In this digital age where technology has intertwined itself into every aspect of our lives, it is essential to have a robust and reliable operating system that can meet our everyday needs. However, the world of operating systems is not limited to the mainstream options that often come pre-installed on our devices. One fascinating alternative that tech enthusiasts often delve into is the realm of open-source operating systems.
Open-source - a term that breathes life into a community built on collaboration, innovation, and freedom. Instead of relying on commercially developed software, open-source operating systems allow users to access and modify their source code, providing a unique level of customization and adaptability.
So, you may wonder, how can you embark on this exciting journey and embrace the world of open-source operating systems?
Well, one of the most popular open-source operating systems out there is Linux. Renowned for its stability, security, and versatility, Linux has garnered a devoted user base over the years. If you are eager to dive into this world and explore all that Linux has to offer, fear not! This guide will walk you through the steps to get Linux up and running on your device.
Why Choose Linux Operating System?

The Linux operating system offers a unique and compelling alternative to other popular operating systems. With its open-source nature and robust community, Linux provides users with a highly customizable and secure platform for their computing needs. Unlike traditional operating systems, Linux offers a wide range of options, allowing users to tailor their experience to suit their preferences.
One of the key advantages of Linux is its open-source nature. This means that the source code is freely available to the public, allowing a global community of developers to contribute to its development. This collaborative approach ensures that Linux remains constantly updated and improved, with a strong focus on security and stability.
Linux also offers a wide variety of distributions, each with its own unique features and design philosophy. Whether you're a tech-savvy user looking for maximum customization or a novice seeking a user-friendly interface, Linux has a distribution to suit your needs. Additionally, Linux supports a vast array of software applications, making it a versatile choice for any task.
Another compelling reason to choose Linux is its superior security. With Linux, you have more control over the privacy and security settings of your system. The open-source nature of Linux allows for faster identification and patching of vulnerabilities, minimizing the risk of malware and other security threats. Additionally, Linux provides strong built-in security features, such as user permissions and encryption, ensuring that your data remains safe and protected.
In conclusion, Linux offers numerous advantages that make it an excellent choice for any computer user. Its open-source nature, customizable options, variety of distributions, and strong security features set it apart from other operating systems. Whether you're a casual user or a seasoned professional, Linux provides a stable, secure, and versatile platform for all your computing needs.
Getting Your System Ready for Linux Installation
In order to successfully set up Linux on your device, it is important to ensure that your system meets the necessary requirements and that you have adequately prepared your computer for the installation process. This section will guide you through the essential steps to prepare your system and make it ready for Linux installation.
| Step 1 | Backing up your data |
| Step 2 | Verifying hardware compatibility |
| Step 3 | Checking system requirements |
| Step 4 | Creating a bootable USB or DVD |
| Step 5 | Partitioning your hard drive |
Before proceeding with the Linux installation, it is crucial to back up any important data and files on your computer to prevent potential data loss. Verify that you have made a secure backup of all your important documents, photos, and other files to an external storage device.
Next, ensure that your hardware is compatible with the Linux distribution you plan to install. Research and consult the official documentation of the Linux distribution to confirm if your computer meets the minimum hardware requirements.
Check the system requirements of the Linux distribution you have chosen. These requirements may include the processor type, RAM capacity, disk space, and any specific hardware, such as graphics cards, that need to be present in your system. Make sure your computer meets these requirements to ensure a smooth installation and optimal performance.
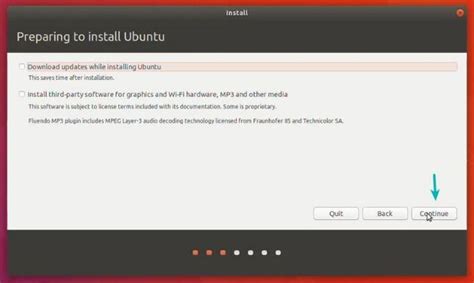
Creating a bootable USB or DVD is an essential step in preparing your computer for Linux installation. This will allow you to boot the Linux distribution from the USB or DVD and begin the installation process. Refer to the documentation or official website of your chosen Linux distribution for detailed instructions on how to create a bootable USB or DVD.
Lastly, consider partitioning your hard drive to allocate space for Linux. This involves dividing your hard drive into separate sections, or partitions, to install Linux alongside your existing operating system. Research the recommended partitioning scheme for your chosen Linux distribution and follow the instructions to set up the partitions.
A Comprehensive Guide to Setting Up Linux on Your Personal Device

In this step-by-step guide, we will walk you through the process of establishing Linux as the operating system on your personal machine. You will learn how to seamlessly integrate the versatile Linux environment, customizing it according to your needs and preferences. By following these instructions, you will be equipped with the necessary knowledge to embark on your Linux journey confidently.
Selecting the Ideal Linux Distribution
Before undergoing the installation process, it is crucial to identify the most suitable Linux distribution for your requirements. With a plethora of choices available, we'll discuss different options, highlighting their unique features and functionalities. By understanding the diverse range of Linux distributions, you can make an informed decision that aligns with your computing objectives.
Preparing Your Device for Linux
Prior to installing Linux, it is necessary to prepare your device adequately. We will guide you through essential steps to ensure a smooth installation process. These steps include backing up your existing files and creating a bootable USB drive or DVD, providing you with options to seamlessly transition to Linux without a hitch.
Installing Linux: Step-by-Step Instructions
Once your device is ready, we will provide you with a detailed walkthrough of the Linux installation process. We will delve into the intricacies of partitioning, formatting, and configuring your system, ensuring a successful Linux installation. Follow the clear instructions to effortlessly transition to the Linux ecosystem.
Post-Installation Optimization and Customization
After installing Linux, we will explore various optimization techniques to enhance your user experience. From software updates to driver installations, we will guide you through essential post-installation steps. Moreover, we will delve into the customization options available, empowering you to personalize your Linux environment according to your preferences.
Getting Started with Linux: Essential Tips and Tricks
In this final section, we will provide you with invaluable tips and tricks to navigate the Linux ecosystem effectively. Discover lesser-known features, command-line shortcuts, and package management techniques that will empower you to maximize your productivity and enjoyment while using Linux.
By carefully following this comprehensive step-by-step guide, you will successfully install and configure Linux on your personal device, opening doors to a world of limitless possibilities and unparalleled customization.
Common Troubleshooting Tips for Setting Up Linux
When attempting to configure a new operating system on your PC, it is not uncommon to encounter various challenges along the way. This section aims to provide you with a comprehensive guide on troubleshooting common issues that may arise during the setup process of a Linux distribution, ensuring a smooth installation experience.
One common roadblock faced by users is the inability to establish a network connection after the Linux installation. This can be rectified by checking and configuring the network settings, such as verifying the network cable connection, resetting the router, or accessing the network settings panel to adjust the IP address and DNS server parameters.
Another frequent obstacle is the failure to detect and activate the device drivers required for proper hardware functionality. To resolve this, it is recommended to visit the manufacturer's website and download the appropriate drivers for your specific hardware. Additionally, using the command line tools provided by Linux distributions can help identify missing or incompatible drivers and enable their installation or configuration.
In some cases, a user may encounter compatibility issues between Linux and certain software applications. A potential solution for this is to research and utilize alternative programs that are compatible with the Linux operating system. Online forums and communities dedicated to Linux can often provide valuable recommendations for alternative software options.
If the Linux installation fails to boot successfully, checking the boot order in the system BIOS or UEFI settings may prove helpful. Ensuring that the Linux bootloader is listed as the top priority boot option can prevent any conflicts and allow the system to seamlessly load the Linux operating system.
Lastly, when experiencing frequent system crashes or freezes post-installation, analyzing system logs and updating the Linux kernel can often resolve underlying stability issues. By keeping your Linux distribution up to date and monitoring system logs using tools like "dmesg" and "journalctl," you can identify potential causes of crashes and apply the necessary fixes or workarounds.
In conclusion, even though setting up Linux on your computer may bring forth obstacles, these troubleshooting tips can assist in overcoming common issues and ensuring a successful installation process. By following these guidelines, you will be better equipped to enjoy the benefits of the Linux operating system without unnecessary setbacks.
FAQ
What are the benefits of installing Linux on your computer?
There are several benefits of installing Linux on your computer. Firstly, Linux is a free and open-source operating system, so you don't have to pay for it. Secondly, Linux is known for its stability and security, making it less prone to viruses and malware. Additionally, Linux offers a wide range of software and applications, as well as customization options, allowing you to tailor your operating system to your specific needs.
Can I install Linux alongside Windows on my computer?
Yes, it is possible to install Linux alongside Windows on your computer. This is known as dual-booting, where you can choose between Windows and Linux each time you start your computer. To do this, you need to create a separate partition on your hard drive to install Linux. During the installation process, you will be prompted to select the desired partition and choose the operating system you want to boot into.
What are the system requirements for installing Linux?
The system requirements for installing Linux may vary depending on the distribution you choose. However, in general, most Linux distributions have lower system requirements compared to Windows. They typically require a minimum of 1GB RAM, 10-20GB of free disk space, and a processor with at least 1GHz clock speed. It is always advisable to check the specific system requirements of the Linux distribution you plan to install.
Can I try Linux without installing it on my computer?
Yes, you can try Linux without actually installing it on your computer. Many Linux distributions offer a "Live CD" or "Live USB" option, which allows you to run Linux directly from a CD or USB drive without making any changes to your existing operating system. This way, you can experience Linux and test its compatibility with your hardware before deciding whether to install it permanently.
Is it possible to switch back to Windows after installing Linux?
Yes, it is possible to switch back to Windows after installing Linux. If you choose to dual-boot Windows and Linux, you can simply select Windows as the default operating system during startup. Additionally, you can uninstall Linux and reclaim the partition it occupied if you no longer wish to use it. However, it's always recommended to backup important files and data before making any changes to your operating system.
What are the benefits of installing Linux on my computer?
There are several benefits of installing Linux on your computer. Firstly, Linux is an open-source operating system, which means it is free to use and modify. It also offers a high level of customization and flexibility, allowing you to tailor your computing experience to your needs. Linux is also known for its stability and security, making it less prone to viruses and malware. Additionally, Linux has a vast online community that provides support and constantly develops new features and updates.