Have you ever pondered the intriguing notion of intertwining two contrasting digital realms? The alluring idea of bridging the boundaries between distinct software ecosystems continues to captivate the minds of tech enthusiasts and developers alike. But can we truly merge the functionalities of two seemingly incompatible giants, like the vibrant universe of Linux and the omnipresent empire of Windows?
Enterprising individuals have fervently embarked upon the audacious pursuit of harmonizing these disparate operating systems, endeavoring to bring the best of both worlds to our fingertips. Assiduous efforts have been made to forge a seamless alliance between the open-source principles of Linux and the user-friendly interface of Windows, striving for a novel experience that transcends the limitations inherent to each.
However, the amalgamation of these two behemoths necessitates a meticulous examination of their intrinsic foundations and a deep understanding of the intricacies that permeate their respective infrastructures. One must tread carefully within this realm of convergence, as the compatibility puzzle poses a formidable challenge, demanding resourcefulness, technical expertise, and an unwavering determination to surmount the obstacles that arise during the harmonization process.
Join us on a thought-provoking expedition as we delve into the depths of the compatability quagmire, exploring the feasibility of integrating the quintessence of Windows into the renowned tapestry of Linux. Unveiling the secrets behind the potential marriage of these two peerless juggernauts, we shall navigate through the stormy seas of hardware and software differences, striving to discover if the dream of a unified experience can truly become a reality.
Can Windows Function on a Linux Operating System?
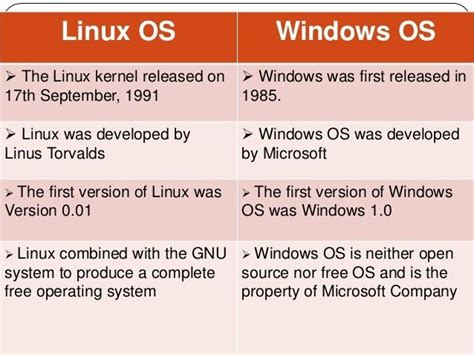
Many individuals in the technology community wonder about the compatibility between Windows and Linux operating systems. The notion of running a Windows-based system on a Linux environment is a topic of curiosity and evaluation.
The intersection of Windows and Linux brings about intriguing possibilities for users seeking to incorporate the functionalities of both systems. However, due to the fundamental differences in architecture, compatibility challenges arise when attempting to integrate these two diverse platforms.
- Can Windows-based applications or software be executed seamlessly on a Linux environment?
- What methods and tools are available for compatibility enhancements?
- Are there any limitations or drawbacks when operating Windows on Linux?
These questions delve into the analysis of the feasibility of running Windows on Linux. The section will delve into various factors that need consideration when attempting such an implementation, highlighting potential advantages and disadvantages that users may encounter.
Understanding Virtual Machines
In the realm of operating systems, there exists a fascinating concept known as virtual machines. These technological marvels provide an avenue for running different operating systems within a host operating system. By leveraging the power of virtualization, users can explore the functionalities and capabilities of various operating systems without the need for traditional installation methods.
Virtual machines create an isolated and self-contained environment where distinct operating systems coexist harmoniously. Within this virtual realm, one can simulate the presence of multiple distinct computers, each running its own operating system. This allows users to delve into the depths of alternate ecosystems, such as Windows or Linux, from the comfort of their current setup.
Virtual machines offer a multitude of benefits. They provide a safe and secure testing ground for experimenting with different operating systems, software configurations, and system setups. They enable developers and IT professionals to separate their working environments from the underlying hardware, facilitating flexible deployments and streamlined maintenance. Additionally, virtual machines enhance resource utilization by efficiently allocating hardware resources among multiple virtual instances.
- Isolation: Each virtual machine operates independently, ensuring isolation and preventing interference between different operating systems.
- Snapshotting: Virtual machines allow users to save and restore system states, creating checkpoints for quick and reliable system backups or experimentation.
- Compatibility: By abstracting the underlying hardware, virtual machines enable the execution of operating systems that may otherwise not be compatible with the host system.
- Efficiency: Virtual machines optimize resource usage by dynamically allocating computing resources based on demand, allowing for efficient utilization of hardware.
Understanding virtual machines is crucial in comprehending the possibilities that arise from the topic of whether it is possible to run Windows on Linux. By harnessing the power of virtualization, individuals can explore the fusion of different operating systems, unlocking new avenues for software development, system administration, and experimentation.
Exploring Dual Booting: Windows and Linux Together

In the realm of operating systems, there exists a fascinating intersection where the worlds of Windows and Linux converge. Dual booting is an intriguing approach that allows users to have both Windows and Linux on the same machine, creating a harmonious coexistence between these two powerful platforms. This article aims to explore the possibilities and benefits of dual booting, providing insights into how this arrangement can be achieved seamlessly.
By embracing dual booting, individuals can harness the unique features and functionalities offered by both Windows and Linux operating systems. This configuration empowers users to leverage the strengths of each platform, enabling them to accomplish a diverse range of tasks, whether for work, entertainment, or personal use. With the ability to seamlessly switch between Windows and Linux, users have the flexibility to access the software, applications, and tools that best suit their needs.
One of the key advantages of dual booting is the opportunity for individuals to explore and learn about different operating systems. By immersing oneself in both Windows and Linux environments, users gain a deeper understanding of the similarities and differences between these platforms. This experience fosters a broader perspective and enhances one's technical prowess, enabling them to adapt and navigate various operating systems effectively.
Setting up a dual boot system requires careful consideration and planning. Users need to allocate sufficient disk space, create separate partitions for Windows and Linux, and choose an appropriate boot manager to seamlessly switch between the two operating systems. Additionally, individuals must ensure compatibility with their hardware and research the specific installation requirements for their chosen versions of Windows and Linux. While slightly complex, the rewards of a well-executed dual boot setup make the effort worthwhile.
| Benefits of Dual Booting: |
|---|
| 1. Versatility: Enjoy the best of both Windows and Linux ecosystems. |
| 2. Learning Experience: Expand your knowledge of different operating systems. |
| 3. Flexibility: Access a wide array of software and applications as per your requirements. |
| 4. Technical Proficiency: Enhance your skills in navigating diverse operating systems. |
| 5. Compatibility: Ensure seamless integration with hardware and software. |
In conclusion, the concept of dual booting opens up a myriad of possibilities for individuals seeking to embrace the best of both Windows and Linux. By understanding the benefits and considerations of dual booting, users can embark on a journey of exploration and productivity, harnessing the strengths of these powerful operating systems in unison.
Using Emulation Software for Running Windows Applications on Linux
In the realm of cross-platform compatibility, exploring ways to utilize emulation software to seamlessly run Windows applications on Linux systems has become a prevalent topic. Emulation software allows users to simulate the environment of one operating system within another, providing a bridge between Windows and Linux without the need for a full installation.
One approach to achieve this integration involves utilizing emulation software, which enables Linux users to enjoy access to a wide range of Windows-specific applications and programs, thereby expanding the functionality and versatility of their Linux-based systems.
- Virtualization: Emulation software provides a virtualization layer that emulates the necessary components and dependencies of the Windows operating system. This allows Windows applications to run seamlessly on a Linux system, with users experiencing little to no difference in performance.
- Compatibility: By leveraging emulation software, Linux users can overcome the traditional barriers that exist between Windows and Linux. This opens up opportunities to utilize industry-specific software, productivity tools, and other applications that are primarily designed for Windows.
- Installation: Emulation software typically requires installation on the Linux system. Once installed, users can configure the emulation settings and establish a virtual environment that mirrors the behavior of Windows. This enables the execution of Windows applications directly on the Linux platform.
- Integration: Emulation software often provides seamless integration between Windows applications and the host Linux system. This means that files and data can be shared between the emulated Windows environment and the Linux environment, enhancing workflow efficiency and enabling collaboration between Windows and Linux users.
- Performance Considerations: While emulation software allows Windows applications to run on Linux, it is essential to consider the impact on performance. The resources required for emulation can vary depending on the software used and the complexity of the Windows applications being executed. Users should ensure that their Linux system has sufficient resources to maintain optimal performance.
In conclusion, using emulation software provides a viable solution for individuals who want to run Windows applications on Linux systems. By creating a virtualized environment that mimics Windows, emulation software enables the seamless execution of Windows-specific applications, thereby expanding the capabilities of Linux and enhancing cross-platform compatibility.
FAQ
Is it possible to install Windows on Linux?
Yes, it is possible to install Windows on a Linux system using virtualization or dual-booting methods. However, it requires some technical knowledge and may have certain limitations.
What is virtualization and how does it allow Windows installation on Linux?
Virtualization is a technology that allows you to create a virtual environment within your Linux system. With virtualization software like VirtualBox or VMware, you can install and run Windows as a virtual machine on your Linux OS.
What is dual-booting and how does it facilitate Windows installation on Linux?
Dual-booting is a process of installing two different operating systems on the same computer, allowing you to choose which one to use during system startup. By partitioning your hard drive and installing Windows alongside Linux, you can switch between the two operating systems on your machine.




