In today's rapidly evolving digital landscape, ensuring a stable and secure internet connection has become an utmost priority. An integral component in achieving this is the ability to configure Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) on your Linux system. By setting up DHCP, you can seamlessly manage and distribute IP addresses to devices within your network, ensuring efficient connectivity and improved network performance.
By implementing DHCP, you unlock a world of possibilities for your network infrastructure. Through its dynamic allocation of IP addresses, DHCP eliminates the need for manual entry, saving valuable time and reducing the risk of human error. With DHCP, your Linux system can act as a centralized server, assigning unique IP addresses to devices and ensuring seamless and reliable internet access for all members of your network.
One of the key advantages of configuring DHCP on your Linux system is enhanced security. By utilizing DHCP, you can implement stringent security measures such as MAC address filtering and IP address reservation. These features enable you to control the devices that have access to your network, protecting against potential unauthorized intrusions. DHCP offers a secure framework for managing and monitoring your network connectivity, allowing you to focus on critical tasks without compromising on protection.
Understanding the Significance of DHCP for Enhanced Online Security
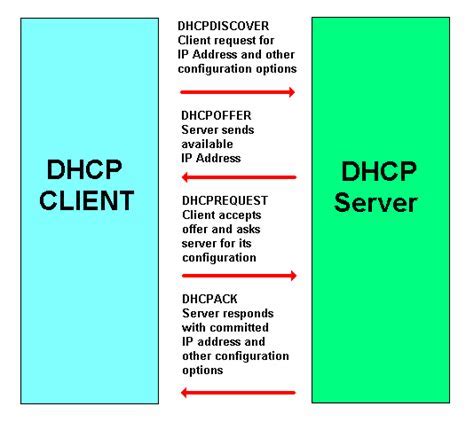
In the ever-evolving digital landscape, the smooth functioning and secure access to the internet are paramount. A crucial aspect that contributes to this seamless experience is the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP). This protocol plays a pivotal role in simplifying and automating network management, ensuring efficient and secure internet connectivity for users.
DHCP serves as the backbone of modern networks, facilitating the automatic assignment of IP addresses to devices connecting to the network. It eliminates the need for manual configuration, making the process more efficient and less prone to human errors. By dynamically assigning IP addresses, DHCP ensures that each device on the network is given a unique identification, promoting secure communication and preventing conflicts.
By intelligently allocating IP addresses, DHCP enhances online security by enabling effective network management. It simplifies the administration of network resources and provides centralized control over the devices accessing the network. This enables network administrators to implement security measures, such as access control lists, firewalls, and secure authentication processes, ensuring that only authorized devices can connect to the network.
Furthermore, DHCP also allows for the allocation of additional network parameters, such as subnet masks, default gateways, and DNS server addresses. These settings contribute to secure internet access by ensuring that devices are configured properly to communicate with the network and external resources securely. DHCP provides a centralized platform for automatically distributing and managing these critical network parameters, eliminating the risk of misconfiguration and reducing the potential vulnerabilities.
| Key Benefits of DHCP for Secure Internet Access: | |
| Efficiency: | DHCP automates the IP address assignment process, saving time and reducing errors caused by manual configuration. |
| Network Management: | Centralized control over network resources enables effective implementation of security measures. |
| Secure Configuration: | Allocation of critical network parameters ensures proper device setup, promoting secure communication. |
In conclusion, DHCP plays a vital role in ensuring secure internet access by automating and simplifying network management. By dynamically assigning unique IP addresses and distributing critical network parameters, DHCP enhances efficiency, enables effective security measures, and ensures proper device configuration. As the digital world continues to evolve, DHCP remains an integral component for a safe and seamless online experience.
Setting up Automatic Network Configuration in a Linux Environment
One of the crucial steps in creating a secure and efficient network environment is configuring automatic network configuration. In a Linux system, this process involves setting up Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) which allows for seamless communication between devices connected to the network.
By implementing DHCP, administrators can automate the assignment of IP addresses and network settings to devices, eliminating the need for manual configuration. This greatly simplifies the network management process, enhances scalability, and improves overall network performance.
When setting up DHCP in a Linux environment, several key considerations come into play. It is essential to establish a well-defined IP address range, configure lease time, and set up a reliable DNS server. Additionally, network administrators should carefully define access controls and security measures to ensure only authorized devices can connect to the network.
There are various tools available in Linux distributions that enable the configuration and management of DHCP. These tools provide a command-line interface or graphical user interface, allowing administrators to easily configure and monitor DHCP settings.
To set up DHCP in Linux, administrators can follow a step-by-step process that involves configuring the DHCP server, defining the DHCP scope, and enabling the necessary firewall rules to protect the network. By properly configuring DHCP, administrators can create a secure and efficient network infrastructure that allows devices to seamlessly connect and communicate.
- Step 1: Install and configure the DHCP server software
- Step 2: Define the DHCP scope and IP address range
- Step 3: Set up lease time for IP addresses
- Step 4: Configure the DNS server
- Step 5: Implement access controls and security measures
- Step 6: Enable firewall rules to protect the network
- Step 7: Test and monitor the DHCP configuration
By following these steps and implementing best practices, Linux administrators can effectively set up DHCP in their network environment, enabling secure and streamlined internet access for connected devices.
Setting up the DHCP Server Software
In this section, we will explore the process of installing the necessary software to configure a DHCP server on a Linux-based system. By following the steps outlined below, you will be able to establish a secure and reliable Internet access for your network.
- Begin by opening the terminal on your Linux system.
- Next, update the package repository by running the command
sudo apt update. This will ensure that you have access to the latest versions of the software packages. - Once the update is complete, proceed to install the DHCP server software by executing the command
sudo apt install isc-dhcp-server. This will download and install the necessary packages onto your system. - After the installation is finished, the DHCP server software will be ready for configuration. However, before proceeding, it is important to backup the default configuration file by running the command
sudo cp /etc/dhcp/dhcpd.conf /etc/dhcp/dhcpd.conf.bak. - Now, you can proceed to edit the configuration file using a text editor of your choice. The configuration file is located at
/etc/dhcp/dhcpd.conf. Make sure to open the file with root privileges by running the commandsudo nano /etc/dhcp/dhcpd.conf. - Within the configuration file, you can specify various DHCP options, such as IP address ranges, subnet masks, default gateway, DNS servers, and lease durations. Make the necessary changes based on your network requirements. Ensure that you save the configuration file after making the modifications.
- Once the configuration file is updated, restart the DHCP server by running the command
sudo service isc-dhcp-server restart. This will apply the changes and start the DHCP server. - Finally, verify that the DHCP server is running correctly by checking its status using the command
sudo service isc-dhcp-server status. If the server is active and running without any errors, you have successfully installed and configured the DHCP server software.
By following the above steps, you have now completed the installation of the DHCP server software on your Linux system. The next sections will focus on further configuring the DHCP server and ensuring secure Internet access for your network.
Setting up the DHCP Server: A Key Component for Network Configuration
In this section, we will focus on the essential steps to configure the DHCP server, an integral part of the network infrastructure, responsible for automating the assignment of network settings to connected devices. Through the DHCP server, network administrators can centrally manage IP addresses, subnet masks, DNS servers, and other vital configuration parameters without manual intervention.
To begin the configuration process, it is necessary to define the DHCP server's settings, including the range of available IP addresses within the network. By specifying the lease time and subnet information, the server can efficiently allocate and renew IP addresses for connected devices, ensuring seamless connectivity without the risk of IP address conflicts.
Another crucial aspect of DHCP server configuration is the definition of DNS server addresses. By specifying the DNS server IP addresses, the DHCP server enables connected devices to resolve domain names into IP addresses, facilitating the seamless and secure access to desired websites and online resources.
In addition to providing IP addresses and DNS server information, the DHCP server can also deliver supplementary configuration parameters, such as gateway addresses and domain names. By utilizing the server's capabilities to distribute this information automatically, network administrators can streamline the configuration process, reducing the workload and potential errors associated with manual device setup.
In summary, configuring the DHCP server plays a vital role in network setup and management, ensuring efficient allocation of IP addresses, seamless DNS resolution, and simplified device configuration. By establishing a properly functioning DHCP server, network administrators can optimize network performance, enhance security, and enable secure internet access for connected devices.
Securing the DHCP Server
In this section, we will explore the essential measures that can be taken to enhance the security of the DHCP server. By implementing these practices, you can ensure the protection of your network infrastructure from potential threats and unauthorized access.
1. Authentication: One of the crucial steps in securing the DHCP server is implementing proper authentication mechanisms. This involves the use of strong passwords, limiting access to authorized personnel only, and regularly updating and rotating these credentials to prevent unauthorized users from gaining control of the server.
2. Encryption: Encrypting communication between the DHCP server and clients is another vital aspect of securing your network. By utilizing encryption protocols such as Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) or Transport Layer Security (TLS), you can ensure that data transmitted during the DHCP process remains confidential and protected from interception.
3. Access Control: Controlling access to the DHCP server is essential in preventing unauthorized configuration changes or malicious activities. Implementing strict access control policies, such as firewall rules and network segmentation, can help restrict access to the DHCP server to only trusted devices and users.
4. Logging and Monitoring: Setting up comprehensive logging and monitoring systems is crucial for detecting and responding to any potential security incidents. By regularly reviewing DHCP server logs, you can identify any suspicious activities or potential vulnerabilities and take prompt action to mitigate them.
5. Regular Updates and Patching: Keeping your DHCP server software up-to-date with the latest security patches is essential to address any known vulnerabilities and protect it from potential exploits. Regularly checking for updates and promptly applying them ensures that your server remains resilient against emerging threats.
6. Restricting DHCP Scope: Limiting the DHCP address range to the minimum required ensures better control over the IP allocation and reduces the risk of IP exhaustion or unauthorized IP assignment. This practice prevents potential security risks posed by rogue DHCP servers and helps maintain a more secure network environment.
By implementing these best practices, you can significantly enhance the security of your DHCP server, minimizing the risk of unauthorized access, data breaches, and potential network disruptions.
Controlling Access to the DHCP Server
In this section, we will explore the configuration of access controls for the DHCP server, ensuring secure and controlled access to network resources. By implementing access controls, network administrators can regulate and restrict the clients that are allowed to request and obtain IP addresses from the DHCP server, enhancing security and preventing unauthorized access.
- Understanding Access Control Lists (ACLs)
- Importance of ACLs in DHCP Server Configuration
- Defining and Configuring ACLs
- Implementing ACLs for Specific Subnets or Network Segments
- Authentication and Authorization Mechanisms
- Implementing Secure User Authentication for DHCP Clients
- Utilizing Techniques such as MAC Address Filtering
- Integrating DHCP Server Access with Existing Authentication Systems
- Monitoring and Logging Access Attempts
- Enabling Logging for DHCP Server
- Analyzing Logs to Identify Unauthorized Access Attempts
- Alerting and Response Mechanisms for Suspicious Activities
- Best Practices for DHCP Server Access Controls
- Updating and Patching DHCP Server Software
- Implementing Regular Audits and Assessments
- Developing and Enforcing Access Control Policies
By following the guidelines presented in this section, network administrators can establish effective access controls for their DHCP servers, safeguarding the network infrastructure from potential security threats and ensuring secure and reliable internet access for authorized users.
Enabling secure DHCP communication
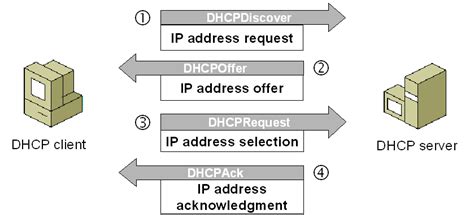
In this section, we will explore the implementation of enhanced security measures for DHCP communication, ensuring a protected and reliable network environment. By establishing a secure DHCP framework, we can minimize potential vulnerabilities and safeguard against unauthorized access or data breaches.
Securing DHCP Messages:
One key aspect of enabling secure DHCP communication is the encryption of DHCP messages. By encrypting these messages, we can protect sensitive information, such as IP addresses, MAC addresses, and lease details, from being intercepted or tampered with by malicious entities. Implementing encryption technologies, such as Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) or Transport Layer Security (TLS), adds an additional layer of protection to DHCP transactions, ensuring secure communication between clients and servers.
Authentication Mechanisms:
In order to prevent unauthorized access and ensure the integrity of DHCP communication, implementing authentication mechanisms is crucial. By utilizing authentication protocols, such as the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol Security (DHCPv6-Sec) or the DHCP Authentication Protocol (DHCAP), we can authenticate DHCP clients and servers, verifying their identities and preventing any potential unauthorized actions within the network. These authentication mechanisms not only enhance security but also provide accountability and traceability within the DHCP infrastructure.
Implementing Access Control:
Another important aspect of enabling secure DHCP communication is implementing access control measures. Through access control lists (ACLs) or firewall rules, we can define and enforce granular policies controlling which devices or entities are allowed to interact with the DHCP server. By restricting access to authorized devices and denying access to potential threats, we can minimize the risk of unauthorized DHCP communication and potential network vulnerabilities.
Monitoring and Auditing:
Finally, to ensure the ongoing security of DHCP communication, it is essential to implement monitoring and auditing mechanisms. By monitoring DHCP server logs and performing regular audits, we can detect any suspicious activity or unauthorized changes within the DHCP infrastructure. This proactive approach allows for the timely identification and mitigation of potential security breaches, ensuring the continued integrity and reliability of the network.
In conclusion, enabling secure DHCP communication involves implementing encryption for messages, utilizing authentication mechanisms, implementing access control measures, and establishing monitoring and auditing procedures. By implementing these measures, organizations can create a robust and secure DHCP environment, safeguarding against potential threats and ensuring reliable internet access.
Ensuring Secure Connectivity for Clients
In this section, we will explore the various measures that can be implemented to guarantee secure internet access for clients. The focus will be on enhancing the safety and protection of client devices when connecting to the internet, thus safeguarding sensitive information and preventing unauthorized access.
Establishing Secure Communication Channels:
One crucial aspect of ensuring secure internet access for clients is to establish secure communication channels through which data can be transmitted. Implementing robust encryption protocols, such as TLS (Transport Layer Security) or SSL (Secure Sockets Layer), can help protect sensitive data from interception and unauthorized access during transmission.
Implementing Strong Authentication Mechanisms:
Another essential measure for secure internet access is the implementation of strong authentication mechanisms. This includes utilizing strong passwords, implementing multi-factor authentication, or utilizing certificate-based authentication. These measures help ensure that only authorized clients can gain access to the network, minimizing the risk of unauthorized access and potential data breaches.
Implementing Network Segmentation:
Network segmentation plays a crucial role in enhancing security for clients. By dividing the network into different segments, each with its own separate set of security controls, it becomes more challenging for attackers to move laterally within the network. Additionally, this helps contain the impact of a potential breach, limiting the exposure of sensitive data to unauthorized individuals.
Regular Software Updates and Patch Management:
Maintaining up-to-date software is vital for ensuring secure internet access. Regularly applying software updates and patches helps mitigate vulnerabilities and ensures that the latest security features and enhancements are in place. This proactive approach helps in preventing potential exploits and reducing the risk of security incidents.
User Education and Awareness:
User education and awareness training play a pivotal role in ensuring secure internet access for clients. By promoting good security practices, such as emphasizing the importance of strong passwords, caution while clicking on suspicious links, and avoiding sharing sensitive information, clients can actively contribute to maintaining a secure internet environment.
In conclusion, secure internet access for clients requires a multifaceted approach that encompasses the establishment of secure communication channels, strong authentication mechanisms, network segmentation, regular software updates, and user education. By implementing these measures, organizations can significantly enhance the security posture of their clients, protecting them from potential threats and ensuring the confidentiality and integrity of their data.
Client Authentication Configuration
In the context of ensuring a protected and authorized access to the network, it is vital to implement appropriate client authentication measures. Client authentication allows the network administrator to verify the identity of the connecting devices, minimizing the risk of unauthorized access and attacks.
By configuring client authentication, administrators can control and manage access to the network based on individual device credentials. This process involves the verification of client-provided information, such as usernames and passwords or digital certificates, before granting network access privileges. Implementing strong authentication mechanisms enhances network security by preventing unauthorized users from connecting to the network and protecting valuable resources from potential threats.
There are various methods available to configure client authentication, including the use of protocols such as Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP) and RADIUS (Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service) servers. These protocols provide a secure framework for the exchange of authentication data and facilitate centralized authentication management.
In addition to username and password-based authentication, network administrators can also explore other authentication techniques, such as certificate-based authentication or token-based authentication. These methods provide an extra layer of security by requiring the use of digital certificates or physical tokens for client verification.
It is essential to tailor the client authentication configuration to the specific needs and security requirements of the network. Careful consideration should be given to the selection of appropriate authentication methods and the implementation of strong password policies to ensure a robust and secure network environment.
Controlling DHCP Lease Time for Enhanced Network Management
In this section, we will explore the importance of implementing lease time controls in DHCP configuration. By carefully managing the duration of IP address leases, network administrators can effectively optimize network resources and improve overall network performance.
Achieving optimal network management involves striking a balance between providing sufficient lease times for client devices to maintain stable connections and avoiding the wastage of valuable IP addresses. With DHCP lease time controls, administrators can ensure that clients can reliably access the network while reducing the likelihood of address conflicts and maximizing address pool utilization.
By implementing shorter lease times, network administrators can enforce regular renewal of IP addresses, allowing for efficient reconfiguration of network settings and the ability to apply necessary security updates or changes without disrupting the entire network. On the other hand, longer lease times may be beneficial for devices that require a more stable connection, such as servers or critical infrastructure.
- Set the DHCP lease time based on the specific requirements of your network.
- Consider the type of devices that will be connecting to the network and their typical usage patterns.
- Evaluate the impact of shorter or longer lease times on network performance and address utilization.
- Regularly review and adjust lease times to adapt to changing network conditions and requirements.
By implementing effective DHCP lease time controls, network administrators can maintain a stable and secure network environment while optimizing the utilization of network resources.
How To Set Up DHCP Server on Ubuntu 22.04 LTS
How To Set Up DHCP Server on Ubuntu 22.04 LTS by ZacsTech 15,543 views 1 year ago 4 minutes, 39 seconds
FAQ
Can I configure DHCP reservations in Linux for specific devices?
Yes, you can configure DHCP reservations in Linux for specific devices. DHCP reservations allow you to assign a specific IP address to a particular device based on its MAC address. This is useful for devices that require a consistent IP address, such as printers or servers. To configure DHCP reservations, you need to identify the MAC address of the device and add an entry in the DHCP server configuration file linking the MAC address with the desired IP address. When the device requests an IP address, the DHCP server recognizes its MAC address and assigns the specified reserved IP address. DHCP reservations provide a convenient way to manage IP addresses for specific devices within a DHCP environment.




