Imagine immersing yourself in the captivating world of gaming, only to be hindered by the limited audio capacities of your average earbuds. Frustrating, isn't it? Well, fear not! Here lies a revolutionary solution that will elevate your sound experience in your Nintendo DS, and all it requires is a few simple modifications to your trusty earphones.
Embarking on this endeavor entails transforming your ordinary earbuds into a powerful sound amplification device. This ingenious method allows you to extract the full potential of your gaming console's audio output, taking you on an auditory journey like never before.
The concept revolves around repurposing your earbuds as a microphone, extracting their hidden potential and utilizing it as a sound capture device for your Nintendo DS. By employing this unconventional approach, the limitations imposed by traditional audio equipment are cast aside in favor of an avant-garde audio experience.
Caution: Before diving into this innovative project, it is crucial to exercise patience and precision. Remember, altering the functionalities of your earbuds requires delicate handling and a steady hand, but fret not as the true reward awaits you at the end of your DIY journey.
Disclaimer: This article assumes basic knowledge of electrical wiring and soldering techniques. If you are unfamiliar with these skills, we recommend seeking guidance from a qualified technician.
Understanding the Components
In this section, we will delve into the various components involved in creating a functional microphone using headphones in the field of Digital Signal Processing (DS). By examining the different elements that make up the microphone, we will gain a deeper understanding of how they interact and contribute to the overall functionality of the device.
- Transducer: This crucial component is responsible for converting sound waves into electrical signals. Common types of transducers used in microphones include condenser, dynamic, and ribbon.
- Diaphragm: The diaphragm acts as the vibrating element of the microphone, capturing sound waves and transmitting them to the transducer. It plays a vital role in determining the microphone's frequency response and sensitivity.
- Capsule: The capsule refers to the assembly that contains both the diaphragm and the transducer. It is responsible for converting sound waves into electrical signals and plays a significant role in determining the overall sound quality.
- Impedance Converter: This component transforms the high impedance of the microphone's output into a low impedance suitable for further signal processing or amplification.
- Circuitry: The circuitry of the microphone includes elements such as preamplifiers, filters, and amplifiers. These components work together to enhance the electrical signal received from the transducer and ensure the accurate reproduction of sound.
- Connector: The connector is the interface that allows the microphone to connect to external devices such as audio interfaces, mixers, or amplifiers.
- Enclosure: The enclosure houses all the internal components of the microphone and also acts as a protective barrier, shielding the sensitive elements from external interference or damage.
By comprehending the roles and functions of these different components, we can start to grasp the complexities behind constructing a microphone from headphones in the realm of Digital Signal Processing (DS).
Step-by-Step Guide to Disassembling the Headphones
In this section, we will outline the sequential process of dismantling the headphone device, allowing you to access its individual components for further modification or repurposing. By carefully following these steps, you will be able to disassemble the headphones without damaging any essential parts. Let's get started!
Step 1: Begin by gently removing the ear cushions or pads from the headphones. These soft coverings can usually be detached by carefully pulling them away from the earpiece.
Step 2: After removing the ear cushions, locate the screws that hold the earpiece together. These screws are often hidden beneath plastic covers or panels. Use a small screwdriver or a similar tool to carefully unscrew them.
Step 3: Once the screws have been loosened, gently separate the earpiece components. Be cautious not to tug forcefully or twist the parts, as this may cause damage to the internal wiring or speaker mechanism.
Step 4: With the earpiece opened, you will now be able to identify the different components inside, such as the speaker driver, wires, and connectors. Take note of their respective positions and orientations for later reassembly.
Step 5: Next, locate the main headband or frame of the headphones. Look for any screws or clips that hold it in place, and carefully remove them using the appropriate tools.
Step 6: After detaching the headband, you can now separate the earpiece from the frame of the headphones. Gently pull or slide the earpiece mechanism away from the headband, taking care not to damage any wires or connectors.
Step 7: At this point, you should have the earpieces and headband disassembled into their individual components. Take a moment to inspect each part for any signs of damage or wear, as this can affect the functionality and performance of the resulting microphone.
Step 8: Congratulations! You have successfully disassembled the headphones, allowing you to proceed with the next steps in creating your homemade microphone device. Keep all the disassembled parts organized and in a safe place, ready for reassembly or further modifications.
Identifying the Element Responsible for Sound Reception
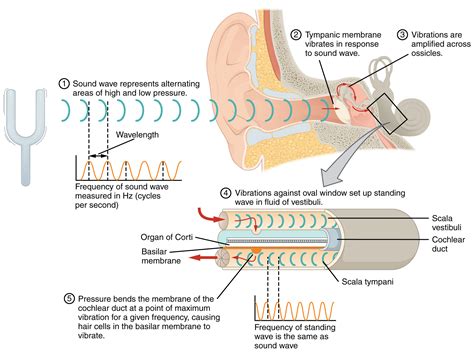
One crucial step in creating a functional microphone using headphones in DS is determining the specific part of the headphones that picks up sound vibrations. Identifying this element is essential as it enables us to modify it to function as a microphone.
When repurposing headphones into a microphone, it is essential to identify the component responsible for sound reception. This component captures sound waves and converts them into electrical signals. By understanding the characteristics and location of this element, we can manipulate it to function as a microphone, allowing us to record audio or communicate effectively.
- Discovering the Sound-Receiving Component: To create a microphone from headphones, the initial step involves identifying the sound-receiving element carefully. This component might vary depending on the headphones' model and design.
- Examining the Transducer: A transducer is a common sound-receiving element found in most headphones. It is typically a small diaphragm that vibrates when exposed to sound waves. Understanding the transducer's location within the headphones is essential for repurposing it as a microphone.
- Exploring Other Possible Elements: Besides the transducer, there might be other components responsible for sound reception in headphones. These can include microphones for noise cancellation or inline controls. It is crucial to differentiate between these elements and the one used for sound capture.
By carefully examining the headphones' internal structure, locating the sound-receiving element, and understanding its functionality, we can successfully identify the specific component that can be repurposed as a microphone. This knowledge is essential for the subsequent modifications required to transform the headphones into a functional microphone in DS.
Connecting the Sound-Capture Component to the DS
In this section, we will discuss how to attach the component responsible for capturing sound, commonly known as the microphone element, to the DS gaming device. This crucial step enables the device to record audio and enhance the user experience.
First and foremost, ensure that all necessary tools and components are available before proceeding with the connection process. Take care to follow the specific instructions provided by the manufacturer of the microphone element to ensure compatibility and optimal performance.
Begin by locating the designated microphone input slot on the DS gaming device. This slot is typically situated on the exterior of the device and may be indicated by a small microphone icon or labeled accordingly. It is essential to connect the microphone element to the correct slot to ensure proper functionality.
Next, gently insert the connector of the microphone element into the microphone input slot. Take care to align the connectors correctly and apply even pressure to avoid any potential damage. A snug fit is necessary to establish a secure and reliable connection.
Once the microphone element is securely connected, give it a slight tug to ensure it is firmly attached and not easily dislodged. This step is crucial to prevent any interruptions or loss of sound during usage.
After the connection is established, power on the DS gaming device and navigate to the audio settings. Adjust the input settings to ensure that the microphone element is recognized by the device and ready to capture sound.
Finally, conduct a brief test to check the functionality of the microphone element. Speak or produce sound near the microphone and verify that the DS gaming device successfully records and captures the audio input. If any issues are encountered, revisit the connection process and double-check the compatibility and alignment of the microphone element.
By diligently following these steps and correctly connecting the microphone element to the DS, users can equip their gaming device with enhanced audio capabilities and unlock new possibilities for communication and interaction.
Testing and Troubleshooting the DIY Sound Capturing Device

In this section, we will cover the process of testing and troubleshooting your self-made sound capturing device, created using alternative techniques and common household items. Here, we will explore various techniques to ensure that your device is functioning properly and address any issues that may arise during the testing phase.
Once you have assembled your makeshift sound capturing device, it is important to assess its functionality through a series of tests. These tests will help determine if the device is capable of accurately capturing sound and if any adjustments or modifications need to be made.
One of the initial tests involves checking the connectivity of the headphone microphone. This can be done by connecting the DIY microphone to a computer or other audio recording device. Speak into the microphone and observe whether the sound is being detected. If you encounter any issues with the sound not registering or recording at a low volume, it may indicate a problem with the wiring or connections.
If there are connectivity problems, you can try adjusting the wires or connections to ensure proper contact. Alternatively, you may need to replace any faulty components or seek assistance from someone with expertise in electronic devices.
| Issue | Possible Solution |
|---|---|
| No sound being recorded | Check wiring and connections for any loose or disconnected parts. Ensure the microphone is properly positioned and aligned. |
| Low volume or distorted sound | Replace the wires or connectors if they are damaged or worn out. Adjust the position of the microphone for optimal sound capture. |
| Interference or background noise | Try using shielded cables to minimize external influences. Move away from potential sources of interference such as electronic devices or power sources. |
| Inconsistent sound quality | Ensure all connections are secure and stable. Consider using additional soundproofing materials to minimize unwanted echoes or reverberations. |
When troubleshooting your DIY microphone, it is essential to approach the process with patience and attention to detail. By following these testing procedures and addressing any issues that arise, you can achieve a functional and reliable sound capturing device that will suit your needs.
Tips for Enhancing Sound Clarity and Quality
In this section, we will explore various techniques to optimize the sonic performance and clarity of your customized microphone, crafted using headphones in an innovative manner. By implementing these tips, you can elevate the audio quality, ensuring an exceptional recording and listening experience.
1. Positioning: Properly positioning your headphone-turned-microphone is crucial for capturing pristine audio. Experiment with different angles and distances to find the sweet spot where the sound is clear and balanced.
2. Noise Reduction: Background noise can greatly affect the quality of your recordings. Consider using noise-cancelling or soundproofing techniques to minimize unwanted interference and focus on capturing only the desired audio.
3. Equalization: Adjusting the frequency response of your microphone can help enhance specific aspects of the sound. Experiment with equalization settings to achieve desired tonal characteristics and balance in your recordings.
4. Room Acoustics: The environment in which you use your homemade microphone can significantly impact the sound quality. Consider optimizing the room acoustics by using absorbing materials, diffusers, or acoustic panels to reduce echoes and reverberation.
5. Amplification and Preamp: Depending on the sensitivity of your microphone, you may need to amplify the signal to achieve optimal recording levels. Investing in a quality preamplifier can provide a clean boost to the microphone's input signal, resulting in improved sound quality.
6. Post-Processing: After recording, consider using audio editing software to further enhance the sound. Techniques like noise reduction, compression, and normalization can help refine the audio and make it more polished.
7. Quality of Connection: Ensure that all cables, connectors, and adapters are of high quality to maintain the integrity of the audio signal. Poor connections can introduce noise and distortion, degrading the audio quality.
8. Monitoring: Use headphones or speakers with accurate frequency response to monitor the audio while recording or listening back. This will allow you to detect any flaws or imperfections in the sound, enabling you to make necessary adjustments for improved clarity.
By implementing these tips, you can optimize the sound quality of your unique microphone creation, crafted creatively from a pair of headphones. Experiment, refine, and enjoy the enhanced audio experience!
FAQ
What is the article about?
The article is about how to make a microphone from headphones using a Nintendo DS.
Why would I want to make a microphone from headphones?
Making a microphone from headphones can be useful if your DS microphone is not working or if you need a microphone for recording audio on your DS.
What materials do I need to make a microphone from headphones?
You will need a pair of headphones with a built-in microphone, a screwdriver, a soldering iron, soldering wire, and electrical tape.




