Are you struggling to keep track of the ever-increasing log data generated by your Linux environment? It's time to simplify your log management process with an efficient solution. In this article, we will dive into the world of log management and explore the precise steps required to set up an invaluable tool that can handle and analyze your logs effortlessly.
Discover an intuitive and powerful log management platform that brings clarity to the chaos of log data. By leveraging cutting-edge technologies, you can harness the true power of log analysis and turn raw data into valuable insights. Whether you need to monitor system performance, troubleshoot issues, or meet compliance requirements, this comprehensive setup guide will walk you through the process and equip you with the knowledge to successfully implement a robust log management solution.
Experience the convenience of a streamlined log management workflow that enhances your Linux system operations. With a step-by-step approach, this guide will empower you to overcome the complexities of setting up a reliable log management system. From the initial installation to advanced configuration options, each stage is presented with precision and clarity, ensuring a smooth and hassle-free experience. Join us on this journey as we demystify the intricacies of log management and unlock the true potential of your Linux infrastructure.
Understanding the Advantages and Features of Graylog
Exploring the Boundless Benefits of Efficient Log Management
In this section, we delve into the remarkable advantages and features that Graylog offers for effective log management and analysis. By comprehending the key attributes of this powerful open-source platform, businesses can gain a deeper understanding of its potential contributions towards enhancing system performance and security.
Unifying Log Data: Graylog enables the consolidation of log data from diverse sources into a single centralized location. This eliminates the need to access multiple systems and streamlines the process of log analysis, leading to improved efficiency.
Powerful Search Functionality: With its advanced search capabilities, Graylog empowers users to quickly and easily sift through large volumes of log data. The ability to search specific terms, filter logs based on custom parameters, and conduct real-time searches ensures efficient troubleshooting and issue resolution.
Flexible and Scalable Architecture: Graylog supports seamless scalability, enabling it to adapt to the varying needs of businesses. Organizations can effortlessly expand their log management infrastructure as their operations grow with minimal disruptions.
Streamlined Alerting Mechanism: Graylog offers robust alerting functionality, notifying users of critical events or discrepancies in log data through diverse notification channels, such as email, Slack, or other third-party integrations. This enables timely actions and proactive resolution of potential security threats or system issues.
Visual and Intuitive Dashboards: Through customizable dashboards, Graylog provides intuitive data visualization capabilities, allowing users to monitor log data in real-time. The intuitive interface assists in identifying anomalies, patterns, and trends, facilitating proactive decision-making and troubleshooting.
Comprehensive Security Features: Graylog ensures the security and integrity of log data through features such as role-based access control, secure data transmission, and encrypted storage. These functionalities safeguard sensitive information and ensure compliance with data protection regulations.
By comprehending and leveraging the notable benefits and functionalities of Graylog, businesses can effectively manage and analyze log data while enhancing system performance, identifying potential issues, and proactively mitigating security risks.
Requirements for the Installation
In order to successfully set up and configure Graylog on a Linux system, it is important to ensure that your system meets all the necessary requirements. These requirements include hardware specifications, operating system compatibility, and other dependencies that are essential for the smooth functioning of Graylog.
- A reliable and stable Linux distribution is recommended for hosting Graylog.
- The system should have a minimum of 4GB of RAM to ensure optimal performance.
- At least 50GB of free disk space is required for storing logs and other related data.
- A modern multi-core processor is highly recommended for efficient log processing.
- For increased reliability and availability, it is recommended to set up a redundant storage configuration.
The installation process also requires certain software dependencies to be installed on the Linux system. These dependencies include:
- Java Development Kit (JDK): Graylog requires JDK to be installed, preferably version 8 or higher, to run the Java-based components.
- Elasticsearch: Graylog relies on Elasticsearch for indexing and searching the log data. Make sure to install a compatible version of Elasticsearch.
- MongoDB: Graylog utilizes MongoDB as a backend database for storing configuration data. Install a compatible version of MongoDB for successful setup.
To ensure a smooth installation process and avoid any compatibility issues, it is recommended to check the official documentation of Graylog for the specific versions of the dependencies that are compatible with the version of Graylog you are planning to install.
Ensuring your Linux system meets the necessary hardware and software requirements
In order to successfully set up and run Graylog on your Linux system, it is crucial to ensure that your system meets the required hardware and software specifications. By ensuring that your system meets these requirements, you can guarantee optimal performance and stability for your Graylog installation.
The hardware requirements for running Graylog may vary depending on the scale of your deployment and the amount of data being processed. Generally, it is recommended to have a system with sufficient processing power, memory, and storage capacity. This ensures that your Linux system can effectively handle the data ingestion and processing tasks performed by Graylog.
Software requirements for Graylog typically include a compatible Linux distribution, Java Development Kit (JDK), and additional dependencies such as Elasticsearch and MongoDB. It is essential to have the appropriate versions of these software components installed and properly configured on your Linux system.
To determine if your Linux system meets the necessary hardware requirements, refer to the following table:
| Hardware Component | Minimum Requirement | Recommended Requirement |
|---|---|---|
| Processor | Dual-core 2.0 GHz | Quad-core 2.5 GHz or higher |
| Memory | 4 GB RAM | 8 GB RAM or higher |
| Storage | 100 GB HDD | 250 GB SSD or higher |
| Network | 1 Gbps Ethernet | 10 Gbps Ethernet |
For the software requirements, ensure that you have a compatible Linux distribution such as Ubuntu, CentOS, or Debian. Install the appropriate version of Java Development Kit (JDK), making sure it is compatible with Graylog. Additionally, set up and configure Elasticsearch and MongoDB to work in conjunction with Graylog.
By taking the time to ensure that your Linux system meets the necessary hardware and software requirements, you can lay a solid foundation for the successful installation and operation of Graylog. This will enable you to effectively manage and analyze your log data, facilitating better visibility and insights into your system's performance and security.
Installing Graylog: A simplified approach to setting up the powerful log management platform
One of the vital steps in implementing Graylog, a feature-rich log management solution, is its installation. By following this comprehensive guide, you will be able to effortlessly configure Graylog on your Linux-based operating system, without the need for complex procedures or extensive technical knowledge.
To begin the installation process, you need to ensure the availability of a compatible Linux distribution. Consider using a widely-used distribution such as Ubuntu, Debian, or CentOS, as they offer extensive support and compatibility with Graylog.
Next, verify that your Linux system has the required resources and dependencies for Graylog. This includes having Java Development Kit (JDK) installed on your system. Ensure that you have the necessary version of JDK that is compatible with the Graylog version you intend to install.
Once the prerequisites are satisfied, it is time to obtain the Graylog package from the official Graylog website or an authorized repository. Ensure that you choose the appropriate package corresponding to your Linux distribution and version.
After downloading the package, proceed to install Graylog using the package manager of your Linux distribution. This simplified method will automatically handle the necessary dependencies and streamline the installation process. Remember to grant the required permissions during the installation to ensure smooth functioning of Graylog.
Following the successful installation, it is crucial to configure Graylog to suit your specific requirements. This involves modifying the configuration files to set up important parameters such as network settings, authentication, and other optional features. Accurate configuration will ensure seamless integration of Graylog into your existing system.
Finally, start the Graylog service using the designated commands specified in the documentation or in the installation package. This will initiate the log management platform, allowing you to centralize, analyze, and gain insights from your logs.
By following this simplified approach to installing Graylog, you can effortlessly deploy the powerful log management platform on your Linux system. With Graylog up and running, you can leverage its robust features to effectively monitor and troubleshoot your system, enabling efficient operations and enhanced security.
A Comprehensive Installation Walkthrough for Graylog on a Linux Environment

In this section, we will explore a detailed guide on how to effortlessly set up the highly efficient and powerful Graylog platform on your Linux system. By following these clear and concise instructions, you will be able to successfully deploy Graylog, an advanced and feature-rich log management solution, on your preferred Linux distribution in no time.
Firstly, we will lay the groundwork by outlining the essential prerequisites and dependencies required for a seamless installation process. Understanding and meeting these prerequisites will ensure a smooth installation and a stable environment for Graylog to operate on. Additionally, we will explore the various options available for obtaining the necessary software packages, enabling you to choose the most suitable method for your specific Linux distribution.
Next, we will delve into the step-by-step procedure of setting up the Graylog platform. This includes the detailed process of downloading and installing Graylog, configuring the necessary system settings, and setting up the required dependencies. Each step will be accompanied by clear and concise instructions, giving you the confidence to carry out the installation process successfully.
Furthermore, we will explore the configuration options available within Graylog, allowing you to tailor the platform to your specific needs. We will walk through configuring essential settings, such as user authentication, enabling SSL encryption, and fine-tuning log inputs and outputs. By familiarizing yourself with these configuration options, you will be able to optimize Graylog's performance and enhance its security features.
To conclude this guide, we will provide additional recommendations and best practices to maximize the effectiveness and performance of your Graylog installation. These tips and tricks will enable you to leverage Graylog's extensive capabilities for log aggregation, analysis, and visualization, empowering you to gain valuable insights from your machine data.
By following this comprehensive step-by-step guide, you will gain the necessary knowledge and understanding to effortlessly install Graylog on your Linux system. With its robust features and exceptional functionality, Graylog will serve as an invaluable tool for managing and analyzing your logs, leading to enhanced system performance and proactive troubleshooting.
Configuration and Administration of Graylog
In this section, we will delve into the various aspects of configuring and managing Graylog, a powerful open-source log management platform. Through the following paragraphs, we will explore the different settings and options available, as well as the administrative tasks that can be performed to optimize and maintain a Graylog installation.
First, we will discuss the initial setup and configuration of Graylog, covering important aspects such as network configuration, user authentication, and data storage. We will explore how to customize the logging settings to suit specific requirements and integrate Graylog with other systems and tools.
Next, we will delve into the management of inputs, which involves the collection and ingestion of log data from various sources. We will explore the configuration of input types, such as syslog, GELF, and Beats, and discuss the best practices for handling input streams efficiently. Additionally, we will explore the concept of extractors, which allow for the parsing of log messages into structured data.
Monitoring and alerting play a vital role in any log management platform. We will discuss the creation and configuration of alerts based on specific conditions, enabling proactive monitoring and issue detection. Moreover, we will explore the integration of external monitoring tools and systems to enhance the overall monitoring capabilities of Graylog.
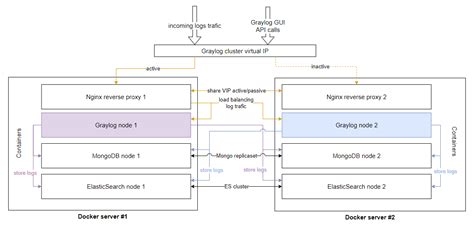
Scaling and performance optimization are crucial considerations for large-scale deployments. We will examine techniques for horizontally scaling a Graylog cluster, ensuring high availability and fault tolerance. Through load balancing, replication, and sharding, we can achieve optimal performance for handling large volumes of logs.
Lastly, we will delve into the maintenance and troubleshooting aspects of Graylog. From managing permissions and user roles to troubleshooting common issues, we will equip administrators with the necessary knowledge and tools to effectively maintain and resolve problems within their Graylog environment.
FAQ
What is Graylog?
Graylog is an open-source log management and analysis tool that collects, indexes, and analyzes log data from various sources.
Why would I want to set up Graylog on my Linux system?
Setting up Graylog on a Linux system allows you to centralize and analyze log data, which can help you identify and troubleshoot issues, monitor system performance, and improve security.
What are the prerequisites for setting up Graylog on a Linux system?
Before setting up Graylog, you need to have a Linux system with a supported version, Java 8 or higher installed, and Elasticsearch and MongoDB running.
Is Graylog suitable for small businesses?
Yes, Graylog is suitable for small businesses as it is a scalable and cost-effective log management solution. It provides essential log analysis capabilities without the need for expensive commercial tools.
What is Graylog and why would I want to set it up on a Linux system?
Graylog is an open-source log management platform that allows you to collect, index, and analyze log data from various sources. Setting up Graylog on a Linux system can provide you with a centralized platform to monitor and manage logs from different applications, servers, and devices. It helps in troubleshooting issues, detecting security threats, and gaining insights into the system's health and performance.
What are the system requirements for setting up Graylog on a Linux system?
The system requirements for Graylog depend on the amount of log data you expect to process and the number of concurrent users. As a general guideline, you will need a Linux system with a minimum of 4 CPU cores, 8 GB RAM, and 30 GB storage. However, it is recommended to have a more powerful server for better performance, especially if you are expecting high log volumes. Additionally, Graylog requires Elasticsearch and MongoDB to be installed on the system.




