Managing and configuring network connections efficiently is pivotal in today's fast-paced digital world. One essential aspect of this process involves the allocation of IP addresses to devices connected to a network. This ensures seamless communication and enables devices to interact with each other seamlessly.
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) is a vital component that simplifies the IP address allocation process, eliminating the need for manual configuration. By automating this task, DHCP servers intelligently assign and manage IP addresses dynamically, streamlining network administration.
This article serves as a comprehensive guide, exploring how to establish and utilize DHCP servers on popular operating systems, providing step-by-step instructions for both Windows and Linux environments. By implementing DHCP servers, network administrators can optimize network management, minimize human errors, and enhance overall productivity.
Benefits of Deploying a Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) Infrastructure
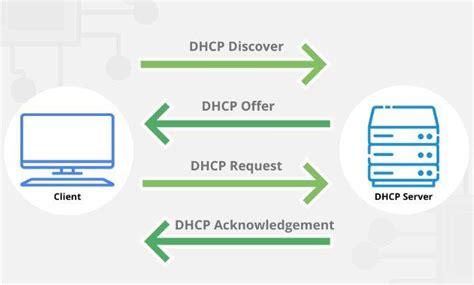
Simplify Network Management: Implementing a DHCP server offers numerous advantages for network administrators. By automating the assignment of IP addresses, DHCP eliminates the need for manual configuration on every device, saving valuable time and reducing human error.
Efficient Resource Allocation: DHCP enables the efficient allocation and reuse of IP addresses within a network. By dynamically assigning IP addresses to devices only when they are connected, DHCP ensures that addresses are not wasted and can be easily managed.
Centralized Control: With a DHCP server in place, network administrators gain centralized control over IP address assignments. This allows for simplified tracking and monitoring of devices, as well as the ability to apply configuration changes across multiple devices from a single point of control.
Scalability and Flexibility: DHCP is scalable and flexible, making it suitable for networks of all sizes. It can easily accommodate new devices and handle IP address allocation based on predefined policies, ensuring a seamless experience for users as the network grows.
Improved Network Security: DHCP offers enhanced security features, such as IP address leasing and renewal. By limiting the duration of IP address assignments, DHCP reduces the risk of unauthorized devices gaining prolonged access to the network. Additionally, DHCP supports the use of authentication and encryption to further protect against unauthorized access.
Streamlined Troubleshooting: When network issues arise, troubleshooting becomes more efficient with DHCP. The centralized management and logging capabilities of a DHCP server allow administrators to quickly identify and resolve IP address conflicts, lease issues, and other network problems.
Enhanced Network Performance: By automating the process of IP address assignment, DHCP helps optimize network performance. It reduces network congestion caused by manual configuration errors and ensures that devices receive the appropriate network settings for efficient communication.
In conclusion, deploying a DHCP server brings numerous benefits to network management, including simplified configuration, efficient resource allocation, centralized control, scalability, improved security, streamlined troubleshooting, and enhanced network performance. By leveraging these advantages, organizations can optimize their network infrastructure and improve overall operational efficiency.
Step-by-Step Guide: Configuring Network Assignment Service on an Operating System
In this section, we will provide a comprehensive step-by-step guide on how to configure the network assignment service on your chosen operating system. By following these instructions, you will be able to set up a network assignment service, which will dynamically allocate IP addresses to devices on your network.
Step 1: Begin the configuration process by accessing the administrative settings of your operating system.
Step 2: Locate the network configuration menu and navigate to the network assignment service settings.
Step 3: Enable the network assignment service by selecting the appropriate option or checkbox.
Step 4: Specify the range of IP addresses that the network assignment service will assign to connected devices. Ensure that the range is compatible with your network's subnet mask and addressing scheme.
Step 5: Set the lease duration for the assigned IP addresses. This determines how long a device can retain its IP address before it is released back into the pool for reassignment.
Step 6: Configure additional network assignment service parameters, such as DNS server information and default gateway settings, if required.
Step 7: Save your configuration changes and restart the network assignment service for the new settings to take effect.
Note: It is recommended to consult the documentation or online resources specific to your operating system for detailed instructions on configuring the network assignment service.
By following these steps, you will successfully set up the network assignment service on your operating system, allowing for automated IP address allocation and network management.
Configuring DHCP Options: Understanding the Basics
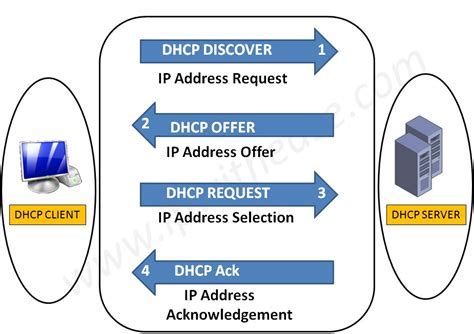
In this section, we will explore the fundamental concepts behind configuring DHCP options. Understanding and properly configuring DHCP options is crucial for efficient network management and optimal client experience. DHCP options provide a way to customize and control various settings for DHCP clients, such as default gateways, DNS servers, and domain names. By familiarizing yourself with the basics of DHCP options, you will be able to tailor your network settings to meet specific requirements and enhance overall network performance.
One of the key aspects of configuring DHCP options is determining the values to be assigned to specific parameters. These parameters dictate the behavior and functionality of DHCP clients within a network. Common DHCP options include subnet masks, default gateways, DNS servers, and time servers. By specifying these options correctly, you ensure that clients receive the necessary information to communicate and operate effectively on the network. Additionally, DHCP options allow for centralized management of network settings, simplifying the administration process and reducing the potential for errors.
| Option Code | Description |
| 1 | Subnet Mask |
| 3 | Default Gateway |
| 6 | DNS Servers |
| 15 | Domain Name |
| 42 | NTP Servers |
To configure DHCP options effectively, it is important to have a clear understanding of the intended purpose of each option. For example, the subnet mask option specifies the network address range and helps in determining the network boundaries. The default gateway option defines the IP address of the router that connects the network to the internet and allows for internet connectivity. DNS server options point clients to the servers responsible for translating domain names into IP addresses, enabling smooth navigation on the web. The domain name option simplifies accessing resources within a specific domain, while NTP server options ensure accurate time synchronization across the network.
By comprehending the various DHCP options and their significance, network administrators can configure DHCP servers to distribute appropriate settings to clients. This level of customization and control allows for optimized network performance, increased security, and streamlined network management. Furthermore, understanding the fundamentals of DHCP options is essential for troubleshooting network issues, as misconfigurations can lead to connectivity problems and suboptimal performance. With a solid understanding of DHCP options, you can fine-tune your network to meet specific requirements and provide an exceptional user experience.
Configuring the DHCP Server on a Linux System: An All-Encompassing Guide
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the detailed configuration process of setting up a DHCP server on a Linux operating system. The DHCP server, also known as the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol server, plays a vital role in automatically assigning IP addresses to devices on a network. By understanding the intricacies of DHCP server configuration on a Linux system, you will be equipped with the knowledge needed to efficiently manage and control network resources.
Before we proceed with the step-by-step setup instructions, it is crucial to grasp the underlying concepts and principles of DHCP server functionality. We will explore the fundamental workings of DHCP, including its role in IP address allocation, network configurations, and lease management. Additionally, we will discuss the benefits of utilizing a DHCP server, such as simplified network administration, enhanced IP address management, and improved scalability.
To successfully configure the DHCP server on your Linux system, we will walk you through various essential components and settings. By the end of this guide, you will have a comprehensive understanding of key aspects, including subnet configuration, address pool allocation, lease duration management, and DHCP options customization. Furthermore, we will provide insightful tips and best practices to optimize the performance and security of your DHCP server.
Throughout this guide, we will showcase practical examples and command-line instructions to ensure a comprehensive learning experience. You will learn how to effectively navigate the Linux system files, modify required configurations, and troubleshoot common DHCP server issues. We aim to equip you with the skills and knowledge necessary to confidently set up and manage a DHCP server, empowering you to streamline network operations and enhance overall efficiency.
- Understanding the DHCP Server Functionality
- Benefits of DHCP Server Implementation
- Configuring Subnets and Address Pools
- Managing Lease Durations
- Customizing DHCP Options
- Optimizing DHCP Server Performance and Security
- Practical Examples and Troubleshooting Tips
DHCP Troubleshooting: Common Issues and Solutions

In the course of working with DHCP networks, various challenges may arise that require troubleshooting and resolution. This section explores common problems that can occur in DHCP systems and provides solutions to resolve them.
- IP Address conflicts: One common issue in DHCP networks is IP address conflicts, where multiple devices end up with the same IP address assigned. This can disrupt network communication and cause connectivity problems. To address this, administrators can implement IP address reservation, which assigns specific addresses to particular devices, ensuring no conflicts occur.
- Lease Expiration: DHCP leases have an expiration time, and if devices fail to renew their leases within the specified timeframe, they may lose network connectivity. Administrators can extend the lease duration to prevent premature expiration and ensure uninterrupted network access.
- Incorrect Subnet Mask: Setting an incorrect subnet mask can lead to communication issues between devices within a network. It is essential to ensure the correct subnet mask is configured to enable proper IP address assignment and network communication.
- Server Unavailability: If the DHCP server becomes unavailable, devices may not be able to obtain IP addresses, resulting in loss of network connectivity. To address this, administrators can implement redundancy by setting up multiple DHCP servers, ensuring network availability even if one server goes down.
- Scope Exhaustion: When the available pool of IP addresses within a DHCP scope is fully utilized, new devices may fail to get assigned an IP address. This can be resolved by expanding the DHCP scope or creating additional scopes to accommodate more devices.
- Incorrect Gateway Configuration: Misconfigured default gateway settings can prevent devices from accessing resources outside their local network. Administrators should double-check the gateway configuration to ensure it aligns with the network topology and ensures proper routing.
- Interference from Rogue DHCP Servers: In some cases, unauthorized DHCP servers may be present on the network, causing conflicts and disruptions. Network administrators should regularly scan for and remove any rogue DHCP servers to maintain proper DHCP functionality.
By understanding these common issues and their respective solutions, network administrators can effectively troubleshoot and resolve DHCP-related problems, ensuring a stable and reliable network environment.
Enhancing DHCP Server Configuration: Customizing Lease Time and Reservations
In this section, we will explore advanced configuration options for DHCP servers, allowing for further customization and optimization of lease time and reservation settings. By adjusting lease time, you can control the duration of IP address allocations to client devices, while reservations ensure specific devices always receive the same IP address within the network.
1. Customizing Lease Time:
- Adjusting lease time allows you to fine-tune the duration for which a client device can retain an assigned IP address.
- Shorter lease times can help in networks with frequent device connections and disconnections, ensuring efficient IP address utilization.
- Longer lease times can be suitable for stable networks where devices remain connected for extended periods.
- Considering factors like network size, device mobility, and network traffic patterns can help determine the optimal lease time for your DHCP server.
2. Managing Reservations:
- Reservations allow you to allocate a specific IP address to a particular client device, ensuring consistency in network configurations.
- By assigning reservations, you can easily identify and manage critical devices within your network.
- Reservations are useful for devices that require constant access, such as servers, printers, or network switches.
- Additionally, you can assign specific configurations, like DNS server or gateway addresses, to reserved devices.
- Having a centralized list of reservations simplifies network maintenance, troubleshooting, and device tracking.
3. Implementing Lease Time and Reservation Settings:
- Accessing the DHCP server configuration file or management interface allows you to modify both lease time and reservation settings.
- Common DHCP server software, such as ISC DHCP server for Linux or Internet Information Services (IIS) for Windows, provides intuitive interfaces for these configurations.
- Ensure you have the necessary privileges to modify DHCP server settings, preferably with administrative access.
- Keep track of the changes made to lease time and reservations to maintain an updated network inventory and address management documentation.
- Regularly evaluate the effectiveness of your lease time and reservation settings to adjust them as per changing network requirements.
By customizing lease time and utilizing reservations effectively, you can enhance the control, stability, and management of your DHCP server, providing a more optimized and reliable network experience for your devices.
DHCP Best Practices: Securing and Optimizing Your Network Configuration

In this section, we will explore essential best practices for maintaining the security and performance of your network configuration. By implementing these strategies, you can ensure that your DHCP infrastructure remains robust and reliable, regardless of the operating system or platform you are using.
1. Secure Your DHCP Server:
| • Utilize strong authentication and access controls to prevent unauthorized access to your DHCP server. |
| • Regularly update your DHCP server software and apply security patches to mitigate vulnerabilities. |
| • Implement firewall rules to restrict access to your DHCP server from external networks. |
| • Disable unnecessary services and features on your DHCP server to reduce potential attack vectors. |
2. Optimize IP Address Allocation:
| • Configure DHCP lease durations appropriately to avoid IP address exhaustion and optimize address utilization. |
| • Implement DHCP reservation for critical devices to ensure they always receive the same IP address. |
| • Regularly monitor IP address usage and adjust DHCP scope accordingly to avoid address conflicts. |
3. Network Segmentation:
| • Implement VLANs or subnetting to separate different types of devices and improve network security. |
| • Use DHCP relay agents to facilitate DHCP communication across different network segments. |
| • Apply appropriate access control lists (ACLs) to restrict DHCP traffic between network segments. |
4. Logging and Monitoring:
| • Enable DHCP server logging to capture critical events and troubleshoot issues effectively. |
| • Regularly review DHCP server logs for security incidents, IP conflicts, and abnormal activities. |
| • Employ network monitoring tools to track DHCP server performance metrics and detect potential bottlenecks. |
5. Disaster Recovery:
| • Implement regular backups of DHCP server configuration and lease database to minimize downtime in case of hardware or software failures. |
| • Test the restoration process from backups to ensure its effectiveness and reliability. |
| • Document the steps and procedures required to recover a DHCP server in the event of a disaster. |
By following these DHCP best practices, you can enhance the security, reliability, and efficiency of your network infrastructure. Implementing these measures proactively will help you avoid potential issues and ensure seamless connectivity for your network users.
Efficient Management of Multiple DHCP Servers for Network Administration
As networks continue to expand and grow in complexity, the need for efficient management of DHCP servers becomes paramount. This section explores various strategies for effectively handling multiple DHCP servers within a network environment, ensuring seamless coordination and optimal resource allocation.
1. Redundancy and Load Balancing: To ensure high availability and reliable DHCP services, network administrators employ redundant DHCP server configurations. By implementing load balancing techniques, DHCP requests can be distributed evenly across multiple servers, preventing any single server from becoming a bottleneck or a single point of failure. This approach guarantees uninterrupted service delivery and ensures network stability.
2. Segmenting and Isolating DHCP Servers: In large network infrastructures, it is often necessary to divide the network into segments or VLANs for better organization and manageability. The same principle can be applied to DHCP servers. By segmenting DHCP services based on different subnets or VLANs, administrators can effectively isolate and dedicate DHCP server resources to specific network segments. This enables centralized management while minimizing potential conflicts and resource contention.
3. DHCP Relay Agents: In scenarios where multiple DHCP servers are spread across different physical locations or subnets, DHCP relay agents play a crucial role. These agents forward DHCP client requests to the appropriate DHCP server, allowing seamless communication between clients and servers despite their geographical or network location differences. DHCP relay agents ensure efficient DHCP address assignment regardless of the network's topological complexity.
4. Centralized Monitoring and Configuration Management: Managing multiple DHCP servers necessitates a centralized approach for monitoring and configuration management. Network administrators can utilize network management tools and protocols to ensure uniform configurations, monitor performance metrics, and troubleshoot any potential issues across all DHCP servers. Centralized management streamlines administration tasks and minimizes the chances of misconfiguration or inconsistencies within the network.
5. Scalability and Planning for Future Growth: As networks evolve, it is crucial to plan for scalability and future growth. Administrators should anticipate the need for additional DHCP servers as the network expands or supports larger user populations. By incorporating scalability into the network design, administrators can proactively allocate resources and optimize DHCP server deployments to meet future demands without compromising network performance or user experience.
By implementing these strategies and best practices, network administrators can efficiently handle multiple DHCP servers, ensuring reliable address assignment, network stability, and seamless communication across complex network infrastructures.
DHCP vs. Static IP Assignment: Pros and Cons
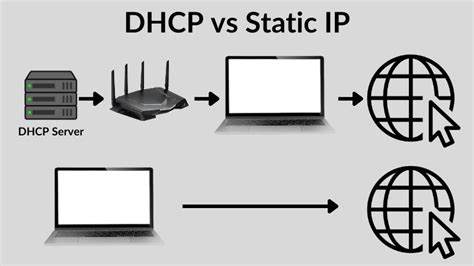
In the context of the topic "How to Set Up DHCP Server on Windows and Linux," it is important to understand the pros and cons of using DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) compared to static IP assignment. This section will explore the advantages and disadvantages of both approaches to IP address management, allowing you to make an informed decision based on your specific requirements.
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP)
DHCP is a network protocol that enables automatic assignment of IP addresses within a network. It offers several benefits, such as simplified network administration, flexibility in managing IP addresses, and efficient resource allocation. With DHCP, devices can obtain IP addresses dynamically, eliminating the need for manual configuration and reducing the chance of address conflicts. Additionally, DHCP allows for easy scalability, making it ideal for networks with a large number of devices or frequent changes in connected devices.
Pros of DHCP:
- Streamlines network administration
- Enables efficient resource allocation
- Reduces the chance of IP address conflicts
- Offers easy scalability for growing networks
Static IP Assignment
On the other hand, static IP assignment requires manually configuring IP addresses for each device on the network. This approach offers more control and stability but requires meticulous planning and administration. With static IP assignment, you have complete control over the IP addresses assigned to devices, which can be advantageous for specific network setups or applications that require fixed IP addresses. However, static IP assignment can be time-consuming, especially in larger networks, and may result in conflicts if not carefully managed.
Pros of Static IP Assignment:
- Provides greater control and stability
- Ensures consistent IP addresses for specific devices
- Facilitates specific network setups or applications
Cons of Static IP Assignment:
- Requires manual configuration for each device
- Can be time-consuming and error-prone
- Potential for conflicts if not carefully managed
In conclusion, both DHCP and static IP assignment have their advantages and disadvantages. DHCP offers automation and scalability, making it suitable for most networks, while static IP assignment provides greater control and stability but requires more manual effort. Ultimately, the choice between DHCP and static IP assignment depends on the specific needs and goals of your network setup.
Install and Configure DHCP Server in Windows Server 2019 Step By Step Guide
Install and Configure DHCP Server in Windows Server 2019 Step By Step Guide by MSFT WebCast 252,060 views 5 years ago 12 minutes, 49 seconds
FAQ
What is DHCP server?
DHCP server stands for Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol server. It is a network management protocol that automatically assigns IP addresses and other network configuration settings to devices on a network.
Why would I need to set up a DHCP server?
You would need to set up a DHCP server if you want to automate the process of assigning IP addresses and network configuration settings to devices on your network. This can save time and effort compared to manually configuring each device's network settings.
Can I set up a DHCP server on both Windows and Linux?
Yes, you can set up a DHCP server on both Windows and Linux operating systems. The process may vary slightly between the two, but the basic functionality remains the same.




