Imagine the unsettling situation of encountering a catastrophic breakdown in your beloved device, rendering it inoperable and leaving you frustrated and uncertain about the next course of action. In the face of such harrowing events, it is crucial to equip yourself with the knowledge of restoring your computer's functionality swiftly and efficiently.
With computers becoming an indispensable tool in our daily lives, it is essential to be well-versed in the process of troubleshooting and recovering from system failures. This article aims to guide you through the intricate steps involved in rejuvenating your computer after a debilitating crash, offering insights and tips to make the journey to system recovery as smooth as possible.
As you embark on this restoration odyssey, it is important to note that the journey may vary depending on the nature and severity of the crash. However, armed with a resilient spirit and a longing for a functional computer, you can take solace in the fact that there are several proven techniques and methodologies available to address these unfortunate situations.
During the course of this guide, we will explore various techniques such as system restore, safe mode booting, and utilizing recovery tools to bring your computer back to life. By embracing these techniques and following the step-by-step instructions provided, you will increase your chances of recuperating your computer's functionality and salvaging valuable data that may have seemed lost forever.
Understanding the Causes of the Technical Failure
In order to effectively recover from a technical failure that has caused a disruption in the normal functioning of your computer, it is essential to first understand the underlying causes of the crash. By gaining a comprehensive understanding of the factors that led to the failure, you will be better equipped to implement the appropriate steps for recovery, minimize the risk of future crashes, and restore your system to its optimal condition.
One possible cause of the crash could be software conflicts or compatibility issues, where certain applications or programs running on your device may be incompatible with the current operating environment. These conflicts can lead to system instability and eventual failure. Additionally, outdated or corrupted device drivers can also contribute to crashes, as they may not function properly within the operating system structure.
Hardware issues, such as faulty components or overheating, are another common cause of crashes. Physical damage to internal hardware parts, insufficient power supply, or improper ventilation can all result in system failures. Moreover, memory-related problems, such as insufficient RAM or defective memory modules, can lead to crashes during resource-intensive tasks.
Viruses, malware, and other types of malicious software can infiltrate your computer system and induce crashes as well. These malicious programs can disrupt the normal functioning of your operating system, corrupt essential files, and cause system instability. It is crucial to regularly update your antivirus software and perform routine scans to detect and eliminate any potential threats.
User error, such as improper system configuration or accidental deletion of critical system files, can also result in crashes. It is important to exercise caution when making system changes or deleting files, as these actions can unintentionally disrupt the proper functioning of your operating system.
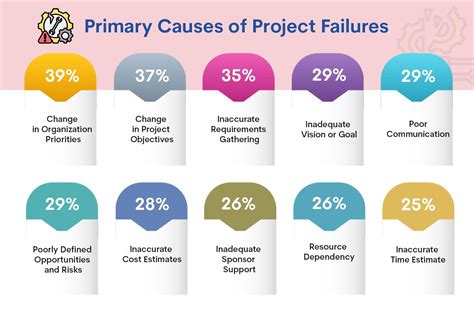
| Possible Causes of the Crash |
|---|
| Software conflicts or compatibility issues |
| Outdated or corrupted device drivers |
| Hardware issues (faulty components, overheating, etc.) |
| Memory-related problems (insufficient RAM, defective memory modules) |
| Viruses, malware, and other malicious software |
| User error (improper configuration, accidental file deletion) |
Creating a System Restore Point
Ensuring the stability and recovery capabilities of your computer is essential in the event of unexpected software issues or crashes. In this section, we will discuss the process of creating a system restore point, a valuable feature present in most operating systems. By creating a system restore point, you can create a predefined backup of your computer's settings, files, and configurations, allowing you to revert to a previously known stable state if any issues occur.
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Open the Start menu and search for "System Restore". |
| 2 | Click on the "Create a restore point" option from the search results. |
| 3 | In the System Properties window, click on the "Create" button. |
| 4 | Provide a descriptive name for the restore point, allowing you to easily identify it in the future. |
| 5 | Click on the "Create" or "OK" button to initiate the creation of the system restore point. |
| 6 | Wait for the system to complete the creation process, which may take a few minutes. |
| 7 | Once the process is finished, you will receive a confirmation message indicating the successful creation of the restore point. |
By regularly creating system restore points, you can safeguard your operating system and important files against unexpected crashes or software errors. This precautionary measure provides the ability to restore your computer to a prior state without losing valuable data, thus minimizing the impact of system failures.
Booting into Safe Mode

In the event of a system failure or unforeseen errors occurring within your computer's software, there is a crucial method called "Booting into Safe Mode" which can help resolve these issues. Safe Mode is a diagnostic startup mode in which the computer operates with basic functionality, allowing you to troubleshoot and fix the problem without the interference of third-party applications or drivers. This section will outline the necessary steps to enter Safe Mode and effectively investigate and address the root cause of the system crash.
Accessing Safe Mode via System Configuration:
To begin the process of booting into Safe Mode, you can utilize the System Configuration tool, commonly known as "msconfig". Firstly, press the Windows key and the letter "R" simultaneously, which will open the Run dialog box. Then, type "msconfig" and press Enter. Within the System Configuration window, navigate to the "Boot" tab. Here, you will find various boot options, including Safe Mode options. By selecting the appropriate Safe Mode option and clicking "Apply" and then "OK", your computer will restart and initiate the boot process in Safe Mode.
Accessing Safe Mode via Advanced Startup Options:
If you are unable to access Safe Mode through the System Configuration tool, an alternative method is to utilize the Advanced Startup Options. Start by pressing the Windows key and the "I" key simultaneously on the keyboard to open the Settings menu. Then, select the "Update & Security" category and click on the "Recovery" option. Under the "Advanced startup" section, click on the "Restart now" button. Once your computer restarts, choose the "Troubleshoot" option, followed by "Advanced options" and finally "Startup Settings". Within the Startup Settings menu, press the appropriate key to enable Safe Mode, usually numbered as "4" or "F4".
Benefits of Safe Mode:
Booting into Safe Mode provides a controlled environment where only essential system files and services are loaded, allowing you to diagnose and resolve software-related issues without interference. It is particularly useful for troubleshooting problems such as application conflicts, driver conflicts, malware infections, or any persistent errors that occur during the normal operating system boot process. By accessing Safe Mode, you can isolate the root cause of the crash and proceed with the necessary steps to resolve it effectively.
Conclusion:
When faced with a system crash or unexpected errors in your Windows computer, booting into Safe Mode can be a valuable technique to regain control and resolve the underlying issues. By following the steps outlined in this section, you can easily access Safe Mode and perform the necessary troubleshooting steps to recover your system. Remember that Safe Mode provides a stable and minimalistic environment, ensuring that you can diagnose and fix problems with ease and efficiency.
Performing System File Checking
One crucial step towards resolving issues that arise due to a computer system malfunction is to conduct a comprehensive analysis of the system files. By running the System File Checker, you can identify and repair corrupted or missing files that might be causing the instability. This tool scans the computer's files and ensures that they are in their correct state, preventing potential errors and enhancing the overall performance of the system.
| Benefits of Running System File Checker |
|---|
|
It is essential to remember that running the System File Checker requires administrative privileges. To initiate the scan, open the Command Prompt as an administrator and execute the command "sfc /scannow". This will trigger the scanning process, which might take some time depending on the size of the system and the number of files being analyzed. It is crucial to refrain from interrupting the scanning process to ensure accurate results. Upon completion, the System File Checker will provide a detailed report on the actions taken and any repairs performed.
By regularly performing system file checks using the System File Checker, you can prevent and address potential issues in your operating system, contributing to a more stable and reliable computing experience.
Restoring or Fixing the Windows OS
In this section, we will explore the essential steps to bring your computer's operating system back to its functional state following an unexpected event. Whether your system encountered a critical failure, experienced a breakdown, or suffered a mishap, this guide will assist you in reestablishing or repairing the Windows OS without losing your valuable data.
Reinstalling Windows:
If your computer encounters significant issues and traditional troubleshooting methods fail to resolve them, reinstalling the Windows operating system might be the most effective solution. Reinstallation involves completely erasing the existing installation and replacing it with a fresh copy of the operating system. This helps to eliminate any software conflicts, fix corrupted files, and restore system stability.
Before proceeding with a reinstallation, it is crucial to back up all important files and documents to prevent data loss.
Repairing Windows:
Repairing the Windows OS is an alternative approach to resolve system issues without complete reinstallation. This method aims to fix specific problems that might be causing the system to malfunction. Various repair options are available, such as using system tools like System File Checker (SFC) to scan and repair corrupted files, utilizing the Windows Recovery Environment (WinRE), restoring the system to a previous working state using System Restore, or running automated repair tools such as DISM (Deployment Image Servicing and Management).
It is vital to note that repair options might not be applicable in all scenarios, especially if the system has suffered extensive damage or hardware failure.
By carefully considering the situation, selecting the appropriate method, and following the recommended steps, you can successfully reinstall or repair the Windows operating system, ensuring the stability and functionality of your computer.
EASY! Windows File Recovery Tutorial: How to Use WINFR for Free
EASY! Windows File Recovery Tutorial: How to Use WINFR for Free by URTechDotCa 9,134 views 7 months ago 5 minutes, 50 seconds
How to fully REPAIR Windows 10 without losing your data - Full Step-by-step Guide
How to fully REPAIR Windows 10 without losing your data - Full Step-by-step Guide by BredzPro 86,452 views 2 years ago 5 minutes, 44 seconds
FAQ
What are the common causes of a Windows operating system crash?
Common causes of a Windows operating system crash include hardware issues, corrupted system files, software conflicts, malware infections, and overheating.
Can I recover my Windows operating system if it crashes?
Yes, it is possible to recover a Windows operating system after a crash by following specific steps such as using system restore, performing a startup repair, reinstalling the operating system, or seeking professional help.
How can I use System Restore to recover my Windows operating system?
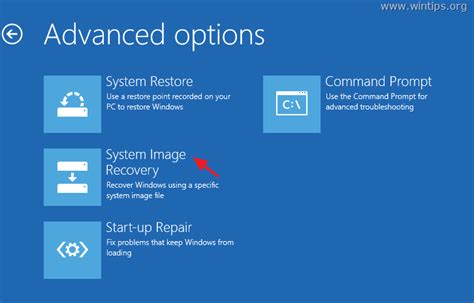
To use System Restore, you can access it through the Advanced Startup Options by restarting your computer, selecting Troubleshoot, then Advanced Options, and finally System Restore. Choose a restore point before the crash occurred and follow the instructions to complete the process.
When should I consider seeking professional help to recover my Windows operating system?
If you have tried various recovery methods like System Restore, startup repair, and reinstallation without success, or if you are not confident in performing these tasks yourself, it is advisable to seek professional help to ensure a successful recovery of your Windows operating system.




