In today's digital landscape, ensuring a seamless and swift browsing experience is paramount. When it comes to optimizing the way your device interacts with Domain Name Systems (DNS), there are several key strategies you can employ. By understanding the intricacies of how your device communicates with DNS servers, you can enhance its performance and reliability, ultimately resulting in faster and more efficient web browsing.
Efficiently configuring your device's DNS settings involves fine-tuning the fundamental infrastructure that facilitates the conversion of human-readable domain names into their corresponding IP addresses. By doing so, you can eliminate potential bottlenecks and ensure a smoother, more streamlined online experience.
Delving into the realm of DNS settings may seem daunting at first, but fear not! With a little guidance and a basic understanding of the concepts involved, you'll be well on your way to optimizing your device's DNS configuration. In this article, we'll explore various techniques and best practices that will empower you to take control of your browsing experience and make the most of your device's capabilities.
Step-by-Step Guide: Setting Up DNS Configuration in the Windows Operating System
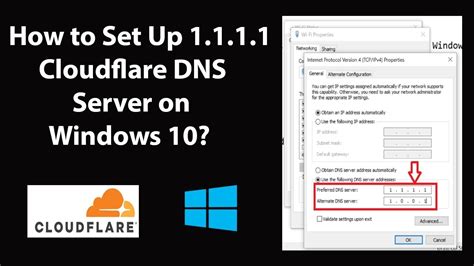
In this section, we will walk you through the process of configuring DNS settings in Windows. By adjusting the DNS configuration, you can enhance the efficiency and accuracy of network communication on your Windows device. Follow these steps carefully to ensure a smooth setup and optimize your browsing experience.
Understanding the Importance of DNS
In the digital world, reliable and efficient communication is crucial for the smooth functioning of various systems and devices. At the core of this communication lies the Domain Name System (DNS), an essential component of the internet infrastructure. Understanding DNS and its importance is key to comprehending how data is transmitted and accessed across the internet.
DNS serves as a decentralized system that converts human-readable domain names, like "www.example.com," into machine-readable IP addresses, such as "192.0.2.1." It acts as a translator, bridging the gap between the easily recognizable domain names and the numerical IP addresses that computers and servers use to identify each other.
Without DNS, accessing websites or sending emails would become a daunting task, requiring users to remember long strings of numbers. The DNS system simplifies this process, allowing users to navigate the internet effortlessly by simply typing in familiar domain names. It plays a vital role in enabling effective communication and data transfer across the internet.
In addition to its role in transforming domain names into IP addresses, DNS also plays a significant role in website performance and security. By utilizing a network of servers, DNS helps distribute website traffic, ensuring that requests are efficiently directed to the nearest and most available server. This load balancing capability improves website performance and user experience.
Moreover, DNS also plays a crucial role in cybersecurity. By implementing security measures such as DNSSEC (DNS Security Extensions), DNS helps protect users from malicious activities, such as phishing attacks and DNS hijacking. Through various mechanisms, DNS safeguards the integrity and authenticity of the data being transmitted, enhancing overall internet security.
- Key points:
- DNS acts as a translator between domain names and IP addresses.
- It simplifies internet navigation and facilitates effective communication.
- DNS improves website performance through load balancing.
- DNS enhances internet security through measures like DNSSEC.
Exploring Network Configuration in Windows
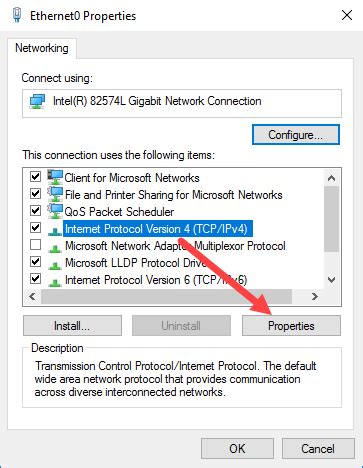
When it comes to managing your network settings in the Windows operating system, there are various options and functionalities to consider. In this section, we will delve into the different ways you can access and modify your network configuration, enabling you to tailor your network settings to suit your specific needs.
One way to access your network settings is through the Control Panel. From here, you can navigate to the "Network and Internet" section, where you will find an array of tools and options that allow you to configure various aspects of your network connectivity. By exploring the options available, you can make changes to your IP settings, network adapters, and proxy settings to optimize your network performance.
Another method to access your network settings is through the Command Prompt. Using specific commands, you can retrieve information about your network interfaces, release and renew IP addresses, and even flush DNS caches. By leveraging the power of the Command Prompt, you can gain more control over your network settings and troubleshoot any connectivity issues that may arise.
If you prefer a graphical user interface, you can also access network settings through the Settings app in Windows. This modern interface provides a simplified approach to configuring your network connections, allowing you to manage Wi-Fi, Ethernet, and VPN settings effortlessly. With just a few clicks, you can connect to new networks, prioritize connections, and troubleshoot network problems.
Furthermore, Windows provides the Network and Sharing Center, which offers an overview of your network connections and their current status. From here, you can access advanced sharing options, set up a homegroup or workgroup, and troubleshoot network issues using various built-in diagnostic tools. This centralized hub gives you a comprehensive view of your network setup, empowering you to make necessary adjustments as needed.
- Access network settings through the Control Panel
- Utilize the Command Prompt for advanced configuration
- Modify network settings using the Settings app
- Manage network connections through the Network and Sharing Center
By familiarizing yourself with these different methods, you will be able to navigate and customize your network settings in Windows efficiently, ensuring a seamless and optimized network experience.
Alter Network Connection's DNS Server Addresses on Your System
Modernize your network experience by modifying the DNS server addresses on your Windows computer. By adjusting these settings, you can enhance your browsing speed, improve security, and gain greater control over your internet connection's behavior.
To change the DNS server addresses on your Windows system, follow these steps:
- Access the network settings menu by clicking on the network icon in the taskbar.
- Select the "Network and Internet Settings" option.
- Choose your network connection type (wired or wireless) and click on it.
- Scroll down and click on "Change adapter options."
- Find your active network connection, right-click on it, and select "Properties."
- In the "Properties" window, scroll down and select "Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4)."
- Click on the "Properties" button beneath the list of protocols.
- In the new window, choose the option to "Use the following DNS server addresses."
- Enter the preferred and alternate DNS server addresses provided by your DNS service provider.
- Click "OK" to save the changes and close the windows.
- Restart your computer to apply the new DNS server settings.
Once you have completed these steps, your Windows system will utilize the specified DNS server addresses for all network connections. This customization allows you to tailor your internet experience to meet your specific needs and preferences.
Troubleshooting DNS Connectivity Issues

In today's interconnected world, having a reliable Domain Name System (DNS) configuration is crucial for seamless network communication. However, despite careful setup and configuration, connectivity issues with DNS may arise, preventing users from accessing websites and services. This section aims to provide troubleshooting techniques and solutions to common DNS connectivity problems, helping you resolve issues and get your network up and running smoothly.
When encountering DNS connectivity issues, it is important to first identify and understand the symptoms. Is it a complete loss of connectivity or intermittent failures? Are all devices experiencing the problem, or is it specific to certain machines or networks? This initial analysis can help narrow down the possible causes and point towards the most appropriate troubleshooting steps.
- Ensure that the DNS server addresses are correctly configured in your network settings. Double-check the settings on the router, computer, or any other devices involved in the network.
- Perform a DNS flush to clear the local DNS cache, which may be storing incorrect or outdated information. This can be done by running the appropriate command in the Command Prompt or Terminal window.
- Check for any firewall rules or security software that might be blocking DNS traffic. Temporarily disabling these measures can help identify if they are the cause of the issue.
- Try using an alternative DNS server, such as those provided by public DNS providers like Google DNS or OpenDNS. This can help determine if the problem lies with the current DNS server being used.
- Investigate any recent changes or updates to the network infrastructure, as they may have inadvertently affected DNS connectivity. Roll back any changes if deemed necessary.
- If none of the above steps resolve the issue, consider reaching out to your Internet Service Provider (ISP) or network administrator for further assistance. They may be able to identify and resolve the problem at a higher level of the network.
By following these troubleshooting steps and employing a systematic approach, you can effectively diagnose and resolve DNS connectivity issues. Remember that patience and persistence are key, as sometimes the solution may require a combination of techniques to pinpoint and rectify the underlying problem.
Enhancing Security and Privacy through DNS Configuration
In our digital age where privacy is a growing concern, configuring DNS settings can play a crucial role in improving both the security and privacy of your browsing experience. By making thoughtful changes to your DNS configuration, you can enhance protection against online threats, prevent unauthorized access to your browsing activities, and minimize the collection and tracking of your personal information.
| Benefits of DNS Configuration | Methods for Enhanced Security | Strategies for Improved Privacy |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Shielding against malicious websites | 1. Implementing DNS filtering | 1. Utilizing encrypted DNS protocols |
| 2. Preventing DNS spoofing attacks | 2. Enforcing DNSSEC validation | 2. Employing DNS-over-HTTPS (DoH) |
| 3. Blocking access to unwanted content | 3. Setting up a DNS firewall | 3. Employing DNS over TLS (DoT) |
| 4. Detecting and blocking malware | 4. Configuring DNS sinkholing | 4. Using VPN with DNS leak protection |
By exploring and implementing these various methods and strategies, you can significantly enhance the security and privacy of your DNS settings. Remember, a well-configured DNS can provide an additional layer of defense against cyber threats while safeguarding your personal data and online activities.
Improving Internet Speed with Optimal DNS Configuration
In today's digital age, having a fast and reliable internet connection is essential for efficient and productive use of your Windows operating system. One often overlooked factor that can greatly impact internet speed is the configuration of DNS settings. By optimizing your DNS settings, you can experience faster web browsing, reduced latency, and improved overall internet performance.
Understanding the Significance of DNS
DNS, or Domain Name System, is like the phonebook of the internet. It translates domain names, such as www.example.com, into numerical IP addresses that computers understand. When you enter a URL into your web browser, your computer sends a DNS query to a DNS server to determine the IP address associated with that domain name.
Choosing the Right DNS Server
By default, your Windows operating system uses the DNS servers provided by your internet service provider (ISP). However, these servers may not always be the fastest or most reliable options available. To optimize your DNS settings for faster internet speed, you can consider switching to alternative DNS servers, such as Google Public DNS or OpenDNS.
Configuring DNS Settings in Windows
To configure DNS settings in Windows, you can start by accessing the Network Connections settings. From there, navigate to the properties of your network connection and select Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4). Here, you can manually enter the preferred and alternate DNS server addresses. Remember to note down the original settings before making any changes, in case you need to revert back.
Regularly Testing and Monitoring Performance
Once you have configured your DNS settings, it's important to regularly test and monitor the performance of your internet connection. You can use online tools or specialized software to measure the speed and latency of your connection. If you notice any issues or inconsistencies, you may need to reassess and adjust your DNS settings accordingly.
By optimizing your DNS settings, you can unleash the true speed potential of your internet connection. With a faster and more reliable internet speed, you can enhance your browsing experience, improve productivity, and seamlessly connect with the digital world.
Using Alternative DNS Servers in Windows
Discover how to enhance your network connectivity by utilizing custom DNS servers on your Windows operating system.
In this section, we will delve into the concept of utilizing alternative DNS servers to optimize your network performance and security. By choosing alternative DNS servers, you can improve the speed and reliability of your internet connection, as well as gain additional control over your DNS settings.
Why Consider Alternative DNS Servers?
While the default DNS servers provided by your internet service provider (ISP) can suffice for most users, opting for custom DNS servers can offer significant advantages. Custom DNS servers enable you to bypass any potential limitations or issues imposed by your ISP, leading to faster and more secure browsing.
Enhanced Privacy and Security: By using custom DNS servers, you can protect your browsing activities from potential surveillance and prevent any data filtering or logging by your ISP.
Improved Performance: Alternative DNS servers allow you to bypass any network congestion, resulting in faster domain name resolution and quicker loading times for websites and online services.
Content Filtering and Access Control: Some alternative DNS servers provide options for content filtering and access control, allowing you to block unwanted content or restrict access to specific websites or categories.
Setting up Alternative DNS Servers in Windows:
To configure custom DNS servers in Windows, follow these steps:
Step 1: Open the Network and Sharing Center through the Control Panel or by right-clicking the network icon in the system tray.
Step 2: Select your network connection, then click on the "Properties" button.
Step 3: In the Properties window, scroll down and select "Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4)", then click on "Properties".
Step 4: Choose the option "Use the following DNS server addresses" and enter the IP addresses of the alternative DNS servers you want to use.
Step 5: Click "OK" to save the changes and close all windows. Your Windows system will now use the custom DNS servers for all network connections.
By following these simple steps, you can easily configure alternative DNS servers in Windows and experience the benefits they provide. Take control of your network connectivity and enjoy improved speed, security, and functionality.
Refreshing DNS Cache in Microsoft Operating Systems

In order to ensure optimal connectivity and efficient web browsing, it is important to periodically update the DNS cache on your Microsoft operating system. This process involves clearing the stored DNS information and obtaining fresh and accurate records. By refreshing the DNS cache, you can resolve common network issues, improve network performance, and ensure that your computer accesses the most up-to-date DNS information.
Clearing the DNS Cache:
To begin the process of updating the DNS cache, you will need to clear the existing cache. This can be done by utilizing the Command Prompt utility. Open the Command Prompt as an administrator by right-clicking on the Start menu and selecting "Command Prompt (Admin)".
Flushing the DNS Cache:
Once the Command Prompt is open, you can proceed to flush the DNS cache. Execute the following command: ipconfig /flushdns. This command will remove all the stored DNS entries and force your computer to resolve the DNS records from scratch.
Verifying DNS Cache Status:
After flushing the DNS cache, it is important to verify the status of the cache to ensure it has been properly updated. You can do this by entering the command ipconfig /displaydns in the Command Prompt. This command will display the current contents of the DNS cache on your Windows system.
Repopulating the DNS Cache:
Finally, you can repopulate the DNS cache by visiting various websites or performing DNS resolve requests. This will allow your computer to obtain fresh DNS records and populate the cache with up-to-date information.
Conclusion:
By regularly updating and refreshing the DNS cache on your Microsoft operating system, you can ensure optimal network connectivity and improved browsing speeds. Clearing the cache, flushing it, verifying its status, and repopulating it are essential steps to maintain an efficient DNS resolver on your Windows system.
How to Configure DNS Server Correctly on Windows Server 2022
How to Configure DNS Server Correctly on Windows Server 2022 by NetITGeeks 27,586 views 1 year ago 10 minutes, 25 seconds
FAQ
I'm having trouble accessing certain websites on my Windows computer. Could this be related to DNS settings?
Yes, incorrect DNS settings can cause issues with accessing certain websites. DNS (Domain Name System) is responsible for translating website addresses (URLs) into IP addresses that computers can understand. If your DNS settings are incorrect or outdated, your computer may not be able to properly resolve the IP addresses associated with certain websites, resulting in access issues.




