Enhancing the way your operating system interacts with the network is vital for smooth and efficient communication. By optimizing the host name resolution configuration, you can ensure that your system seamlessly connects to other devices and services on the network, improving your overall browsing experience.
Host name resolution serves as a vital component in establishing connections between computers, allowing them to communicate by using recognizable names instead of complex IP addresses. By modifying the parameters related to this system, you can accelerate the process of hostname resolution, resulting in faster network connections and reduced loading times.
In this article, we will explore the best practices and techniques to fine-tune your host name resolution configuration on Windows. By making strategic adjustments to network settings, you can leverage the power of DNS services, optimize your computer's performance, and enhance your overall browsing experience. Let's dive into the world of host name resolution configuration and discover how to maximize its potential.
Understanding the Mechanism of Resolving Host Names
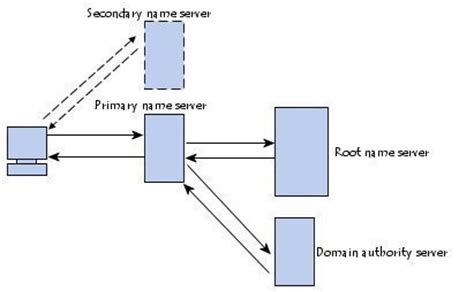
In this section, we will delve into the intricate workings of the system responsible for resolving host names into IP addresses. Through this understanding, we can grasp the underlying concepts and mechanisms that facilitate the smooth functioning of network communication.
Host name resolution, also known as name resolution or DNS resolution, acts as an essential component in establishing connections between devices on a network. It serves as the bridge between human-readable host names and their corresponding numerical IP addresses.
The process involves a series of steps that allow a device to translate a given host name into the associated IP address. These steps include sending a DNS query, contacting DNS servers, and receiving a response containing the IP address. The response is then stored in a cache to optimize future lookups and reduce network traffic.
Various methods are employed for host name resolution, one of which is the popular Domain Name System (DNS). DNS utilizes a hierarchical structure that involves a system of domain names, such as top-level domains (TLDs) and subdomains, to organize and manage host names and their corresponding IP addresses.
- Iterative DNS resolution involves querying different DNS servers until a response with the IP address is obtained.
- Recursive DNS resolution delegates the resolution process to other DNS servers, minimizing the workload on the querying device.
- Alternate methods of host name resolution, such as NetBIOS and LMHOSTS, are used in specific scenarios or legacy systems.
Understanding the host name resolution system is crucial for network administrators and IT professionals as it empowers them to troubleshoot network issues, configure DNS settings, and optimize network performance. With this knowledge, they can effectively manage and maintain an efficient and reliable network environment.
Choosing the Appropriate Method for Mapping Hostnames
The key to efficient host name resolution lies in selecting the most suitable approach to map hostnames to their corresponding IP addresses. This section aims to explore various methods available for achieving this, highlighting the benefits and considerations of each approach.
Using DNS for Host Name Resolution in Windows Configuration
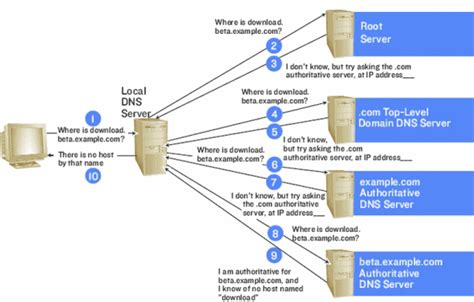
In this section, we will explore the process of setting up the Domain Name System (DNS) in Windows to enable efficient host name resolution. By configuring Windows to utilize DNS, users can easily retrieve the IP addresses associated with specific host names, allowing for seamless connectivity and efficient network communication.
The DNS, often referred to as the internet's phone book, serves as a crucial system that translates human-readable domain names into machine-readable IP addresses. By configuring Windows to use DNS, users can rely on this centralized and widely adopted system to resolve host names, reducing the need for manual configuration and simplifying the process of connecting to other devices on a network.
To configure Windows to use DNS for host name resolution, users can utilize the intuitive and user-friendly interface provided by the operating system. By accessing the network settings, users can locate the DNS configuration options and input the DNS server addresses provided by their internet service provider (ISP) or network administrator. Alternatively, users can choose to manually specify alternative DNS server addresses, such as public DNS servers offered by Google or Cloudflare.
| Advantages of using DNS for host name resolution in Windows: |
|---|
| - Enhanced network connectivity through efficient resolution of host names. |
| - Simplified network management by relying on a widely adopted system. |
| - Reduced need for manual configuration and troubleshooting. |
| - Access to reliable and up-to-date DNS server addresses provided by ISPs or public DNS providers. |
| - Improved security through DNS-based threat protection and filtering. |
In conclusion, by configuring Windows to use DNS for host name resolution, users can harness the benefits of a widely adopted system that provides efficient and reliable translation of domain names to IP addresses. This simplifies the process of connecting to devices on a network and enhances overall network connectivity.
NetBIOS Configuration in Windows for Host Name Resolution
In this section, we will explore the process of setting up NetBIOS on a Windows operating system in order to enable host name resolution. NetBIOS, an acronym for Network Basic Input/Output System, is a legacy networking protocol that facilitates communication between devices within a local network. By configuring Windows to use NetBIOS for host name resolution, you can enhance the network's ability to identify and connect to devices using their distinct NetBIOS names.
NetBIOS can be an effective way to streamline host name resolution in a Windows environment. By enabling NetBIOS over TCP/IP, Windows can leverage the NetBIOS Name Service (NBNS) to map specific NetBIOS names to their corresponding IP addresses. This means that instead of relying solely on traditional DNS (Domain Name System) mechanisms, such as DNS servers, a Windows system can utilize NetBIOS to resolve host names within its local network.
Configuring Windows to use NetBIOS involves a few simple steps. Firstly, you need to access the network adapter's properties in the Windows Control Panel. From there, you can locate the TCP/IP settings and navigate to the "Advanced" options. Within the Advanced settings, you will find a section related to WINS (Windows Internet Naming Service) settings, which includes the option to enable NetBIOS over TCP/IP.
Once NetBIOS over TCP/IP is enabled, Windows will utilize the NBNS to perform host name resolution. By enabling this feature, you can enhance the efficiency and accuracy of host name resolution within your local network. It should be noted, however, that NetBIOS is primarily designed for smaller, local networks and may not provide the same level of scalability and reliability as DNS for larger networks or wide area networks (WANs).
In conclusion, by configuring Windows to use NetBIOS for host name resolution, you can take advantage of the NetBIOS Name Service to map NetBIOS names to IP addresses. While NetBIOS may not be suitable for all network environments, it can be a valuable tool for streamlining host name resolution within smaller, local networks.
Configuring Windows to Use LLMNR for Host Name Resolution
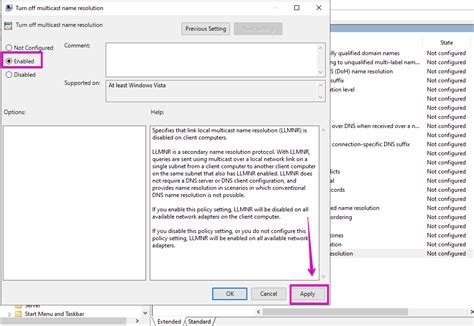
In this section, we will explore the process of setting up the LLMNR (Link-Local Multicast Name Resolution) protocol on your Windows operating system to improve host name resolution. By utilizing LLMNR, you can enhance the efficiency and accuracy of identifying and connecting to devices within your local network without relying solely on traditional DNS (Domain Name System) servers.
Firstly, we will delve into the concept of LLMNR and its benefits, explaining how it works as an alternative name resolution system. Next, we will guide you through the step-by-step process of configuring your Windows settings to enable LLMNR for host name resolution. This includes accessing the Network and Sharing Center, navigating to the Network Connections settings, and locating the specific network adapter to modify.
We will highlight the importance of ensuring LLMNR is enabled and how it complements other name resolution protocols such as DNS and NetBIOS. Additionally, we will emphasize the significance of verifying proper network connectivity and security settings after making the necessary configuration changes.
Throughout this section, we will provide clear instructions and explanations, accompanied by relevant examples and illustrations. By the end, you will have a comprehensive understanding of how to leverage the LLMNR protocol within Windows to optimize host name resolution and streamline network communication within your local environment.
How to Point a Domain Name to an IP Address (DNS A record example)
How to Point a Domain Name to an IP Address (DNS A record example) by Tony Teaches Tech 252,046 views 2 years ago 11 minutes, 53 seconds
How To Configure DNS on Windows Server 2019 | Joining Client In Server 2019
How To Configure DNS on Windows Server 2019 | Joining Client In Server 2019 by KapTechPro 16,190 views 3 years ago 7 minutes, 59 seconds
FAQ
How can I configure Windows to work with the host name resolution system?
To configure Windows to work with the host name resolution system, you need to manually edit the "hosts" file located in the Windows directory. You can open this file using a text editor, such as Notepad. The file contains mappings of IP addresses to host names, allowing your system to resolve host names to specific IP addresses. Simply add the desired host name and its corresponding IP address in the following format: "IP_address hostname" without the quotes. Save the file and restart your computer for the changes to take effect.
What is the purpose of host name resolution in Windows?
Host name resolution in Windows is essential for translating domain names (such as www.example.com) into IP addresses. This translation enables your computer to connect to specific websites or servers on the internet. By resolving the host names to their corresponding IP addresses, Windows can establish the necessary network connections and ensure that data is sent and received accurately.
Is it possible to configure host name resolution for multiple domains in Windows?
Yes, you can configure host name resolution for multiple domains in Windows by adding entries for each domain in the "hosts" file. Each entry should consist of an IP address followed by the corresponding domain name. By including multiple domain entries, you can ensure that your computer can resolve the host names of various websites or servers, allowing you to access them without any issues.
Are there any alternative methods to configure host name resolution in Windows?
Yes, apart from manually editing the "hosts" file, you can also configure host name resolution in Windows by using the Domain Name System (DNS) server. DNS servers are responsible for resolving domain names to their respective IP addresses. By configuring your computer to use specific DNS server addresses, you can enable automatic host name resolution without the need to manually update the "hosts" file. This method is especially useful for scenarios where you frequently access websites and servers from different domains.
What can I do if host name resolution is not working correctly on my Windows system?
If host name resolution is not working correctly on your Windows system, there are a few troubleshooting steps you can try. First, check the "hosts" file to ensure that the necessary entries are present and correctly formatted. Additionally, you can try flushing the DNS cache by running the command "ipconfig /flushdns" in the Command Prompt. If the issue persists, you may need to check your network settings, such as the DNS server configuration, or contact your network administrator or Internet Service Provider for further assistance.
What is host name resolution system?
Host name resolution system is a mechanism in Windows that allows the operating system to translate a host name (such as www.example.com) to an IP address.
Why is it important to configure Windows to work with the host name resolution system?
Configuring Windows to work with the host name resolution system is important because it enables the operating system to correctly resolve and connect to the desired destination when accessing websites, services, or network resources using host names instead of IP addresses.




