In today's digital era, a well-optimized and smoothly running network infrastructure is crucial for organizations of all sizes. To ensure the seamless flow of data and the provision of network services to clients, it becomes imperative to allocate resources intelligently and distribute the workload efficiently. One effective strategy in achieving this is by implementing Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) load balancing.
With DHCP load balancing, network administrators can effortlessly distribute the load across multiple servers, thus ensuring high availability and fault tolerance. By strategically distributing the workload, the overall system performance is enhanced, minimizing the chances of network congestion and bottlenecks.
Moreover, DHCP load balancing offers an additional layer of reliability and fault tolerance by providing redundancy in case of server failures. By maintaining a synchronized database between servers, client requests can be instantaneously serviced by any available DHCP server, further minimizing downtime and improving overall network resilience.
Understanding the Significance of Load Balancing in Windows Server
Load balancing plays a crucial role in optimizing the performance and reliability of servers in a Windows environment. By distributing incoming network traffic across multiple servers, load balancing ensures efficient utilization of resources and prevents overburdening of any single server. This not only enhances the overall stability and availability of the server infrastructure but also improves responsiveness and user experience.
- Improved Performance: Load balancing enables efficient allocation of workloads, ensuring that each server operates within its capacity. By evenly distributing incoming requests, load balancing minimizes the response time and eliminates bottlenecks, resulting in enhanced performance.
- Scalability: With load balancing, it becomes easier to scale server resources in response to increasing demands. By adding or removing servers from the load balancing pool, administrators can dynamically allocate resources to meet changing capacity requirements.
- High Availability: Load balancing improves the fault tolerance of a server infrastructure by distributing workloads across multiple servers. In the event of a server failure, the load balancer automatically redirects traffic to other functioning servers, ensuring uninterrupted service availability.
- Optimized Resource Utilization: Load balancing intelligently distributes incoming requests based on factors such as server load, network conditions, and geographic proximity. This helps in maximizing the utilization of server resources, minimizing idle time, and avoiding resource congestion.
- Flexibility and Redundancy: Load balancing allows for the deployment of redundant servers to provide backup and failover capabilities. In case of a server failure, the load balancer automatically redirects traffic to the redundant servers, ensuring minimal impact on ongoing operations.
In conclusion, load balancing is a critical component of a Windows Server environment that optimizes performance, enhances availability, and improves resource utilization. By distributing incoming traffic across multiple servers, load balancing ensures efficient handling of requests, scalability, and fault tolerance. Understanding the importance of load balancing is essential for administrators seeking to design a robust and reliable server infrastructure.
Configuring Load Distribution for Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol in Microsoft Server
The Significance of Load Distribution in Microsoft Server for Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
When it comes to managing network resources efficiently, load distribution plays a crucial role in ensuring optimal performance and availability. In the context of Microsoft Server, load distribution for the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) is a vital configuration aspect that allows for the distribution of client requests across multiple DHCP servers. By distributing the workload, the system can handle a higher number of clients, balance the traffic, and prevent any single server from becoming overwhelmed or a single point of failure.
Configuring Load Distribution in Microsoft Server for DHCP
In order to configure load distribution for DHCP in Microsoft Server, several steps need to be followed. Firstly, it is important to set up multiple DHCP servers in the network environment. These servers can be physically separate or virtual machines running on a single physical server, ensuring redundancy and high availability. Next, load distribution algorithms need to be implemented to determine how the client requests will be distributed across the DHCP servers. Microsoft Server provides several load distribution algorithms, such as round-robin, IP hash, and source IP and port hash, each with its own benefits and considerations.
Once the DHCP servers and load distribution algorithms are in place, the next step is to configure the DHCP scopes and exclusions on each server. Scopes define the range of IP addresses that a DHCP server can assign to clients, while exclusions specify any IP addresses that should not be distributed. It is crucial to ensure that the DHCP scopes and exclusions are synchronized across all the DHCP servers to avoid any conflicts or inconsistencies in IP address allocation.
Additionally, monitoring and adjusting the load distribution settings should be an ongoing process to ensure optimal performance. Regularly reviewing system logs and network traffic patterns can help identify any bottlenecks or issues, allowing for timely adjustments to the load distribution configuration.
In conclusion, configuring load distribution for DHCP in Microsoft Server is a critical aspect of network management. By implementing proper load balancing techniques and ensuring the synchronization of DHCP scopes and exclusions, organizations can enhance the performance, availability, and resilience of their network infrastructure.
Enabling Load Balancing for DHCP Servers: A Step-by-Step Guide
In this section, we will explore the process of enabling load balancing for DHCP servers in a Windows environment. We will discuss the necessary steps and configurations that need to be undertaken to ensure the efficient distribution of DHCP requests across multiple servers.
Introduction to Load Balancing for DHCP Servers
Load balancing for DHCP servers is a crucial aspect when it comes to managing and distributing IP addresses efficiently in a network. By implementing load balancing, organizations can ensure that DHCP requests are evenly distributed across multiple servers, preventing any single server from becoming overwhelmed and causing bottlenecks in the network. This step-by-step guide will walk you through the process of configuring load balancing for DHCP servers in a Windows environment.
Step 1: Planning Your DHCP Server Infrastructure
Before implementing load balancing, it is important to plan your DHCP server infrastructure properly. Consider factors such as the number of users, the network size, and the expected DHCP request load. This planning stage will help determine the number of DHCP servers required and the appropriate load balancing configuration.
Step 2: Installing and Configuring DHCP Servers
The next step is to install the DHCP server role on each of the servers that will be part of the load balancing configuration. Once installed, ensure that each server has the necessary network connectivity and IP configurations. Configure the DHCP scopes and options according to your network requirements.
Step 3: Configuring the Failover Relationship
In this step, you will need to configure the failover relationship between the DHCP servers. This will involve specifying the primary and secondary DHCP servers, setting up the mode (load balancing in this case), and configuring the load balancing algorithm to determine how DHCP requests are distributed across the servers.
Step 4: Monitoring and Managing the Load Balancing Configuration
Once the load balancing configuration is in place, it is important to regularly monitor and manage the DHCP servers. This involves keeping track of server health, monitoring DHCP request distribution, and making any necessary adjustments to the load balancing configuration based on network demands.
Conclusion
Enabling load balancing for DHCP servers in a Windows environment is a critical step in ensuring the efficient allocation of IP addresses and preventing server overload. By following this step-by-step guide, you can successfully configure load balancing for DHCP servers and ensure a stable and reliable network infrastructure.
Factors to Consider before Implementing DHCP Redundancy
Implementing a reliable and efficient DHCP load balancing solution requires careful consideration of various factors. Before diving into the technical details, it is important to assess your network infrastructure, understand the potential benefits and drawbacks, and evaluate the impact on overall network performance.
1. Scope of Network: The size and complexity of your network play a crucial role in determining the need for DHCP redundancy. Large networks with numerous subnets and a high volume of DHCP requests are more likely to benefit from load balancing.
2. DHCP Server Workloads: Analyze the current and projected DHCP server workloads to determine the level of redundancy required. Consider factors such as the number of clients, IP lease durations, and DHCP options. This will help you determine the appropriate load balancing configuration.
3. Network Availability Requirements: Evaluate the availability requirements for your network. Identify critical services and applications that heavily rely on DHCP, and assess the potential impact of DHCP server failures. This will help you determine the level of fault tolerance needed.
4. Scalability and Growth Plans: Consider your organization's growth plans and potential changes in network requirements. Ensure that the chosen load balancing solution can scale and accommodate future expansion without significant disruptions.
5. Hardware and Software Compatibility: Verify the compatibility of your existing networking hardware and software with DHCP load balancing features. Ensure that your equipment and operating systems support the required load balancing protocols and configurations.
6. Configuration Complexity: Evaluate the administrative overhead and complexity associated with implementing DHCP load balancing. Assess the skills and resources available within your IT team to ensure they are proficient in configuring and managing a load balanced DHCP environment.
7. Operational Considerations: Take into account any operational considerations specific to your organization. This may include compliance requirements, security concerns, or unique network architectures that need to be considered when implementing DHCP load balancing.
By considering these factors before implementing DHCP load balancing, you can ensure a successful and effective deployment that enhances network reliability and performance.
Assessing Network Infrastructure and DHCP Server Capacity
When it comes to optimizing your network infrastructure and ensuring efficient DHCP server performance, a crucial step is assessing the capacity and capabilities of your existing setup. By thoroughly evaluating your network infrastructure and DHCP server capacity, you can identify potential bottlenecks, plan for growth, and make informed decisions to support your organization's needs.
Start by examining the overall design and architecture of your network infrastructure. Consider factors such as the number of subnets, the topology of your network, and the distribution of DHCP clients across different locations. This analysis will provide insights into the overall complexity and scalability requirements of your DHCP server setup.
Next, evaluate the capacity of your DHCP servers. Assess the hardware specifications, including the CPU, memory, and storage resources, to determine if they can effectively handle the anticipated DHCP workload. Additionally, consider the network bandwidth available for DHCP traffic and ensure that it can support the expected number of clients and DHCP lease requests.
It is also crucial to consider the redundancy and resilience of your DHCP server setup. Assess if you have sufficient failover mechanisms in place to ensure uninterrupted DHCP service in case of hardware failures or other disruptions. Explore options like DHCP failover or clustering to enhance the availability and reliability of your DHCP infrastructure.
Lastly, consider the future growth and scalability needs of your organization. Evaluate if your current DHCP setup can accommodate the projected increase in the number of clients, subnets, or network expansion. Assess the potential impact of adding more DHCP scopes and leases to your existing servers, and plan accordingly to avoid performance degradation or resource exhaustion.
- Perform a comprehensive review of your network infrastructure design and architecture.
- Evaluate the hardware specifications of your DHCP servers.
- Assess the network bandwidth capacity for DHCP traffic.
- Ensure redundancy and resilience in your DHCP server setup.
- Consider future growth and scalability requirements.
By thoroughly assessing your network infrastructure and DHCP server capacity, you can proactively address any limitations or bottlenecks, optimize performance, and ensure a reliable and efficient DHCP service for your organization.
Best Practices for Setting Up Efficient Distribution of IP Addresses
In this section, we will discuss the recommended strategies and guidelines for configuring an optimal distribution of IP addresses in a network environment. By following these best practices, you can ensure a reliable and efficient DHCP load balancing setup for your organization.
1. Planning IP Address Allocation:
Prior to implementing DHCP load balancing, it is vital to plan and allocate IP addresses effectively. Consider the number of devices on your network, the potential growth of your organization, and the subnetting requirements. By carefully planning IP address allocation, you can avoid conflicts, ensure sufficient address pools, and minimize the chances of IP address exhaustion.
2. Configuring Redundant DHCP Servers:
Distributing the DHCP workload across multiple servers enhances the availability and reliability of IP address assignment. A key best practice is to configure redundant DHCP servers, located on separate physical machines or virtual environments. This ensures high availability, prevents a single point of failure, and provides fault tolerance in case of server failures.
3. Enabling DHCP Failover:
To further enhance DHCP load balancing, it is recommended to enable DHCP failover. This feature allows for automatic replication of IP address lease information between the primary and secondary DHCP servers. With failover enabled, you can ensure continuity of IP address assignment even in the event of server downtime or network connectivity issues.
4. Monitoring and Performance Tuning:
Regular monitoring of DHCP server performance is crucial for maintaining optimal load balancing. Keep track of IP address assignment rates, DHCP server response times, and overall network performance. By identifying and addressing any bottlenecks or performance issues, you can fine-tune your DHCP load balancing configuration to achieve maximum efficiency.
5. Regular Backups and Disaster Recovery:
Always maintain regular backups of your DHCP server configurations and lease databases. In the event of server failures, natural disasters, or any other unforeseen events, having up-to-date backups ensures the ability to quickly recover and restore DHCP services. Implement a disaster recovery plan that includes regular backup routines and procedures for seamless restoration.
Conclusion:
By adhering to these best practices, you can ensure a robust and efficient DHCP load balancing setup, minimizing IP address conflicts, maximizing availability, and optimizing network performance. Following these guidelines will help you achieve a stable and scalable DHCP solution for your Windows network environment.
Optimizing Load Balancing Algorithm and Thresholds
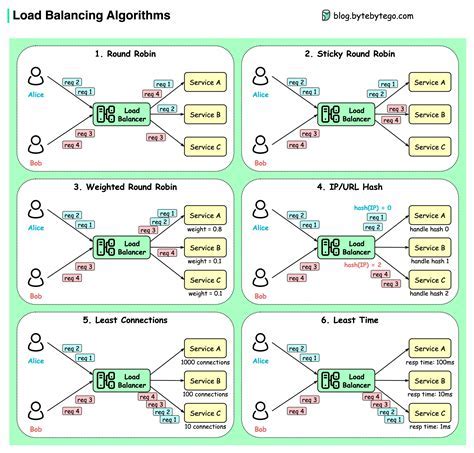
In the context of configuring DHCP load balancing, a crucial aspect to consider is the optimization of load balancing algorithm and thresholds. By fine-tuning these parameters, administrators can ensure efficient distribution of client requests and maximum utilization of server resources.
When it comes to load balancing algorithms, it is important to select the most appropriate one for your specific network environment. Different algorithms, such as round-robin, least connections, or weighted round-robin, offer unique advantages and trade-offs in terms of request distribution and server utilization. Analyzing the characteristics of your network and workload patterns can help in determining the most suitable algorithm.
Thresholds play a vital role in load balancing as they define the conditions at which client requests are redirected to different servers. Setting appropriate thresholds based on factors like server capacity, network traffic, and utilization can significantly optimize the load balancing process. By carefully examining historical data and conducting performance analysis, administrators can effectively identify the thresholds that yield optimal results.
Moreover, it is essential to regularly monitor and adjust the load balancing algorithm and thresholds to adapt to changing network conditions and workload patterns. This continuous optimization process can ensure that the DHCP load balancing configuration remains efficient and capable of handling increasing demands.
In conclusion, optimizing load balancing algorithm and thresholds is crucial in configuring DHCP load balancing. By carefully selecting the appropriate algorithm, setting suitable thresholds, and regularly monitoring and adjusting these parameters, administrators can maximize the efficiency and effectiveness of their DHCP load balancing setup.
Monitoring and Troubleshooting DHCP Load Balancing
In the context of configuring DHCP load balancing in a Windows Server environment, it is crucial to implement effective monitoring and troubleshooting practices to ensure smooth operation and optimal performance of the DHCP servers.
Monitoring DHCP Load Balancing:
To effectively monitor DHCP load balancing in a Windows Server environment, administrators can utilize various tools and techniques to gather and analyze relevant data. This includes regularly monitoring the DHCP server logs to identify any potential issues or errors, such as lease conflicts or failures in load balancing distribution. Additionally, administrators can utilize network monitoring tools to monitor DHCP response times and ensure that each server in the load balancing configuration is handling an appropriate share of the client requests. By closely monitoring these parameters, administrators can proactively identify and address any imbalances or performance bottlenecks in the load balancing setup.
Troubleshooting DHCP Load Balancing:
In the event of any issues or disruptions in DHCP load balancing, troubleshooting becomes crucial to quickly identify and rectify the problems. Administrators should first review the DHCP server logs to identify any error messages or warning signals that may indicate a specific issue. Additionally, they can perform network connectivity tests to ensure that all servers in the load balancing configuration are reachable and properly synchronized. If issues persist, administrators can also review the DHCP server configuration settings to ensure correct load balancing parameters and verify that the servers are correctly configured to participate in the load balancing operation. In cases where troubleshooting efforts do not yield a resolution, it may be necessary to seek assistance from Microsoft support or knowledgeable professionals specializing in DHCP load balancing.
Using Event Logs and Performance Counters to Diagnose Issues
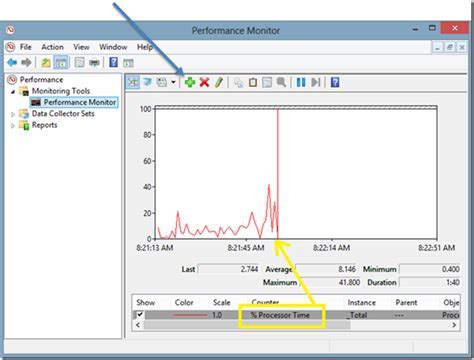
When working with DHCP load balancing in a Windows Server environment, it is crucial to have a comprehensive understanding of how to identify and troubleshoot potential issues. By leveraging event logs and performance counters, network administrators can gain valuable insights into the underlying causes of problems and implement effective solutions.
Event logs serve as a central repository for recording various system events and errors that occur within the DHCP load balancing infrastructure. By examining these logs, administrators can track the sequence of events leading up to an issue and identify any patterns or recurring errors. Additionally, event logs provide valuable information about the time, date, and specific details of each event, enabling administrators to pinpoint the root cause accurately.
Performance counters offer real-time data regarding the performance and health of the DHCP load balancing configuration. By monitoring key performance indicators, such as CPU usage, network latency, and memory utilization, administrators can identify potential bottlenecks or resource constraints that may impact the DHCP servers' performance. Analyzing performance counters provides insights into the system's overall stability and enables administrators to proactively address any impending issues before they impact network availability.
By proactively utilizing event logs and performance counters, network administrators can gain a deeper understanding of the DHCP load balancing environment's performance and detect underlying issues. Armed with this information, they can then develop targeted strategies to effectively diagnose and resolve any problems, ensuring a stable and reliable DHCP service for their network.
FAQ
What is DHCP load balancing in Windows Server?
DHCP load balancing in Windows Server is a feature that allows distributing the DHCP service load across multiple DHCP servers. It helps in sharing the DHCP workload, providing redundancy, and improving performance and availability.
Why would I need to configure DHCP load balancing?
Configuring DHCP load balancing ensures high availability of DHCP services by distributing the workload across multiple servers. It helps in avoiding a single point of failure and provides redundancy, ensuring that DHCP clients can always obtain IP addresses and other network configuration settings.
How can I configure DHCP load balancing in Windows Server?
To configure DHCP load balancing in Windows Server, you need to have multiple DHCP servers that meet the requirements for load balancing. Then, you can use the DHCP management console to create a new load-balanced DHCP failover relationship, configure the load balance mode, specify the load balance percentage, and specify other settings as required.




