In this era of advanced technology and fast-paced developments, it is crucial to stay ahead of the curve. One of the key areas that constantly evolves is the world of operating systems. Among the myriad choices available, Linux distributions hold a prominent position.
With their versatility, robustness, and open-source nature, these distributions have gained immense popularity over the years. They offer a plethora of options for users to tailor their operating systems to their liking, making them an ideal choice for both beginner and advanced users.
This comprehensive guide aims to delve into the depths of the leading Linux distributions, shedding light on their individual strengths, characteristics, and suitability for various purposes. From powerful enterprise solutions to user-friendly options, this article will provide a clear roadmap for navigating the Linux landscape.
So, if you are ready to embark on a journey through the intricate world of Linux operating systems, fasten your seatbelts and get ready to discover the diverse array of options that await you. Whether you are an enthusiastic tinkerer, a dedicated professional, or a curious individual wanting to explore the possibilities, this guide will equip you with the knowledge to make an informed decision tailored to your needs.
Understanding Linux: An Overview

Exploring the essence of Linux goes beyond a mere understanding of its main distributions. In this section, we delve into the fundamental principles and concepts that underlie the Linux operating system. By gaining an overview of Linux, you will acquire a deeper comprehension of its open-source nature, robust security features, and powerful command-line interface.
Embracing Open-Source Freedom
At the core of Linux lies its open-source philosophy, empowering users with the freedom to access, modify, and distribute the source code. This collaborative approach fosters an extensive global community of developers who continuously enhance Linux, resulting in innovation, stability, and unmatched customizability.
Unyielding Security Paradigm
Linux's reputation for being highly secure is well-deserved. With its robust security architecture, Linux offers multiple layers of protection against malware, viruses, and unauthorized access. Its proactive response to security vulnerabilities, coupled with frequent updates, ensures a safe environment for both individual users and enterprise-grade systems.
The Power of Command-Line Interface
Linux distinguishes itself from other operating systems with its powerful command-line interface (CLI), often referred to as the terminal. The CLI provides seasoned users with unparalleled control over the system, allowing for efficient software installation, management, and automation. Mastering the command-line interface grants users the ability to perform complex tasks swiftly and confidently.
Understanding the fundamental concepts that underpin Linux is essential for any enthusiast or professional seeking a comprehensive grasp of this versatile operating system. Embracing its open-source nature, appreciating its robust security, and harnessing the power of the command-line interface will unlock endless possibilities on your Linux journey.
Popular Linux Distributions: A Brief Comparison
In this section, we will provide a concise overview and comparison of some widely-used Linux operating systems. We will explore their key features, strengths, and weaknesses, enabling readers to make informed decisions about which distribution best suits their needs.
Ubuntu: Ubuntu is a highly popular Linux distribution known for its user-friendly interface and extensive software library. It offers a stable and secure environment for both beginners and advanced users. Its versatility allows it to be used on various platforms, including desktops, servers, and cloud environments.
Debian: Debian is one of the oldest and most respected Linux distributions. It prioritizes stability and reliability, making it a preferred choice for servers and critical systems. Debian's package management system is robust, with a vast software repository that ensures timely updates and security patches.
Fedora: Fedora focuses on providing the latest cutting-edge technologies and innovations in the Linux world. It is backed by the open-source community and features a rapid release cycle. Fedora is an excellent choice for developers and enthusiasts who want to experience the latest software advancements.
Arch Linux: Arch Linux appeals to experienced Linux users who prefer a minimalist and customizable system. It follows a rolling release model, offering continuous updates instead of versioned releases. Arch Linux provides a lightweight environment and grants users full control over their system's configuration.
OpenSUSE: OpenSUSE is a versatile distribution suitable for various use cases, including desktop, server, and development environments. It offers a choice between the stable release and the rolling release known as "Tumbleweed." OpenSUSE's YaST (Yet another Setup Tool) simplifies system administration with its graphical interface.
CentOS: CentOS is a popular choice for server deployments due to its close relation to Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL). It focuses on stability and long-term support, providing a secure and reliable environment for mission-critical applications. CentOS offers compatibility with RHEL, allowing easy transition and seamless integration.
As you can see, each Linux distribution has its own strengths, catering to different user requirements. By understanding the key features of these various distributions, you can select the one that aligns best with your needs and goals.
Choosing Your Ideal Linux Distribution
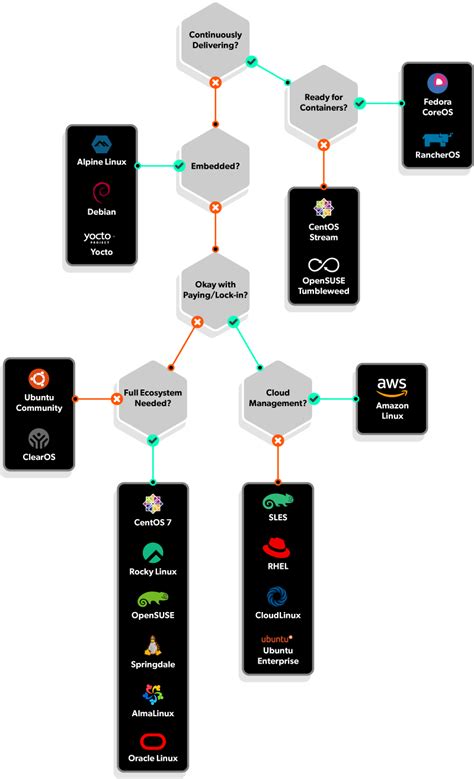
Discovering the perfect Linux distribution that suits your needs can be a challenging task. With a vast array of options available, it's important to understand the key factors to consider when making your selection. This section will provide you with essential guidelines to assist you in choosing the right Linux distribution for a seamless and optimized computing experience.
1. Hardware Compatibility:
| Ensure that your chosen Linux distribution supports your hardware specifications. Check for compatibility with your computer's processor, graphics card, network adapters, and other essential components to avoid any compatibility issues or performance limitations. |
2. User Interface:
| Consider the user interface (UI) that best suits your preferences and computing habits. Linux distributions offer a variety of UI options, ranging from sleek and modern to more traditional. Experiment with different interfaces to find one that is intuitive and visually appealing to you. |
3. Package Management:
| Explore the package management system of each Linux distribution. Different distributions use distinct package managers that handle software installation, updates, and dependency management. It's vital to choose a distribution with a package management system that you find user-friendly and efficient. |
4. Community and Support:
| Assess the community and support available for each Linux distribution. An active and helpful community can significantly enhance your Linux experience, providing resources, forums, and assistance when encountering technical challenges. Look for a distribution with a vibrant and engaged community that aligns with your needs. |
5. Purpose and Use Cases:
| Consider the primary purpose and use cases for your Linux installation. Are you using it for general computing, development, server deployments, or specialized tasks such as multimedia editing or ethical hacking? Different Linux distributions are tailored to specific use cases, so selecting one that aligns with your intended purpose is crucial. |
By carefully evaluating these factors, you can choose a Linux distribution that not only meets your technical requirements but also aligns with your personal preferences and goals. Remember that the beauty of Linux is the abundance of choices available, allowing you to customize and tailor your computing experience to suit your unique needs.
Getting Started with Linux: Installation and Setup
In this section, we will explore the initial steps you need to take in order to start using Linux on your computer. We will delve into the process of installing a Linux distribution, setting up your system, and configuring essential components to ensure a smooth and optimized experience.
Choosing the Right Linux Distribution
Before diving into the installation process, it is crucial to select a Linux distribution that best suits your needs. There are various distributions available, each with its own characteristics and target audience. We will discuss popular options and guide you towards making an informed choice.
Preparing for Installation
Installing Linux requires careful preparation to avoid any data loss or conflicts with existing systems. We will outline the necessary steps to take before initiating the installation process, such as backing up your data, checking hardware compatibility, and creating installation media.
Installation Process
Once you have prepared your system, we will walk you through the step-by-step installation process. We will cover common installation methods, such as dual-booting with an existing operating system or performing a clean installation. You will learn how to partition your hard drive, select installation options, and configure essential settings.
Initial System Setup
After the installation, there are essential configurations to be made to optimize your Linux experience. We will guide you through setting up user accounts, configuring network settings, installing necessary drivers, and updating your system to ensure you have the latest software and security patches.
Exploring Desktop Environments
Linux offers a wide range of desktop environments, each providing a different user experience. We will introduce you to popular options and explain how to switch between them, customize their appearance, and utilize their unique features.
Installing and Managing Software
Once your Linux system is set up, you'll want to install useful software packages to enhance its functionality. We will cover different methods for installing software on Linux, including package managers and graphical software centers. Additionally, we will discuss software repositories, dependency management, and best practices for maintaining and updating installed software.
Getting Help and Troubleshooting
As you explore and use Linux, you may encounter challenges or have questions. We will provide resources and tips for accessing support communities, forums, and documentation. We will also discuss common troubleshooting steps and techniques to help you resolve any issues you may encounter.
| Section | Content |
|---|---|
| 1 | Choosing the Right Linux Distribution |
| 2 | Preparing for Installation |
| 3 | Installation Process |
| 4 | Initial System Setup |
| 5 | Exploring Desktop Environments |
| 6 | Installing and Managing Software |
| 7 | Getting Help and Troubleshooting |
Exploring Advanced Features: Tips and Tricks for Linux Users

In this section, we will delve into the vast array of advanced features available to Linux users, providing valuable tips and tricks to enhance your Linux experience. Discover hidden gems and explore powerful functionalities that can boost your efficiency, productivity, and overall enjoyment of Linux.
- Unleashing the Power of the Terminal
- Mastering Shell Scripting Techniques
- Customizing Your Linux Environment
- Optimizing System Performance
- Enhancing Security and Privacy
- Exploring Networking Capabilities
- Utilizing Virtualization and Containerization
- Managing Software Packages
- Unlocking the Potential of Command-Line Tools
- Overcoming Common Challenges and Troubleshooting
Whether you are an experienced Linux user or just starting your journey, this section aims to be a valuable resource for unlocking the full potential of your Linux distribution. From mastering the art of the command line to optimizing system performance, these tips and tricks will empower you to become a more proficient and efficient Linux user.
New Linux User: 10 Things I Wish I Knew When I First Started
New Linux User: 10 Things I Wish I Knew When I First Started by Learn Linux TV 358,782 views 1 year ago 23 minutes
Top 5 Linux Distros for Beginners
Top 5 Linux Distros for Beginners by Mental Outlaw 214,118 views 3 years ago 11 minutes, 40 seconds
FAQ
What are the main Linux distributions?
The main Linux distributions include Ubuntu, Debian, Fedora, CentOS, and Arch Linux.
Which Linux distribution is recommended for beginners?
Ubuntu is often recommended for beginners due to its user-friendly interface and large user community that provides extensive support.
What is the difference between Ubuntu and Fedora?
Ubuntu and Fedora are both Linux distributions, but they differ in terms of package management systems (Ubuntu uses dpkg and Debian packages, while Fedora uses rpm and Red Hat packages), release cycles (Ubuntu has regular releases every six months, while Fedora has a new version every six months), and their default desktop environments (Ubuntu uses GNOME, while Fedora uses GNOME or KDE Plasma).
What is CentOS and who is it suitable for?
CentOS is a Linux distribution that is based on Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL). It is suitable for individuals and organizations who require a stable and reliable operating system. CentOS is often used for web servers, hosting services, and enterprise applications.
What is Arch Linux and why is it considered different from other distributions?
Arch Linux is a lightweight and highly customizable Linux distribution. It follows a "rolling release" model, which means that updates are released frequently and users have access to the latest software versions. Arch Linux also requires users to have a deeper understanding of Linux and its command line interface, making it popular among advanced users and Linux enthusiasts.
Which are the main Linux distributions?
The main Linux distributions include Ubuntu, Fedora, Debian, CentOS, and Arch Linux.




