When it comes to the digital infrastructure of an organization, there exist key elements that are absolutely critical for efficient daily operations. One such integral component is the mechanism responsible for storing and managing data. An operating system data storage unit plays a pivotal role in supporting the organization's file management needs, while also offering a range of diverse functionalities.
Enhanced Security: When it comes to safeguarding sensitive information, businesses cannot afford to take any risks. The data storage unit provides a means to implement robust security measures, ensuring that critical data remains protected from unauthorized access or potential cyber threats. By employing a multitude of encryption methods, administrators can rest assured that their files are kept safe and confidential.
Streamlined Collaboration: Modern-day organizations heavily rely on teamwork and collaboration. The data storage unit facilitates seamless collaboration by allowing multiple users to access and work on the same files simultaneously. With features such as file versioning and real-time editing, team members can efficiently contribute to projects, significantly improving productivity levels and speeding up the overall workflow.
Scalability and Flexibility: As an organization grows, so does its data storage requirements. The data storage unit offers scalability, allowing businesses to expand their storage capacity effortlessly. Whether it is through the addition of physical storage devices or the implementation of cloud-based solutions, the system can adapt to the evolving needs of the organization, ensuring a seamless transition without any disruptions.
Centralized Data Storage and Access Control
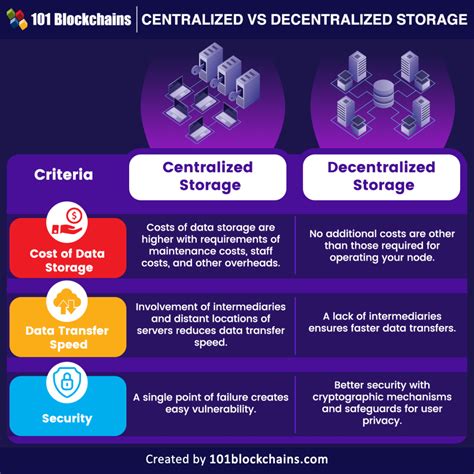
A crucial aspect of managing a network infrastructure is the establishment of a centralized data storage system that provides secure and controlled access to files and folders. By implementing a centralized data storage and access control solution, organizations can efficiently manage and secure their data, enhance collaboration among users, and enforce data protection policies.
Centralized data storage involves the consolidation of files and folders from multiple sources into a central location. This enables efficient organization and management of data, eliminating the need for multiple copies and reducing storage costs. Additionally, centralized storage improves data accessibility by providing a single point of access for authorized users, facilitating streamlined collaboration and data sharing.
| Benefits of Centralized Data Storage |
|---|
| 1. Enhanced data security: Centralized storage allows organizations to enforce access control policies, ensuring that only authorized individuals can access sensitive data. This reduces the risk of data breaches and unauthorized data modifications. |
| 2. Simplified data backups: With centralized storage, organizations can easily schedule and automate data backups, ensuring that critical data is protected and can be easily restored in the event of data loss or system failures. |
| 3. Improved data management: Centralized storage provides a unified view of data, allowing administrators to efficiently manage and organize files and folders. This simplifies tasks such as file indexing, content searching, and data archiving. |
| 4. Scalability and flexibility: A centralized data storage system can easily scale to accommodate growing storage needs, allowing organizations to adapt to changing data requirements without disrupting operations. |
| 5. Compliance and auditing: Centralized storage enables organizations to implement data retention and compliance policies, ensuring regulatory requirements are met. It also facilitates auditing and monitoring of data access and modifications. |
Overall, the implementation of a centralized data storage and access control solution on a Windows Server empowers organizations to efficiently manage data, enhance collaboration, maintain data security, and comply with regulatory standards. By consolidating data into a central repository, organizations can streamline data management processes, improve productivity, and protect critical information from unauthorized access or loss.
High Availability and Redundancy
In the realm of Windows Server File Servers, achieving high availability and redundancy plays a crucial role in ensuring uninterrupted access to critical data and minimizing downtime. By implementing robust and redundant systems, organizations can enhance their overall operational resilience and mitigate the risks associated with hardware failures and network outages.
This section delves into the significance of high availability and redundancy and explores various strategies and technologies that can be leveraged to achieve these objectives. It examines the importance of having multiple servers that can seamlessly take over in case of failure, ensuring uninterrupted access to files and data. Additionally, it explores the concept of redundant storage, where data is duplicated and distributed across multiple drives or storage devices, safeguarding against data loss in the event of a storage device failure.
Moreover, this section highlights the role of load balancing, which enables even distribution of user requests across multiple servers, optimizing performance and preventing overload on a single server. It also explores the concept of failover clustering, where multiple servers work together as a cluster to provide high availability and automatic failover capabilities, ensuring seamless continuity in the event of a server failure.
Another aspect of achieving high availability and redundancy is implementing network redundancy, involving the setup of redundant network infrastructure components such as switches, routers, and network connections. This minimizes the risk of network failures and ensures continuous network connectivity, allowing clients to access the file server without any disruptions.
Ultimately, by implementing high availability and redundancy measures, Windows Server File Servers can mitigate the impact of hardware failures, network interruptions, and other unforeseen events, providing reliable and uninterrupted access to critical data for organizations of all sizes.
Efficient Data Replication and Backup

In this section, we will explore the efficient ways to replicate and backup data on a Windows server file sharing system. Effective data replication and backup solutions play a crucial role in ensuring the availability, integrity, and security of critical data. By implementing robust data replication and backup strategies, organizations can minimize the risk of data loss, ensure business continuity, and improve overall system performance.
- Data Replication: Replicating data involves creating copies of data and distributing them across multiple server nodes. This process helps to enhance data accessibility and availability, especially in environments with geographically dispersed users or branch offices. Synonyms: Data mirroring, data duplication, data synchronization.
- Data Backup: Backing up data involves creating additional copies of data for safekeeping and disaster recovery purposes. Regular backups safeguard data against accidental deletions, hardware failures, malicious attacks, and other unexpected events. Synonyms: Data protection, data archiving, data preservation.
- Differential Backup: A differential backup technique involves backing up only the modified or changed data since the last full backup. This approach reduces backup time and storage space requirements compared to full backups while providing the ability to restore data to a specific point in time. Synonyms: Incremental backup, partial backup.
- Snapshot: A snapshot is a read-only point-in-time copy of data. It captures the state of a file or volume at a specific moment, allowing users to revert to previous versions or recover from unintended modifications. This feature is particularly useful for business-critical files and applications. Synonyms: Data image, data point-in-time copy.
- Offsite Replication: Offsite replication involves copying and storing data in a remote location or data center, separate from the primary server's physical location. This practice protects against localized disasters or disruptions and ensures data availability in the event of a site-wide outage. Synonyms: Remote replication, disaster recovery replication.
Implementing an efficient data replication and backup strategy is essential for maintaining data integrity, meeting compliance requirements, and reducing data loss risks. By utilizing a combination of replication, backup, and snapshot techniques, organizations can create robust data protection mechanisms that ensure timely data recovery and minimize potential downtime.
Top 20 Server Types & Functions | Servers Explained
Top 20 Server Types & Functions | Servers Explained by Tech With Emilio 37,047 views 3 years ago 19 minutes
FAQ
What is a Windows Server File Server?
A Windows Server File Server is a feature of the Windows Server operating system that allows users to store, manage, and share files within a network. It provides a centralized storage location for files that can be accessed by multiple users simultaneously.
What are the benefits of using a Windows Server File Server?
Using a Windows Server File Server has several benefits, such as improved file organization and security, centralized management and backup, easier file sharing and collaboration among users, and enhanced performance for file access and retrieval.
Can a Windows Server File Server handle large amounts of data?
Yes, a Windows Server File Server is designed to handle large amounts of data. It has scalable storage options, such as using RAID configurations or adding additional hard drives, to accommodate growing storage needs. Additionally, it supports advanced file systems like NTFS, which can handle large file sizes and offer better performance.
Can a Windows Server File Server be accessed remotely?
Yes, a Windows Server File Server can be accessed remotely. Users can connect to the file server from remote locations using protocols like FTP, SMB, or WebDAV. This allows users to access their files and collaborate with others even when they are not physically present in the network where the server is located.
Is it possible to set up access permissions and restrictions on a Windows Server File Server?
Yes, it is possible to set up access permissions and restrictions on a Windows Server File Server. Administrators can define user or group-specific permissions, such as read, write, or delete access, to control who can access and modify files and folders. This helps to ensure data confidentiality and security.
What are the possible capabilities of a Windows Server File Server?
The Windows Server File Server has a wide range of capabilities, including file sharing, access control, backup and restore, data deduplication, quota management, and network storage. It allows users to easily share files and folders within a network and provides granular access control to ensure data security. The server also offers built-in backup and restore features to protect important files and enables data deduplication to optimize storage efficiency. Additionally, administrators can set and manage quotas to control the amount of disk space used by users. It acts as a central repository for network storage, providing fast and reliable access to data.
How does a Windows Server File Server facilitate file sharing?
A Windows Server File Server simplifies file sharing by allowing users to easily share files and folders within a network. It provides a centralized location where users can upload and store their files, making them accessible to other authorized users. The server uses the Server Message Block (SMB) protocol to enable file sharing across different operating systems and devices. With the server's permission settings, administrators can control who can access, read, modify, or delete specific files and folders. It provides a seamless and secure way to collaborate and share information within an organization.




