
In today's interconnected world, where the internet plays a central role, it is crucial to be vigilant when it comes to the security of your Linux environment. With the continuous evolution of technology, it has become easier than ever for malware to infiltrate our systems, leading to potential data breaches, privacy invasion, and financial loss.
Securing your Linux ecosystem against these malicious programs is paramount to maintaining the integrity and functionality of your system. By implementing robust security measures, you not only protect your personal or business data but also contribute to the collective efforts in creating a safer digital landscape. However, achieving a high level of protection requires a comprehensive understanding of the potential threats and the strategies to mitigate them.
As you delve into the realm of Linux security, you will discover a vast array of techniques, tools, and best practices that can significantly enhance your system's defenses. From utilizing advanced firewalls, implementing access controls, to regularly updating software and employing strong encryption protocols, each element plays a pivotal role in creating a resilient barrier against malware attacks. The journey towards safeguarding your Linux environment against malicious programs is an ongoing process that demands knowledge, awareness, and active participation.
Understanding the Evolving Landscape of Digital Threats

In the dynamic world of technology, an in-depth understanding of the continuously evolving threat landscape is crucial for safeguarding your Linux environment from malicious entities. To ensure the protection of your system, it is essential to comprehend the diverse array of risks and vulnerabilities that can compromise the integrity and security of your digital assets.
Recognizing the Dangers:
Within the vast realm of cybersecurity, it is imperative to be cognizant of the multifaceted nature of threats that exist in the digital world. These threats encompass a wide range of menacing activities, such as computer viruses, worms, Trojans, ransomware, spyware, and other forms of malicious software. The diverse tactics employed by threat actors necessitate an unwavering vigilance and a comprehensive understanding of their methods.
Exploring Attack Vectors:
Threat actors consistently seek new ways to infiltrate systems, exploiting vulnerabilities in software, networks, and human behaviors. These vulnerabilities serve as entry points for attackers, enabling them to carry out their nefarious activities. Understanding the various attack vectors, including social engineering, software vulnerabilities, and network weaknesses, is paramount in comprehending how malicious actors exploit vulnerabilities to gain unauthorized access.
The Ever-Evolving Nature of Threats:
As technology advances, so too do the techniques used by cybercriminals and malicious entities. It is vital to stay up-to-date with the latest threats, as the threat landscape is constantly evolving. This requires proactive measures, including frequent software updates, staying informed about emerging vulnerabilities, and adopting strong security practices to thwart the ever-changing tactics employed by threat actors.
Embracing a Security Mindset:
Understanding the evolving threat landscape necessitates an ongoing commitment to learning and adaptability. Recognizing the potential risks and vulnerabilities inherent in digital systems empowers you to implement robust security measures effectively. By adopting a proactive security mindset, you can stay one step ahead of the adversaries, ensuring the continued protection and resilience of your Linux environment.
Choosing a Robust Antivirus Solution
In today's rapidly evolving digital landscape, it is essential to prioritize the protection of your computer system from malicious software. To ensure the security and integrity of your Linux environment, selecting a reliable antivirus solution is crucial. This section will provide valuable insights into the factors to consider when choosing an antivirus solution that can effectively combat malware threats.
| Factors to Consider | Description |
|---|---|
| 1. Detection and Removal Capabilities | Ensure that the antivirus solution offers comprehensive detection and swift removal of malware, including viruses, worms, trojans, and other malicious programs. |
| 2. Real-time Protection | Look for an antivirus solution that provides real-time protection, constantly monitoring incoming and outgoing data to proactively detect and block potential threats. |
| 3. System Performance Impact | Consider the impact an antivirus solution may have on your system's performance. Opt for a solution that strikes the right balance between robust protection and minimal resource consumption. |
| 4. Regular Updates | Choose an antivirus solution with a reliable update mechanism to stay up-to-date with the latest malware definitions and proactive security measures. |
| 5. Compatibility | Ensure that the antivirus solution is compatible with your specific Linux distribution and version, taking into account any potential conflicts with existing software or system configurations. |
| 6. User-Friendly Interface | Consider the ease of use and intuitiveness of the antivirus solution's interface, as it contributes to efficient system management and user experience. |
| 7. Reputation and Reviews | Research the antivirus solution's reputation in terms of effectiveness, customer support, and reliability. Read reviews and seek recommendations from trusted sources. |
| 8. Additional Features | Assess whether the antivirus solution offers any supplementary features, such as email scanning, web protection, firewall integration, or ransomware detection/prevention. |
By considering these essential factors, you can make an informed decision when selecting a robust antivirus solution for your Linux system. Remember, investing in the right antivirus software is a proactive step towards ensuring the security of your valuable data and protecting your system from the ever-evolving malware landscape.
Implementing Robust Firewall Configurations
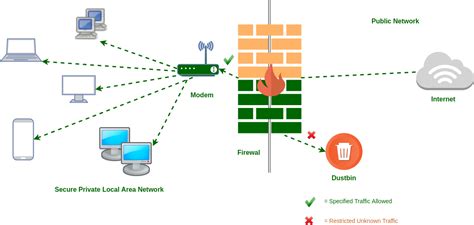
Enhancing the security measures of your Linux environment requires the implementation of strong firewall settings. By carefully configuring the firewall, you can effectively safeguard your system against potential threats and malicious activities. Firewall settings act as a protective barrier, filtering incoming and outgoing network traffic, and evaluating the legitimacy of each connection attempt.
One crucial aspect of implementing a strong firewall is defining well-defined rules. These rules establish a set of criteria that determine whether specific network packets should be allowed or denied. By carefully crafting these rules, you can control access to various network services and protect your system from potential vulnerabilities.
When configuring your firewall, it is essential to prioritize the specific requirements of your system. Consider the services and applications that need to communicate externally and internally, and only allow the necessary protocols and ports. By doing so, you can minimize the potential attack surface and limit exposure to potential threats.
- Enforcing strict inbound and outbound traffic filtering: Configure your firewall to restrict incoming and outgoing network traffic to only necessary and trusted sources while blocking potentially malicious connections.
- Implementing stateful packet inspection: This advanced firewall technique examines the context of network packets, allowing only packets that are part of a valid connection while blocking any suspicious or unauthenticated ones.
- Utilizing network address translation (NAT): NAT enables the translation of private IP addresses into public ones, providing an additional layer of security by hiding internal network structures from potential attackers.
- Logging and monitoring firewall activity: Regularly reviewing firewall logs helps in identifying potential threats or unauthorized access attempts, allowing you to take timely actions to mitigate them.
Remember, firewall configuration is an ongoing process. Regularly review and update your rules to adapt to the evolving threat landscape and the changing needs of your system. By implementing strong firewall settings, you can significantly enhance the security of your Linux environment and fortify it against potential malware and cyberattacks.
Regularly Updating Your Linux Distribution
Ensuring the latest and most secure features for your Linux operating system
One crucial aspect of maintaining a resilient and well-protected Linux environment is regular updates and keeping your distribution up to date.
By regularly updating your Linux distribution, you can ensure that you have access to the latest security patches, bug fixes, and critical software updates.
Updating your Linux distribution enables you to benefit from the continuous efforts of the development community, who are constantly working to enhance the features, performance, and security of the operating system.
New vulnerabilities and exploits are discovered regularly, and by updating your Linux distribution, you are proactively addressing these security risks.
Furthermore, updating your distribution also provides you with the latest versions of essential software packages and applications, ensuring that you have access to new features and improvements.
With each update, you strengthen the overall security posture of your Linux system, reducing the potential for malware infections, unauthorized access, and other security threats.
Additionally, through regular updates, you contribute to the stability and longevity of your Linux installation, as outdated software can lead to compatibility issues and a less reliable computing experience.
To ensure an efficient update process, it is recommended to configure automatic updates or establish a regular updating schedule that suits your needs and minimizes disruptions to your workflow.
Remember, regularly updating your Linux distribution is an essential security measure that helps protect your system and ensure a stable and optimized computing environment.
Protecting Your Browser and Email Client

Guarding your web browser and email client against potential security threats is an essential step in safeguarding your computer. By implementing effective strategies and following best practices, you can significantly reduce the risk of malware infiltration and protect your sensitive information.
One of the key aspects of securing your browsing experience is to ensure that your web browser and email client are always up to date. Regularly updating them with the latest security patches and bug fixes can address vulnerabilities that could be exploited by attackers.
Furthermore, it is crucial to exercise caution when accessing unknown or suspicious websites and opening email attachments from unfamiliar sources. These actions can expose your system to various types of malicious software, such as viruses, ransomware, or phishing attempts.
Enable robust security features within your browser and email client, such as pop-up blockers, anti-phishing filters, and automatic malware scanning. These built-in defenses can help detect and prevent potential threats before they can compromise your system.
Another essential practice is to utilize strong and unique passwords for your browser and email accounts. Consider using a password manager to generate complex passwords and ensure that you regularly change them to minimize the risk of unauthorized access.
Additionally, exercising discretion when granting permissions or granting access to your browser or email client can help mitigate potential risks. Avoid installing unnecessary browser extensions or plugins, as they may introduce vulnerabilities or collect your personal information without your consent.
In conclusion, protecting your browser and email client is paramount in maintaining the security of your Linux system. By staying vigilant, keeping your software up to date, and adopting best practices, you can enhance your overall cybersecurity posture and reduce the likelihood of falling victim to malware attacks.
Protecting Your Data with Disk Encryption
In this section, we will explore the crucial step of enabling disk encryption on your Linux operating system to safeguard your valuable data. By implementing this security measure, you can enhance the protection of your files and personal information from unauthorized access or theft.
Disk encryption is a powerful technique that transforms your data into an unreadable format using cryptographic algorithms. This ensures that even if your device falls into the wrong hands, the data stored on it remains inaccessible without the appropriate decryption key.
By enabling disk encryption, you provide an additional layer of defense against potential threats and malicious activities. Whether you use your Linux system for personal or professional purposes, safeguarding your data is essential to maintain confidentiality and prevent unauthorized disclosure.
Implementing disk encryption on your Linux system may require setting up various encryption methods such as full disk encryption or encrypting individual partitions. Additionally, you will need to generate and securely store encryption keys to unlock the encrypted data when needed.
Enabling disk encryption not only protects your sensitive information but also ensures compliance with data privacy regulations and industry standards. It is crucial to understand the encryption options available on your Linux distribution and configure them appropriately to suit your security needs.
In the upcoming sections, we will delve into the process of enabling disk encryption in detail, providing step-by-step instructions on how to protect your data effectively on Linux systems.
Avoiding Suspicious Software and Downloads

In this section, we will explore strategies to protect your Linux setup from potentially harmful software and downloads. By being cautious and aware of the potential risks, you can safeguard your system and sensitive information from malware and other threats.
- Exercise caution when downloading software:
- Verify the integrity of software:
- Keep your software up to date:
- Use package managers:
- Beware of phishing emails and websites:
- Enable a firewall:
Ensure that the software you download is from a reputable source. Stick to trusted websites and official repositories to minimize the risk of downloading malicious programs or software with hidden malware.
Before installing any software, always verify its integrity using cryptographic signatures or checksums provided by the developer. This ensures that the software has not been tampered with and is authentic.
Regularly update your system and software to protect against known vulnerabilities and security flaws. Many malware attacks exploit outdated software versions, so staying updated is crucial to maintaining a secure system.
Package managers provided by your Linux distribution offer a secure and reliable way to install software. They handle dependencies, security patches, and updates, reducing the risk of inadvertently downloading unsafe software.
Exercise caution when interacting with emails or websites that request personal information or prompt you to download attachments or click on suspicious links. Always verify the authenticity of the source before taking any action.
Configure and enable a firewall to monitor incoming and outgoing network traffic. This will help block unauthorized access and protect your system from external threats.
By following these guidelines and maintaining a proactive approach, you can significantly reduce the risk of encountering malware and ensure the security of your Linux system.
Protecting Your Linux Environment with Strong Passwords and Secure Authentication
Ensuring the security of your Linux environment goes beyond defending against malware. One crucial aspect is the implementation of robust password management practices and secure authentication methods. By utilizing strong passwords and implementing secure authentication mechanisms, you can significantly enhance the overall security of your system.
Creating Strong Passwords:
When creating passwords, it is essential to use a combination of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters. Avoid using easily guessable information such as names, birth dates, or commonly used phrases. Instead, opt for unique and complex passwords that are challenging for attackers to guess or crack.
Enforcing Password Policies:
To further enhance password security, enforce stringent password policies within your Linux environment. Set policies that require regular password updates, maintain a minimum password length, and restrict the reuse of previously used passwords. Implementing these policies ensures that users regularly update their passwords and avoid using weak or compromised passwords.
Implementing Multi-Factor Authentication:
Multi-factor authentication adds an additional layer of security to your Linux system by requiring users to provide multiple forms of identification. This could include something the user knows, such as a password, something the user possesses, such as a hardware token, or something the user is, such as biometric information. By implementing multi-factor authentication, even if an attacker manages to obtain a user's password, they would still need the additional authentication factor to gain access.
Regularly Auditing User Accounts:
Periodically auditing user accounts is crucial to ensure that only authorized individuals have access to your Linux system. Remove any inactive or unnecessary accounts, and closely monitor user privileges and permissions. Additionally, review and revoke access for users who no longer require it. Regularly auditing user accounts helps mitigate the risk of unauthorized access and potential security breaches.
Educating Users on Secure Authentication Practices:
Finally, as a Linux system administrator, it is essential to educate users on secure authentication practices. Encourage them to create unique passwords, avoid sharing their credentials, and be cautious of phishing attempts. By promoting a culture of security awareness, you empower users to actively contribute to the protection of the Linux environment.
Implementing secure passwords and authentication practices significantly strengthens the security of your Linux system. By creating strong passwords, enforcing password policies, implementing multi-factor authentication, regularly auditing user accounts, and educating users on secure practices, you can fortify your Linux environment against potential threats.
Regular Security Checks and Evaluations for Your Linux Environment
Regular system scans and audits are crucial in ensuring the ongoing security and integrity of your Linux environment. By performing these checks on a routine basis, you can effectively identify and address potential vulnerabilities, detect any signs of malware presence, and mitigate security risks before they can cause harm.
During regular system scans, your Linux environment is examined thoroughly to identify any abnormalities or suspicious activities. These scans involve assessing system logs, analyzing file and folder permissions, monitoring network traffic, and examining user account settings. By reviewing these aspects, you can gain insight into potential vulnerabilities and take appropriate action to mitigate them.
In addition to system scans, conducting regular audits enables you to evaluate the effectiveness of your security measures and identify areas for improvement. Audits involve assessing the configuration settings of your Linux system, reviewing security policies and procedures, and analyzing the overall security posture of your environment. By conducting these audits periodically, you can ensure that your security measures are up to date and aligned with industry best practices.
It is essential to use various tools and techniques to conduct these scans and audits effectively. This may involve utilizing specialized security software, employing intrusion detection systems, and leveraging log analysis tools. Additionally, manual checks and assessments are valuable in uncovering hidden or nuanced security issues that automated tools may overlook.
Regular system scans and audits should be incorporated into your overall security strategy as an essential component of maintaining a secure and malware-free Linux environment. By proactively identifying and addressing security vulnerabilities and conducting ongoing evaluations, you can ensure the continued protection and stability of your system.
Remember, prevention is always better than cure when it comes to securing your Linux environment against malware and other security threats. By investing time and effort into regular system scans and audits, you can stay one step ahead of potential threats and keep your Linux system secure.
Installing Anti-Virus on Linux | Linux gets infected!
Installing Anti-Virus on Linux | Linux gets infected! by Chris Titus Tech 118,626 views 4 years ago 8 minutes, 44 seconds

Network Security Tools to stop hackers
Network Security Tools to stop hackers by The PC Security Channel 135,084 views 1 year ago 9 minutes, 24 seconds

FAQ
What is malware and why is it a threat to Linux systems?
Malware refers to malicious software that is designed to harm or exploit computer systems. While Linux systems are generally considered to be more secure than other operating systems, they are not immune to malware. Threats such as viruses, worms, and Trojans can pose a risk to Linux systems by compromising data, stealing sensitive information, or causing system malfunctions.
What are some common indications that a Linux system is infected with malware?
There are several signs that may suggest a Linux system is infected with malware. These include a sudden slowdown in system performance, unexpected crashes or system freezes, unusual network activity, the presence of unknown or suspicious files, unauthorized changes to system settings or configurations, and the appearance of new or altered icons or desktop backgrounds.
How can I protect my Linux system from malware?
There are several steps you can take to secure your Linux system against malware. First, ensure that your system is up to date by regularly applying security patches and updates. Additionally, use a reliable antivirus software specifically designed for Linux systems, enable a firewall to control network traffic, be cautious while installing software from untrusted sources, and practice safe browsing habits by avoiding suspicious websites and not clicking on suspicious links or email attachments.
Are there any specific tools or software that can help in securing a Linux system against malware?
Yes, there are various tools and software available for securing Linux systems against malware. Some popular ones include ClamAV, an open-source antivirus engine, Lynis, a security auditing tool, Tripwire, a file integrity checker, and AppArmor, a mandatory access control framework. These tools can help in detecting and preventing malware infections, performing system audits, and enforcing security policies.
What should I do if I suspect my Linux system has been compromised by malware?
If you suspect your Linux system has been compromised by malware, it is important to take immediate action. Disconnect the system from the network to prevent further damage or unauthorized access. Then, run a thorough system scan using an updated antivirus program. If malware is detected, follow the antivirus software's instructions for removal. It may also be necessary to restore your system from a clean backup or seek assistance from a professional to ensure the complete removal of the malware.
How can I protect my Linux system from malware?
There are several steps you can take to secure your Linux system against malware. Firstly, make sure to always keep your system updated with the latest security patches and updates. Additionally, install a reliable antivirus program and regularly scan your system for potential threats. It is also crucial to practice safe browsing habits, such as avoiding suspicious websites or downloading files from untrusted sources. Finally, consider configuring a firewall to monitor incoming and outgoing network traffic and implement strong passwords for your system and user accounts.
Is it necessary to install an antivirus on my Linux system?
While Linux systems are generally less prone to malware compared to other operating systems, it is still advisable to install an antivirus program. Although the number of Linux-specific malware may be relatively low, it can still be problematic if your system gets infected. Additionally, an antivirus program can help detect and eliminate Windows malware that may be present on your Linux system, preventing it from spreading to other Windows machines. It is recommended to choose a reputable antivirus software that is designed for Linux systems and regularly update it for optimal protection.




