Embark on a journey of discovery as we delve into the world of personalization and customization in the Linux operating system. Today, we explore the art of configuring the boot menu, the first step towards molding your Linux experience to fit your unique needs and preferences.
Picture this - you power on your computer, and a beautiful, sleek boot menu gracefully greets you, enticing you to choose the operating system you desire. With strategic nuances, you can craft a boot menu that not only serves as a functional gateway but as a reflection of your personality and style. Imagine the satisfaction of having complete control over your Linux boot process!
Indulge in the thrill of uncovering the secrets behind the powerful Grub2 bootloader, a cross-platform boot manager that offers unparalleled flexibility. By exploring the intricacies and inner workings of Grub2, you unlock a treasure trove of possibilities, enabling you to blaze a trail of uniqueness in the Linux Mint ecosystem.
Throughout this captivating journey, we will walk you through the essential techniques and tips required to effortlessly manipulate the boot menu. From customizing the appearance, adding personal icons, and reordering the boot options, we will equip you with the knowledge and confidence to transform the boot menu into a captivating masterpiece that showcases your individual flair.
Customizing the Boot Menu in Linux Mint: A Guide to Configuring Grub2
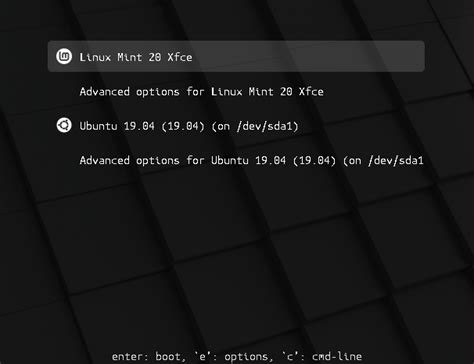
In this section, we will explore the various ways of personalizing the boot menu in Linux Mint by customizing Grub2. By tailoring the appearance and functionality of the boot menu, you can enhance your Linux Mint experience and make it uniquely yours.
Overview
In this section, we will provide a comprehensive overview of the configuration process for the GRUB bootloader in the Linux Mint operating system.
We will explore various aspects of customizing GRUB2, an essential component responsible for managing the startup process of your Linux system. Through a series of steps and explanations, we will delve into the intricacies of modifying GRUB2's behavior without explicitly mentioning the specific details related to the Linux Mint distribution.
You will gain a deeper understanding of how to personalize the appearance, add and remove boot entries, set default options, and troubleshoot issues that may arise while configuring GRUB2. By following the instructions and tips provided, you will be equipped with the knowledge to effectively tailor the behavior of the bootloader to your preferences and requirements.
Understanding the Basics of the GRUB2 Bootloader
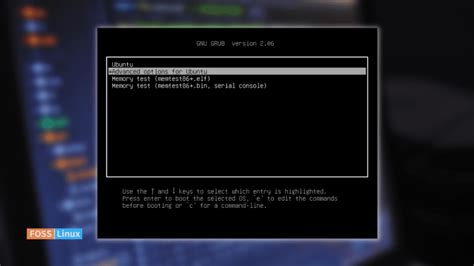
In this section, we will delve into the fundamental concepts and workings of the GRUB2 bootloader, a crucial component of the Linux Mint operating system. By gaining a comprehensive understanding of how GRUB2 functions, you will be better equipped to make changes to its configuration to suit your needs.
The GRUB2 bootloader is a powerful tool that plays a pivotal role in the boot process of a Linux Mint system. It acts as an intermediary between the computer's firmware and the operating system, enabling you to choose the desired operating system or kernel to boot.
An essential feature of GRUB2 is its ability to present a boot menu, where you can select among different operating systems or various kernel versions installed on your system. It allows you to switch between different operating systems effortlessly, providing you with flexibility and convenience.
Additionally, GRUB2 provides advanced features such as customizable boot entries, the ability to control the boot parameters, and an interactive command line interface. It also supports a wide range of file systems, enabling you to boot from various storage devices.
Understanding the inner workings of GRUB2 involves grasping concepts such as boot stages, configuration files, menu entries, and the role of the command line interface. By exploring these concepts, you will gain insights into how GRUB2 processes the boot sequence and how you can modify its behavior effectively.
Having a solid understanding of GRUB2 is essential for troubleshooting boot-related issues, customizing the boot process, and ensuring a seamless experience when using Linux Mint. So, let's dive into the world of GRUB2 and unravel its mysteries!
Accessing the Grub Configuration File
In the realm of customizing your Linux Mint experience, understanding how to access the Grub configuration file is key. This important file holds the settings that control the boot process and can be modified to suit your specific needs and preferences. By gaining access to this file, you will be able to make changes to your boot options, such as adjusting the default operating system or enabling a dual-boot setup.
To access the Grub configuration file, you will need to navigate to the designated location on your Linux Mint system. This file is typically located in the /etc directory. It is important to note that modifying the Grub configuration file requires administrative privileges, so be sure to have the necessary permissions before proceeding.
Once you have located the Grub configuration file, you can open it using a text editor. This will allow you to view and modify the various settings within the file. It is important to approach this task with caution, as any incorrect modifications to the file can potentially render your system unbootable. It is recommended to make a backup of the file before making any changes, just in case.
Within the Grub configuration file, you will find a variety of options that can be adjusted to customize your boot process. These options include setting the default operating system, adjusting the timeout for the boot menu, and enabling or disabling certain features. Each option is accompanied by a description, making it easier to understand its purpose and potential effects.
Once you have made the desired changes to the Grub configuration file, you will need to save the file and exit the text editor. Afterward, it is important to update the Grub bootloader for the changes to take effect. This can be done using the appropriate terminal command, such as "sudo update-grub".
By accessing and modifying the Grub configuration file, you can take control of your Linux Mint boot process and customize it to perfectly suit your needs. Whether you want to change the default operating system or enable advanced boot options, understanding the workings of the Grub configuration file is essential.
FAQ
What is Grub2 and why is it important?
Grub2 is a bootloader that allows users to choose which operating system to boot into when starting their computer. It is important because it is responsible for loading the kernel and initializing the operating system.
How can I configure Grub2 in Linux Mint?
You can configure Grub2 in Linux Mint by modifying the configuration file located at /etc/default/grub. This file allows you to change settings such as the default operating system, boot timeout, and kernel parameters.
Can I change the default operating system that Grub2 boots into?
Yes, you can change the default operating system that Grub2 boots into. By modifying the GRUB_DEFAULT parameter in the configuration file, you can specify the index number of the desired operating system in the boot menu.
Is it possible to change the boot timeout in Grub2?
Yes, it is possible to change the boot timeout in Grub2. By modifying the GRUB_TIMEOUT parameter in the configuration file, you can set the amount of time (in seconds) that the boot menu will be displayed before the default operating system is automatically booted.
Can I add custom kernel parameters in Grub2?
Yes, you can add custom kernel parameters in Grub2. By modifying the GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX parameter in the configuration file, you can append additional parameters to be passed to the kernel during boot.




