Efficient network management is paramount in a modern enterprise, and IP address assignment is a crucial aspect of this process. Identifying and utilizing the most suitable method for delivering IP addresses to devices within a Windows network environment is essential for ensuring seamless connectivity and optimal resource allocation.
While various approaches exist, employing a Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) server stands out as a reliable and flexible solution. By automating IP address assignments, a DHCP server streamlines network administration, minimizing manual configuration efforts and reducing the risk of human error.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the process of setting up and configuring a DHCP server within a Windows server environment. Throughout the article, we will delve into the principles behind DHCP, the benefits it offers, and the step-by-step procedures required to establish a functional DHCP server in your corporate network.
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol: Simplifying Network Management
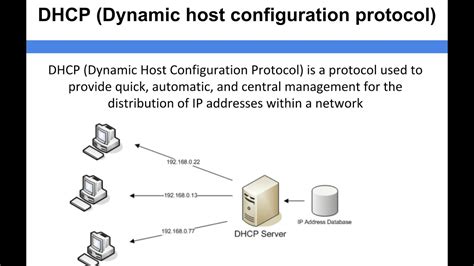
In any modern computer network, the reliable and efficient allocation of IP addresses is crucial for seamless communication between devices. This is where the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) plays a paramount role. In this section, we will explore the essence of DHCP and its importance in simplifying network management and improving connectivity.
Understanding the Importance of Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) and Its Role in Network Connectivity
In any network environment, efficient and seamless connectivity is crucial for smooth and uninterrupted communication between devices. To achieve this, a reliable and efficient network infrastructure is required. One key component that plays a vital role in network connectivity is the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) server.
The DHCP server acts as a central hub that dynamically assigns IP addresses, subnet masks, default gateways, and other network configuration parameters to devices within a network. By eliminating the need for manual configuration of network settings on each individual device, the DHCP server simplifies the process and drastically improves network management efficiency.
By automating the allocation of network settings, the DHCP server ensures that devices can seamlessly connect to the network without any conflicts or errors. It eliminates the possibility of IP address clashes, enabling multiple devices to coexist on the network without manual intervention. Additionally, the DHCP server aids in centralizing and managing changes in network configurations, making it easier to scale and accommodate a growing number of devices.
The DHCP server also plays a crucial role in network security. By assigning IP addresses dynamically, it becomes more challenging for hackers or unauthorized users to pinpoint a specific device or exploit its vulnerabilities. It provides an additional layer of protection by constantly monitoring and regulating the allocation of IP addresses within the network.
- Streamlines network configuration and management
- Eliminates manual IP configuration on individual devices
- Prevents IP address conflicts
- Allows easy scalability and addition of new devices
- Enhances network security
In summary, the DHCP server acts as a crucial element in a network environment, ensuring efficient connectivity, simplifying network management, and enhancing network security. Its ability to automate the allocation of network configuration settings makes it an indispensable component for any network infrastructure.
Building a Dynamic Network Configuration System in a Windows-Based Infrastructure
Enhancing network connectivity and ensuring efficient allocation of IP addresses within a modern IT ecosystem is a crucial aspect of maintaining a stable and reliable infrastructure. In this section, we will explore the process of establishing a flexible network configuration solution in a Windows-based environment.
Streamlining Network Management:
Efficiently managing and maintaining an extensive network infrastructure is essential in today's rapidly evolving technological landscape. By implementing a Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) server, organizations can automate the process of assigning IP addresses, subnet masks, default gateways, and other network configuration parameters to network devices, reducing the administrative overhead and ensuring optimal resource allocation.
Configuring DHCP Server:
Configuring a DHCP server entails defining a range of available IP addresses, lease durations, and other network parameters to effectively cater to dynamic network requirements. This section will delve into the step-by-step process of configuring a DHCP server, including creating address pools, scopes, and options, as well as exploring various advanced configuration settings for seamless network connectivity.
Customizing DHCP Options:
While DHCP servers typically aim to provide basic network configuration parameters, the system's flexibility allows for the customization of additional DHCP options. Learn how to utilize this capability to specify DNS servers, time servers, WINS servers, and other essential network-specific options tailored to meet the unique requirements of your organization.
Monitoring and Troubleshooting:
Implementing a DHCP server requires continuous monitoring to ensure its smooth operation and prompt identification of any potential issues. Discover the built-in tools and techniques available within a Windows-based environment to monitor DHCP server performance, troubleshoot connectivity problems, track lease durations, and detect unauthorized DHCP servers.
Step-by-step Guide: Setting Up DHCP Server Role on a Windows Server
In this section, we will provide a comprehensive step-by-step guide on how to install the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) server role on a Windows Server operating system. This guide will walk you through the necessary configuration steps using concise and clear instructions, ensuring a successful setup.
Step 1: Preparation
Before proceeding with the installation, it is important to gather the necessary information and ensure proper network connectivity. This includes obtaining the server's IP address, subnet mask, default gateway, and DNS server addresses. Additionally, verify that the server is connected to the network and has access to the internet.
Step 2: Accessing Server Manager
Open the Server Manager console, located in the taskbar or through the Start menu. Once opened, navigate to the "Manage" tab and select "Add Roles and Features."
Step 3: Role-Based or Feature-Based Installation
Choose whether to proceed with a Role-Based or Feature-Based installation. For this guide, select the Role-Based option and click "Next" to continue.
Step 4: Selecting the Server
Select the appropriate server on which you want to install the DHCP server role. Ensure the desired server is highlighted and click "Next" to proceed.
Step 5: Choosing the DHCP Role
In the Server Roles section, locate and select the "DHCP Server" role. A pop-up window will appear, detailing the dependencies and recommendations for the DHCP server role. Review the information and click "Add Features" to proceed.
Step 6: Installing Additional Features
If prompted to install additional features that are required by the DHCP server role, review the list and click "Next" to continue. Then, click "Install" to begin the installation process. Wait for the installation to complete.
Step 7: DHCP Server Configuration
After the installation is complete, open the DHCP console from the Server Manager or the Start menu. Navigate to the "IPv4" or "IPv6" section, depending on your network configuration. Right-click on the desired section and select "New Scope" to create a new DHCP scope and configure its settings according to your network requirements.
Step 8: Scope Options and Reservations
Within the newly created DHCP scope, configure additional options such as lease duration, router address, DNS server addresses, and any required exclusions or reservations. Ensure that the scope settings align with your network's needs.
Step 9: Activation and Testing
Once all necessary configurations are complete, activate the DHCP scope to begin serving IP addresses to network clients. To ensure the DHCP server is functioning correctly, test the lease process by connecting a client device to the network and verifying its receipt of a valid IP address from the DHCP server.
Step 10: Monitoring and Maintenance
It is essential to regularly monitor the DHCP server's performance and address any potential issues promptly. This includes observing lease renewals, addressing conflicts, and keeping track of the address usage within the scope. Additionally, perform routine maintenance tasks such as database backups and updates when necessary.
By following this step-by-step guide, you will be able to successfully install and configure the DHCP server role on a Windows Server, ensuring efficient IP address allocation within your network.
Configuration of DHCP Scope and Options in a Microsoft Server Environment
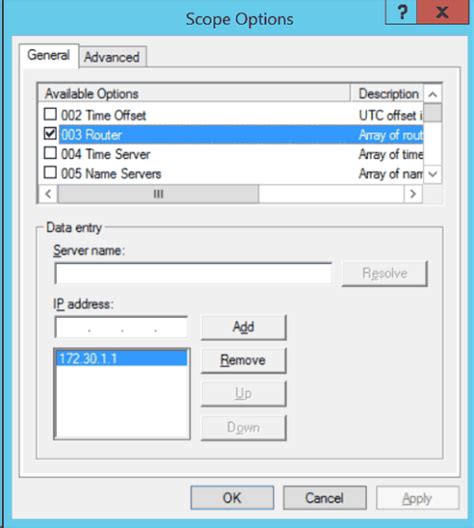
In this section, we will discuss the process of setting up and configuring the DHCP scope and options in a Microsoft Server environment. The DHCP scope defines the range of IP addresses that the DHCP server can assign to client devices on the network. Additionally, DHCP options allow administrators to customize various network settings for the clients, such as DNS servers, default gateway, and domain name.
When configuring the DHCP scope, administrators need to consider the network requirements and available IP address range. The scope should be designed to prevent IP address conflicts and ensure efficient allocation of addresses. This can be achieved by defining the appropriate range of IP addresses, subnet masks, and lease duration.
Furthermore, administrators can configure DHCP options to provide additional network settings to the client devices. These options include the IP addresses of DNS servers, WINS servers, and gateways, as well as specific configuration parameters for the clients. By customizing these options, administrators can optimize the network connectivity and functionality for the client devices.
The configuration of DHCP scopes and options can be performed using the DHCP Management Console, which provides a graphical interface for managing DHCP servers. Administrators can create multiple scopes to accommodate different subnets or VLANs within the network. Additionally, the console allows the configuration of options on a per-scope basis or globally for all scopes.
- Define the DHCP scope range and subnet masks
- Configure lease duration and address conflict detection
- Customize DHCP options for network settings
- Use DHCP Management Console for easy configuration
- Create multiple scopes for different subnets
- Optimize network connectivity with customized options
By properly configuring the DHCP scope and options in a Microsoft Server environment, administrators can ensure efficient and seamless network connectivity for client devices. The ability to customize network settings allows for flexibility and optimization based on specific network requirements.
DHCP Lease Management and IP Address Reservation
In the intricate landscape of network administration, it is crucial to ensure efficient management of IP addresses and timely assignment of dynamic host configuration protocol (DHCP) leases. By effectively managing DHCP lease duration and implementing IP address reservation, network administrators can optimize network performance and strengthen network security.
Efficient DHCP Lease Management
Efficient DHCP lease management is essential for maintaining a stable and reliable network. By setting appropriate DHCP lease durations, network administrators can strike a balance between IP address utilization and lease churn. Shorter lease durations can accommodate frequent changes in network devices and prevent IP address exhaustion, while longer lease durations can reduce DHCP server load and network traffic.
Network administrators should also consider implementing DHCP lease renewal policies, which allow devices to proactively renew their leases to ensure continuous network connectivity. This prevents unexpected disruptions and minimizes the impact of lease expiration on device functionality.
IP Address Reservation
IP address reservation plays a vital role in network management by ensuring that specific IP addresses are always assigned to designated devices. This feature allows critical devices, such as servers or printers, to have consistent IP addresses, simplifying network troubleshooting and access control.
By reserving IP addresses, network administrators can prevent IP conflicts caused by multiple devices attempting to use the same IP address. This helps to maintain network stability and reliability.
In conclusion, proficient management of DHCP leases and implementing IP address reservation are crucial elements in a well-organized network environment. By adopting sound practices in these areas, network administrators can optimize network performance, improve security, and enhance overall network administration efficiency.
Monitoring and troubleshooting the DHCP service in a Windows Server network

In this section, we will explore various methods for monitoring and troubleshooting the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) service in a network running on a Windows Server operating system. Effective monitoring and troubleshooting of the DHCP service is essential for ensuring reliable and efficient network connectivity and IP address management.
Monitoring the DHCP service involves tracking and analyzing various parameters and statistics related to the allocation and lease of IP addresses, network traffic, and DHCP server performance. By regularly monitoring these metrics, network administrators can identify and resolve issues related to IP address exhaustion, DHCP server overload, and abnormal network traffic patterns.
One of the key tools for monitoring the DHCP service is the DHCP management console, which provides a centralized interface for viewing and managing DHCP servers and their configuration. Through the DHCP management console, administrators can monitor the DHCP server's operational status, view allocated IP addresses, track lease durations, and identify IP address conflicts.
In addition to the DHCP management console, network administrators can utilize command-line tools such as ipconfig, netstat, and nslookup to gather real-time information about DHCP leases, network connections, and DNS resolutions. These tools can aid in troubleshooting issues related to DHCP client configuration, network connectivity, and name resolution.
To ensure effective troubleshooting of the DHCP service, it is crucial to maintain comprehensive DHCP server logs. These logs record key events and activities related to DHCP server operations, including lease allocations, renewals, and releases, as well as any encountered errors or warnings. Analyzing DHCP server logs can help identify and resolve issues related to misconfigurations, DHCP client request failures, and network connectivity problems.
Another aspect of monitoring and troubleshooting the DHCP service is proactive network monitoring with the help of network monitoring tools. These tools can continuously monitor the availability and performance of DHCP servers, detect abnormalities in network traffic patterns, and send alerts or notifications in case of any issues or anomalies. By leveraging network monitoring tools, administrators can promptly address DHCP service-related problems before they negatively impact network connectivity.
| Monitoring and Troubleshooting Techniques | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Regularly monitoring DHCP server performance metrics | Identifying and resolving potential performance bottlenecks. |
| Utilizing DHCP management console and command-line tools | Gathering real-time information for diagnosing DHCP-related issues. |
| Maintaining comprehensive DHCP server logs | Identifying and resolving configuration and connectivity problems. |
| Proactive network monitoring with network monitoring tools | Quickly addressing DHCP service-related problems to ensure uninterrupted network connectivity. |
Best practices for securing and optimizing the DHCP server
Ensuring the security and optimization of your DHCP server is critical for maintaining a stable and efficient network environment. By implementing best practices, you can minimize potential vulnerabilities and enhance overall performance.
- Regular Updates: Keeping your DHCP server up to date with the latest patches and security updates is essential. It helps protect against known vulnerabilities and ensures better compatibility with the network infrastructure.
- Secure Network Segmentation: Segmenting your network into smaller subnets can provide added security by isolating different user groups and reducing the scope of potential attacks.
- Implement DHCP Relay Agents: DHCP relay agents can help distribute DHCP requests across different servers, reducing the load on a single server and improving response times.
- Use DHCP Snooping: Enabling DHCP snooping helps prevent unauthorized DHCP servers from operating on your network, mitigating the risk of rogue DHCP servers and potential IP address conflicts.
- Enable DHCPv6 Guard: DHCPv6 guard is essential when deploying IPv6 networks, as it helps prevent malicious or unauthorized DHCPv6 servers from distributing invalid or unauthorized configuration information.
- Implement Network Access Control: Utilizing network access control mechanisms such as 802.1X authentication and MAC address filtering can further enhance the security of your DHCP server by ensuring that only authorized devices can connect to the network.
- Monitoring and Logging: Implementing robust monitoring and logging practices helps detect and analyze potential security incidents, DHCP server performance, and utilization patterns.
By following these best practices, you can significantly improve the security and performance of your DHCP server, leading to a more reliable and efficient network environment.
Exploring Alternative Solutions for DHCP Services in a Windows Server Setting
In a network environment where Windows Server is utilized as the primary infrastructure, there are various options to consider for alternative DHCP server solutions. These alternatives offer distinctive features and functionalities, providing flexibility and customization for network administrators.
1. Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) Relay Agents:
By implementing DHCP relay agents, network administrators can extend the DHCP server's capabilities beyond the Windows Server environment. These relay agents can be deployed in segments of the network where direct access to the DHCP server is not feasible or efficient.
2. Open Source DHCP Servers:
Open source DHCP server solutions offer cost-effective alternatives to Windows Server's built-in DHCP functionality. These solutions are community-driven and provide customizable options to meet specific network requirements.
3. Third-Party DHCP Server Software:
There are several third-party DHCP server software options available for Windows Server environments. These solutions often offer enhanced features, such as advanced lease management, options for failover and redundancy, and increased control over DHCP deployment.
4. Virtual Appliance DHCP Servers:
Virtual appliance DHCP servers leverage virtualization technologies to provide DHCP services within a Windows Server environment. These appliances offer scalability, ease of deployment, and the ability to allocate resources dynamically.
Considering these alternative DHCP server options can help network administrators tailor their infrastructure to specific needs while maximizing efficiency and functionality within a Windows Server environment.
Configure DHCP Server and WDS PXE Booting for MDT Build 8443
Configure DHCP Server and WDS PXE Booting for MDT Build 8443 by BTNHD 100,709 views 7 years ago 11 minutes, 40 seconds
FAQ
What is DHCP and why is it important in a Windows Server environment?
DHCP stands for Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol and it plays a crucial role in a Windows Server environment. It is responsible for automatically assigning IP addresses, subnet masks, default gateways, and other network configuration parameters to client devices. DHCP simplifies the network management process by eliminating the need to manually configure IPs for each device, ensuring efficient allocation and management of IP addresses.
Can I set up multiple DHCP servers in a Windows Server environment?
Yes, it is possible to set up multiple DHCP servers in a Windows Server environment. However, it is important to ensure that these servers are configured correctly to prevent conflicts and duplicate IP address assignment. It is recommended to use DHCP failover clustering or split scopes to distribute the DHCP workload and provide redundancy in case one server goes down. By implementing redundancy, you can ensure high availability of DHCP services and avoid potential network disruptions.




