
The Origins of Android
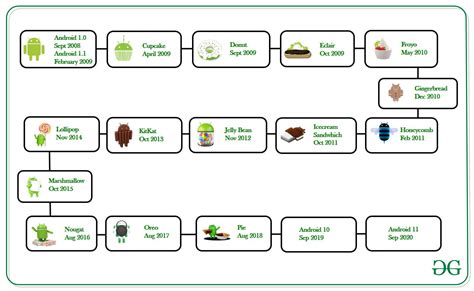
The inception and development of the Android operating system can be traced back to its early beginnings. It emerged as a result of a unique blend of ideas, innovations, and collaborations in the realm of technology.
- Formation of Android Inc.
- Andy Rubin's Vision
- Google's Entry
- Open Source Philosophy
- Early Versions of Android
Android's infancy saw the formation of Android Inc., a company founded by a group of entrepreneurs. Andy Rubin, one of the key figures, envisioned a mobile operating system that would revolutionize the way people interacted with their smartphones. His vision emphasized openness, flexibility, and customization possibilities.
Recognizing the potential of this concept, Google stepped into the picture by acquiring Android Inc. in 2005. With Google's resources and expertise, Android gained the necessary foundation to thrive and become a dominant force in the mobile market. The collaboration brought together the power of Google's services and the innovation of the Android platform.
One of the defining characteristics of Android is its open-source philosophy. By embracing open-source principles, Android empowered developers and manufacturers worldwide to contribute and customize the operating system according to their needs. This approach fostered a vibrant ecosystem that encouraged creativity, diversity, and rapid evolution.
Android's evolution unfolded through various versions, each bringing improvements and new features to the platform. From Cupcake to Oreo, each iteration showcased the relentless pursuit of innovation, enhanced performance, and user-centric design.
The origins of Android highlight a journey shaped by collaboration, innovation, and a commitment to openness and customization. Understanding the roots of Android sets the stage for comprehending the distinctive features and differences it possesses compared to other operating systems in the market today.
The User Interface Experience
When it comes to the look and feel of mobile devices, both iOS and Android offer distinct user interface experiences that set them apart.
One key aspect of the user interface experience is the visual design. Each operating system has its own unique design language, with iOS featuring a sleek and minimalist aesthetic, while Android boasts a more customizable and diverse approach. From the icons to the system fonts, every element contributes to the overall visual experience.
Another important consideration is navigation and interaction. iOS uses a straightforward and intuitive navigation system, with a focus on swiping gestures and minimal button usage. Android, on the other hand, provides users with a wider range of options for customization and control, including physical buttons and an extensive notification center.
In terms of functionality and features, both operating systems offer a vast array of options. iOS tends to prioritize simplicity and ease of use, providing users with a curated selection of built-in apps and a streamlined user experience. Android, on the other hand, offers a more open-ended approach, allowing users to personalize their devices with a wide range of third-party apps and customizable settings.
Overall, the user interface experience on iOS and Android differs in terms of visual design, navigation, customization options, and functionality. Understanding these differences can help users choose the operating system that aligns with their preferences and needs.
App Selection and Availability
In the realm of app selection and availability, iOS and Android exhibit distinct characteristics that set them apart from one another. Both platforms offer a wide array of applications for users to choose from, but their approaches to curating and distributing these apps differ significantly.
When it comes to app selection, iOS emphasizes a more curated experience, ensuring that all apps available on the platform meet certain quality standards. Apple's strict review process aims to maintain a high level of user satisfaction and security. On the other hand, Android adopts a more open approach, allowing developers greater freedom in uploading their apps to the Google Play Store. As a result, Android boasts a larger number of available apps compared to its counterpart.
Besides the quantity and curation of apps, availability is another differentiating factor. iOS apps are exclusive to the Apple ecosystem, meaning that they can only be downloaded and used on Apple devices such as iPhones and iPads. Android, on the other hand, provides greater accessibility by allowing apps to be installed on a wide range of devices from various manufacturers.
Furthermore, due to the varying licensing policies of iOS and Android, certain apps may be available on one platform but not the other. This can be a crucial consideration for users who rely on specific apps for their daily needs or professional use.
In summary, while both iOS and Android offer a diverse selection of apps, their methods of curation, availability, and platform exclusivity present distinguishable characteristics. It ultimately comes down to individual preferences and requirements when it comes to choosing between the two operating systems for app selection and availability.
Customizability and Personalization: Tailoring your Mobile Experience
When it comes to mobile operating systems, one key aspect that sets them apart is their level of customizability and personalization options. Both iOS and Android offer a range of features that allow users to tailor their devices to their unique preferences, making their mobile experience truly their own.
- Home Screen Customization: Whether it's Android's ability to add widgets, rearrange app icons, or iOS's feature-rich app folders, both operating systems provide users with the flexibility to organize their home screens in a way that suits their needs.
- Theme and Wallpaper Selection: With access to a vast library of themes, wallpapers, and live wallpapers, users can easily give their device a fresh new look. They can choose from a wide range of colors, patterns, and designs, allowing them to express their personality through their mobile device.
- Notification Management: Both iOS and Android offer various notification settings, including the ability to prioritize notifications from certain apps, customize the appearance of notifications, and control how and when notifications are displayed. This level of control ensures that users are not overwhelmed by unnecessary alerts and can stay focused on what matters most to them.
- Keyboard Customization: Typing preferences can vary from person to person, and both operating systems recognize this by allowing users to choose from a wide range of keyboards, including third-party options. Whether you prefer swipe typing, predictive text, or specialized layouts, the options are there to make your typing experience as comfortable and efficient as possible.
- Accessibility and Ease of Use: Customization options extend to accessibility features as well. Both iOS and Android offer features such as text size adjustment, color inversion, and screen magnification, catering to individuals with different needs and preferences.
These are just a few examples of the customization and personalization options available on iOS and Android. Whether you prioritize a personalized visual aesthetic, a streamlined notification experience, or enhanced accessibility, both operating systems offer a range of tools and settings that allow you to tailor your device to your liking.
Privacy and Security Features
In today's digital landscape, protecting personal information and ensuring data security are essential considerations for mobile operating systems. Both iOS and Android offer a range of privacy and security features to address the needs and concerns of users.
- Privacy Settings: Both operating systems provide options to control and manage the privacy settings for individual apps and device functionalities. Users can customize permissions for accessing location data, contacts, photos, and more.
- App Permissions: Android and iOS require apps to request user permission before accessing specific resources or functionalities. Users have the ability to grant or deny access, allowing them to maintain control over their personal data.
- Biometric Authentication: Both platforms support biometric authentication methods, such as fingerprint recognition or face unlock, to enhance device security. These features provide a convenient and secure way to unlock devices and authorize transactions.
- Secure App Stores: Android and iOS have their respective app stores, Google Play and the App Store, which enforce strict guidelines for app approval and security screening. This helps to minimize the risk of downloading and installing malicious software.
- Data Encryption: Both operating systems use data encryption techniques to protect user data at rest and in transit. This ensures that sensitive information is stored and transmitted in a secure manner.
- Security Updates: Regular security updates are crucial in addressing vulnerabilities and protecting devices from evolving threats. Both iOS and Android release frequent updates to patch any identified security gaps.
- Device Tracking and Remote Wiping: In case of a lost or stolen device, both platforms offer features that allow users to track their devices' location or remotely wipe the device to prevent unauthorized access to personal data.
- App Sandboxing: iOS and Android employ app sandboxing, isolating each app's data and resources to prevent unauthorized access or interference between apps.
Overall, iOS and Android prioritize user privacy and security by offering comprehensive features and controls to safeguard personal data and enhance device security.
Integration with Other Devices and Services
When it comes to connecting and working seamlessly with various devices and services, both the iOS and Android operating systems exhibit unique approaches, each with its own distinct advantages and offerings. Both ecosystems provide users with options for integrating their smartphones or tablets with a diverse range of devices including smartwatches, fitness trackers, smart TVs, and smart home devices.
Android offers a more open and flexible approach to integration, allowing users to connect their devices to a wider array of third-party accessories and services. With its open-source nature, Android allows for customization and compatibility with a greater variety of devices, empowering users to choose from an extensive range of options.
On the other hand, iOS, being a closed ecosystem, offers a more controlled and seamless integration experience. With its tightly integrated hardware-software combination, Apple ensures that its devices work harmoniously with other Apple products, providing a seamless user experience. Using features like AirPlay, Apple users can effortlessly connect their iOS devices to Apple TVs, speakers, and other compatible devices.
Furthermore, both operating systems incorporate cloud services to enhance integration across multiple devices. Android users can leverage Google's cloud platform, which seamlessly syncs apps, settings, and media across devices, allowing for a consistent user experience. Similarly, Apple users can take advantage of iCloud, which syncs data, documents, and settings across their iOS and macOS devices.
Overall, while Android offers greater flexibility for users to connect diverse devices and services, iOS's closed ecosystem ensures a more seamless and integrated user experience within the Apple ecosystem. The choice between the two depends on individuals' preferences and requirements, whether they prioritize openness and customization or crave a cohesive and interlinked ecosystem.
| Android | iOS |
|---|---|
| Open and flexible integration | Controlled and seamless integration |
| Customizable compatibility with a variety of third-party devices and services | Tightly integrated hardware-software combination for seamless connection with other Apple products |
| Google cloud platform for syncing apps, settings, and media | iCloud for syncing data, documents, and settings across iOS and macOS devices |
Pricing and Affordability

One crucial aspect when considering mobile operating systems is the cost and accessibility they offer. Both iOS and Android platforms have their own unique pricing structures and affordability options, making them suitable for different user preferences and financial circumstances.
Apple's iOS, known for its sleek design and seamless user experience, tends to be associated with a higher price range. Apple devices, such as iPhones and iPads, often come with premium price tags, reflecting the brand's reputation for quality and innovation. While this may limit affordability for some users, it allows Apple to maintain a certain level of exclusivity and provide a consistently high-end user experience.
On the other hand, Android, being an open-source platform, offers a wider range of devices at varying price points. Many manufacturers, including Samsung, Google, and Huawei, produce Android-powered smartphones and tablets that cater to different budget constraints. This versatility makes Android a more accessible option for users seeking a cost-effective mobile experience without compromising on features.
Additionally, Android devices often provide more options for users to customize their interface and personalize their devices according to their preferences. This flexibility, coupled with the affordability options available, allows Android to appeal to a broader user base, including those who prioritize budget-friendly choices.
| iOS | Android |
|---|---|
| Higher price range | Wide range of price points |
| Premium and exclusive | Accessible and customizable |
| Consistent high-end experience | Varied user experience |
In summary, while iOS is associated with a more premium and exclusive pricing structure, Android offers a wider range of affordability options and customization possibilities. The decision between the two ultimately depends on an individual's preference for premium features and a consistent user experience, or a more cost-effective and customizable mobile platform.
Overall User Satisfaction: iOS vs Android
When it comes to measuring the overall satisfaction of users, there are key aspects that can determine which operating system, be it iOS or Android, offers a more gratifying experience. While both platforms have their own unique features and functionalities, it is crucial to delve into the user satisfaction factor, which can significantly impact one's long-term loyalty and preference towards a particular operating system.
In order to provide a comprehensive analysis of user satisfaction, we will explore various aspects such as user interface, customization options, app ecosystem, hardware integration, and security measures. By considering these factors, we can gain insights into how iOS and Android cater to the diverse needs and preferences of their users.
| Aspect | iOS | Android |
|---|---|---|
| User Interface | iOS offers a sleek and intuitive interface that is consistent across all Apple devices. | Android provides a customizable interface, allowing users to personalize their devices according to their preferences. |
| Customization Options | While iOS has limited customization options, it ensures a streamlined user experience with a cohesive design language. | Android offers extensive customization options, giving users the freedom to modify various aspects of their devices. |
| App Ecosystem | iOS boasts a curated app ecosystem, with stringent quality control measures, ensuring a vast selection of high-quality apps. | Android provides an open ecosystem, allowing developers to publish apps more easily, resulting in a wider range of applications. |
| Hardware Integration | iOS has seamless hardware integration, as it is exclusively developed for Apple devices, optimizing performance and functionality. | Android supports various hardware manufacturers, resulting in a wider choice of devices but with potential inconsistencies in performance. |
| Security Measures | iOS prioritizes security, with regular updates and stringent approval processes for apps, ensuring a more secure user experience. | Android emphasizes flexibility, offering users the ability to set security preferences, but with a higher risk of malware and other security vulnerabilities. |
Ultimately, the satisfaction of iOS and Android users depends on individual preferences, needs, and priorities. While iOS focuses on providing a seamless and secure experience with a consistent interface, Android offers a customizable and diverse ecosystem. By evaluating these aspects, users can make an informed decision based on their specific requirements, resulting in a more satisfying operating system choice.
FAQ
What are the main differences between iOS and Android operating systems?
iOS and Android have several key differences. Firstly, iOS is exclusively developed by Apple and is only available on Apple devices such as iPhones and iPads, whereas Android is an open-source platform developed by Google and is used by multiple smartphone manufacturers. Additionally, iOS has a more closed ecosystem, meaning it has stricter control over apps and software updates, whereas Android allows for more customization and has a more open app ecosystem.
Which operating system is more user-friendly, iOS or Android?
Both iOS and Android have their own user-friendly features, but it ultimately depends on personal preference. iOS is often praised for its simplicity and ease of use, as it has a more consistent and streamlined interface. On the other hand, Android offers more customization options and allows users to personalize their devices according to their preferences. Some people find Android to be more user-friendly as it offers a higher level of flexibility and control.
Do iOS and Android have different app stores?
Yes, iOS and Android have separate app stores. iOS devices use the App Store, which is curated and controlled by Apple. This means that all apps go through a strict review process before being allowed into the store. Android devices, on the other hand, use the Google Play Store, which has a more open approach. The Google Play Store has a wider variety of apps, but there is also a higher risk of encountering malware or low-quality apps.
Can iOS apps run on Android devices?
No, iOS apps cannot run on Android devices directly. This is because iOS and Android have different operating systems and use different programming languages. Apps developed for iOS are written in Objective-C or Swift, while apps for Android are written in Java or Kotlin. However, some developers may create separate versions of their apps for iOS and Android, allowing users to access similar functionalities on both platforms.
Which operating system is more secure, iOS or Android?
iOS is generally considered to be more secure than Android. Apple's closed ecosystem and strict app review process help prevent malicious apps from being available on the App Store. Additionally, iOS provides frequent security updates, and its devices have built-in hardware security features. Android, being an open-source platform, is more susceptible to malware and security vulnerabilities, especially on devices that do not receive regular software updates from manufacturers.
What are the main differences between iOS and Android operating systems?
iOS and Android are two different mobile operating systems with various distinctions. One key difference is that iOS is exclusive to Apple's iPhones and iPads, while Android is used by numerous manufacturers on their devices. Another significant distinction is the user interface, with iOS offering a more streamlined and consistent design, while Android provides greater customization options. Additionally, iOS tends to have stricter app store guidelines, resulting in a more curated selection of apps, while Android has a more open app ecosystem.