When it comes to the technological backbone of a network infrastructure, the significance of a well-structured and efficient Domain Name System (DNS) cannot be overstated. With its unrivaled ability to translate human-friendly domain names into IP addresses, DNS serves as a pivotal component in enabling seamless communication and connectivity across the digital landscape.
Presenting a robust suite of features, Windows DNS emerges as a highly versatile tool that empowers organizations to optimize their network performance, increase productivity, and foster effective collaboration. In this article, we will delve into the myriad capabilities of Windows DNS, exploring how it facilitates streamlined access to online resources, enhances security measures, and empowers administrators with centralized management options.
Accelerating Resource Accessibility: The fundamental function of Windows DNS lies in its ability to provide a simplified and accessible gateway to the vast realm of online resources. By converting domain names into machine-readable IP addresses, Windows DNS seamlessly connects users to websites, applications, and services, eliminating the need for cumbersome manual address input.
Furthermore, Windows DNS offers extensive support for various record types such as A records, CNAME records, MX records, and more, catering to the diverse requirements of different network environments. With the flexibility to configure specific DNS records, organizations can effortlessly streamline their internal and external web hosting, email delivery, and other essential network operations.
The Significance of Domain Name System (DNS) in Windows

In the realm of operating systems, the Domain Name System (DNS) plays a pivotal role in enabling seamless connectivity and facilitating efficient communication between devices within a Windows environment. It serves as a fundamental component, acting as a bridge between user-friendly domain names and their corresponding IP addresses.
Empowering Accessibility: DNS ensures that users can easily access various resources, such as websites, email servers, and other networked applications, by translating human-readable domain names into machine-readable IP addresses. This conversion enables individuals to navigate the internet effortlessly and access desired services with just a few clicks.
Enabling Network Efficiency: The DNS system efficiently manages and distributes the workload by enabling the caching of IP address translations. By storing these translations locally on devices or within network infrastructure, DNS reduces the need for repetitive translation requests, resulting in reduced network traffic and improved overall performance.
Enhancing Security: DNS plays a crucial role in enhancing security within a Windows environment. It facilitates the implementation of various security mechanisms, such as Domain Name System Security Extensions (DNSSEC) and DNS-based Authentication of Named Entities (DANE), which help validate the authenticity and integrity of DNS information, mitigating potential risks such as DNS spoofing and pharming attacks.
Supporting Scalability: Windows DNS has the ability to scale and adapt to growing network requirements. It supports various features, such as load balancing, round-robin, and fault tolerance, allowing network administrators to efficiently manage and distribute incoming requests, ensuring optimal performance even in high-demand scenarios.
Driving Business Continuity: DNS redundancy and failover mechanisms within the Windows ecosystem ensure uninterrupted access to critical resources. By implementing primary and secondary DNS servers and leveraging DNS zone transfers, Windows DNS provides built-in measures to safeguard against server failures and maintain continuous availability of services.
In summary, the domain name system is an integral part of Windows infrastructure, enabling accessibility, optimizing network efficiency, ensuring security, supporting scalability, and driving business continuity. Understanding its importance and leveraging its capabilities can significantly enhance the overall efficiency and productivity of Windows-based environments.
DNS Resolution
The process of DNS resolution involves the translation of domain names into IP addresses, enabling the efficient communication between devices on a network. It plays a crucial role in the seamless functioning of various online activities, such as browsing the web, accessing email services, or joining networked applications.
During the DNS resolution process, a client device sends a request to a DNS server, which then looks up the corresponding IP address associated with the requested domain name. This translation is achieved through a hierarchical system of DNS servers, known as the DNS hierarchy. The DNS hierarchy consists of multiple levels, including the root servers, top-level domain (TLD) servers, authoritative name servers, and caching resolvers.
The DNS resolution process utilizes various mechanisms to optimize efficiency and reduce latency. Caching is one such mechanism, where DNS servers store previously resolved domain name-to-IP address mappings. This caching mechanism allows subsequent requests for the same domain name to be resolved more quickly, improving overall performance.
In addition to caching, DNS resolution also supports load balancing and fault tolerance mechanisms. Load balancing helps distribute incoming DNS requests across multiple servers, ensuring efficient resource utilization and preventing overloads. Fault tolerance mechanisms, such as redundancy and backup servers, ensure continuous DNS resolution even in the event of server failures or network disruptions.
Overall, DNS resolution is a fundamental component of network infrastructure that enables the seamless and efficient communication between devices. It employs various mechanisms, such as caching, load balancing, and fault tolerance, to optimize performance and ensure reliable connectivity for a wide range of online activities.
Domain Name Resolution with Windows DNS: Mapping Domain Names to IP Addresses
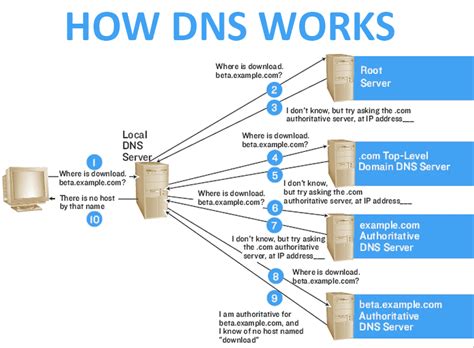
One of the fundamental functions of Windows DNS is to resolve domain names into their corresponding IP addresses. This essential process allows users to access websites, send emails, and connect to various services on the internet.
Domain name resolution is the process of converting user-friendly domain names, such as www.example.com, into the numeric IP addresses that computers use to identify each other on the internet. This translation is crucial for establishing connections and ensuring efficient communication between different devices and services.
When a user enters a domain name in a web browser or attempts to access a network resource, the Windows DNS server takes on the task of resolving this domain name. It starts by checking its local DNS cache for a pre-existing mapping of the domain name to its associated IP address. If the mapping is found, the DNS server can quickly return the corresponding IP address without contacting the root servers or performing any further lookups.
If the DNS server does not have a cached mapping for the domain name, it proceeds with a series of queries to determine the IP address. The server starts by contacting a root name server, which holds information about the top-level domains (TLDs) such as .com, .org, or .net. The root name server directs the DNS server to the authoritative name server responsible for the specific TLD.
The authoritative name server responds with the IP address for the queried domain name or refers the DNS server to another name server responsible for the next level of the domain hierarchy. This process continues until the authoritative name server is reached that can provide the final IP address for the domain name. The DNS server then caches this mapping to improve future lookup performance and returns the IP address to the requesting client.
Domain name resolution is a critical component of Windows DNS that enables efficient communication and seamless browsing experience for users. By effectively mapping domain names to their corresponding IP addresses, Windows DNS ensures proper connectivity and facilitates the efficient flow of information across the internet.
DNS Caching
In the realm of computer networking and connectivity, the efficient utilization of resources is of utmost importance. One of the key elements in this regard is the Domain Name System (DNS) caching. This mechanism plays a pivotal role in enhancing the speed and effectiveness of network communication by storing previously resolved domain name queries.
DNS caching involves the temporary storage of domain name to IP address mappings on the local system or network devices. When a user attempts to access a website or any network resource, their device first checks if the required information is available in the cache. If so, it retrieves the IP address from the cache instead of querying the DNS server, resulting in quicker response times and reduced network traffic.
This caching feature significantly improves the overall efficiency of network operations by minimizing the need for repetitive DNS lookups. It optimizes the time required to fetch the associated IP addresses for websites, servers, and other online resources, thereby enhancing the user experience.
Moreover, DNS caching also contributes to the stability and resilience of network connections. In the event of DNS server unavailability or latency issues, cached records can continue to be utilized, ensuring uninterrupted access to previously visited websites. This redundancy adds an extra layer of reliability to the network infrastructure.
The functionality and effectiveness of DNS caching can be further customized and optimized based on the specific requirements of a network. Different caching policies, such as time-to-live (TTL) values, can be set to control the duration for which DNS records are held in the cache. This flexibility allows network administrators to strike a balance between performance and freshness of DNS information, resulting in an efficient and reliable network environment.
Overall, DNS caching offers valuable benefits in terms of network performance, speed, reliability, and resource optimization. By leveraging this feature, organizations can achieve more efficient and seamless network operations, leading to enhanced productivity and user satisfaction.
The Impact of Windows DNS Cache on Enhancing Performance
When it comes to optimizing the efficiency of a Windows-based network infrastructure, understanding the role of the DNS cache is essential. The DNS cache plays a crucial part in improving performance by storing recently accessed hostnames and their corresponding IP addresses locally on the system. This allows for quicker retrieval of information, reducing the need for repetitive DNS lookups and minimizing network latency.
The DNS cache acts as a repository of previously resolved domain names, serving as a temporary storage mechanism. By keeping a copy of the resolved IP addresses, the cache eliminates the need to query external DNS servers repeatedly. This not only enhances the response time for subsequent requests but also reduces the overall network traffic, resulting in a more efficient and seamless user experience.
Utilizing the Windows DNS cache brings several benefits. Firstly, it promotes faster browsing and application usage by reducing the time required to resolve domain names. As popular websites and frequently accessed resources are stored locally, the DNS cache enables quicker access to these resources, resulting in improved performance and productivity.
Moreover, the DNS cache contributes to network reliability. In scenarios where external DNS servers may experience downtime or latency issues, the locally stored DNS entries can serve as a backup, ensuring that users can still access websites and services without interruptions. This ability to provide resilience and prevent service disruptions is a significant advantage of leveraging the Windows DNS cache.
From a security perspective, the DNS cache also plays a role in mitigating potential threats. By storing verified DNS resolutions, the cache can detect and flag any suspicious or malicious responses. This enables the network administrators to proactively protect the system and its users from accessing harmful websites or falling victim to phishing attempts, enhancing overall security.
In conclusion, the Windows DNS cache serves as a vital component in optimizing the performance of a network infrastructure. Its ability to store and retrieve resolved IP addresses locally reduces network latency, enhances user experience, promotes resilience against server failures, and bolsters security. Understanding and effectively utilizing the DNS cache can significantly contribute to an efficient and productive working environment.
DNS Forwarders
One key aspect of enhancing the efficiency and functionality of your network infrastructure is the implementation of DNS forwarders. These forwarders serve as intermediary entities within the Domain Name System (DNS) hierarchy, facilitating the resolution of domain names into their corresponding IP addresses.
By configuring DNS forwarders, you can streamline the process of resolving queries for domains that are not hosted on your local DNS server. Instead of traversing the entire DNS hierarchy to obtain the necessary information, the DNS forwarder directly requests the required data from external DNS servers. This approach not only improves the speed and reliability of DNS resolution but also reduces the workload on your local DNS server.
When configuring DNS forwarders, you have the flexibility to designate specific DNS servers as forwarders based on your network requirements. These forwarders can include your Internet service provider's DNS servers, public DNS resolvers like Google DNS or OpenDNS, or even the DNS servers of other organizations within your network. By selecting appropriate forwarders, you can ensure efficient and optimized DNS resolution for your network users.
- Improved DNS resolution speed and reliability
- Reduced load on local DNS server
- Flexibility in selecting forwarders based on network requirements
- Ability to configure multiple forwarders for redundancy
Implementing DNS forwarders is a vital strategy for optimizing the performance and functionality of your Windows DNS infrastructure. By intelligently selecting and configuring forwarders, you can enhance the efficiency of DNS resolution and ensure seamless access to resources on your network.
Utilizing Windows DNS Forwarders for Optimal Name Resolution
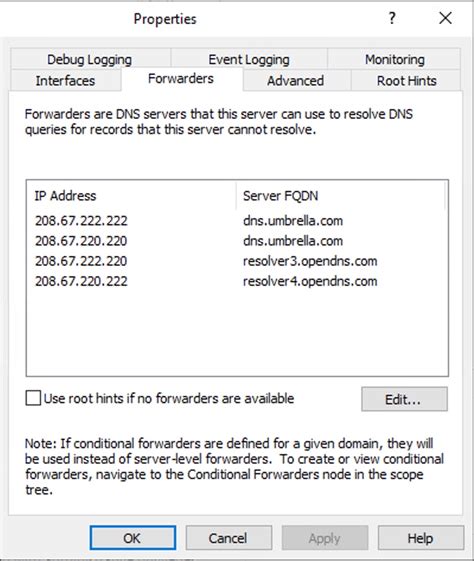
Efficiently resolving domain names is a crucial aspect of network functionality. In the context of Windows DNS, one approach to achieve efficient name resolution is through the utilization of forwarders.
Forwarders, also known as forward resolver servers, play a significant role in the name resolution process. By configuring Windows DNS forwarders, organizations can enhance the speed and reliability of DNS queries within their network environment.
When a Windows DNS server receives a query for a domain name that it cannot resolve locally, it forwards the request to a designated forwarder. This forwarder server acts as an intermediary, seeking the necessary information from authoritative DNS servers on behalf of the requesting DNS server.
By utilizing forwarders, organizations can benefit from several advantages. Firstly, forwarders allow for caching of responses, reducing the need for repeated queries to external DNS servers. This caching mechanism improves the overall responsiveness of the DNS resolution process.
Moreover, forwarders enable organizations to exert control over the external DNS servers utilized by their DNS infrastructure. By selecting trusted and well-performing forwarders, administrators can ensure reliable name resolution while minimizing the exposure to potential security risks.
In addition to the performance benefits, configuring Windows DNS forwarders is a straightforward process that can be easily set up and managed within the DNS server settings. Administrators have the flexibility to specify multiple forwarders, allowing for redundancy and fault tolerance in the event of a forwarder becoming unavailable.
In conclusion, leveraging Windows DNS forwarders is a recommended strategy for optimizing name resolution in a Windows DNS environment. By effectively configuring and managing forwarders, organizations can enhance the efficiency, reliability, and control of their DNS infrastructure.
Windows Server vs Regular Windows - How Are They Different?
Windows Server vs Regular Windows - How Are They Different? ThioJoe দ্বারা 7,27,123টি ভিউ 2 বছর পূর্বে 10 মিনিট, 4 সেকেন্ড
BEST DNS For Gaming on Windows 11 PC (Easy Guide!) How to Find The Best DNS Server For Your Internet
BEST DNS For Gaming on Windows 11 PC (Easy Guide!) How to Find The Best DNS Server For Your Internet Chad Reddings দ্বারা 41,702টি ভিউ 7 মাস আগে 1 মিনিট, 38 সেকেন্ড
FAQ
What are the main features of Windows DNS?
Windows DNS provides features such as domain name resolution, caching, forwarders, zone transfers, dynamic updates, and conditional forwarding. These features ensure efficient and reliable DNS operation within a Windows network.
How does Windows DNS caching improve network performance?
Windows DNS caching stores recently accessed DNS information, reducing the need to perform repetitive DNS queries. This improves network performance by decreasing the response time for subsequent DNS resolutions.
Can I set up Windows DNS forwarders?
Yes, Windows DNS allows you to configure forwarders. Forwarders are DNS servers to which queries are forwarded if the local DNS server does not have the requested information. This helps in efficient resolution of DNS queries by leveraging the capabilities of external DNS servers.
What are zone transfers in Windows DNS?
Zone transfers in Windows DNS refer to the process of replicating DNS zone information between DNS servers. This is crucial for maintaining consistency and redundancy in DNS data across multiple servers, ensuring reliable name resolution within a network.
How does dynamic update work in Windows DNS?
Dynamic update is a feature of Windows DNS that allows DNS clients to register their own resource records dynamically. This simplifies the administration of DNS records by automating the process of adding and removing records, improving efficiency and accuracy in DNS management.
What are the key features of Windows DNS?
Windows DNS has several key features that make it efficient for work. These include support for both forward and reverse lookup zones, integration with Active Directory for easy management and replication, the ability to use conditional forwarding to improve query performance, support for dynamic updates, and the option to configure DNSSEC for increased security.
How does Windows DNS integrate with Active Directory?
Windows DNS integrates seamlessly with Active Directory, allowing for easy management and replication of DNS zones. When Active Directory is installed, DNS zones can be stored as Active Directory-integrated zones, which simplifies administration and improves fault tolerance. DNS data is stored in the Active Directory database, and DNS updates are replicated along with Active Directory data, ensuring consistency across domain controllers.




