Streamlining the harmonious synergy between software systems and the vital day-to-day operations of a warehouse environment is an imperative task for businesses seeking to enhance efficiency and productivity. In today's ever-evolving technological landscape, integrating a Warehouse Management System (WMS) into the intricate framework of Windows operating system holds the key to unlocking unparalleled operational fluidity.
Embarking on a successful integration journey necessitates a comprehensive understanding of the intricate configurations and optimal settings that facilitate the seamless collaboration between the Windows environment and the WMS solution. By leveraging the power of harmonious integration, businesses can efficaciously automate processes, optimize inventory management, and empower their workforce to thrive amidst the dynamic and demanding warehouse ecosystem.
Within this informative guide, we will embark on an exploration of the essential steps needed to configure the Windows system to seamlessly accommodate the integration of a WMS. From configuring system permissions and user access levels to establishing reliable network connections, we will delve deep into the intricacies of this integration endeavor, empowering businesses to embrace a future-driven approach to warehouse management system integration.
Understanding the Advantages of WMS Integration
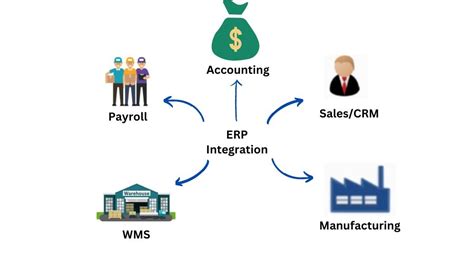
Efficient warehouse management is essential for businesses looking to streamline their operations and gain a competitive edge in the market. One integral aspect of optimizing warehouse processes is the integration of a Warehouse Management System (WMS) into the existing infrastructure. By merging the WMS seamlessly with other software solutions, businesses can enhance their logistical capabilities and reap a multitude of benefits.
First and foremost, WMS integration improves inventory accuracy and visibility. With real-time tracking and monitoring capabilities, businesses can effectively manage stock levels, track product movements, and minimize discrepancies. This enhanced visibility enables more accurate supply chain planning, reduces the risk of stockouts or overstocking, and ultimately leads to improved customer satisfaction.
Another significant benefit of WMS integration is increased productivity. By automating routine tasks such as inventory processing, order fulfillment, and shipment tracking, businesses can significantly reduce manual effort and human error. This not only speeds up processes but also allows employees to focus on more value-added activities, leading to increased overall efficiency.
WMS integration also facilitates better decision-making and data-driven insights. By consolidating data from various sources into a centralized system, businesses can gather valuable information on key performance indicators, sales trends, and customer behavior. This data-driven approach enables businesses to make informed decisions, identify opportunities for improvement, and adjust strategies accordingly.
Furthermore, WMS integration promotes seamless collaboration within the warehouse and throughout the supply chain. By connecting different departments, suppliers, and customers through a unified system, businesses can ensure better communication, coordination, and collaboration. This interconnectedness leads to improved order accuracy, faster order processing times, and stronger relationships with stakeholders.
In conclusion, WMS integration offers numerous benefits, including enhanced inventory accuracy and visibility, increased productivity, better decision-making capabilities, and improved collaboration. By investing in WMS integration, businesses can optimize their warehouse operations and position themselves for long-term success in the competitive market.
Choosing the Ideal Solution for Seamless Warehouse Operations
When it comes to enhancing the efficiency and productivity of your warehouse operations, selecting the most suitable warehouse management system (WMS) becomes imperative. An effective WMS enables businesses to streamline their processes, optimize inventory management, and improve overall performance.
In order to choose the right WMS for your organization, it is crucial to carefully assess your unique requirements and consider key factors such as scalability, integration capabilities, and user-friendliness. Additionally, evaluating the system's ability to adapt to your specific industry needs and accommodate future growth is essential.
- Define your goals: Begin by outlining your specific objectives and goals for implementing a WMS. This could include increasing order accuracy, reducing inventory costs, improving order fulfillment speed, or enhancing customer satisfaction.
- Assess your current warehouse operations: Evaluate your existing workflows, processes, and infrastructure to identify pain points and areas that require improvement. This will help you determine the functionalities and features that are necessary in a WMS.
- Consider scalability: Anticipate future growth and assess whether the WMS can accommodate increased inventory volume, expanding operations, and additional warehouses or distribution centers.
- Integration capabilities: Ensure that the WMS can seamlessly integrate with existing software systems such as enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems, barcode scanners, or automated material handling systems to facilitate efficient data exchange and real-time inventory updates.
- User-friendliness: Look for a WMS that is intuitive and easy to navigate, as this will minimize training requirements and enable smooth adoption by warehouse staff.
By thoroughly considering these factors and conducting a comprehensive evaluation of available WMS options, you can make an informed decision and choose a solution that aligns perfectly with your warehouse needs, ultimately contributing to increased productivity, accuracy, and overall success.
Requirements for WMS Integration on Windows
In order to successfully integrate a Warehouse Management System (WMS) on the Windows operating system, certain system requirements must be met. These requirements encompass both hardware and software components that are essential for the smooth functioning of the WMS integration.
- A system running on the Windows operating system (compatible versions include Windows 7, Windows 8, and Windows 10).
- A minimum of 4GB RAM to ensure efficient processing and execution of the WMS integration.
- A dual-core processor or higher is recommended to handle the computational requirements of the WMS integration.
- A stable internet connection with adequate bandwidth to enable real-time data transfer between the WMS and other systems.
- The latest version of the Warehouse Management System software, compatible with Windows, must be installed.
In addition to the hardware and software requirements, proper configuration of the Windows operating system is crucial for seamless WMS integration. This includes:
- Creating user accounts with the appropriate permissions to access and manage the WMS integration.
- Ensuring that firewall settings are configured to allow communication between the WMS and other systems.
- Configuring antivirus software to exclude any potential conflicts with the WMS integration.
- Regularly updating the Windows operating system and other software components to maintain compatibility and security.
By meeting these system requirements and properly configuring the Windows operating system, businesses can ensure a stable and efficient integration of their Warehouse Management System, enabling seamless management of warehouse operations.
Setting up and Configuring the Essential Software
In this section, we will explore the steps involved in installing and configuring the necessary software for integrating a Warehouse Management System. The successful integration of a WMS relies on the setup of specific software components that enable seamless communication and data exchange between the system and various warehouse processes.
Firstly, it is crucial to identify and install an appropriate database management system. This software will serve as the foundation for storing and managing data related to inventory, orders, and other essential warehouse information. Look for a reliable and robust database management system that aligns with your specific requirements, taking into consideration factors such as scalability, security, and compatibility with your WMS.
Next, you will need to set up the necessary middleware software. This software acts as a bridge between the WMS and other applications/systems within the warehouse environment. It enables smooth data integration, real-time updates, and efficient communication between the WMS and other components or devices such as barcode scanners, RFID readers, and conveyor systems. Ensure that the chosen middleware software is compatible with your WMS and supports the required communication protocols and data formats.
In addition, installing and configuring the appropriate communication software is vital to enable seamless data exchange between the WMS and external systems such as ERP or e-commerce platforms. This software facilitates the integration of data related to orders, shipments, inventory updates, and other crucial information required for effective warehouse management. Choose a communication software solution that offers reliable connectivity, supports the required protocols (e.g., API, EDI), and allows for real-time or batch data transfers.
Lastly, it is important to consider any additional software components that may be required based on the specific functionalities and requirements of your warehouse management system. These could include specialized modules for tasks such as labor management, automated picking, or inventory tracking. Evaluate the need for such additional software components and ensure their proper installation and configuration.
By following these steps and carefully setting up and configuring the necessary software components, you will lay a solid foundation for the successful integration of a Warehouse Management System into your organization's operations, enhancing efficiency, accuracy, and overall warehouse management capabilities.
Setting Up Network and Connectivity for WMS Integration
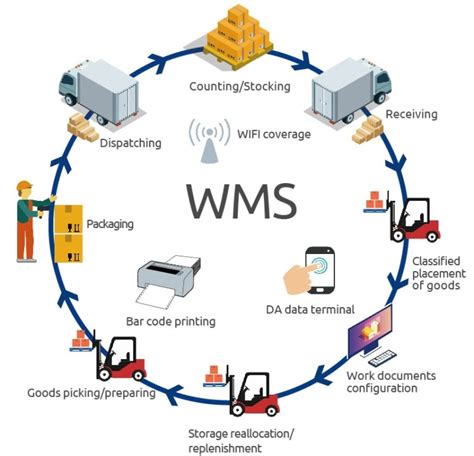
In this section, we will explore the necessary steps to establish a reliable network and ensure seamless connectivity for integrating your warehouse management system (WMS) into your existing infrastructure. Efficient network setup and robust connectivity are crucial for the successful implementation of WMS integration.
To begin, you need to assess your current network infrastructure and determine if any enhancements or upgrades are needed. This evaluation will help identify potential bottlenecks or limitations that could hinder WMS integration. It is important to ensure that your network can handle the increased traffic and data exchange that comes with a WMS.
Next, you should consider implementing a reliable network architecture that supports the required bandwidth and provides redundancy for maximum uptime. Redundant network connections and backup systems can minimize downtime and ensure continuous access to the WMS, even in the event of a network failure.
Furthermore, establishing secure connectivity is essential to protect sensitive data and prevent unauthorized access. Consider implementing robust firewall protocols, encryption mechanisms, and secure VPN connections to safeguard your WMS integration. This will help maintain the integrity and confidentiality of your warehouse management system.
Additionally, network monitoring and troubleshooting mechanisms should be in place to proactively identify and address any network issues that may arise during WMS integration. Regular network performance assessments, bandwidth monitoring, and timely problem resolution can help optimize the functionality and reliability of your WMS integration.
Lastly, documentation and proper labeling of network equipment, cables, and configurations are necessary for efficient management and maintenance of your network infrastructure. This will enable seamless troubleshooting and future scalability of your warehouse management system integration.
Configuring Security and Access Control for WMS Integration
In this section, we will explore the essential steps to ensure the secure and controlled integration of a Warehouse Management System (WMS). An effective security configuration is crucial to protect sensitive data and maintain the integrity of the overall system. Additionally, access control measures need to be implemented to restrict unauthorized access and ensure that only authenticated personnel can interact with the WMS.
To configure security for WMS integration, it is important to start by identifying the specific security requirements of your organization. This involves assessing the level of data confidentiality, integrity, and availability required for proper WMS operation. By comprehensively understanding these needs, you can determine the appropriate security measures to implement.
Next, a robust authentication mechanism should be established to verify the identity of individuals accessing the WMS. This can be achieved through the implementation of strong passwords, two-factor authentication, or biometric identification methods. By enforcing strict authentication protocols, unauthorized access attempts can be significantly minimized.
Furthermore, role-based access control can be implemented to assign specific privileges to users based on their roles and responsibilities within the organization. This ensures that individuals only have access to the relevant functionalities and data they necessitate to perform their duties. Regular access reviews and audits should also be conducted to prevent any unauthorized modifications to access control settings.
Encrypting data during transmission and storage is another critical aspect of configuring security for WMS integration. This prevents unauthorized individuals from intercepting or tampering with sensitive information. Secure socket layer (SSL) or transport layer security (TLS) protocols can be utilized to establish secure communication channels between the WMS and other systems.
Lastly, regular security updates and patches should be applied to the underlying operating system and WMS software. These updates address vulnerabilities and ensure that the system remains protected against evolving threats. It is also essential to establish proper backup and disaster recovery procedures to mitigate the risks associated with data loss or system failures.
- Identify specific security requirements
- Establish robust authentication mechanisms
- Implement role-based access control
- Encrypt data during transmission and storage
- Apply regular security updates and patches
- Establish backup and disaster recovery procedures
Testing and Troubleshooting WMS Integration on Windows
In this section, we will explore the necessary steps to test and troubleshoot the integration of a Warehouse Management System (WMS) on Windows. By conducting thorough testing and proactive troubleshooting, businesses can ensure the smooth and efficient functioning of their WMS integration, enhancing overall warehouse operations.
- Define Testing Objectives: Before diving into the testing phase, it is crucial to establish clear objectives. These objectives may include validating data accuracy, verifying real-time updates, ensuring proper communication between different software components, and assessing overall system performance.
- Create Test Scenarios: Develop a comprehensive set of test scenarios that cover various aspects of WMS integration. These scenarios should mimic real-life warehouse operations, encompassing tasks such as order processing, inventory management, and system synchronization.
- Execute Testing Procedures: Implement the defined test scenarios, meticulously following the steps outlined for each scenario. Monitor the flow of data between the WMS and other integrated systems, identify any issues or discrepancies, and record observations for further analysis.
- Analyze Test Results: Thoroughly examine the test results to identify patterns, trends, and potential areas for improvement. Compare the expected outcomes with the actual results and document any deviations or inconsistencies.
- Troubleshoot Integration Issues: Inevitably, challenges may arise during the WMS integration process. Employ a systematic troubleshooting approach to identify the root causes of issues. This may involve checking system logs, analyzing error messages, and collaborating with relevant stakeholders.
- Implement Fixes and Retest: Based on the identified issues, implement appropriate fixes or configuration changes. Retest the integration to ensure that the fixes have addressed the problems and that the WMS functions seamlessly with other systems.
- Document Testing Procedures: Document the testing procedures, including the test scenarios, outcomes, and any troubleshooting steps. This documentation will serve as a valuable resource for future reference, helping streamline future integration processes.
- Continuous Monitoring and Improvement: Testing and troubleshooting should not be seen as one-time activities. Continuously monitor the WMS integration, track performance metrics, and proactively address any emerging issues or bottlenecks. Regularly review and enhance the integration process to optimize overall warehouse management operations.
By adhering to a structured testing and troubleshooting approach, businesses can minimize disruptions, enhance system reliability, and maximize the benefits of their Warehouse Management System integration on Windows.
Optimal Strategies for Configuring Windows in WMS Integration
In the realm of streamlining the amalgamation of a Warehouse Management System (WMS) with the Windows operating system, employing effective practices for Windows configuration is paramount. This section will delve into the best approaches and guidelines for configuring Windows in WMS integration, ensuring seamless and efficient system collaboration.
1. Embracing Hardware Compatibility
One crucial aspect of configuring Windows for WMS integration is acknowledging the significance of hardware compatibility. It is imperative to ensure that all hardware components, such as servers, workstations, and mobile devices, are fully compatible with the selected Windows operating system. This compatibility fosters optimal performance and minimizes potential bottlenecks during system integration.
2. Establishing Robust Security Measures
Security forms the bedrock of any WMS integration, and Windows configuration plays a vital role in fortifying the overall system security. Implementing stringent security measures, such as robust user access controls, firewall configuration, and encryption protocols, safeguards sensitive data and mitigates the risk of unauthorized access. By prioritizing security during the Windows configuration process, businesses can guarantee the integrity and confidentiality of their warehouse management system.
3. Leveraging Network Optimization Techniques
The efficient integration of a WMS relies heavily on network connectivity and speed. To optimize network performance, configuring Windows settings that enhance network stability and minimize latency is crucial. Employing techniques such as adjusting network adapter settings, optimizing TCP/IP configurations, and prioritizing network traffic facilitates smooth communication between the WMS and Windows operating system, ensuring real-time data exchange and timely decision-making.
4. Streamlining System Performance through Resource Allocation
Configuring Windows for WMS integration involves judicious resource allocation to maximize system performance. Employing effective strategies like allocating sufficient system memory and CPU resources, optimizing disk space, and managing background processes ensures that the WMS operates at its peak efficiency. Adequate resource allocation guarantees minimal system downtime and enhances the overall productivity of warehouse operations.
5. Implementing Regular Updates and Patch Management
Keeping the Windows operating system up-to-date by installing regular updates and patches is essential for a secure and reliable WMS integration. Regular updates introduce bug fixes, security enhancements, and feature improvements, thereby preventing potential vulnerabilities. By adhering to a proactive update management approach, businesses can guarantee system stability, minimize downtime, and stay ahead of emerging security threats.
Conclusion
Adhering to best practices for Windows configuration in WMS integration is vital for ensuring a seamless and efficient collaboration between the warehouse management system and the Windows operating system. By embracing hardware compatibility, establishing robust security measures, leveraging network optimization techniques, streamlining system performance through resource allocation, and implementing regular updates, businesses can maximize the potential of their WMS integration and enhance warehouse operations.
FAQ
What is a Warehouse Management System (WMS)?
A Warehouse Management System (WMS) is a software application that helps manage and control warehouse operations. It typically includes functionalities such as inventory management, order fulfillment, picking and packing, and shipping.
Why is integrating a Warehouse Management System with Windows important?
Integrating a Warehouse Management System with Windows allows for seamless communication and data synchronization between the WMS and other systems within the organization. This integration helps enhance operational efficiency, reduce errors, and improve overall productivity.
Can I integrate multiple Warehouse Management Systems with Windows simultaneously?
Yes, it is possible to integrate multiple Warehouse Management Systems with Windows simultaneously. However, it may require additional configuration and customization to ensure compatibility and smooth data exchange between the systems.
What is a Warehouse Management System (WMS) integration?
Warehouse Management System (WMS) integration is the process of connecting a WMS software with other systems or applications used in a warehouse, such as inventory management systems, order management systems, shipping carriers, and more. This integration allows for seamless data flow and real-time information exchange between different systems, improving overall warehouse operations.
Why is it important to configure Windows for Warehouse Management System integration?
Configuring Windows for Warehouse Management System integration is important to ensure smooth communication between the WMS software and other systems. This configuration allows for proper data transfer, seamless integration, and avoids compatibility issues. It is crucial for efficient warehouse operations and accurate inventory management.




