Imagine a scenario where your computer encounters an unexpected glitch or a malicious program manages to infiltrate your system, causing it to act strangely or become unresponsive. In situations like these, it becomes crucial to have a fail-safe mechanism that allows you to regain control and diagnose and rectify any potential issues. This is where the concept of initiating your computer in a protected state proves to be invaluable.
When you work with your computer each day, you familiarize yourself with various technical terms and jargon. However, for the purpose of this guide, let's embark on a journey to understand a feature that enables your computer to commence its operations with a heightened sense of security – an environment where only essential applications and services are loaded, allowing you to remedy any software or hardware-related problem without interference.
In the following paragraphs, we will delve into the art of accessing your computer's secure startup state. A state that can be likened to an impregnable fortress, shielding your system from potential threats. By exploring the steps involved in entering this mode, you will equip yourself with the knowledge to troubleshoot, repair, and ultimately, restore your computer to its optimal functionality.
Exploring the Shift + Restart Option
Discover a powerful technique to effectively access a specialized feature of your computer system known as Safe Mode, through the utilization of the Shift + Restart option. This innovative method provides a convenient and efficient way to troubleshoot and resolve any issues encountered during the boot process. By employing this alternative pathway, users can bypass the traditional startup sequence and initiate a streamlined start in a secure environment, facilitating the identification and resolution of any potential software conflicts or system instability.
Unleashing the Potential of the Shift + Restart Option
By employing the Shift + Restart option, users can harness the hidden capabilities of their computer system and gain exclusive access to the distinctive Safe Mode safeguard. This specialized mode of operation permits users to diagnose and troubleshoot various software and hardware issues, ensuring the smooth and stable functioning of their device. This unique approach empowers users by providing them with the tools and resources necessary to efficiently resolve any problems, without compromising the integrity or functionality of their operating system.
Engaging the Shift + Restart option can prove to be an invaluable asset when encountering unforeseen technical difficulties, enabling users to embark on a journey of effective problem-solving and system optimization.
Using the System Configuration Tool (MSConfig)
In this section, we will explore an efficient approach to booting your computer into a secure state, by utilizing a powerful utility known as the System Configuration Tool, also referred to as MSConfig. By leveraging this tool, users can access a comprehensive array of advanced options and settings that can aid in troubleshooting and resolving issues with their Windows operating system.
The System Configuration Tool grants users the ability to modify the startup configuration settings, including disabling or enabling specific programs or services that launch during the boot process. This level of control allows users to customize their startup environment, ensuring that only essential programs and services are loaded, promoting a safer and more efficient system performance.
With the System Configuration Tool, users can take advantage of its intuitive interface and streamlined design. It provides users with a clear overview of the various startup settings and allows for easy customization with just a few clicks. Whether you want to disable unnecessary startup programs or troubleshoot issues that may arise, MSConfig offers a simplified yet comprehensive solution.
In addition to its functionality in configuring the startup behavior, MSConfig also includes a diagnostic tool that assists in identifying problematic startup items or services that may cause system instability. By enabling the diagnostic mode, users can selectively choose which items to load, making it easier to pinpoint the cause of any issues and resolve them effectively.
To access the System Configuration Tool, users can simply follow a few easy steps. By opening the "Run" dialog, either through the start menu or by pressing the Windows key + R, and typing "msconfig" followed by Enter, the tool will appear. From there, users can navigate through its different tabs, such as "General," "Boot," "Services," and "Startup," where they can make the desired changes to their system configuration.
Overall, utilizing the System Configuration Tool (MSConfig) is a valuable method to start Windows in a secure and customized manner. By taking advantage of its features and functionalities, users can optimize their computer's performance while ensuring a safe and stable operating environment.
Accessing Safe Mode via the Advanced Boot Options Menu
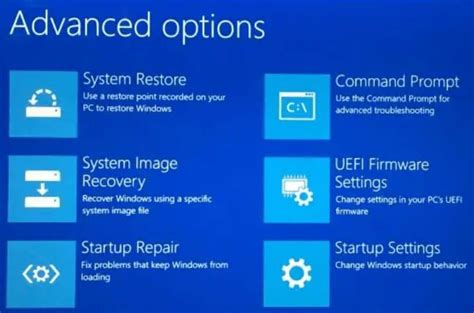
In certain situations, it may become necessary to access a specialized mode within the operating system that provides a more basic and secure environment for troubleshooting or fixing issues. This mode, known as Safe Mode, is accessible through the Advanced Boot Options Menu.
The Advanced Boot Options Menu is a powerful tool that allows users to access various advanced features and modes of the operating system. One of these features is the ability to start the computer in Safe Mode, which can be useful for troubleshooting software conflicts, removing viruses or malware, or resolving system errors.
To access the Advanced Boot Options Menu and boot into Safe Mode, you will need to restart your computer and press a specific key during the boot process. The specific key may vary depending on your computer's manufacturer, but common keys include F8, Shift+F8, or Esc.
- Start by restarting your computer.
- As the computer starts up, continually tap the appropriate key to access the Advanced Boot Options Menu.
- Once the menu appears, use the arrow keys to highlight the "Safe Mode" option.
- Press Enter to start Windows in Safe Mode.
It's important to note that the Advanced Boot Options Menu may also offer additional options such as Safe Mode with Networking, which allows you to connect to the internet while in Safe Mode, or Safe Mode with Command Prompt, which provides a command line interface for advanced troubleshooting.
Safe Mode provides a stripped-down version of the operating system that loads only the essential drivers and services, which can often help isolate and resolve issues that may be causing problems in normal mode. If you encounter persistent issues with your computer, accessing Safe Mode via the Advanced Boot Options Menu can be a valuable step in troubleshooting and resolving them effectively.
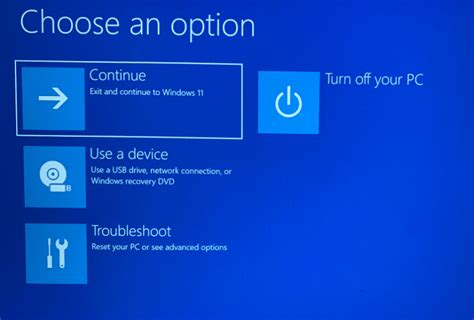
Accessing Safe Mode through the Windows Recovery Environment
Exploring alternative pathways to operating systems in a protected state can be achieved with the utilization of the Windows Recovery Environment.
During the troubleshooting process, when encountering persistence issues or software conflicts, it becomes imperative to reach the Safe Mode option through the platform's built-in recovery tools.
One effective technique to access the Safe Mode feature involves activating the hidden Windows Recovery Environment (WinRE). By utilizing this powerful tool, users can launch the system in an isolated state without compromising the core functionality of the main operating system.
Before proceeding, it is important to note that accessing the Windows Recovery Environment may vary depending on the version of the operating system. However, the general steps remain consistent across the majority of Windows releases.
Firstly, start by shutting down the computer completely. Upon restarting, be prepared to intercept the boot process through the designated key or key combination that triggers the WinRE menu. This key may differ, so it is recommended to consult the computer manufacturer's documentation or refer to the operating system's official support pages for accurate information.
Once inside the Windows Recovery Environment, users should navigate through the available options until the Advanced Startup section is located. Within this section, a range of troubleshooting choices will become accessible.
Locate and select the "Startup Settings" option. This progressive step will lead to an additional screen where various startup configurations can be modified to accommodate Safe Mode activation.
Lastly, upon selecting the "Restart" button, the computer will reload and present a list of startup options. To access Safe Mode, users can choose the predetermined key corresponding to that particular mode. Following this selection, the operating system will reboot and initiate the desired Safe Mode state.
The ability to access Safe Mode through the Windows Recovery Environment empowers users with an alternative pathway to navigate the operating system while troubleshooting issues and resolving conflicts. By following these steps, users can confidently execute the process and effectively utilize the Safe Mode feature.
Activating Safe Mode through Command Prompt
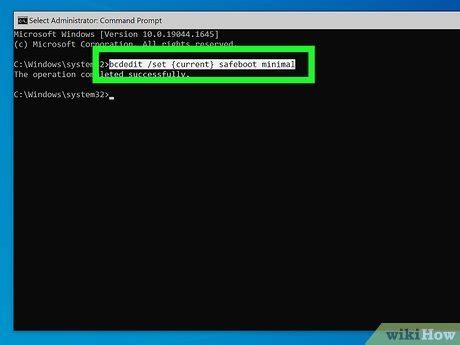
In this section, we will explore an alternative method to access Safe Mode on your computer using the Command Prompt. The Command Prompt is a powerful tool that allows you to execute various commands and functions on your system.
- Open the "Start" menu by pressing the Windows key on your keyboard or clicking the Windows icon in the taskbar.
- Type "Command Prompt" in the search bar or navigate to the "Windows System" folder in the "All Apps" section.
- Right-click on the "Command Prompt" app and select "Run as administrator" to open the Command Prompt with administrative privileges.
- A new window will appear displaying the Command Prompt interface.
- Type the following command and press Enter:
bcdedit /set {current} safeboot minimal - Wait for the "The operation completed successfully" message to confirm that the command has been executed successfully.
- Restart your computer. It will automatically start in Safe Mode.
Please note that when your computer starts in Safe Mode, only essential system services and drivers will be loaded, allowing you to troubleshoot and resolve any issues you may be experiencing.
To disable Safe Mode and return your system to its normal state, follow the same steps as above but use the following command in the Command Prompt: bcdedit /deletevalue {current} safeboot. Restart your computer to exit Safe Mode.
The Command Prompt method provides an efficient way to activate Safe Mode on your Windows system when other methods may not be available or suitable.
Booting into Safe Mode using a Windows Installation Disc or USB
In this section, we will explore an alternative method to access Safe Mode on a Windows operating system, which involves using a Windows Installation Disc or USB drive. This approach allows users to start their computer in a limited configuration, which can be helpful in troubleshooting various issues or performing advanced tasks.
To begin, you will need a Windows Installation Disc or a bootable USB drive with the Windows operating system. The installation disc or USB can be created using the Windows Media Creation Tool or obtained from a trusted source.
Once you have the installation media ready, insert it into the corresponding drive or USB port, and restart your computer. Make sure to set your computer to boot from the CD/DVD drive or USB drive in the BIOS settings.
When the computer starts up, it will prompt you to press any key to boot from the installation media. Press the appropriate key to continue, and the Windows Setup screen will appear.
On the Windows Setup screen, select your language preferences and click on the "Next" button. Then, click on the "Repair your computer" option located at the bottom left corner of the screen.
In the next window, select "Troubleshoot" to proceed with advanced recovery options. Then, choose "Advanced options" and click on the "Startup Settings" option.
A new window will open with several startup settings. Press the "Restart" button to restart the computer and access advanced startup options.
When the computer restarts, a list of startup settings will be displayed. To boot into Safe Mode, press the corresponding number key associated with the "Enable Safe Mode" option. This number may vary depending on your system.
Your computer will then start in Safe Mode, with a limited set of drivers and services running. From here, you can troubleshoot issues or perform tasks that require a minimal system configuration.
Once you have completed your tasks in Safe Mode, you can restart your computer normally to exit Safe Mode and return to the standard operating mode.
| Summary: |
|---|
| The process of booting into Safe Mode using a Windows Installation Disc or USB involves inserting the installation media, configuring the boot order in BIOS settings, accessing advanced recovery options, and selecting the "Enable Safe Mode" option from the startup settings menu. Safe Mode allows users to troubleshoot issues or perform tasks with a limited system configuration. |
Accessing Safe Mode with Networking to Connect to the Internet

When encountering issues with your computer's operating system, it can be helpful to enter Safe Mode with Networking to troubleshoot and access the internet. This mode, known for its secure and limited functionality, allows users to connect to the internet and perform necessary tasks without the risk of certain software or drivers interfering with their system.
To enable Safe Mode with Networking, follow the steps outlined below:
1. Restart or power on your computer.
2. As your computer boots up, repeatedly press the designated key or combination, such as F8 or Shift+F8, that will bring up the Advanced Boot Options menu.
3. In the Advanced Boot Options, use the arrow keys to navigate to the "Safe Mode with Networking" option and press Enter to select it.
4. Your computer will now start in Safe Mode with Networking, providing you with access to the internet.
It is important to note that enabling Safe Mode with Networking is primarily meant for diagnostic and troubleshooting purposes. While connected to the internet in this mode, it is advisable to only visit trusted websites and avoid downloading or installing any unnecessary software or files.
Once you have resolved or identified the issue, you can exit Safe Mode with Networking by restarting your computer and allowing it to boot up normally.
Exiting Safe Mode and Returning to Normal Windows Startup
After successfully resolving any issues or troubleshooting in Safe Mode, it is time to exit this mode and return to the normal startup of your Windows operating system. By following a few simple steps, you can seamlessly transition back to the regular functioning of your system.
Firstly, it is crucial to ensure that all your work is saved and any open applications or files are closed. This will prevent any data loss or potential conflicts during the transition. Once you have completed this step, you can proceed with exiting Safe Mode.
To exit Safe Mode, you need to restart your computer. You can do this by clicking on the "Start" menu and selecting the "Restart" option. Alternatively, you can use the keyboard shortcut by pressing the "Ctrl + Alt + Delete" keys simultaneously and then choosing the "Restart" option from the menu that appears.
As your computer restarts, pay close attention to the screen. Usually, a black screen with white text will appear, displaying information about your system's startup. At this point, press the key associated with accessing the BIOS or the boot menu. This key may vary depending on your computer's manufacturer, but commonly used keys are F2, F8, or Esc.
Once you have entered the BIOS or boot menu, navigate to the "Boot" tab or section. From there, you will find options related to the startup sequence of your computer. Locate the option that mentions Safe Mode or a similar description and disable it. This will ensure that your system boots up in the normal mode.
After making the necessary changes, save the settings and exit the BIOS or boot menu. Your computer will then proceed to restart, but this time it will start in the normal mode rather than Safe Mode. You will be able to access all the features, applications, and settings you usually have without any restrictions or limitations.
It is important to note that if you encounter any additional issues or recurring problems after exiting Safe Mode, it may be necessary to seek further assistance or perform more advanced troubleshooting steps. However, in most cases, simply returning to the normal Windows startup should resolve any temporary issues or conflicts you were experiencing in Safe Mode.
In conclusion, exiting Safe Mode and returning to normal Windows startup is a straightforward process that requires a computer restart and some adjustments in the BIOS or boot menu. By following the steps outlined above, you can resume regular operation of your system and continue using your computer as usual.
[MOVIES] [/MOVIES] [/MOVIES_ENABLED]FAQ
Why would I need to start Windows in Safe Mode?
There are several reasons why you might need to start Windows in Safe Mode. It is a troubleshooting mode that allows you to diagnose and fix problems with your operating system. It is often used when your computer is experiencing issues such as crashes, freezes, or malware infections. Safe Mode loads only the essential drivers and services, which can help you identify and resolve the underlying problem.
Does Safe Mode have any limitations?
Yes, Safe Mode has some limitations. In Safe Mode, only a limited set of drivers and services are loaded, so not all features and functionality of your operating system will be available. For example, networking capabilities might be limited, and certain programs or hardware devices could be disabled. However, these limitations are necessary to isolate and troubleshoot issues with your system.
How can I exit Safe Mode?
To exit Safe Mode and restart your computer in normal mode, you can simply restart your computer. Once your computer starts up, it will boot into the regular operating mode. You can also manually disable the Safe Mode boot option by following the same steps as starting Windows in Safe Mode, unchecking the "Safe boot" box, and clicking OK.




