In the vast realm of operating systems, one particularly popular option for enthusiasts and professionals alike is the open-source platform commonly known as Linux. When it comes to setting up this cutting-edge system on your personal computer, certain intricacies may arise, requiring careful navigation. This article sets out to illuminate some of the common hurdles and obstacles faced during the installation and configuration process, providing insights and solutions for a smoother transition.
Embarking on the journey of integrating Linux into your personal computing environment warrants a thorough understanding of the potential roadblocks that may lay ahead. From the initial choice of distribution to exploring hardware compatibility, each step demands meticulous attention to detail. Delving into the intricacies of installation processes and adapting to the Linux environment can be daunting tasks, particularly for those accustomed to more mainstream operating systems.
One prevalent challenge that often arises during Linux installation is the bewildering array of distributions available. While variety is generally seen as a virtue, it can also lead to confusion and uncertainty. Different distributions cater to varying user needs, specifications, and preferences, resulting in a diverse array of features, interface designs, and package managers. The daunting task of choosing the most suitable distribution can easily overwhelm those unfamiliar with the intricacies of Linux, leading to hesitation and uncertainty.
Common Challenges Encountered during the Installation Process of Linux Operating Systems
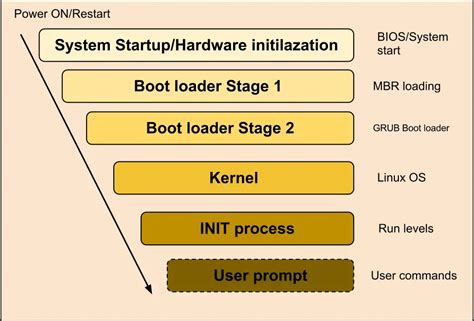
When attempting to install a Linux operating system on a personal computing device, users may come across various difficulties and obstacles that hinder the successful completion of the installation process. These challenges can arise from different aspects of the installation procedure, including hardware compatibility, partitioning management, driver installation, and bootloader configuration, among others.
Hardware compatibility issues often pose a significant challenge during the installation of a Linux operating system. Certain hardware components might not be recognized or supported by the chosen Linux distribution, resulting in driver conflicts or the inability to fully utilize the device's capabilities. This can lead to suboptimal performance or even system instability.
| Common Challenges | Description |
|---|---|
| Partitioning Management | The process of dividing the computer's storage into separate sections, or partitions, may be unfamiliar to some users, leading to confusion or mistakes that can potentially disrupt the installation process. |
| Driver Installation | Installing the necessary drivers for various hardware components can be a complex task, especially when dealing with proprietary or non-standard devices. Without proper drivers, certain functionalities may be limited or completely unavailable. |
| Bootloader Configuration | The configuration of the bootloader, a program that enables the computer to start the operating system, can be challenging for users with limited knowledge of system boot procedures. Mistakes in this process might result in an inability to boot the installed Linux system or a dual-boot setup with another operating system. |
These are just a few examples of the common challenges that users might encounter when attempting to install a Linux operating system on their computer. It is important to approach the installation process with patience, research, and a willingness to troubleshoot and overcome any issues that may arise. Consulting user forums, official documentation, and seeking assistance from experienced users can greatly aid in resolving these challenges and successfully installing Linux on a computer.
Difficulty in Selecting the Appropriate Linux Distribution
Choosing the right Linux distribution for your computer can be a challenging task due to various factors that need to be considered. Each distribution offers a unique set of features and capabilities, making it essential to thoroughly understand your requirements in order to make an informed decision.
| Factors to Consider | Explanation |
| Hardware Compatibility | Ensuring that the Linux distribution you choose is compatible with your computer's hardware components such as the processor, graphics card, and network adapter is crucial. Incompatibility issues can lead to poor performance or even complete failure to install Linux. |
| User-Friendliness | Consider whether you prefer a beginner-friendly distribution with a graphical user interface (GUI) or if you are comfortable with a more advanced, command-line-based distribution. The level of technical expertise you possess will influence your decision. |
| Software Requirements | Take into account the specific software applications you need to run on your Linux system. Different distributions may have varying levels of compatibility with certain software, so it is important to verify compatibility before installation. |
| Community and Support | Research the availability of active online communities, forums, and support channels for the Linux distribution you are considering. Having access to a supportive community can greatly assist in troubleshooting issues and acquiring knowledge. |
| Security and Stability | Consider the level of security and stability offered by the distribution. Some distributions prioritize frequent updates and cutting-edge features, while others focus on long-term stability. Evaluate your needs and priorities in terms of security and stability. |
By carefully evaluating these factors and conducting thorough research, you can increase your chances of selecting a Linux distribution that best aligns with your needs and preferences. Keep in mind that it may be beneficial to try out different distributions through live USB or virtual machine environments before committing to a full installation. Remember, the process of selecting the right Linux distribution may require some trial and error, but ultimately it plays a vital role in determining your overall experience and success with Linux on your computer.
Troubleshooting Installation Problems in Linux
Addressing and resolving difficulties encountered during the installation process of a Linux operating system is essential for a successful setup. In this section, we will explore various troubleshooting methods and potential solutions to aid in overcoming installation obstacles and achieving a functional Linux system.
Dealing with Incompatibility Challenges of Linux Drivers
In the realm of Linux installations, one might encounter certain hurdles related to the integration of drivers. These challenges can arise due to compatibility issues between the hardware devices of a computer and the Linux operating system.
When embarking on the process of installing Linux, it is crucial to be aware of the potential complications that may arise with drivers. Incompatibility between the operating system and hardware can lead to malfunctioning or non-functioning devices, such as graphics cards, network adapters, or audio devices.
Identifying the root cause of driver compatibility issues:
One of the primary steps in addressing driver compatibility issues is to identify the source of the problem. The use of diagnostic tools and thorough research can help pinpoint whether the issue lies with the Linux distribution, specific hardware components, or the configuration of the system.
Searching for Linux-compatible drivers:
After identifying the conflicting drivers, the next step is to search for Linux-compatible alternatives. This process might involve visiting the manufacturer's website, community forums, or specialized Linux driver repositories. It is important to note that these driver alternatives may not always have the same feature set as the original drivers, but they should ensure basic functionality.
Compiling custom drivers:
In some cases, Linux-compatible drivers might not be readily available for certain hardware components. In such situations, one may need to resort to custom driver compilation. This process requires obtaining the source code of the driver and following specific steps to compile it on the Linux system.
Testing and troubleshooting:
Once the new drivers are installed, it is necessary to thoroughly test the functionality of the respective hardware devices. This may involve verifying if all features and functionalities are working as expected and addressing any unforeseen issues that may arise.
Maintaining up-to-date drivers:
Finally, it is crucial to stay vigilant about keeping the drivers updated for both the Linux distribution and the hardware devices. Regularly checking for updates and applying them can help prevent compatibility issues and improve overall system performance.
By following these steps and considering the unique characteristics of each individual Linux installation, users can address driver compatibility issues and maintain a stable and functional Linux system.
Resolving Booting and GRUB Errors during Linux Installation
In the process of setting up Linux on a system, users may encounter a number of challenges that prevent proper booting or cause errors related to the GRUB bootloader. This section aims to provide guidance on addressing these issues and ensuring a successful Linux installation.
Troubleshooting Booting Errors:
When attempting to boot into the Linux operating system, users may encounter various errors that prevent the system from starting up. These errors can be attributed to a range of factors, such as incorrect boot device settings, hardware compatibility issues, or corrupted system files.
To resolve booting errors, it is important to carefully review the system's BIOS/UEFI settings and ensure that the appropriate boot device is selected. Verifying hardware compatibility and compatibility with the chosen Linux distribution is also crucial. Additionally, trying alternative boot options or updating system firmware can often help resolve booting issues.
Addressing GRUB Errors:
The GRUB bootloader is a crucial component for successfully booting into a Linux system. However, during the installation process, users may encounter errors related to GRUB, such as a missing or corrupted bootloader, or a failure to load the Linux kernel properly.
To address GRUB errors, users can start by attempting to repair or reinstall the GRUB bootloader. This can often be done using a Linux live USB or CD, booting into a rescue mode, and running the appropriate commands to reinstall or repair the bootloader.
Another common solution is to manually edit the GRUB configuration file to fix any issues with boot options, kernel parameters, or the order of operating systems listed in the bootloader menu.
Conclusion:
Booting and GRUB errors can be common obstacles when installing Linux on a computer. By troubleshooting booting errors and addressing GRUB-related issues, users can overcome these challenges and successfully install and run Linux on their system.
Tackling Bootloader Configuration Problems
In the realm of installing Linux on a system, one of the hurdles that users often encounter is related to the bootloader configuration. This aspect of the installation process can sometimes be challenging and cause difficulties in successfully running Linux on a computer. This section aims to address some of the common problems that arise and offer strategies to overcome them.
Handling Disk Partitioning and Formatting during Linux Installation
Managing disk partitioning and formatting is a crucial step in the process of installing a Linux operating system on a computer. This section will explore the various considerations and potential challenges that can arise when creating and formatting disk partitions during the Linux installation process.
- Understanding Disk Partitioning:
- Partition Layout:
- Partitioning Tools:
- Considerations for Dual Boot:
- Format Options:
- Handling Partitioning Errors:
Before proceeding with the installation, it is important to have a basic understanding of disk partitioning. Disk partitioning involves dividing the hard drive into separate sections called partitions, which can be used to organize the file system and store data. Different types of partitions, such as primary, extended, and logical partitions, serve various purposes and have specific limitations.
Creating an optimal partition layout is essential to ensure efficient usage of disk space and smooth system performance. This includes determining the number and size of partitions required for the Linux installation, as well as deciding on the file system types, such as ext4, xfs, or btrfs, which will be used for formatting the partitions.
Linux installation provides partitioning tools like GParted, fdisk, or parted, which offer a graphical or command-line interface for managing disk partitions. Familiarizing yourself with these tools and their functionalities is essential in order to effectively create, resize, or modify partitions during the installation process.
If you plan on dual-booting Linux with another operating system on the same machine, additional considerations must be made when partitioning the disk. Ensuring compatibility and proper allocation of space for both operating systems is vital to maintain a stable and functional dual-boot configuration.
Choosing the appropriate file system format is an important decision during the Linux installation process. Different file systems have varying capabilities, such as handling large file sizes, supporting encryption, or providing better data recovery options. Evaluating the specific requirements of the system and its intended use will aid in selecting the most suitable file system format.
During the Linux installation, errors or issues may arise when partitioning the disk. Common problems can include partition table errors, insufficient disk space, or conflicts with existing partitions. Understanding how to troubleshoot and resolve these errors will help ensure a successful installation.
By carefully considering and managing the disk partitioning and formatting process during Linux installation, users can avoid potential complications and create a stable and efficient operating system environment.
[MOVIES] [/MOVIES] [/MOVIES_ENABLED]FAQ
What are some common issues that people face when installing Linux on a computer?
There are several common issues that people often encounter when installing Linux on a computer. These include compatibility issues with hardware, problems with partitioning the hard drive, difficulties in getting the right drivers, and issues with the bootloader.
How can I resolve compatibility issues with hardware while installing Linux?
To resolve compatibility issues with hardware during the Linux installation, it is advisable to research and choose Linux distributions that are known to have better hardware support. Additionally, keeping the kernel and drivers up to date can help resolve such problems. In some cases, manually installing or configuring specific drivers may be required.
Why do I face problems while partitioning the hard drive during Linux installation?
Many users face problems while partitioning their hard drive during Linux installation because they may not be familiar with the partitioning process or have made incorrect choices. It is crucial to have a backup of important data before partitioning. Additionally, understanding the difference between primary and logical partitions, as well as the various file systems, can help avoid such issues.




