Embark on a journey to unlock the endless possibilities offered by the renowned and versatile open-source operating system. In this comprehensive article, we will walk you through the meticulous process of installation and configuration, enabling you to harness the power of this dynamic platform on your personal computer.
With this step-by-step tutorial, you will gain invaluable insights into the seamless installation procedure that has attracted tech enthusiasts worldwide. Explore the fascinating realm of Linux, where innovation flourishes and customization knows no boundaries.
Unveil the path to transforming your desktop or laptop into a cutting-edge Linux-enabled device. In this carefully crafted guide, we will delve into the intricacies of the setup, equipping you with the knowledge required to make an informed decision.
Understanding Linux: An Introduction to the Powerful Operating System
Linux, renowned for its stability, flexibility, and security, has emerged as a popular operating system choice for desktops and laptops. In this section, we delve deep into the essence of Linux, exploring what it truly represents and the reasons why it has gained widespread adoption among both tech enthusiasts and corporate users.
An Open-Source Marvel
Linux, a free and open-source operating system, stands apart from its proprietary counterparts due to its collaborative development approach. The open-source nature of Linux encourages a global community of developers to contribute their expertise, leading to constant evolution and innovation. This collaborative spirit has nurtured a vibrant ecosystem of software applications, ensuring a vast array of options for users seeking customized solutions.
Linux extends an invitation to users to actively participate in its development, encouraging personalization and adaptation to specific needs and preferences.
Flexibility Unleashed
The adaptability of Linux enables it to run on a diverse range of hardware architectures and devices. From smartphones and tablets to embedded systems and servers, Linux can seamlessly power various computing platforms. This inherent flexibility makes Linux an ideal choice for optimizing resource usage and achieving peak performance.
Linux stands as a testament to the scalability and versatility it offers, paving the way for streamlined efficiency regardless of the hardware environment it inhabits.
A Champion of Security
With security threats constantly evolving, Linux has established itself as a stalwart defender against malicious activities. The robust security features inherent in Linux, such as mandatory access controls and regular security updates, provide users with a reliable shield against potential vulnerabilities. This dedication to security has made Linux a go-to option for privacy-conscious individuals and organizations.
Linux's stalwart security measures instill confidence by protecting sensitive data and ensuring a safe computing experience in an increasingly interconnected world.
In conclusion, Linux's open-source nature, adaptability, and focus on security have solidified its position as a formidable operating system. By utilizing Linux, users gain access to a rich ecosystem of software, unmatched versatility across various hardware platforms, and a fortified defense against security threats. In the next section, we will explore the step-by-step process of installing Linux on your desktop or laptop, enabling you to harness the power and potential of this impressive operating system.
Choosing the Ideal Linux Distribution for Your Requirements
When it comes to exploring the world of Linux, the first step is to select the most suitable distribution that caters to your specific needs and preferences. With a wide range of Linux distributions available, each offering distinct features and capabilities, it is important to make an informed decision.
One of the primary considerations in choosing a Linux distribution is its intended use. Some distributions are designed for general-purpose computing, while others focus on specific areas such as gaming, multimedia production, or server management. Identifying your requirements will help narrow down the choices and select the distribution that aligns best with your intended use.
Another aspect to consider is the level of technical expertise you possess. While some distributions are user-friendly and designed for beginners, others may require a deeper understanding of Linux systems. It is important to assess your comfort level with Linux and choose a distribution accordingly to ensure a seamless experience.
Package management is another key factor to consider. Different distributions use various package managers, which handle the installation, update, and removal of software packages. Researching and understanding the package management system of a distribution will enable you to gauge its compatibility with your requirements and ease of use.
It is also worth exploring the community support and documentation available for a particular distribution. A strong community and comprehensive documentation can prove invaluable, especially for beginners and those seeking assistance with troubleshooting or learning new features. Checking forums, user guides, and online resources will provide insights into the quality of support offered by the distributions you are considering.
Furthermore, consider the release model of the distribution, whether it follows a fixed release cycle or a rolling release. Fixed release distributions offer regular updates on a predetermined schedule, ensuring stability and reliability. On the other hand, rolling release distributions provide continuous updates, keeping your system up-to-date with the latest software versions.
- Identify your requirements and intended use
- Assess your technical expertise level
- Research the package management system
- Explore community support and documentation
- Consider the release model of the distribution
By carefully considering these factors and exploring the world of Linux distributions, you can choose the one that perfectly matches your needs and embark on a rewarding Linux journey.
Preparing Your Computer for Linux Installation
Before embarking on the journey of installing a new operating system on your computer, it is imperative to properly prepare your system to ensure a smooth installation process. This section will guide you through the initial steps you need to take to ensure your computer is ready for the Linux installation.
Firstly, it is crucial to create a backup of all your important data. This includes documents, photos, videos, and any other files that are valuable to you. By taking this precautionary measure, you can safeguard your data in case anything goes wrong during the installation process.
Next, you should check the system requirements of the specific Linux distribution you intend to install. Each distribution has its own set of minimum hardware requirements, such as processor speed, memory, and storage space. Ensure that your computer meets or exceeds these requirements to guarantee optimal performance.
Additionally, it is advisable to update your computer's firmware, especially the BIOS (Basic Input/Output System). Upgrading the firmware ensures compatibility and can potentially resolve any issues that may arise during installation. You can usually find the latest firmware updates on the manufacturer's website or through their dedicated software.
Another important step is to disable any secure boot features or settings that may be active on your computer. Secure boot is a security measure implemented to protect the computer against unauthorized operating systems. Disabling this feature will allow you to install Linux without any hindrances.
Finally, you should gather all the necessary installation media and tools. This may include a USB drive or a DVD containing the Linux distribution you wish to install. Make sure to download the latest version of the distribution and verify its integrity using cryptographic hashes, if available. Additionally, you might need a bootable USB creator tool or DVD burning software to create the installation media.
By following these preliminary steps, you can ensure that your computer is well-prepared for the Linux installation process. Taking the time to properly prepare your system will mitigate potential issues and allow for a successful installation of the Linux operating system.
Step 1: Configuring a Bootable USB Drive or DVD
Preparing a bootable USB drive or DVD is the first crucial step in the process of installing a Linux operating system on your device. This section will guide you through the necessary steps to create a bootable media using simple and accessible methods.
- Gather the required materials:
- A USB drive with a minimum capacity of 4GB or a blank DVD.
- A computer with internet access and a working USB port or DVD drive.
- A reliable internet connection to download the Linux distribution.
- A file archiving tool like 7-Zip or WinRAR (if using Windows as the primary operating system).
- Research and select the Linux distribution that best suits your needs.
- Consider factors such as ease of use, hardware compatibility, and available software.
- Visit the official website of the chosen Linux distribution.
- Locate the download section and select the appropriate version for your system architecture (32-bit or 64-bit).
- Click on the download link and save the ISO file to your computer.
- If using a USB drive, insert it into the USB port of your computer.
- Launch the file archiving tool and locate the downloaded ISO file.
- Extract the contents of the ISO file to the USB drive, ensuring that the file system remains intact.
- Wait for the extraction process to complete.
- If using a DVD, insert a blank DVD into the DVD drive of your computer.
- Launch the file archiving tool and locate the downloaded ISO file.
- Burn the ISO file to the DVD using the appropriate option in your archiving application.
- Wait for the burning process to complete.
Once you have successfully created a bootable USB drive or DVD, you are now ready to proceed to the next step of the Linux installation process.
Booting from the Bootable Media
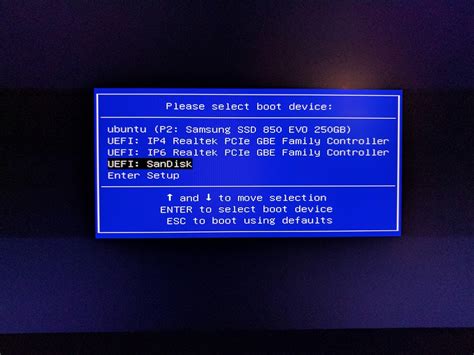
In this section, we will explore the second step in the process of installing Linux on your desktop or laptop: booting from the bootable media. Now that you have prepared your bootable USB or DVD, it's time to initiate the installation process.
Before you begin, ensure that your computer is turned off. Insert the bootable media into the appropriate port (USB or DVD drive) and then power on your device. Next, you will need to access the boot menu. The specific key to access the boot menu may vary depending on your computer's manufacturer, but common keys include F12, F2, or Del. Consult your device's manual or search online for the correct key for your machine.
Once you have accessed the boot menu, you will see a list of devices from which you can boot. Use the arrow keys to navigate and select the bootable media you inserted earlier. Press Enter to confirm your selection and initiate the booting process.
Your computer will now boot from the bootable media, and you will be presented with the Linux installation options. Follow the on-screen instructions to proceed with the installation process. Keep in mind that the specific steps may vary depending on the Linux distribution you have chosen.
It is important to note that during this stage, your computer will primarily be running on the bootable media, and any changes you make will not affect your existing operating system. This allows you to test out Linux before committing to a full installation.
Once you have completed the installation process, you can remove the bootable media and restart your computer. Your device will now boot into the newly installed Linux operating system, ready for you to explore its features and functionality.
Step 3: Initiating the Linux Installation Procedure
Once you have completed the necessary preparations and gathered the required resources, it is time to begin the process of installing Linux on your system. In this step, we will take you through the initial stages of the installation procedure.
1. Booting from the Installation Media
First, you need to boot your computer using the Linux installation media. This can be a USB flash drive or a DVD containing the Linux distribution of your choice. Access the boot menu by pressing the appropriate key during startup (usually indicated on the screen) and select the option to boot from the media.
2. Selecting the Installation Preference
Once the system boots from the Linux installation media, you will be presented with a menu displaying various installation options. Choose the appropriate option, such as "Install Linux," to proceed with the installation process.
3. Language and Localization Settings
Next, you will be prompted to select your preferred language and localization settings for the Linux installation. This includes the language for the installation interface, keyboard layout, and time zone. Make the necessary selections and proceed to the next step.
4. Disk Partitioning
In this stage, you will need to configure the disk partitions for your Linux installation. You can either select an automatic partitioning option recommended for beginners or customize the partition layout according to your specific requirements. Carefully review and confirm your selections before proceeding.
5. User Account and Password
Creating a user account is a vital step in the Linux installation process. Provide the necessary information, including your desired username and password, which will be used to log in to the system subsequently. It is advised to choose a strong password for enhanced security.
6. Commencing the Installation
After all the required settings have been configured, you are ready to initiate the actual installation process. Double-check all the selected options and confirm the installation to start installing Linux on your desktop or laptop. The installation progress will be displayed, and you may be required to restart your system once the installation is complete.
| Key Points: |
|---|
| - Boot your computer using the Linux installation media. |
| - Select the preferred installation option. |
| - Choose language and localization settings. |
| - Configure disk partitions. |
| - Create a user account with a secure password. |
| - Confirm the installation and commence the process. |
Step 4: Partitioning Your Hard Drive
After completing the initial steps, you are now ready to move on to the crucial process of partitioning your hard drive. Partitioning allows you to divide your hard drive into multiple sections, each functioning as a separate entity. This ensures that you can effectively organize your files and allocate resources as per your needs.
An essential aspect of partitioning is to determine the number of partitions you require and their respective sizes. This decision primarily depends on your intended use of the system. For instance, if you plan to have a separate partition for your operating system, another for your personal files, and perhaps another for a dual-boot setup, you will need to assign appropriate sizes to each partition.
There are various partitioning tools available that can assist you in this process. Some popular options include GParted, fdisk, and the partitioning tools provided by the Linux installation process itself. These tools offer user-friendly interfaces and step-by-step instructions to guide you through the partitioning process easily.
- GParted: GParted is a graphical partition editor that provides a straightforward interface for creating, resizing, and deleting partitions. It supports a wide range of file systems, making it suitable for most users.
- fdisk: fdisk is a command-line tool that offers advanced partitioning capabilities. It allows you to create, delete, and modify partitions through a series of commands. Although it requires a basic understanding of partitioning concepts, fdisk provides greater flexibility and control.
- Linux installation process: Many Linux distributions provide built-in partitioning tools during the installation process. These tools allow you to create and customize partitions specific to your requirements while setting up the operating system.
Before proceeding with the partitioning process, it is essential to back up any important data stored on your hard drive. Partitioning involves modifying disk partitions, which can potentially lead to data loss if not done correctly. Taking a backup ensures that your data remains safe in case of any unforeseen issues during the partitioning process.
Once you have chosen a suitable partitioning tool and backed up your important data, you can begin creating the necessary partitions on your hard drive. Follow the instructions provided by your chosen tool to specify the partition sizes, file systems, and other relevant parameters for each partition.
With your hard drive successfully partitioned, you are now equipped with a well-organized system that allows for efficient utilization of resources and effortless organization of your files and data. Proceed to the next step to continue the installation process and bring your Linux system to life!
Step 5: Choosing Installation Options and Packages
In this step, we will now proceed to select the installation options and packages that suit your requirements, allowing you to customize your Linux setup according to your preferences.
Customizing Your Linux Installation
During the installation process, you have the freedom to customize various aspects of your Linux setup. This includes selecting the desired language, keyboard layout, and time zone, among other options. By personalizing these settings, you can ensure a seamless and efficient user experience tailored to your needs.
Selecting Packages
Once you have configured the installation settings, you will be presented with the option to select the packages you want to include in your Linux installation. Packages are pre-compiled software bundles that provide additional functionality and applications for your system.
You can choose from a wide range of packages, such as productivity tools, development libraries, multimedia software, and more. It's essential to consider your specific requirements and intended use of the Linux system when selecting packages, as this will determine the software and features that will be available to you.
Package Managers
Linux distributions typically include a package manager, which is responsible for managing software installation, updates, and removal. The package manager helps you easily install, update, and remove packages, ensuring that your system remains up to date and secure.
Common package managers in Linux include apt, yum, and pacman, depending on the distribution you choose. These tools provide a user-friendly interface to search and install packages from official repositories or third-party sources.
Considerations when Choosing Packages
While selecting packages, it's important to strike a balance between including the necessary software for your tasks and avoiding unnecessary bloat. Including too many packages can consume additional disk space and potentially slow down your system.
Additionally, consider the system requirements of the packages you intend to install. Some software may have higher resource demands and might not perform optimally on low-spec hardware.
Take some time to research and carefully select the packages that align with your needs, ensuring a streamlined and efficient Linux system.
Step 6: Finalizing the Installation and Configuring Your System
Now that you've successfully completed the installation of your chosen Linux distribution on your device, it's time to finish the setup and optimize your system for optimal performance and personalized use. In this step, we will guide you through the post-installation process, where you will configure essential settings, install necessary software, and customize your Linux environment.
| 1. System Updates: | Start by updating your newly installed Linux distribution to ensure that you have the latest security patches, bug fixes, and software updates. Open the package manager or terminal and run the appropriate command(s) to update your system. |
| 2. User Accounts: | Create additional user accounts or modify the existing ones according to your requirements. This allows you to have separate profiles for different users and manage their privileges and settings individually. |
| 3. Network Configuration: | Configure your network settings, including establishing a wired or wireless connection, setting up a static IP address, and configuring DNS servers. These settings ensure that your device can connect to the internet and communicate with other devices on the network. |
| 4. Software Installation: | Install additional software packages and applications that are not included in the default Linux distribution. Depending on your needs, you can install productivity tools, media players, development environments, or specialized software for specific purposes. |
| 5. System Settings: | Explore your system settings and customize them to suit your preferences. Adjust the display resolution, configure power management options, personalize the desktop environment, and enable/disable system services as needed. |
| 6. Data Backup: | Set up a regular backup system to safeguard your important files and data. You can use built-in backup tools or install third-party applications that provide advanced backup and recovery features. |
| 7. Security Measures: | Enhance your system's security by enabling the built-in firewall, installing antivirus software, and practicing safe browsing habits. Regularly update your system and software to protect against potential threats and vulnerabilities. |
| 8. Troubleshooting: | Familiarize yourself with common troubleshooting techniques in case you encounter any issues with your Linux system. Learn how to identify and resolve software conflicts, hardware compatibility problems, or system errors effectively. |
By following these post-installation steps, you can ensure that your Linux system is fully optimized, secure, and tailored to your specific needs. This concludes the installation guide, and you are now ready to explore the vast possibilities and advantages of using Linux on your desktop or laptop device.
FAQ
Is it possible to install Linux on a desktop computer or laptop?
Yes, it is absolutely possible to install Linux on desktop or laptop computers. In fact, Linux offers a wide range of distributions specifically designed for various computer hardware.
What are the advantages of installing Linux?
There are several advantages to installing Linux. Firstly, it is an open-source operating system, which means it's free to use and modify. Additionally, Linux is known for its stability, security, and flexibility. It also provides a vast array of software options and customization possibilities.
How do I choose the right Linux distribution for my computer?
Choosing the right Linux distribution depends on your specific needs and preferences. Popular distributions like Ubuntu, Fedora, and Linux Mint are user-friendly and ideal for beginners. If you have older hardware, you may choose a lightweight distribution like Xubuntu or Lubuntu. Researching different distributions and their features will help you make an informed decision.
Can I dual boot Linux with Windows?
Yes, it is possible to dual boot Linux with Windows. During the Linux installation process, you can choose to install it alongside your existing Windows operating system. This will set up a boot menu, allowing you to select the desired operating system each time you start your computer.
What are the system requirements for installing Linux on a desktop or laptop?
The system requirements for installing Linux may vary depending on the distribution you choose. However, in general, you would need a minimum of 2GB RAM, 20GB free disk space, and a 1GHz processor.




