Welcome to a realm where boundaries cease to exist, where cultural exchange flows freely, and where understanding knows no limits. In our interconnected world, the ability to comprehend and be understood in different languages has become an indispensable skill. This article unveils a practical guide to shifting the language of your operating system, opening doors to a whole new universe of possibilities.
In this digital era, the capability to navigate a foreign interface emerges as a valuable asset, enabling seamless interaction with individuals from diverse backgrounds. By adapting your computer's linguistic framework, you can effortlessly connect with people across the world, fostering communication, collaboration, and ultimately, understanding. Let us embark on a journey of exploration, where the path to linguistic fluency lies just a few clicks away.
The power of language lies not solely in words but in the emotions they convey and the connections they forge. By immersing ourselves in unfamiliar linguistic environments, we gain access to an abundance of knowledge and experiences, expanding our horizons beyond measure. With a few keystrokes, we can transcend the limitations imposed by monolingualism and embrace the richness of another culture.
In this article, we will delve into the art of software localization, shedding light on the steps required to transform your Windows system into a vessel of multilingualism. Embracing various tools and techniques, we will unravel the secrets to customizing your user interface, enabling you to fashion an environment that resonates with your individuality, and facilitates global connections. Are you ready to embark on this transformative journey of linguistic discovery? Let us commence our exploration.
Comprehending the Language Preferences in the Operating System
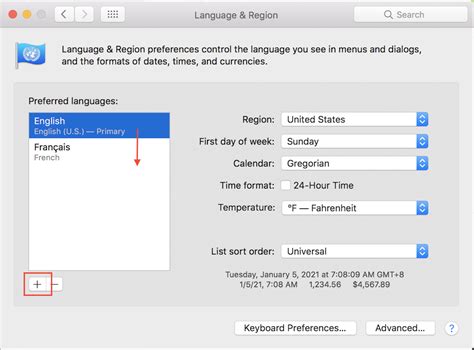
Within the realm of customizing your linguistic experience on a diverse operating system, it is essential to acquaint oneself with the language options available. Understanding the language preferences and settings in the computer's interface presents users with the opportunity to personalize their interaction and enhance their overall user experience.
One of the fundamental aspects to take into consideration is the versatility in the display language, enabling individuals to navigate through various menus, dialog boxes, and notifications effortlessly. The system's language preferences provide users with the ability to select and configure their desired display language, opening up a world of possibilities to interact with the operating system using their preferred dialect, accent, or regional variations.
Moreover, comprehending the input method editor (IME) options plays a vital role in facilitating the utilization of different writing systems, such as non-Latin alphabets or complex character-based languages. By understanding the various IMEs offered by the operating system, users can seamlessly input text and express themselves in languages that require more intricate writing mechanisms.
In addition to these aspects, exploring the language settings within the operating system grants users the power to modify the formatting conventions to align with their cultural and linguistic preferences. This entails customizing date and time formats, number systems, currency symbols, and other regional parameters, enabling a more personalized and culturally relevant computing experience.
Overall, understanding the intricacies of language options in the operating system empowers users to tailor their linguistic environment, making it more conducive to their individual preferences and language needs. By delving into the intricacies of display language, IME options, and formatting conventions, users can create a more immersive and enjoyable computing experience that aligns with their linguistic and cultural identity.
Choosing the Appropriate Version of Windows for Language Localization
When it comes to customizing the user interface of your operating system to match your preferred language, it is essential to select the right edition of Windows that facilitates smooth language translation. A correct choice of Windows version ensures a hassle-free process of adapting the user interface elements, menus, and dialog boxes into the desired language.
There are various editions of Windows available, each tailored to specific needs and requirements. It is crucial to understand the differences between these editions to make an informed decision and choose the most suitable one for your language translation needs.
- Windows Pro Edition: This edition is ideal for individuals and small businesses that require advanced features such as remote desktop, domain join, and group policy management. It provides flexibility and control over language translation in an enterprise setting.
- Windows Home Edition: Geared towards home users, this edition offers a user-friendly interface and caters to basic computing needs. Although it may have limitations in terms of language translation capabilities, it can still be customized to a certain extent.
- Windows Education Edition: Designed specifically for educational institutions, this edition provides additional language support and management functionalities. It offers advanced language translation options to meet the specific needs of students and educational professionals.
- Windows Enterprise Edition: This version is geared towards large organizations and businesses and provides comprehensive language localization features. It offers enhanced language customization options and centralized management capabilities.
- Windows Server Edition: Primarily used for server environments, this edition allows for language customization at a system level. It provides robust language translation capabilities while ensuring stability and security.
By carefully considering the features and capabilities offered by each edition of Windows, you can select the most appropriate version for your language translation requirements. It is essential to assess your specific needs, whether it is for personal use, small businesses, educational institutions, or enterprise environments, to ensure a seamless and efficient translation process.
Installing Language Packs on Your Operating System
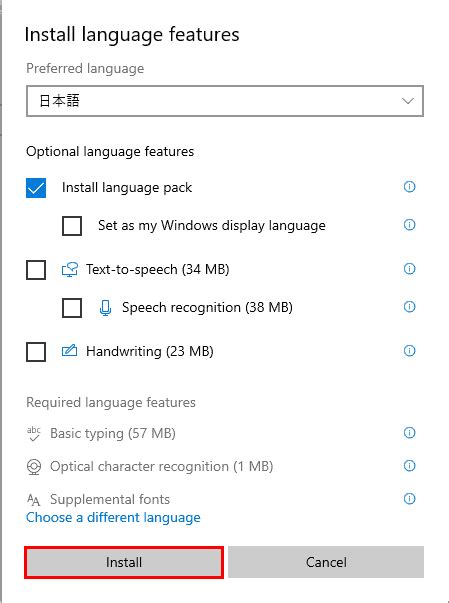
Enhancing your computing experience by incorporating different languages into your operating system can greatly expand your global opportunities. This section will guide you through the process of installing language packs, allowing you to effortlessly navigate your device in your preferred language.
Language packs provide localized versions of your operating system's interface, ensuring seamless communication and user interaction. Whether you want to switch to a language that reflects your cultural background or simply explore new linguistic horizons, installing language packs enables you to personalize your Windows experience.
Below, you will find step-by-step instructions on how to install language packs in Windows. Although the specific steps may vary depending on your operating system version, this comprehensive guide will serve as a general reference to help you navigate through the process with ease.
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| Step 1 | Access the Control Panel: Locate and open the Control Panel on your device by searching for it in the Start menu or through the Windows search function. |
| Step 2 | Navigate to the Language Settings: Once the Control Panel is open, search for the language settings option. It may be labeled as "Language," "Region and Language," or "Clock and Region." |
| Step 3 | Add a Language: In the language settings, select the "Add a language" option to access the list of available languages. Choose the language you desire to install by selecting it from the provided options. |
| Step 4 | Download and Install the Language Pack: After selecting your desired language, click on the "Options" button next to it. From the options menu, click on the "Download" button to start the language pack installation process. |
| Step 5 | Apply the Language Pack: Once the language pack is downloaded and installed, go back to the language settings menu. Select the newly installed language and click on the "Set as default" button to apply it as your system's primary language. |
| Step 6 | Log Out and Log In: To ensure that the changes take effect, log out of your user account and then log back in. Upon logging back in, your operating system will be in the language you have installed. |
By following these easy steps, you can effortlessly install language packs on your Windows device and seamlessly switch between languages at your convenience. Unlock the full potential of your operating system by embracing linguistic diversity and expanding your horizons!
Changing the Display Language in Windows
In this section, we will explore the process of altering the presentation language on your Windows operating system. Each interface element, from menus to dialog boxes, can be customized to suit your language preferences. Discover how to modify the display language seamlessly and effortlessly.
- Access the Language Settings: Begin by navigating to the language settings menu, where all the necessary options are located. Locate the settings icon and proceed to the language settings section.
- Select your Desired Language: Once in the language settings section, choose the language you wish to use on your Windows system. Explore the available options and find the one that matches your preferred language.
- Apply the Changes: After selecting your desired language, apply the changes to ensure that the display language switches accordingly. Confirm the modifications and wait for the system to adjust to the new language settings.
- Restart your System: To complete the process, restart your Windows system. This step finalizes the language change and allows the modifications to take effect across all aspects of the operating system.
- Enjoy a New Language Experience: Once your system reboots, you can revel in a fresh language experience on Windows. Discover how your preferred language transforms the user interface and enhances your overall usage.
With these simple steps, you can effortlessly change the display language on your Windows system. Enjoy the freedom to interact with your operating system in a language that suits your preferences and enhances your overall computing experience!
Localization of System Applications and Menus in Microsoft Operating Systems
Successful implementation of a localized user interface is crucial for ensuring a seamless computing experience for non-English speaking users. This section will explore the intricate process of transforming the language of system applications and menus in Microsoft operating systems, allowing users to navigate through the interface in their native language.
Localization, the process of adapting software to a specific language or region, involves translating not only the textual content but also the non-verbal elements, such as icons and images, to provide a comprehensive user experience. Microsoft operating systems offer robust tools and resources to simplify the translation process and enable users to switch seamlessly between languages.
When it comes to translating system apps and menus, the first step is to identify the specific elements that need to be localized. These elements include menus, dialog boxes, buttons, and other graphical user interface components that users interact with on a daily basis. A thorough understanding of the software's structure and functionality is essential to ensure a complete translation.
One approach to localizing system apps and menus is by utilizing language resource files, which store different language versions of the user interface components. These files can be modified or replaced with translated versions to customize the system's language display. Microsoft provides a comprehensive language pack that includes translations for various system components, making it easier for users to switch to their desired language.
- Identify the specific elements to be translated, such as menus, dialog boxes, and buttons.
- Gain a deep understanding of the software's structure and functionality.
- Utilize language resource files to customize the language display.
- Explore language packs provided by Microsoft for comprehensive system component translations.
Localization goes beyond basic translation, requiring attention to cultural nuances, linguistic idioms, and formatting conventions. Translation quality assurance, user testing, and continuous refinement are essential to ensure a seamless and user-friendly multilingual interface.
Adapting system applications and menus to different languages allows users to fully engage with their computing environment, opening up opportunities for increased productivity and enhanced user satisfaction. With precise localization techniques, Microsoft operating systems can truly become a global platform for users around the world.
Customizing Language Preferences for Specific Apps
In this section, we will explore the process of personalizing the language settings for individual applications. By tailoring the language preferences to specific apps, users can enhance their overall experience and ensure optimal usability.
When it comes to adapting language preferences for particular applications, it is vital to understand the importance of customization. By customizing language settings, users can align the interface, menus, and commands of their favorite apps with their language preferences, enhancing overall usability and efficiency.
Personalization of language preferences for specific applications allows users to feel more comfortable and familiar while navigating through software interfaces. Whether it's configuring language settings for productivity apps, creative tools, or specialized software, by customizing language preferences, users can optimize their workflow and maximize productivity.
One of the key benefits of customizing language preferences for specific apps is the ability to seamlessly switch between languages. This feature proves particularly useful for bilingual individuals or those who work in multicultural environments, enabling them to effortlessly adapt the language settings to suit their needs.
With customization options available for numerous software applications, users can select their desired language for specific apps, ensuring a consistent experience across the board. This way, users can enjoy software functionalities while communicating in their preferred language, further enhancing their overall user experience.
Overall, by delving into the customization of language preferences for specific applications, users can unlock a whole new level of usability, personalization, and efficiency. Tailoring the language settings to individual app preferences not only enhances overall user experience but also empowers users to fully utilize the functionality of their preferred software applications.
Expanding Your Keyboard and Input Language Options
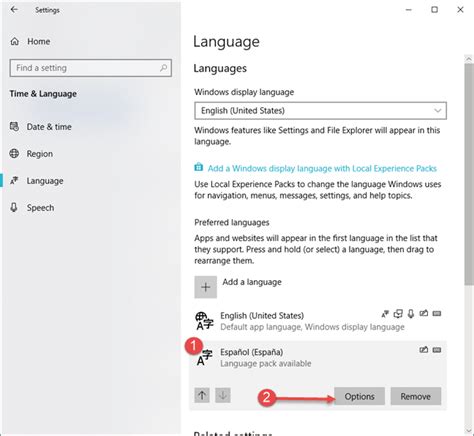
In this section, we will explore the process of adding additional keyboards and input languages to your operating system. By expanding your language options, you can enhance your typing and communication experience with a wider range of languages and characters.
One way to expand your keyboard and input language options is by adding additional keyboards to your system. This allows you to type in different languages using different keyboard layouts. By adding a new keyboard, you can easily switch between different languages without the need to change your entire operating system language.
Another way to expand your language options is by adding additional input languages. Input language determines the language used for spelling and grammar checks, as well as the language used for the system's user interface and menus. By adding a new input language, you can customize your system to better suit your language preferences.
To add additional keyboards and input languages, you can use the language settings in your operating system. These settings provide a user-friendly interface to manage and customize your language options. You can access the language settings through the control panel or settings menu, depending on your Windows version.
- Open the language settings in your operating system.
- Select "Add a language" to browse and choose the desired language from the available options.
- Once you have added a new language, you can customize its settings, such as the keyboard layout and input method.
- You can also set a specific language as the default input language for your system.
- To switch between different keyboards and input languages, you can use the language bar, which appears on your taskbar once you have added multiple languages.
By following these steps, you can easily expand your keyboard and input language options, allowing you to communicate and work in multiple languages effortlessly. Whether you need to type in a different language for personal or professional reasons, adding additional keyboards and input languages can greatly enhance your Windows experience.
Translating File Names and Folder Labels in the Operating System
In the operating system, there is a need to customize and localize file names and folder labels to enable seamless navigation and understanding for users in different linguistic environments. This section will explore the process of translating these essential elements without altering the system's functionality or stability.
When adapting file names and folder labels into another language, it is crucial to ensure accurate translations that accurately convey the intended meaning while considering cultural differences. Each translated element must fit within the character limitations of the operating system and maintain consistency with its original purpose and context.
One method of translating file names and folder labels involves working directly with the operating system's localization settings. Through this approach, users can customize the interface by replacing default file names and folder labels with equivalent terms in their desired language. This ensures a seamless transition for non-English speakers, enhancing their overall user experience.
In addition to the built-in localization options, third-party software tools can assist in the translation process. These tools provide advanced features such as automatic translation, consistency checks, and bulk editing capabilities, making them invaluable for extensive localization projects. They offer a streamlined workflow, ensuring accuracy and efficiency when translating file names and folder labels.
While localization tools can simplify the translation process, it is essential to consider potential challenges that may arise. Language nuances, character limitations, and the need for linguistic accuracy can pose difficulties during translation. Therefore, it is crucial to employ a comprehensive quality assurance process to ensure the translated file names and folder labels retain their integrity in the target language.
Translating file names and folder labels is a fundamental aspect of creating a user-friendly operating system that caters to the linguistic preferences of diverse users. By following best practices and utilizing the available localization options and tools, the process can be streamlined and efficient, resulting in a seamless user experience in any language.
Troubleshooting Localization Challenges

When encountering difficulties with adapting software interfaces to different languages and cultures, it is essential to address and resolve the issues effectively. This section will guide you through common challenges that may arise during the language translation process, offering troubleshooting techniques to overcome them.
One common challenge that may occur is the improper display of translated text. This can manifest as incorrect spacing, overlapping characters, or even the omission of certain words or phrases. To troubleshoot this, ensure that the translated text fits within the designated space, making adjustments to the UI layout if necessary. Additionally, check for any inconsistent font sizes or styles that could affect the overall readability of the translated content.
Another issue that may arise is the incorrect interpretation of cultural references within the translated text. When translating into another language, it is crucial to consider cultural nuances and avoid potential misunderstandings. Troubleshoot this by conducting thorough research on the target culture, ensuring that idiomatic expressions, symbols, and metaphors are appropriately adapted to convey the intended meaning without causing offense or confusion.
Compatibility issues can also pose challenges when translating software interfaces. Sometimes, the translation process may involve the use of characters or fonts that are not supported by the operating system or software being localized. To overcome this, troubleshoot by selecting compatible fonts or adjusting the encoding settings to ensure that the translated content displays correctly in the target language.
A lack of context in the translation can also lead to confusion for users. Troubleshooting this involves providing translators with comprehensive contextual information, such as screenshots and descriptions of the user interface elements. This will enable them to accurately capture the intended meaning, resulting in a more effective translation.
Furthermore, testing and quality assurance are integral to identifying and resolving translation issues. Troubleshoot by conducting rigorous testing with native speakers of the target language, paying close attention to any inconsistencies, unnatural phrasing, or functional errors that may occur. Incorporating user feedback and iterating on the translation will help refine the localized version and ensure a seamless user experience.
| Common Challenges | Troubleshooting Techniques |
|---|---|
| Improper display of translated text | Ensure appropriate spacing and check font styles |
| Incorrect interpretation of cultural references | Research target culture and adapt appropriately |
| Compatibility issues with characters or fonts | Select compatible fonts and adjust encoding settings |
| Lack of context in translation | Provide comprehensive contextual information to translators |
| Inconsistencies, unnatural phrasing, or functional errors | Rigorously test with native speakers and iterate on the translation |
Tips for Effectively Localizing Operating Systems into Different Languages
In this section, we will discuss some helpful strategies and techniques to successfully adapt operating systems to various linguistic environments. By embracing these tips, you can streamline the localization process and ensure a seamless user experience across different cultures and languages.
- 1. Prioritize Cultural Sensitivity: Understanding and respecting cultural nuances is crucial when translating an operating system. Tailor your language choices, symbols, and icons to resonate with the target audience's cultural preferences.
- 2. Engage Native Speakers: Collaborating with bilingual individuals or hiring professional translators fluent in the target language can significantly improve the accuracy and quality of the translation.
- 3. Develop a Glossary: Creating a comprehensive glossary that includes essential technical terms and commonly used phrases specific to the operating system will ensure consistency throughout the localization process.
- 4. Analyze User Interface Design: Assess the user interface elements' layout, including buttons, menus, and dialog boxes, to ensure they can accommodate the translated text without appearing crowded or causing truncation issues.
- 5. Keep Text Expansion in Mind: Languages may have different sentence structures and word lengths, which impacts text expansion. Design user interface elements with enough space to accommodate potential increases in text length during translation.
- 6. Test and Iterate: Thoroughly test the localized operating system by involving representative users who are native speakers of the target language. Collect feedback and iterate on the translations based on the user experience and comprehension.
- 7. Conform to Localization Standards: Familiarize yourself with industry-recognized localization best practices, conventions, and guidelines to ensure accurate translation and adherence to international standards.
- 8. Encourage Community Involvement: Consider involving the target language community in the localization process, allowing users to provide feedback, contribute suggestions, and report any linguistic or cultural inaccuracies.
By implementation of these effective strategies, you can optimize the localization of operating systems into different languages, ensuring a seamless user experience and widespread adoption in diverse linguistic environments.
How to Translate a Document in Any language using Google Docs
How to Translate a Document in Any language using Google Docs by digitidea 186,677 views 4 years ago 2 minutes, 25 seconds
FAQ
Can I change the language of my Windows operating system?
Yes, you can change the language of your Windows operating system. Windows provides language packs that allow you to translate the user interface into different languages.
How can I install a language pack on Windows?
To install a language pack on Windows, go to the "Settings" menu, then click on "Time & Language," and select "Language." Click on "Add a language" and choose the language pack you want to install. Windows will download and install the necessary files for the selected language.
Do I need to restart my computer after installing a language pack?
No, you don't need to restart your computer immediately after installing a language pack. However, some changes may take effect only after a restart, so it is recommended to restart your computer to ensure that the language pack is fully applied.
Can I change the display language for specific apps only?
Yes, you can change the display language for specific apps in Windows. To do this, go to the "Settings" menu, then click on "Time & Language," and select "Language." Under "Preferred languages," click on the language you want to use for specific apps and click on "Options." From there, you can select "Override for this app" and choose the desired display language for each individual app.
Is it possible to switch back to the original language after installing a language pack?
Yes, you can switch back to the original language after installing a language pack. Simply follow the same steps to install a new language pack and select your original language as the preferred language. Windows will change the user interface back to the original language.




