As network infrastructures continue to evolve, the need for efficient management and distribution of IP addresses becomes paramount. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the process of setting up DHCP relays on a Linux system, providing step-by-step instructions and valuable insights.
Why is DHCP relay important?
For networks with multiple subnets, DHCP relay acts as a bridge between the DHCP server and the client devices. By forwarding DHCP messages across different subnets, it ensures that devices can obtain IP addresses and other network configuration information seamlessly, regardless of their location within the network.
Streamlining the configuration process
By following this in-depth guide, network administrators and system operators will gain a comprehensive understanding of the DHCP relay configuration process on Linux systems. We will explore various command-line tools and configurations, all aimed at simplifying the setup and management of DHCP relays.
Understanding DHCP Relay on Linux

In this section, we will delve into the concept of DHCP relay on Linux systems. We will explore the fundamental principles and functionality behind the DHCP relay feature, examining how it enables the efficient distribution of IP addresses within a network environment.
By delving into the intricacies of DHCP relay, we gain a better understanding of how it operates as a vital component in network architecture. This allows us to grasp its importance in facilitating communication between DHCP servers and DHCP clients, without resorting to manual IP address assignment.
This section investigates the underlying mechanisms of DHCP relay, shedding light on the key roles and responsibilities it assumes in the network environment. We will explore how DHCP relay agents act as intermediaries, forwarding DHCP messages between DHCP servers and clients, ensuring a seamless exchange of network configuration data.
Furthermore, we will examine the benefits that DHCP relay brings to network administrators. By reducing administrative overhead and simplifying the management of IP addressing, DHCP relay assists in the smooth operation of complex networks. We will also touch on the potential challenges and considerations when configuring DHCP relay on Linux systems.
Understanding DHCP relay on Linux empowers network administrators to make informed decisions when designing and implementing IP address management strategies. By comprehending the intricacies of the DHCP relay mechanism, network professionals can optimize network performance and streamline the allocation of IP addresses, leading to a more efficient and reliable network infrastructure.
Exploring the fundamentals of DHCP relay
In this section, we will delve into the essential concepts of DHCP relay and understand its significance in network configurations. DHCP relay plays a crucial role in facilitating the communication between DHCP clients and servers in a network environment. By acting as an intermediary, the DHCP relay agent efficiently forwards DHCP messages across different subnets or network segments.
DHCP relay enables the allocation of IP addresses and other network configuration information to clients in a centralized manner, even if the DHCP server is located on a different subnet. Instead of each subnet having its own DHCP server, DHCP relay simplifies network management and reduces administrative overhead by allowing a single DHCP server to serve multiple subnets.
With DHCP relay, client requests for IP addresses are intercepted by the relay agent on the local subnet. The relay agent then encapsulates the DHCP messages and forwards them to the appropriate DHCP server. The server processes the requests and responds back to the relay agent, which then relays the responses back to the clients.
One of the key benefits of DHCP relay is its ability to extend the reach of DHCP services across different network segments, enabling seamless communication and network connectivity. By strategically placing DHCP relay agents in network topologies, organizations can efficiently manage IP address assignments, DNS configurations, and other network parameters.
- Understanding the role of a DHCP relay agent
- Working principles of DHCP relay
- Benefits and advantages of using DHCP relay
- Configuration considerations for DHCP relay agents
- Best practices for deploying DHCP relay in network architectures
By exploring the basics of DHCP relay, network administrators can gain a deeper understanding of its functionality and significance in managing network resources effectively.
Enhancing Network Efficiency with DHCP Relay on Linux: The Benefits You Need to Know
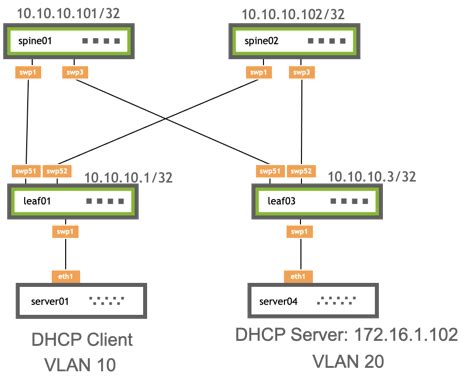
When it comes to optimizing network performance and facilitating seamless communication between clients and servers, the importance of DHCP relay on Linux cannot be overstated. By serving as a bridge between different network segments, DHCP relay allows for the efficient allocation of IP addresses, improved network management, and enhanced overall productivity.
One of the key benefits of DHCP relay is its ability to extend the reach of DHCP servers beyond the local network, enabling the allocation of IP addresses to clients located in different subnets or VLANs. This eliminates the need for separate DHCP servers on each network segment and ensures centralized control and administration of IP address assignments.
Additionally, DHCP relay reduces network traffic by eliminating the need for broadcast messages to be sent to all hosts within a network segment. Instead, DHCP relay agents selectively forward DHCP requests to the appropriate DHCP server, resulting in optimized network utilization and reduced bandwidth consumption.
Another advantage of DHCP relay on Linux is its ability to provide fault tolerance and redundancy. By configuring multiple DHCP servers and relay agents, network administrators can ensure uninterrupted DHCP services even in the event of server failures. This promotes network reliability and resilience, minimizing downtime and maximizing user satisfaction.
The use of DHCP relay also simplifies network management by centralizing the configuration and administration of IP address assignments. This allows for easier monitoring, troubleshooting, and control of IP address allocation, leading to streamlined network operations and increased efficiency.
| Benefits of DHCP Relay on Linux: |
|---|
| 1. Extension of DHCP server coverage beyond local network boundaries |
| 2. Reduction of network traffic and bandwidth consumption |
| 3. Provision of fault tolerance and redundancy for uninterrupted DHCP services |
| 4. Centralized configuration and administration of IP address assignments |
In conclusion, the utilization of DHCP relay on Linux offers numerous advantages that contribute to a more efficient and manageable network infrastructure. From extending DHCP server coverage to reducing network traffic and simplifying administration, harnessing the power of DHCP relay facilitates optimal network performance and maximizes the potential of your Linux-based systems.
Prerequisites for Setting Up DHCP Relay
Before you can start configuring DHCP relay on your Linux system, there are a few prerequisites that need to be met to ensure a successful setup. These requirements are essential for the smooth functioning of the DHCP relay and its communication with the DHCP server and client devices.
Firstly, you need to have a basic understanding of networking concepts and protocols such as IP addressing, subnets, and broadcast domains. This knowledge will help you comprehend the configuration process and troubleshoot any issues that may arise during the setup.
In addition, it is crucial to have a Linux distribution installed on your system with administrative privileges. This will enable you to access and modify the necessary configuration files and network settings required for DHCP relay configuration.
Furthermore, ensure that the DHCP server and client devices are already set up and operational within your network environment. The DHCP relay relies on the presence of a functioning DHCP server to obtain IP address information and configuration parameters for the client devices.
Lastly, you will need the IP address of the DHCP server to configure the DHCP relay. Make sure to acquire this information before proceeding with the setup, as it will be required during the configuration process.
Ensuring Reliable Network Connectivity and DHCP Server Availability
Establishing a robust network infrastructure requires reliable network connectivity and the availability of a DHCP server. This section explores essential considerations and best practices to ensure a stable and uninterrupted network environment.
1. Network Redundancy |
Building a resilient network involves implementing network redundancy measures to minimize the risk of single points of failure. This can be achieved through redundant network links, switches, routers, and power sources. |
2. High-Availability DHCP Server |
Deploying a high-availability DHCP server is crucial to maintain uninterrupted IP address allocation. Multiple DHCP servers can be configured in failover mode, ensuring that if one server fails, the secondary server will take over and seamlessly continue serving DHCP requests. |
3. Load Balancing |
Implementing load balancing mechanisms across DHCP servers optimizes resource utilization and enhances overall performance. Load balancers distribute incoming DHCP requests evenly across multiple servers, preventing any single server from becoming overwhelmed with traffic. |
4. Monitoring and Alerting |
Deploying a robust monitoring and alerting system allows network administrators to proactively detect and address network issues. This includes monitoring DHCP server availability, network traffic, and DHCP lease usage to ensure prompt resolution of any potential problems. |
5. Regular Backup and Disaster Recovery |
Implementing regular backups of DHCP server configurations and configurations of network devices ensures quick recovery in case of hardware failure or other catastrophic events. Having a disaster recovery plan in place reduces the downtime and helps maintain the availability of DHCP services. |
Verifying system requirements and compatibility
Ensuring that your system meets the necessary prerequisites and is compatible is crucial before configuring DHCP relays on a Linux system. In this section, we will discuss the various aspects to consider and steps to take to ensure a smooth and successful configuration process.
Setting up DHCP Relay on a Linux Server
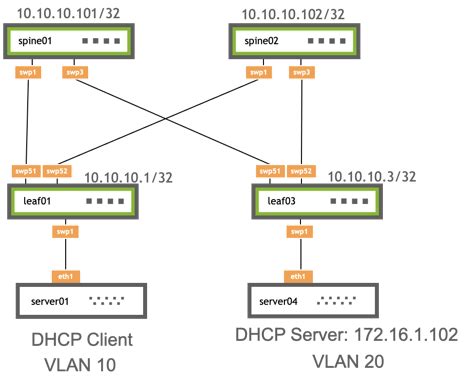
In this section, we will explore the process of configuring the DHCP relay functionality on a Linux server. The DHCP relay allows for efficient communication between DHCP clients and DHCP servers in different network segments. By enabling the DHCP relay, we can ensure that clients located on separate subnets can obtain IP address configuration information from a centralized DHCP server.
The DHCP relay feature acts as a middleman, forwarding DHCP messages from clients to the DHCP server and vice versa, effectively extending the reach of the DHCP service across multiple network segments.
By following the steps outlined in this guide, you will gain a comprehensive understanding of how to set up a DHCP relay on your Linux server, allowing for seamless IP address allocation and configuration in your network environment.
Prerequisites:
- A running Linux server with root access
- Basic understanding of networking concepts
- Knowledge of IP addressing and subnetting
Step 1: Install DHCP Relay
To begin configuring the DHCP relay, we need to first install the necessary software package on our Linux server. You can use your preferred package manager, such as apt or yum, to install the DHCP relay package. Make sure to update your package repository before proceeding with the installation.
Step 2: Configure DHCP Relay
Once the DHCP relay package is installed, we can proceed with configuring the relay settings. This involves specifying the IP address of the DHCP server and the network interfaces that will participate in the relay process. It is essential to ensure that the relay agent is correctly configured to forward DHCP messages to the appropriate server.
Step 3: Test DHCP Relay Functionality
After configuring the DHCP relay, it is crucial to verify its functionality. You can do this by connecting a client device to a different subnet and ensuring that it successfully obtains IP address configuration from the DHCP server. Additionally, monitoring DHCP relay logs and network traffic can help troubleshoot any potential issues.
By following these steps, you will be well-equipped to configure and utilize the DHCP relay functionality on your Linux server, facilitating efficient IP address allocation and configuration in your network infrastructure.
Step 1: Installing necessary packages for Linux configuration
In this section, we will focus on the initial step of preparing your Linux system for configuring DHCP relays. This involves installing the essential packages required to enable the smooth setup and operation of the DHCP relays.
Package installation:
To begin configuring DHCP relays on your Linux system, you need to ensure that all the necessary packages are installed. These packages provide the required tools and libraries to effectively manage DHCP relay functionality. Installing these packages will allow you to seamlessly proceed with the configuration process.
Package manager:
Before proceeding with the installation, it is important to identify the package manager for your specific Linux distribution. The package manager is the tool you will use to download and install the required packages. Popular package managers include apt/yum for Debian-based and Red Hat-based systems, respectively.
Package installation procedure:
Once you have identified the package manager for your Linux distribution, you can follow these general steps to install the necessary packages:
- Open a terminal or command prompt on your Linux system.
- Update the package manager's repository by executing the appropriate command, such as 'sudo apt update' for Debian-based systems or 'sudo yum update' for Red Hat-based systems.
- Use the package manager to install the required packages. For example, you can use 'sudo apt install' followed by the package names for Debian-based systems, or 'sudo yum install' followed by the package names for Red Hat-based systems.
- Wait for the package manager to download and install the packages. This process may take some time, depending on the size of the packages and your internet connection.
- Verify the successful installation of the packages by checking for any error messages or confirmation prompts from the package manager.
Once you have successfully completed the package installation process, your Linux system will be equipped with the necessary tools and libraries to proceed with the DHCP relay configuration.
How to Install DHCP Server in Ubuntu Server 20.04
How to Install DHCP Server in Ubuntu Server 20.04 by root tech 45,237 views 3 years ago 7 minutes, 43 seconds
FAQ
What is DHCP relay and why do we need it?
DHCP relay is a network device or service that allows DHCP messages to be forwarded between clients and servers across different IP networks. It is needed in situations where DHCP server and clients are not located on the same subnet.
How can I configure DHCP relay on a Linux system?
In order to configure DHCP relay on a Linux system, you need to install and configure the dhcrelay package. Once installed, you can edit the /etc/dhcrelay.conf file to specify the DHCP server IP address and interface to relay DHCP requests to.
Can I configure multiple DHCP relays on a single Linux system?
Yes, you can configure multiple DHCP relays on a single Linux system. Each DHCP relay can be configured to relay DHCP requests to different DHCP server IPs and interfaces.
What are the common issues faced when configuring DHCP relays on Linux?
Some common issues faced when configuring DHCP relays on Linux include incorrect configuration of dhcrelay, network connectivity problems between the relay and DHCP server, and firewall settings blocking DHCP traffic.
Is it possible to troubleshoot DHCP relay configuration issues on Linux?
Yes, it is possible to troubleshoot DHCP relay configuration issues on Linux. You can use tools like tcpdump or Wireshark to capture and analyze DHCP traffic, check system logs for any error messages related to DHCP relay, and verify network connectivity between the relay and DHCP server.
What is DHCP relay?
DHCP relay is a feature that allows a server to receive DHCP requests from clients on one subnet and forward them to a DHCP server located on another subnet, enabling DHCP functionality across different network segments.




