When it comes to building a robust and efficient data management system, one cannot underestimate the significance of a well-implemented file storage solution. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the intricate world of Windows Storage Spaces, where we explore the nuances of establishing a reliable and scalable file storage setup. Through a series of carefully crafted steps, we will unlock the secrets to leveraging the full potential of Microsoft's cutting-edge Dynamic Capacity Pool technology.
With a keen eye on optimizing performance and ensuring data availability, our step-by-step walkthrough equips you with the knowledge needed to conquer the complexities of configuring file storage. Harnessing the power of strategic allocation and dynamic pooling, you will gain invaluable insights into architecting a storage system that seamlessly caters to your unique organizational requirements.
Throughout this guide, we will emphasize the significance of thoughtful planning and mindful decision-making, highlighting the importance of understanding the underlying concepts and terminologies. Armed with this knowledge, you will be empowered to make informed choices and implement a File Storage solution that not only meets your current needs but also lays a solid foundation for future scalability.
As we embark on this enlightening journey, be prepared to decipher the intricacies of storage virtualization, resilience, and fault tolerance. Our aim is to equip you with the necessary tools and techniques to navigate the complex terrain of File Storage configuration, ensuring your data remains secure, easily accessible, and adaptable to the ever-evolving needs of your business.
Understanding Windows Storage Spaces: A Valuable Solution for Data Management
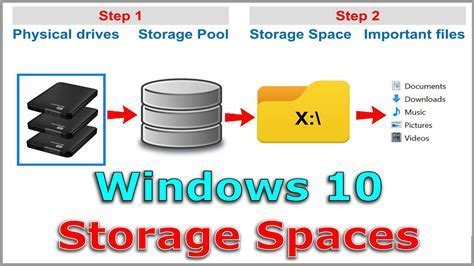
Windows Storage Spaces is a powerful and versatile feature that offers an efficient and cost-effective solution for managing data in a variety of scenarios. This advanced tool enhances data organization, protection, and performance, making it a valuable asset for both personal and business users.
Windows Storage Spaces provides a flexible and scalable platform for creating virtualized storage pools by combining physical drives, regardless of their size or type, into a single logical unit. This enables users to leverage the available storage capacity effectively and optimize resource utilization.
One of the notable advantages of Windows Storage Spaces is its ability to enhance data resiliency through data redundancy techniques such as mirroring or parity. By allocating redundant copies of data across different drives within the storage pool, the system can automatically repair and recover data in the event of a drive failure. This ensures that important data remains accessible and protected, minimizing the risk of data loss.
Additionally, Windows Storage Spaces offers improved performance by utilizing techniques like striping and tiering. Striping involves distributing data across multiple drives to enhance read and write speeds, while tiering intelligently assigns data to different classes of storage devices based on their performance characteristics. This allows for optimized data access and retrieval, catering to the specific needs of different applications and workloads.
Furthermore, Windows Storage Spaces provides a convenient and user-friendly management interface, allowing users to easily create, configure, and monitor storage spaces. The integration with Windows operating systems ensures seamless compatibility and accessibility, making it straightforward to incorporate Windows Storage Spaces into existing workflows.
| Benefits of Windows Storage Spaces |
|---|
| Efficient resource utilization |
| Data redundancy for enhanced resiliency |
| Improved performance through striping and tiering |
| User-friendly management interface |
| Seamless integration with Windows operating systems |
Hardware Requirements for Configuring Windows Storage Spaces
In this section, we will explore the essential hardware prerequisites you need to consider while setting up your Windows Storage Spaces. Understanding these requirements will ensure a smooth and efficient setup process.
Before configuring your Windows Storage Spaces, it is important to keep in mind that certain hardware components are necessary to establish a reliable and high-performing storage system. These components include:
| Hardware Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Hard Disk Drives | Provide the physical storage space for your data. |
| Solid-State Drives (SSDs) | Offer enhanced performance and caching capabilities for improved system speed. |
| SATA, SAS, or NVMe Controllers | Enable the connection between your hard drives and the computer. |
| RAID Controllers | Ensure data redundancy and protection through RAID configurations. |
| Network Interfaces | Facilitate network connectivity for shared storage spaces. |
It is crucial to ensure that your hardware meets the minimum requirements for Windows Storage Spaces in order to achieve optimal performance and reliability. By considering these hardware prerequisites, you can effectively plan and configure your Windows Storage Spaces to efficiently store and manage your data.
What hardware is necessary to begin?

To establish a reliable and efficient file storage solution using Windows Storage Spaces, it is crucial to ensure the presence of appropriate hardware components. The hardware requirements play a significant role in the overall functionality and performance of the system. By carefully selecting and assembling the necessary hardware, users can guarantee a seamless and effective file storage experience without encountering any compatibility or performance issues.
1. Drives: The core component of any file storage setup is the storage drives. It is vital to have a sufficient number of drives available for creating storage pools and virtual drives. These drives can range from traditional hard disk drives (HDDs) to solid-state drives (SSDs). Selecting high-quality drives with ample storage capacity is crucial for accommodating the data volumes required.
2. Controller: Depending on the scale and complexity of the file storage system, a suitable controller may be required. Controllers are responsible for managing the drives and handling the data flow between them. They can be integrated into the motherboard or provided as separate hardware. Choosing a controller with adequate performance capabilities is essential for maintaining optimal data transfer speeds and storage management.
3. Expansion Enclosures: In scenarios where additional drive capacity is necessary, expansion enclosures can be employed. These devices connect to the main storage system and provide additional drive bays for expanding the storage capacity. Expansion enclosures should be compatible with the chosen controller and should support the desired drive types (HDD or SSD).
4. Redundancy Mechanisms: To ensure data integrity and minimize the risk of data loss, incorporating redundancy mechanisms is crucial. Redundancy is achieved through methods such as RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) or mirroring. These mechanisms require additional drives and may also involve specialized RAID controllers. The selection of redundancy mechanisms depends on the desired level of fault tolerance and data protection.
By understanding the hardware requirements of setting up file storage in Windows Storage Spaces, users can meticulously plan and acquire the necessary components. Adequate drives, controllers, expansion enclosures, and redundancy mechanisms are all crucial elements in establishing a robust and efficient file storage system.
Creating a Pool in Windows Storage Spaces: Simplifying Data Organization
Step 2: Establishing a Pool in the Windows Storage Spaces environment is an essential process that streamlines the organization and management of data. By creating a pool, users can combine multiple physical drives into a cohesive storage system, enhancing storage capacity and optimizing data accessibility.
To create a pool in Windows Storage Spaces, follow these simple steps:
- Select the drives: Choose the physical drives that you want to include in the pool. These drives can be internal or external, and they may vary in size and type.
- Decide on resiliency type: Determine the level of data protection you require by selecting the appropriate resiliency type within the Windows Storage Spaces interface. This choice involves considerations such as redundancy and fault tolerance.
- Configure the pool: Assign a name and letter to your newly created pool. Additionally, designate the desired size for the pool, or allow it to consume the entire capacity of the selected drives.
- Create the pool: Activate the creation process, which will amalgamate the chosen drives into a single pool, ready to be utilized for storing and managing your files.
- Verify and customize: Review the pool properties and make any necessary adjustments, such as enabling or disabling features like data deduplication or tiered storage.
The process of creating a pool in Windows Storage Spaces provides users with the flexibility and efficiency needed to organize and manage their data effectively. By carefully selecting drives, determining the required level of data protection, and configuring the pool according to specific needs, users can establish a robust storage solution tailored to meet their unique requirements.
Combining Multiple Drives into a Unified Storage Pool
One of the essential tasks in setting up an efficient file storage system is to combine multiple drives into a single storage pool. By consolidating several drives into a unified pool, you can create a larger storage space to meet your growing data storage needs. This guide will walk you through the step-by-step process of combining drives to create a seamless storage solution without the need for additional hardware or complex configurations.
To begin, you will need to navigate to the storage settings on your Windows system. Once there, you can access the necessary tools to create and manage storage spaces. By using the built-in functionality provided by Windows, you can easily combine multiple drives of various sizes and types into a single logical storage space.
First, identify the drives you want to combine and ensure they are connected to your computer. You can use any combination of internal and external drives, as long as they are recognized by your Windows operating system. Make sure all drives are initialized and formatted if necessary before proceeding.
Next, open the Storage Spaces control panel, or search for it using the Windows search function. Here, you will find an option to create a new storage pool. Click on this option to begin the process.
In the following window, you will be prompted to select the drives you want to include in the pool. Take note of the drive names and select the desired drives from the list. You can choose to utilize the entire capacity of each drive or allocate specific amounts of storage space to the pool.
Once you have selected the drives, you will be prompted to provide a name for the storage pool. Choose a descriptive name that reflects the purpose or usage of the pool. Additionally, you can choose the resiliency type that determines the level of data protection for your storage pool.
After configuring the necessary settings, confirm your choices and proceed with the creation of the storage pool. Windows will automatically combine the selected drives into a unified storage space, and you can begin using it immediately.
By combining multiple drives into a single storage pool, you can effectively enhance your data storage capabilities. Whether you are managing a personal media collection or running a small business, this step-by-step guide provides you with the knowledge and tools to create a seamless and efficient storage solution.
| Benefits of Combining Drives into a Storage Pool | Steps to Combine Drives into a Storage Pool |
|---|---|
| 1. Increased storage capacity | 1. Navigate to the storage settings |
| 2. Improved data redundancy | 2. Identify and connect the drives |
| 3. Simplified data management | 3. Open the Storage Spaces control panel |
| 4. Flexibility to add or remove drives | 4. Select the drives to include |
| 5. Easy expansion of storage capacity | 5. Provide a name for the storage pool |
Creating Virtual Drives in Windows Storage Spaces
In this section, we will explore the process of setting up virtual drives within the Windows Storage Spaces feature. By creating virtual drives, you can efficiently manage and organize your data without the need for individual physical disks.
To begin, you will need to access the Storage Spaces control panel, which allows you to configure and manage your storage pool. Once you have accessed the control panel, you can choose the option to create a new virtual drive.
When creating a virtual drive, you will have the flexibility to choose various settings to tailor it to your specific requirements. You can select the desired drive letter, file system, and allocation unit size, among other options.
After selecting your preferred settings, you can then choose the drives to include in the virtual drive. Windows Storage Spaces allows you to combine different physical drives of various sizes and types, maximizing your available storage capacity.
Once the virtual drive is created, you can assign a meaningful name to help you easily identify its purpose. You can also choose to enable data resiliency options, such as mirroring or parity, to protect your data against drive failures.
With the virtual drive successfully created, you can now start using it as a single logical drive, simplifying your data management tasks. You can access the virtual drive like any other drive on your computer, allowing you to conveniently store and retrieve files and folders.
Overall, the process of creating virtual drives in Windows Storage Spaces provides a flexible and efficient solution for managing your data storage needs. By combining multiple physical drives into a single virtual drive, you can optimize your storage capacity while maintaining data protection.
[MOVIES] [/MOVIES] [/MOVIES_ENABLED]FAQ
What is Windows Storage Spaces?
Windows Storage Spaces is a feature in Windows operating system that allows users to combine multiple physical drives into a virtual pool, creating a storage space that can be used to store and manage data.
Why should I set up File Storage in Windows Storage Spaces?
Setting up File Storage in Windows Storage Spaces provides several benefits such as improved data redundancy, increased storage capacity, and flexibility in managing and organizing data. It also allows for easy expansion of storage space by simply adding more drives to the pool.
Can I add more drives to the storage pool after setting it up?
Yes, you can easily add more drives to the storage pool in Windows Storage Spaces. Simply open the Storage Spaces control panel, select the storage pool, and click on the "Add drives" option. You can then choose the drives you want to add to the pool and they will be included in the storage space.
What is Windows Storage Spaces?
Windows Storage Spaces is a technology in Windows operating systems that allows users to pool multiple physical drives together to create a single logical unit. It provides resiliency, performance optimization, and capacity scaling for file storage.
Why would I want to set up File Storage in Windows Storage Spaces?
Setting up File Storage in Windows Storage Spaces can be beneficial for several reasons. It allows you to combine multiple drives into one logical unit, providing increased storage capacity. It also offers data redundancy, ensuring that your files are protected in case of disk failure. Additionally, it helps improve performance by distributing data across multiple drives.




