Traversing across the vast and boundless realm of serene tranquility lies a surreal vision that captivates the human imagination. A scene where the tranquil waters merge seamlessly with the icy plains, creating an ethereal landscape that stretches as far as the eye can see.
Within this dreamscape, an icy tapestry unfolds, portraying nature's delicate and intricate artistry. The frozen skin of the water, adorned with elaborate patterns and crystalline formations, paints a picture of pure enchantment. Each shimmering ice crystal possesses a unique identity, as if tailor-made by the hands of an invisible artist.
This frozen wonderland engulfs its surroundings, evoking a sense of grandeur and awe. The stillness of the air and the quiet whispers of the wind lend an air of mystery, as if the very essence of nature itself is holding its breath. It is in this mystical scene that time seems to stand still, allowing one to forge a deeper connection with the natural world that envelops them.
As one ventures into this mesmerizing dreamscape, a symphony of solitude unfolds. The gentle lapping of waves against the icy shore forms a soothing melody, creating a surreal ambiance that lulls the soul into a state of serene contemplation. In this tranquil realm, one can't help but be humbled by the sheer beauty and vastness that stretches out before them.
The Formation of Juxtaposed Ocean Floes
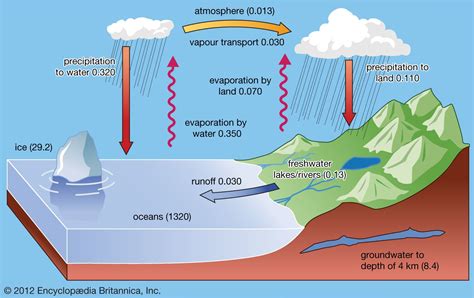
In this section, we will explore the mesmerizing process behind the genesis of expansive and interconnected sheets of frozen seawater. Delve into the intricate dance of natural elements as they transform liquid ocean into a breathtaking arctic landscape.
- The Power of Low Temperatures
- Water's Solid Transformation
- Intertwining of Salinity and Freezing Point
- Mechanical Forces at Play
- Nurturing the Growth of Sea Ice
- Influence of Wind and Currents
- Fascinating Patterns of Crack Formation
- Microscopic Structures within Sea Ice
- An Ecosystem in the Making
Through the exploration of these aspects, we will unravel the captivating story of how ephemeral dreams of frozen expanses materialize as intricate networks of icefloes that mesmerize the eyes and inspire the imagination.
The Impact of Changing Climate
In the realm of imagination, where frozen expanses stretch endlessly across the open waters, lies a pressing concern that pervades our reality: the impact of climate change. The delicate balance of our planet's natural systems is being disrupted, leading to far-reaching consequences for both humans and the environment.
1. Altered Ecosystems and Species' Survival
The changing climate, characterized by shifting temperatures, altering precipitation patterns, and diminishing ice coverage, profoundly influences ecosystems worldwide. Species that have adapted to specific environmental conditions now face the challenge of adapting or migrating to new habitats. Their survival is threatened as they encounter unfamiliar conditions, compete for resources, and face increased vulnerability to pests and diseases.
2. Rising Sea Levels and Coastal Vulnerability
As global temperatures rise, the polar ice caps and glaciers undergo significant melting, contributing to the rise in sea levels. This phenomenon poses a direct threat to coastal communities and low-lying areas, leading to coastal erosion, inundation, and displacement of human settlements. The increased frequency and intensity of storms further exacerbate the vulnerability of these regions, amplifying the risk of devastating floods and destructive storm surges.
3. Changes in Weather Patterns and Extreme Events
Climate change is accompanied by shifts in weather patterns, causing alterations in long-established climatic conditions. Increased frequency of heatwaves, droughts, and intense rainfall events are among the consequences. These extreme weather events not only disrupt ecosystems and agricultural practices but also pose risks to human health, infrastructure, and food security.
4. Socioeconomic Implications and Global Inequalities
The impact of climate change extends beyond the environmental sphere and significantly affects socioeconomic systems. Impacts on agriculture, water availability, and energy resources can have far-reaching consequences for economies, livelihoods, and geopolitical dynamics. Moreover, vulnerable communities, particularly those in developing countries, bear the brunt of climate change's effects, exacerbating existing social inequalities.
In conclusion, the ramifications of climate change permeate multiple aspects of our lives. Addressing this global challenge requires collective action, sustainable practices, and innovative solutions to preserve our planet's fragile ecosystems and secure a resilient future for generations to come.
The Significance of Sea Ice in Ecosystems

Sea ice plays a vital role in the intricate balance and functioning of diverse ecosystems in polar regions. Its presence or absence greatly influences the distribution and behavior of various species, thereby shaping the overall dynamics of these fragile habitats.
- 1. Habitat for Marine Organisms: Sea ice acts as a crucial habitat for a multitude of marine organisms, including algae, bacteria, zooplankton, and fish. These organisms rely on the ice for shelter, feeding, and reproduction, contributing to the overall biodiversity of the marine ecosystem.
- 2. Primary Production and Carbon Cycle: Sea ice acts as a platform for primary production by providing a surface on which microscopic algae can grow, a process known as ice algae bloom. These algae form the base of the food web, supporting the entire marine ecosystem and influencing the cycling of carbon in the ocean.
- 3. Effects on Marine Mammals and Birds: Sea ice serves as a critical hunting ground and breeding site for marine mammals, such as polar bears, seals, and walruses. It also provides a resting place for migratory birds during their long journeys. Changes in sea ice extent and thickness can have profound impacts on these species' reproductive success and overall population dynamics.
- 4. Climate Regulation: The presence of sea ice helps regulate Earth's climate by reflecting sunlight back into space, thus contributing to the cooling of the planet. Melting sea ice, on the other hand, leads to the absorption of more solar energy by the dark ocean, resulting in increased warming and potentially contributing to climate change.
- 5. Importance for Indigenous Communities: Sea ice is deeply intertwined with the cultural and economic practices of indigenous communities in polar regions. It provides essential resources for hunting, fishing, and transportation, serving as a foundation for their traditional way of life. Changes in sea ice conditions directly impact these communities' livelihoods and cultural identity.
Understanding the intricate relationships between sea ice and ecosystems is crucial for effective conservation and management efforts. The fragile nature of polar ecosystems highlights the importance of preserving sea ice and mitigating the impacts of climate change to ensure the resilience and survival of these unique habitats and the species that depend on them.
Challenges of Navigating through Frozen Waters
Traversing icy expanses presents a myriad of obstacles and difficulties, requiring great skill and expertise from those who dare to navigate through these treacherous seas. The frozen and vast waters pose unique challenges that demand careful planning, advanced technology, and a resilient spirit.
1. Ice Formation: The process of the formation of ice on the sea creates a barrier that hinders navigation. The freezing temperatures cause seawater to transform into solid ice, restricting the movement of ships and vessels. Captains and crew must be well-prepared to face this formidable challenge.
- Floe Ice: Floes are large pieces of floating ice that can collide, creating hazards for ships. Navigating through these ice formations requires precise maneuvering to avoid collisions that can lead to vessel damage or even sinking.
- Pack Ice: Pack ice refers to a collective mass of floating ice that covers a significant portion of the sea's surface, causing further difficulties for navigation. Ships must find safe paths to navigate through the pack ice, avoiding areas of concentrated thickness.
- Icebergs: These massive pieces of ice that break off from glaciers can pose a grave threat to ships. The challenge lies in spotting and avoiding icebergs, as they can be unpredictable and difficult to detect, especially during icy weather conditions or in areas with poor visibility.
2. Poor Visibility: In icy conditions, visibility becomes severely limited, increasing the risk of accidents and collisions. Heavy snowfall, fog, and icy mist create a veil of uncertainty, making navigation even more perilous. Ship captains rely on advanced navigational equipment and radar systems to overcome this challenge and maintain a clear course.
3. Constantly Changing Conditions: The state of ice-covered seas is never static. The movement and shifting of ice formations pose an ongoing challenge. What may appear as a navigable path one moment may become impassable the next. Captains and crew must constantly assess and adapt to changing conditions, seeking alternative routes and adjusting their strategies accordingly.
4. Isolation and Limited Support: Ice-covered seas often lack the infrastructure and support systems available in more accessible waters. Engaging in navigation in remote areas means facing long distances from emergency services and limited access to supplies and repairs. Ship crews must be self-sufficient and prepared to handle emergencies and equipment failures with minimal external assistance.
Navigating through ice-covered seas demands a combination of experience, skill, and a deep understanding of the ever-changing environment. It is a test of courage and resilience, where successfully overcoming these challenges rewards sailors with breathtaking views of the frozen beauty that surrounds them.
The Enchanting Splendor of Icebergs

Immerse yourself in the extraordinary world of frozen marvels, where towering monoliths emerge from the icy depths, captivating with their ethereal grandeur and captivating beauty.
Icebergs, also referred to as frozen behemoths, are magnificent formations sculpted by nature's immortal touch. These colossal masses of ice, shaped by millennia of freezing Arctic winds and relentless tides, stand as majestic symbols of serene power and sublime grace.
Each iceberg, a unique masterpiece, boasts an array of mesmerizing hues and spectacular textures that tell the tale of its journey through time. Translucent blues, radiant turquoise, and shimmering whites intertwine to create a kaleidoscope of breathtaking colors, evoking a sense of wonder and awe.
As these glacial giants traverse the open seas, they become veritable art galleries, displaying their dramatic morphology and serene demeanor to fortunate onlookers. Their massive yet delicate structures convey a sense of fragility and strength, beckoning one to observe their majesty from a distance while embracing their captivating pull.
| The Magical Elements of Icebergs | The Mystical Allure of Icebergs | The Enigmatic Charm of Icebergs |
| • Sublime formations shaped by natural forces | • Ethereal beauty that captivates the senses | • Awe-inspiring presence amidst the open seas |
| • Mesmerizing colors and breathtaking textures | • A sublime interplay of hues and shades | • Radiant spectrums that evoke a sense of wonder |
| • Delicate yet sturdy structures that endure | • A harmonious blend of fragility and strength | • Captivating allure that beckons exploration |
Exploring the Enigmatic Life Below the Frozen Ocean Expanse
Delving into the depths of the icy marine realm, a fascinating and mysterious world unfolds beneath the frozen expanse. In this section, we embark on a captivating journey to uncover the enigmatic life that thrives beneath the ice. Using innovative techniques and unwavering curiosity, scientists and explorers venture into the frigid depths to study the remarkable organisms that call this hidden ecosystem home.
As we descend into this ethereal underworld, an astonishing array of adaptations and survival strategies are revealed. Discovering how these tenacious creatures withstand the harsh conditions, we witness their incredible resilience and ingenuity. From fish species that possess antifreeze proteins to cope with the subzero temperatures, to mesmerizing sea anemones that thrive on the limited sunlight penetrating the ice, each organism has found incredible ways to adapt and flourish in this extreme environment.
Unveiling the intricacies of the food web beneath the ice, we unravel the delicate balance that sustains life in this frozen ecosystem. Tiny planktonic organisms, such as diatoms and copepods, serve as the foundation of the food chain, supporting a diverse community of higher trophic levels. Exploring the feeding habits and interdependencies of these organisms illuminates the complex web of interactions that governs the ecological dynamics in this secluded realm.
Moreover, this exploration goes beyond basic biological investigations. It extends to understanding the potential impacts of climate change on these fragile ecosystems. By gathering data on changes in ice coverage, temperature, and nutrient availability, scientists strive to forecast the effects that alterations in these environmental factors may have on the species inhabiting this icy domain.
Together, this section offers a glimpse into the mesmerizing wonders of the life hidden beneath the frozen seas. Through scientific inquiry and exploration, we gain a deeper appreciation for the resilience and adaptability displayed by the organisms that call this unique environment home.
Traditional Utilization of Sea Ice by Indigenous Communities

Within the cultural fabric of indigenous communities inhabiting regions characterized by frozen expanses of water, the ice that covers the sea holds immense significance. Across generations, these communities have forged a deep connection with the frozen landscape, utilizing its resources in unique and resourceful ways.
Sea ice serves as a vital platform for a plethora of activities, ranging from transportation to hunting and fishing. Indigenous communities have honed their knowledge and skills over time, further solidifying their bond with the frozen environment. The traditional practices and techniques employed by these communities showcase their resourcefulness and adaptability.
Hunting: The expansive and solid ice surface provides indigenous hunters with an extended range for pursuing marine mammals. Utilizing traditional hunting methods, such as igloo hideouts and kayaks, they skillfully navigate through the frozen landscape, relying on the ice as a vital tool and ally. This timeless practice enables sustenance and preservation of cultural heritage.
Fishing: Indigenous communities have developed ingenious techniques for ice fishing, enhancing their access to vital food resources. Utilizing ice holes and specialized tools, they harvest fish beneath the icy surface. This traditional method not only provides sustenance but also strengthens the bond between community members as they gather together in collective fishing expeditions.
Transportation: Sea ice serves as a natural highway for indigenous communities, enabling efficient travel across vast frozen expanses. Sleds and dog teams, as well as snowmobiles in more modern times, have been utilized to traverse the frozen sea. The ability to navigate the ice swiftly and safely is a testament to the traditional knowledge passed down through generations.
Cultural and Spiritual Significance: Sea ice is deeply intertwined with the identities, traditions, and spiritual beliefs of indigenous communities. It serves as a foundation for cultural ceremonies, storytelling, and traditional performances. Indigenous individuals consider the ice as a guardian, a provider, and a key element in their spiritual connection to the natural world.
Throughout history, indigenous communities have adapted to the ever-changing nature of sea ice, harnessing its resources to sustain their communities and uphold their cultural heritage. The utilization of sea ice in hunting, fishing, transportation, and spirituality reflects the profound knowledge and deep respect indigenous communities have for their frozen environments.
The Significant Role of Ice-Associated Industries in the Economy
As the depths of the arctic regions coalesce under the crystalline embrace of freezing temperatures, a multitude of industries thrives amidst the icy panorama, contributing considerably to economic growth and development. The economic importance of these ice-related sectors cannot be understated, as they encompass a wide array of activities that harness the raw power and potential of this frozen domain, leveraging it to generate employment, drive innovation, and enhance trade opportunities.
Implicitly embedded within the very core of these industries is an intricate web of interdependence that extends beyond the surface of the ice. From the extraction and transportation of natural resources to the provision of crucial logistical support, various sectors rely on the ice as a vital medium that facilitates their operations. The significance of this symbiotic relationship transcends geographical boundaries, as nations and regions with access to icy territories harbor a unique advantage in their ability to exploit these resources and capitalize on the economic opportunities they present.
One of the most prominent ice-related industries revolves around the extraction and production of energy resources, primarily oil and gas. The ice acts as a natural barrier, necessitating the development and implementation of specialized technologies and techniques to access these valuable deposits. Such endeavors result in a myriad of employment opportunities, both directly and indirectly, from engineers and geologists to logistics providers and equipment manufacturers.
Transportation and shipping industries constitute another crucial facet of the ice-associated economic landscape. These industries rely on the formation of solid ice to create ice roads and bridges, enabling the movement of goods and people across frozen expanses. Additionally, icebreakers, specially designed vessels equipped to navigate icy waters, play a pivotal role in ensuring safe and efficient shipping routes, thus facilitating global trade and commerce.
Beyond extractive and logistical activities, ice-related industries also encompass tourism and research ventures. The allure of the frozen landscapes has captivated adventurers and scientists, leading to the establishment of unique experiences for thrill-seekers and the exploration of scientific frontiers. Tourist attractions and research stations dotting icy regions generate revenue and contribute to the global pool of knowledge and understanding.
In conclusion, the economic importance of ice-related industries permeates various sectors, capitalizing on the distinctive characteristics of frozen landscapes. From energy extraction to transportation, tourism, and research, these industries continue to shape the economic landscape, stimulating growth and offering a plethora of opportunities for individuals and nations alike.
Preserving and Conserving Frozen Expanse for Future Generations

As we look towards the future, it is crucial to recognize the significance of safeguarding and maintaining the vast frozen landscape that extends across the ocean. Ensuring the continuity of this natural wonder is of utmost importance for generations to come.
Here are some essential measures and strategies that can be employed to preserve and conserve the ice-cloaked realm:
- Enhancing Awareness and Education: Educating individuals about the fragile nature of the frozen expanse can foster a sense of responsibility towards its preservation. Raising awareness through various channels such as schools, media, and community outreach programs can cultivate a collective commitment towards conserving this unique environment.
- Implementing Sustainable Fishing Practices: Addressing the impact of fishing activities on the ice-covered sea is vital in maintaining the delicate balance of the ecosystem. Introducing and enforcing regulations that promote sustainable fishing techniques, such as reduced bycatch and selective harvesting, can mitigate potential damage to the frozen habitat.
- Reducing Pollution and Carbon Emissions: Recognizing the role of human activities in accelerating climate change, it is imperative to take concrete steps towards reducing pollution and carbon emissions. Implementing stricter regulations on industrial emissions, promoting cleaner energy alternatives, and advocating for sustainable transportation methods can help slow the melting of sea ice.
- Monitoring and Research: Regular monitoring and scientific research are invaluable in understanding the current state and future prospects of sea ice. Investing in comprehensive studies, satellite monitoring, and data collection initiatives can provide essential information for informed decision-making and facilitate timely conservation efforts.
- Encouraging International Cooperation: Addressing the challenge of conserving sea ice requires collaborative efforts on a global scale. Building partnerships and fostering international cooperation through forums, treaties, and agreements can help ensure the preservation of this unique environment for future generations.
By implementing these measures and more, we can aspire to preserve and conserve the frozen expanse, allowing future generations to witness the awe-inspiring beauty of this natural phenomenon. Protecting the ice-covered sea is not just an obligation but also a testament to our commitment towards a sustainable and thriving planet.
FAQ
What is the article "In a Dream: Ice Spreads Wide on the Sea" about?
The article "In a Dream: Ice Spreads Wide on the Sea" is about the phenomenon of ice spreading over a wide area on the sea.
Why does ice spread wide on the sea?
Ice spreads wide on the sea due to the low temperatures causing the freezing of seawater, creating a layer of ice on the surface.
How does the spreading of ice on the sea affect marine life?
The spreading of ice on the sea can have a significant impact on marine life. It can restrict the movement of marine animals, limit their access to food, and alter their habitats. Some species, such as polar bears and seals, rely on sea ice for survival and hunting.




