In today's fast-paced digital world, protecting and preserving data has become paramount. As businesses and organizations increasingly rely on technological infrastructure to store and manage their valuable information, it is crucial to establish robust backup and recovery systems. This comprehensive guide aims to assist administrators and IT professionals in effectively establishing and maintaining backup and restore procedures on Windows Server.
Within the dynamic technological landscape, unforeseen events such as hardware failures, data corruption, or malicious attacks can pose significant threats to the integrity of a system's data. The need for a well-designed backup strategy cannot be overstated, as it serves as a safety net to ensure business continuity and minimize the potential risks associated with data loss.
By implementing efficient backup and restore protocols, organizations can safeguard critical information, maintain compliance with data protection regulations, and reduce the downtime caused by potential disruptions. This guide will delve into the best practices for configuring and optimizing backup solutions, leveraging the powerful capabilities of Windows Server to protect data against any unexpected contingencies.
Understanding the Process of Data Protection and Recovery in the Windows Server Environment

In order to ensure the safety and integrity of valuable information stored within a Windows Server environment, it is crucial to comprehend the intricate process of data protection and recovery. By grasping the fundamental principles and strategies employed in this domain, administrators can effectively safeguard their data from potential threats and increase the chances of successful data restoration in the event of unforeseen disasters.
In this section, we will delve into the underlying concepts and mechanisms that form the backbone of data protection and recovery in the Windows Server environment. We will explore various techniques, methodologies, and best practices that enable administrators to create resilient backup solutions while also understanding their significance in maintaining the overall stability and reliability of an organization's IT infrastructure.
- Exploring the Importance of Data Protection
- Understanding the Different Types of Data Backup
- Examining Various Recovery Strategies
- Analyzing the Role of Backup Storage
- Implementing Data Retention Policies
- Evaluating the Impact of Backup and Recovery on Business Continuity
By gaining a comprehensive understanding of these topics, IT professionals can make informed decisions when it comes to selecting appropriate backup and recovery solutions, configuring backup schedules, and streamlining the overall data protection process. This knowledge equips them with the necessary tools to ensure seamless operations, mitigate risks, and minimize the potential impact of data loss or system failures.
How Does Data Protection and Data Recovery Work?
In this section, we will explore the mechanisms involved in safeguarding and recovering valuable information without explicitly referring to the specific actions of configuring and managing backups and restores in Windows Server environments. By understanding the underlying principles, you will gain insight into the intricacies of data protection and restoration.
Data protection ensures the preservation and security of crucial data, shielding it from potential loss or corruption due to various factors such as hardware failures, human errors, or malicious activities. By employing robust techniques, organizations can minimize the risks associated with data loss and maintain business continuity.
At its core, data protection involves creating multiple copies of important data that are stored on separate and redundant storage devices, ensuring redundancy and fault tolerance. This redundancy allows for the retrieval of data from alternate sources in the event of primary data becoming inaccessible or compromised.
Data recovery is the process of retrieving and restoring data from backups when the need arises. It involves identifying and accessing the appropriate backups, extracting the required data, and effectively restoring it to its original state. The recovery process must be efficient and reliable to minimize any potential downtime or disruption to operations.
Various methodologies and technologies exist for backup and restore operations, including full backups, incremental backups, differential backups, and snapshots. Each approach offers distinct advantages and trade-offs, depending on specific requirements, such as the acceptable recovery time and storage capacity.
Additionally, organizations may choose to implement additional data protection measures, such as encryption, to safeguard sensitive information during transit or storage. By encrypting data, even if it falls into the wrong hands, it remains unreadable, maintaining confidentiality and integrity.
| Benefits of Data Protection: | Importance of Data Recovery: |
|---|---|
| - Reduces the risk of irreversible data loss | - Minimizes downtime and preserves productivity |
| - Ensures compliance with data privacy regulations | - Recovers critical data needed for business operations |
| - Provides resilience against hardware failures | - Restores data in its desired state with minimal effort |
Understanding Different Approaches for Data Protection and Retrieval
In the realm of safeguarding information and facilitating its retrieval, various methods are available that cater to different scenarios and requirements. This section aims to delve into the diverse approaches one can undertake to secure and restore data effectively, enhancing the reliability and resilience of your system.
1. Full Backup:
An absolute replication of all data elements within a system is encapsulated in a full backup. This comprehensive method facilitates complete restoration, ensuring that every file and folder, regardless of size or location, is recovered. While full backups encompass the entire dataset, their frequent execution can consume significant storage space and processing time.
2. Incremental Backup:
In contrast to full backups, incremental backups prioritize efficiency by solely recording changes made since the last backup. This approach necessitates a foundation of at least one full backup, subsequently capturing and storing only modified or newly created data. As a result, incremental backups require less storage space and generally execute faster. However, when the need for data restoration arises, it is essential to have all incremental backups available, starting from the initial full backup.
3. Differential Backup:
Differential backups strike a balance between full and incremental backups by preserving changes made since the last full backup. While similar to incremental backups in terms of capturing modified data, differential backups do not rely on a succession of cumulative backups. Retrieving data from a differential backup necessitates only the main full backup and the latest differential backup. This approach reduces the time required for data recovery and minimizes storage requirements compared to full backups.
4. Mirror Backup:
Considered a real-time replication, mirror backups instantaneously copy changes made to the primary data source to a separate destination. This secondary location remains an identical replica of the original files and folders throughout the specified interval. Mirror backups offer the advantage of immediate availability of the replicated dataset, which can be seamlessly accessed in the event of data loss or corruption in the primary system. However, this method also necessitates significant storage space and diligent monitoring to ensure consistency between the source and destination.
5. Hybrid Backup:
Hybrid backups combine two or more backup methods, tailoring the approach to meet specific objectives. By employing a hybrid backup strategy, organizations can optimize resource allocation, maximize efficiency, and address various data protection needs. A common example is a combination of full and incremental backups where regular full backups are complemented by frequent incremental backups, balancing comprehensive data capture and reduced storage consumption.
Each backup and restore method holds unique benefits and limitations, demanding a careful analysis of the specific requirements, system characteristics, and available resources. By understanding the diverse approaches discussed above, you can effectively establish an appropriate backup and restore strategy, ensuring the security and availability of critical data.
Choosing the Ideal Backup Storage Solution
In the hustle and bustle of managing your data, it is crucial to select the perfect backup storage solution to ensure the safety and security of your valuable information. This section will guide you through the key considerations to help you identify the right backup storage solution for your specific needs.
- Capacity and Scalability
- Speed and Efficiency
- Reliability and Durability
- Security and Encryption
- Cost and Affordability
First, evaluating the capacity and scalability of potential backup storage solutions is essential. You need to consider the volume of data you have and anticipate future growth. Ensuring the solution can accommodate your current and future backup needs is paramount.
The speed and efficiency of a backup storage solution play a pivotal role in your data management strategy. It is advisable to choose a solution that offers fast backup and restore speeds, minimizing any potential downtime or business disruptions.
Reliability and durability are vital attributes to consider when selecting a backup storage solution. A reliable solution should guarantee data integrity and consistently perform without any hiccups. Durability entails protection against physical damage or data loss due to factors like power outages or hardware failure.
When it comes to data security, encryption is crucial to protect your sensitive information from unauthorized access. Look for a backup storage solution that offers robust encryption methods to ensure the privacy and confidentiality of your data.
Cost is always an important factor to consider. While there are various backup storage options available, it is essential to find a solution that meets your budget constraints without compromising on the necessary features and functionality.
By carefully evaluating these aspects and finding the right balance for your specific requirements, you can confidently select the ideal backup storage solution that will safeguard your data and provide peace of mind.
Comparison of Local Storage and Network Storage
When it comes to storing and preserving data, two primary options are commonly available: local storage and network storage. Understanding the differences and benefits of each option is essential for selecting the most suitable data storage solution for your needs.
Local storage refers to storing data on physical storage devices connected directly to a single computer or server. This includes hard drives, solid-state drives, and external storage devices. Local storage offers the advantage of quick and easy access to data, as it is directly connected to the system. It provides a reliable and secure option for keeping sensitive information within a controlled environment.
On the other hand, network storage involves the storing and accessing of data on remote devices connected through a network. This can include network-attached storage (NAS) devices or cloud-based storage solutions. Network storage offers the advantages of centralized data management and accessibility from multiple devices and locations. It provides flexibility for collaboration and allows for scalability as storage can be easily expanded as needed.
When considering which option to choose, it is important to assess your specific requirements and consider factors such as data volume, security, accessibility, and cost. Local storage may be more suitable for small-scale operations with limited data and limited accessibility needs. Network storage, on the other hand, is ideal for larger organizations or those with distributed teams that require seamless data sharing and remote access capabilities.
- Local Storage:
- Directly connected to the system
- Quick and easy access to data
- Reliable and secure
- Network Storage:
- Connected through a network
- Centralized data management
- Accessibility from multiple devices and locations
- Flexibility for collaboration
- Scalability
In conclusion, the choice between local storage and network storage depends on various factors and specific needs. Both options offer unique advantages and should be carefully evaluated to ensure the most efficient and effective data storage solution is implemented.
Selecting the Appropriate Storage Hardware
When it comes to safeguarding your crucial files and ensuring their availability when needed, choosing the right storage hardware is paramount. In this section, we will explore the key factors to consider when selecting the most suitable storage devices for your backup and restore needs.
Reliability: One of the fundamental aspects to consider while selecting storage hardware is its reliability. Opt for hardware that is known for its durability and long lifespan. This will help ensure that your data remains secure and accessible for an extended period.
Capacity: Another crucial factor to consider is the storage capacity provided by the hardware. Assess your data storage requirements and opt for a device that offers ample space to accommodate your backup and restore operations effectively. Keep in mind that the storage needs may vary over time, so selecting hardware with scalable capacity options can be advantageous.
Speed and Performance: The speed at which data can be read from or written to the storage hardware is another aspect that deserves attention. Look for devices with fast transfer rates and low latency to minimize the time needed for backup and restore processes. This will ensure that you can efficiently complete these operations without causing any significant disruption.
Connectivity Options: Consider the connectivity options provided by the storage hardware. Ensure compatibility with your existing infrastructure and assess the available interfaces, such as USB, Ethernet, or Fibre Channel. Choosing hardware that seamlessly integrates into your network will simplify the backup and restore workflows.
Security Features: Safeguarding your data against unauthorized access is crucial, especially in an era of increased cybersecurity threats. Look for storage hardware that offers robust security features, such as encryption and access controls, to add an extra layer of protection to your backups and restores.
Scalability: As your business grows and your data storage requirements increase, having the ability to scale your storage setup becomes essential. Select hardware that allows easy expansion, either through additional drives or by accommodating larger storage configurations, to ensure future-proofing and avoid the need for frequent replacements.
In conclusion, selecting the appropriate storage hardware involves considering various factors like reliability, capacity, speed, connectivity options, security features, and scalability. Evaluating these criteria and aligning them with your backup and restore requirements will help you make an informed decision and ensure the successful safeguarding of your data.
Configuring Backup Settings in the Windows Server Environment
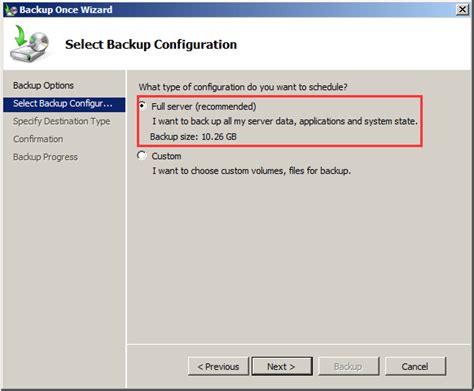
In this section, we will explore the process of customizing and managing backup settings within the Windows Server ecosystem. By adjusting these settings, users can ensure the protection and availability of vital information stored on their systems. This article will guide you through the steps required to configure backup settings, allowing you to tailor the backup process to your specific needs and mitigate potential data loss risks.
One essential aspect of configuring backup settings is determining the frequency and timing of backups. This involves setting up a schedule that aligns with your organization's operational requirements. Windows Server offers various scheduling options, including daily, weekly, or monthly backups, allowing users to create a backup cadence that suits their unique data protection needs. Additionally, users can specify the exact time of backup initiation to minimize impact on system performance during high-traffic periods.
Another crucial consideration in configuring backup settings is selecting the appropriate storage destination. Depending on the available resources and redundancy requirements, Windows Server enables users to choose between different storage options, such as external hard drives, network-attached storage (NAS) devices, or cloud storage services. By strategically selecting the storage destination, users can enhance the security and accessibility of their backup data.
Windows Server also provides flexibility in defining the scope of backup operations. Users can specify which files, folders, or entire volumes to include in the backup process. This granular control ensures that critical data is adequately protected while avoiding unnecessary duplication of nonessential files. Moreover, users can exclude specific file types or directories, optimizing the backup process and reducing the overall storage footprint.
Within the Windows Server environment, you can configure backup settings to enable incremental or differential backups. These methods consume fewer system resources and storage space compared to full backups, as they only capture and store changes made since the last backup operation. By implementing incremental or differential backups, users can expedite the backup process, enhance backup window efficiency, and minimize the impact on system performance.
| Key Considerations for Configuring Backup Settings: |
|---|
| - Choosing the appropriate backup scheduling to align with operational requirements. |
| - Selecting the optimal storage destination for backup data. |
| - Defining the scope of backup operations to include or exclude specific files and folders. |
| - Implementing incremental or differential backups to optimize system resources. |
FAQ
What is the importance of setting up backup and restore data in Windows Server?
Setting up backup and restore data in Windows Server is crucial as it helps protect the valuable data stored on the server. In case of hardware failure, accidental deletion, or other disasters, having a backup ensures that the data can be recovered easily, minimizing downtime and potential loss of critical information.
How can I set up backup and restore data in Windows Server?
To set up backup and restore data in Windows Server, you can use the built-in Windows Server Backup feature. First, open the Server Manager and navigate to the "Local Backup" option. From there, click on "Backup Schedule" and configure the backup settings, such as frequency, destination, and type of backup (full, incremental, or differential). Once set up, the backup operation will run automatically according to the configured schedule.
Can I choose different destinations for backup and restore in Windows Server?
Yes, you have the flexibility to choose different destinations for backup and restore in Windows Server. When setting up the backup schedule, you can specify the backup destination, which can be a local drive, external storage device, network share, or even a cloud service. Similarly, during the restore process, you can select a specific location from where the backup data will be restored.
Is it possible to automate the backup process in Windows Server?
Absolutely! Windows Server provides the option to automate the backup process. You can use the command-line tool "wbadmin" to create scripts and schedule them using the Task Scheduler. By automating the backup process, you can ensure that regular backups are performed without manual intervention, saving time and effort.




