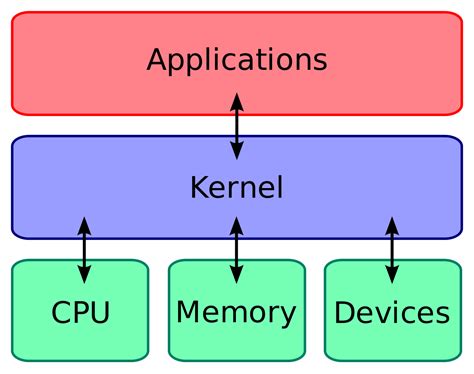
When exploring the realm of computer operating systems, one encounters a multifaceted landscape that presents a plethora of options. Amidst this intricacy, one encounters a particularly distinctive entity known as Linux. This remarkable creation stands apart from its counterparts and boasts unique attributes that captivate both novices and experts alike.
Linux possesses a remarkable versatility, granting its users an unparalleled level of freedom and control over their computing experience. Recognized for its open-source nature, this extraordinary operating system is fueled by collaboration, knowledge sharing, and limitless customization possibilities. A vibrant community of developers continually enhances Linux, resulting in an ever-evolving entity that meets the diverse needs and desires of its users.
Moreover, Linux stands out for its remarkable stability and security. Its robust architecture prevents the occurrence of system crashes, ensuring a seamless and uninterrupted workflow. With Linux, one can rest assured that their digital interactions remain shielded from potential threats due to the meticulous attention to security measures implemented by its developers.
In essence, Linux emerges as a distinctive force within the realm of computer operating systems. Its unrestricted nature, combined with its stability and security, serve as captivating factors that distinguish it from its counterparts. The world of technology looks to Linux with admiration as it continues to redefine the boundaries of what an operating system can achieve.
Introduction: Understanding Linux in Comparison to Alternative Operating Systems

Linux stands as a distinguishable alternative when evaluating the landscape of modern operating systems. Treading a unique path, Linux showcases distinctive characteristics that set it apart from its counterparts. Grasping the essence of Linux and its divergence from other operating systems calls for an exploration of its inherent traits and functionalities.
Linux presents a plethora of divergences when contrasted with its peers. It holds a distinctive identity owing to its dissimilar approaches in terms of user interface, system architecture, and software compatibility. This juxtaposition delves beyond surface disparities, illuminating the fundamental disparities that underpin Linux's distinctiveness.
While traditional operating systems often rely on proprietary and closed-source solutions, Linux embraces openness and collaboration. It fosters a community-driven development approach, inviting users worldwide to contribute to its evolution. This stark contrast imparts Linux with unparalleled flexibility and adaptability, enabling it to cater to a broad range of user groups and requirements.
Another compelling facet highlighting Linux's uniqueness is its extensive support for a wide array of hardware platforms. Unlike other operating systems primarily designed for specific hardware configurations, Linux has been tirelessly expanded and optimized to run on various architectures. This universality allows Linux to thrive across diverse devices, ranging from traditional desktop computers to smartphones, servers, and even embedded systems.
The modular nature of Linux further solidifies its divergence from the conventional operating systems. A wealth of open-source software exists in the Linux ecosystem that enables users to customize their systems according to their needs. The flexibility to handpick and mix different components grants users unparalleled control and the ability to fine-tune their Linux experience.
In conclusion, while Linux shares the foundational purpose of operating systems, it deviates markedly from other alternatives through its open-source nature, hardware versatility, and modular design. These distinguishing aspects collectively contribute to Linux's uniqueness and its position as a compelling option for those seeking a flexible and customizable operating system.
Understanding the Fundamentals of Linux and its Distinctive Qualities
In the vast realm of computing systems, there exist various operating environments that differ significantly from one another. This section aims to shed light on the distinct characteristics and underlying principles of Linux, a notable player in the operating system landscape.
Linux distinguishes itself from other operating systems with its open-source nature, allowing any individual to access and modify its source code freely. This unique feature fosters a culture of collaboration and innovation, enabling developers to contribute to the system's growth and tailor it to their specific needs.
Additionally, Linux is renowned for its robust security framework, providing a secure environment for users, even in the face of evolving cyber threats. This heightened security stems from strong permission structures, rigorous access controls, and a proactive approach to vulnerability management.
Moreover, Linux is highly customizable, flexible, and scalable, making it suitable for a wide range of applications. Its modular structure enables users to build unique configurations tailored to their requirements, whether for embedded systems, servers, or desktop environments.
Linux also excels in terms of stability and uptime, thanks to its efficient memory management, process isolation mechanisms, and reliable error handling capabilities. These features contribute to its reputation for being a reliable choice for critical tasks and high-performance computing.
Furthermore, Linux enjoys strong community support, with a vast network of enthusiasts and professionals readily offering assistance and sharing their expertise. This collaborative spirit creates an environment conducive to continuous improvement, nurturing a thriving ecosystem of software and tools.
In summary, Linux stands out from other operating systems through its open-source nature, robust security, customization options, stability, and vibrant community. Understanding these distinctive qualities lays the foundation for delving deeper into the intricacies and benefits of utilizing Linux in various computing scenarios.
Advantages of Linux in Comparison to Alternative Operating Systems

When considering the various options available for operating systems, it becomes evident that Linux stands out due to its unique strengths and features. Unlike its counterparts, Linux offers distinct advantages that set it apart in terms of flexibility, security, and customization.
One of the key distinguishing factors of Linux is its unparalleled flexibility. Unlike other operating systems, Linux allows users to modify and customize virtually every aspect of their operating environment, truly tailoring it to their specific needs. This level of flexibility empowers users to optimize their system's performance, improve productivity, and adapt the interface to suit their preferences.
Furthermore, Linux offers enhanced security compared to alternative operating systems. Built on an open-source foundation, Linux benefits from a vast community of developers who continually review and update its source code. This collaborative approach results in quicker detection and resolution of security vulnerabilities, ensuring a highly secure environment. Moreover, Linux's modular structure and fine-grained access controls offer additional layers of protection against unauthorized access and malware attacks.
Another significant advantage of Linux is its vast array of software options. With Linux, users have access to a diverse range of free and open-source software that caters to various needs and preferences. This vast software ecosystem provides users with countless options for productivity tools, multimedia applications, development environments, and more. The ability to choose from a wide variety of software not only reduces costs but also promotes innovation and customization.
Finally, Linux's stability and reliability make it an ideal choice for many users. Linux-based operating systems have a reputation for their ability to run for extended periods without requiring frequent updates or reboots. The robustness of Linux ensures reliability, minimizing system crashes and enhancing overall user experience.
In conclusion, Linux offers a multitude of advantages over alternative operating systems. Its flexibility, security, software options, and stability make it a preferred choice for those seeking a customizable, secure, and reliable operating environment.
Exploring the Strengths and Benefits of Embracing Linux
In this section, we will delve into the unique advantages and valuable attributes that come with adopting Linux, a robust and versatile operating system. By stepping outside the realm of conventional operating systems, users can unlock a plethora of benefits and tap into the true potential of their computing experience. Linux presents a refreshing alternative, offering unmatched freedom, superb customization options, exceptional security, and a vibrant community that fosters continuous innovation and collaboration.
Unparalleled Freedom: Linux embodies the essence of open-source philosophy, allowing users to truly take control of their computing environment. With Linux, you are not restricted by proprietary software or limited functionality. You have the freedom to customize every aspect of the system, from the user interface to the core components, tailoring it to meet your precise needs.
Endless Customization: Linux empowers users to transform their operating system into a tailored, efficient, and visually appealing platform. With multiple desktop environments and countless customization options, Linux accommodates a wide range of preferences and ensures that the user interface aligns with individual workflows, making it a flexible and user-centric choice.
Superior Security Measures: Linux has long been heralded for its robust security features, offering an inherently secure foundation. Thanks to its open-source nature, Linux benefits from continuous scrutiny by a global community of developers who work tirelessly to detect and resolve vulnerabilities promptly. Not only does this foster a proactive approach to security, but it also ensures a rapid response to emerging threats, making Linux an ideal choice for privacy-conscious individuals and businesses.
A Thriving Community: One of the remarkable aspects of Linux is its vast and passionate user community. Whether you are a novice seeking assistance or an expert willing to contribute, Linux offers a vibrant ecosystem that encourages knowledge sharing, collaboration, and development. The community-driven nature of Linux results in an expansive array of resources, support forums, and regular updates, ensuring a constantly evolving and improving operating system.
Embracing Linux means embracing a powerful operating system that empowers users to unleash their creativity, optimize productivity, and achieve a secure and personalized computing experience. With its unparalleled freedom, endless customization options, rock-solid security measures, and vibrant community, Linux offers a truly unique and fulfilling operating system alternative.
Security Features: Linux versus Alternative Operating Systems
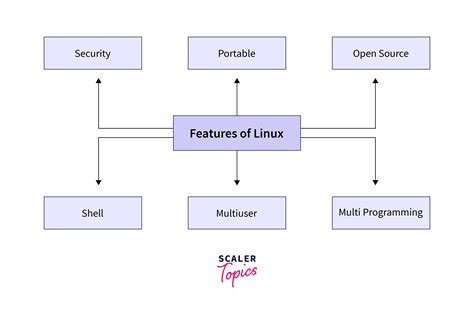
In the realm of security features, Linux deviates significantly from alternative operating systems. This section examines the distinguishing characteristics that set Linux apart from its counterparts in terms of protecting user data and safeguarding against potential threats.
Linux stands out due to its robust security infrastructure and its ability to provide a reliable defense against unauthorized access and malicious activities. Its security features are designed to mitigate the risks associated with cybersecurity breaches, ensuring the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of user information.
One key aspect that sets Linux apart is its open-source nature, allowing the security community to scrutinize and enhance its code continuously. This transparency enables quick identification and patching of vulnerabilities, enhancing the security of the system. Conversely, alternative operating systems tend to use proprietary code, limiting the number of individuals who can audit and contribute to their security processes.
Linux also incorporates stringent access control mechanisms, granting users granular control over file and folder permissions. By implementing this principle of least privilege, Linux minimizes the risk of unauthorized access and prevents sensitive data from falling into the wrong hands. This level of control is often not as comprehensive in other operating systems.
Furthermore, Linux provides a robust firewall system that allows for fine-grained configuration to filter incoming and outgoing network traffic. This firewall capability adds an additional layer of protection by regulating network communications and safeguarding against potential attacks. Some alternative operating systems may lack this flexibility or rely on external firewall software, which can introduce additional complexity and potential vulnerabilities.
Linux's continuous improvement and rapid response to security issues, coupled with its emphasis on user control and strong firewall capabilities, make it an appealing choice in terms of security. While other operating systems may offer similar security measures, Linux's open-source nature, efficient access control, and integrated firewall system contribute to its reputation as a highly secure operating system.
An In-depth Look at the Security Measures in Linux and its Comparisons
The security measures implemented in Linux make it a standout operating system when compared to others in the market. Linux boasts a comprehensive security framework that encompasses various components, such as access control, user authentication, and data encryption. This section delves into the intricate details of Linux's security features, discussing their significance and how they compare to those of other operating systems.
| Security Aspect | Linux | Other Operating Systems |
|---|---|---|
| Access Control | Linux utilizes a robust permissions system based on users, groups, and file permissions. This granular approach allows for fine-grained control over access to resources. | Other operating systems may have more limited access control mechanisms, resulting in potential security vulnerabilities. |
| User Authentication | Linux provides a variety of authentication methods, including passwords, public key cryptography, and two-factor authentication. This multi-factor authentication approach significantly enhances user identity verification. | Other operating systems may offer fewer authentication options, potentially making them more susceptible to unauthorized access. |
| Data Encryption | Linux incorporates strong encryption techniques, such as the widely-used OpenSSH protocol, to protect sensitive data during transmission and storage. | Other operating systems may have less advanced encryption capabilities, leaving data more vulnerable to theft or interception. |
| Security Updates | Linux benefits from its open-source nature, as a large community actively contributes to identifying and patching security vulnerabilities. This collaborative effort ensures a rapid and continuous release of security updates. | Other operating systems may have a slower response time in addressing security flaws, potentially leaving systems exposed to known threats for longer periods. |
| System Auditing | Linux offers comprehensive auditing tools that enable system administrators to monitor and track various activities, helping detect and investigate potential security breaches. | Other operating systems may lack robust auditing functionality, limiting the ability to identify and analyze security incidents effectively. |
Overall, Linux's security measures outshine those of many other operating systems. Its focus on access control, user authentication, data encryption, seamless security updates, and system auditing contributes to its reputation as a highly secure platform. By prioritizing security, Linux sets itself apart and remains a popular choice for individuals and enterprises concerned about protecting their sensitive information.
Customization and Adaptability: Linux's Advantage in Comparison to Other Operating Systems

One remarkable aspect setting Linux apart from alternative operating systems lies in its unparalleled customizability and flexibility. Unlike its counterparts, Linux allows users to extensively modify their system, tailoring it according to their specific needs and preferences.
Linux offers a wide range of options and tools that enable users to personalize and adapt their operating environment to their liking. Whether it's the graphical user interface, system settings, or software packages, Linux provides the freedom to customize almost every aspect of the operating system.
Another distinguishing feature of Linux is its open-source nature, which allows users to access and modify the source code of the operating system itself. This open environment fosters a large and vibrant community of developers and enthusiasts who contribute to the ongoing development and enhancement of Linux, resulting in a constantly evolving and improving system.
The flexibility of Linux also extends to the choice of desktop environments and window managers. Linux offers a multitude of options, each with its unique set of features, allowing users to select the interface that best suits their workflow and aesthetic preferences. From lightweight and minimalistic interfaces to highly customizable and feature-rich desktop environments, Linux provides a vast array of choices.
Furthermore, Linux's adaptability extends beyond the desktop environment. It can run on a wide range of hardware architectures, including older and less powerful machines, making it a viable option for repurposing older hardware or maximizing the performance of resource-constrained devices.
In conclusion, Linux excels in the realm of customization and adaptability, granting users the power to tailor their operating system experience to their liking. Its open-source nature, extensive customization options, and compatibility with various hardware architectures make Linux stand out as a highly flexible and versatile operating system.
Exploring Linux's Capacity for Personalization and Flexibility
Linux stands out from other operating systems by offering unparalleled levels of personalization and adaptability. This aspect sets Linux apart, allowing users to tailor their computing experience according to their unique needs and preferences.
Unlike its counterparts, Linux grants users the ability to modify and customize virtually every aspect of their system. This includes the desktop environment, the file system, and even the kernel itself. This high level of personalization empowers individuals to create an operating system that is truly suited to their requirements, enhancing both efficiency and user satisfaction.
With Linux, customization can extend beyond visual aesthetics, encompassing the overall functionality and behavior of the operating system. Users have the freedom to choose from a vast selection of software packages, each serving specific purposes and offering distinct features. Additionally, Linux provides extensive options for customizing command line tools, giving advanced users the flexibility to optimize their workflow and automate tasks.
Moreover, Linux supports a diverse range of hardware architectures, making it adaptable to various devices and platforms. Whether it is a desktop computer, a server, or even embedded systems, Linux can be tailored to fit the specific hardware and computing requirements of each device. This inherent flexibility positions Linux as a versatile and widely-used choice across different industries and applications.
To navigate through the vast array of customization options available with Linux, various communities and user groups have emerged, offering support, guidance, and a platform for sharing knowledge. This fosters a collaborative environment where users can learn from each other, troubleshoot issues, and stay up-to-date with the latest technological advancements.
- Unparalleled personalization and adaptability
- Customization of desktop environment, file system, and kernel
- Extensive range of software packages for specific needs
- Flexibility in customizing command line tools
- Support for diverse hardware architectures
- Community-driven platforms for guidance and collaboration
Advantages of Linux in Terms of Performance and Stability

When it comes to the realm of operating systems, Linux undeniably stands out with its exceptional performance and enviable stability compared to its competitors. In this section, we will explore the unique features and benefits that Linux offers, setting it apart in terms of performance and stability.
One notable aspect of Linux is its remarkable efficiency in utilizing system resources. Through its sleek and optimized architecture, Linux ensures that computing power and memory are utilized to their fullest potential, resulting in a responsive and smooth user experience. This efficiency allows Linux to excel even on less powerful hardware, making it an ideal choice for a wide range of devices, from embedded systems to high-performance servers.
In addition to its efficient resource management, Linux boasts exceptional stability, particularly when it comes to handling heavy workloads and mission-critical tasks. Its robust design and reliable kernel contribute to a minimal level of system crashes or failures, providing unparalleled uptime and productivity. This reliability makes Linux the preferred choice for running servers, where uninterrupted operation and data integrity are of utmost importance.
Furthermore, Linux's open-source nature plays a significant role in enhancing its performance and stability. A vast community of developers and enthusiasts constantly collaborates to detect and fix any potential vulnerabilities or bugs, ensuring quick and continuous improvements to the system. This active ecosystem also encourages the development of various software tools and applications tailored to meet specific performance requirements, further enhancing Linux's capabilities.
Linux's performance and stability are also influenced by its extensive customization options and flexibility. With a wide range of distributions available, each designed to cater to specific needs and preferences, users can tailor their Linux setup to optimize performance or prioritize stability as required. This versatility allows Linux to adapt to various use cases, whether it be for personal computing, development environments, or enterprise-grade systems.
In conclusion, Linux surpasses other operating systems in terms of both performance and stability, thanks to its resource efficiency, reliable kernel, open-source nature, and customizable nature. Whether for personal or professional use, Linux proves to be an exceptional choice, providing a solid foundation for seamless computing experiences and reliable operations.
An Analysis of Linux's Superiority in terms of Speed and Reliability
In the realm of operating systems, the domain of efficiency and dependability is where Linux undeniably triumphs. This article explores the distinct factors that contribute to Linux's exceptional performance and steadfast reliability, setting it apart from its counterparts. By delving into its optimized coding techniques, streamlined processes, and robust architecture, we unravel the remarkable capabilities of Linux.
1. Efficient Kernel Design
At the core of Linux's swiftness and resilience lies its meticulously crafted kernel design. The kernel, akin to the brain of an operating system, ensures the efficient allocation of system resources, facilitates swift data processing, and enables seamless multitasking. With its lightweight and modular structure, Linux boasts impressive start-up times and excels in managing system resources, leading to an optimum utilization of hardware capabilities.
2. Vast Array of Device Drivers
Linux's extensive array of device drivers contributes significantly to its unparalleled speed and reliability. Being an open-source system, Linux benefits from its vast community of developers constantly working to create and refine drivers for a wide range of hardware devices. This comprehensive library of drivers ensures seamless compatibility, accelerated device response times, and exceptional performance across an extensive array of hardware configurations.
3. Solid System Stability
Linux's rock-solid stability is a testament to its robust architecture and rigorous testing procedures. The constant scrutiny from a passionate community of developers, along with rigorous testing practices, ensures the identification and elimination of bugs and vulnerabilities. As a result, Linux systems experience minimal crashes, maintain high levels of uptime, and provide a reliable foundation for critical operations.
4. Efficient Process Management
Efficient process management is another key attribute contributing to Linux's remarkable speed and reliability. Through its sophisticated process scheduler, Linux optimizes the allocation of CPU time to different processes, ensuring fairness, responsiveness, and maximum system throughput. Additionally, Linux employs advanced memory management techniques, such as virtual memory and memory caching, further enhancing overall system performance.
5. Continuous Improvement and Customization
The open-source nature of Linux grants users and developers the freedom to continuously improve and customize the system according to their specific needs. This results in a constant stream of updates, bug fixes, and performance optimizations. Moreover, Linux's modular architecture allows users to tailor their operating system for specific use cases, eliminating unnecessary components and further boosting performance and reliability.
In conclusion, Linux's supremacy in terms of speed and reliability stems from its efficient kernel design, vast array of device drivers, solid system stability, efficient process management, and the virtue of continuous improvement and customization. By harnessing these strengths, Linux outshines other operating systems and remains a prime choice for high-performance computing environments, critical systems, and resource-constrained devices.
Difference Between Linux And Windows?-Class Series
Difference Between Linux And Windows?-Class Series by Class Series 8,997 views 1 year ago 3 minutes, 44 seconds
Most Popular Operating Systems (Desktop & Laptops) 1978 - 2023
Most Popular Operating Systems (Desktop & Laptops) 1978 - 2023 by Alternative Wars 1,356,784 views 8 months ago 4 minutes, 14 seconds
FAQ
What is the main difference between Linux and other operating systems?
The main difference between Linux and other operating systems is that Linux is an open-source operating system, meaning that its source code is freely available for anyone to view, modify, and distribute. This allows users to have more control and flexibility over their operating system compared to proprietary systems like Windows or macOS.
Can you explain the advantages of Linux over other operating systems?
Linux offers several advantages over other operating systems. Firstly, it is highly customizable, allowing users to tailor their system to their specific needs. It is also known for its stability and security, as many developers continuously work to improve its performance and fix any vulnerabilities. Additionally, Linux is often preferred by developers and programmers due to its extensive command-line interface and compatibility with a wide range of software and tools.
What are some popular Linux distributions?
There are several popular Linux distributions, each with its own set of features and target audience. Some of the most widely-used distributions include Ubuntu, Debian, Fedora, and CentOS. Ubuntu, for example, is known for its user-friendly interface and extensive software repository, making it a popular choice for beginners. Debian, on the other hand, emphasizes stability and reliability, making it a favored choice for servers. Fedora focuses on the latest software advancements, while CentOS is often used in enterprise environments due to its long-term support.
Is it difficult to switch from Windows or macOS to Linux?
The difficulty of switching from Windows or macOS to Linux depends on the individual's familiarity with the operating system and their specific needs. While there is a learning curve associated with any new operating system, Linux distributions like Ubuntu and Linux Mint offer user-friendly interfaces that make the transition smoother for beginners. Additionally, many software applications have Linux versions or suitable alternatives available. However, if a person heavily relies on software that is exclusive to Windows or macOS, they may face challenges with compatibility.